16 Best Home Remedies For Skin Pigmentation & Prevention Tips
The right ingredients can help you manage and restore your complexion with ease.

Image: Shutterstock
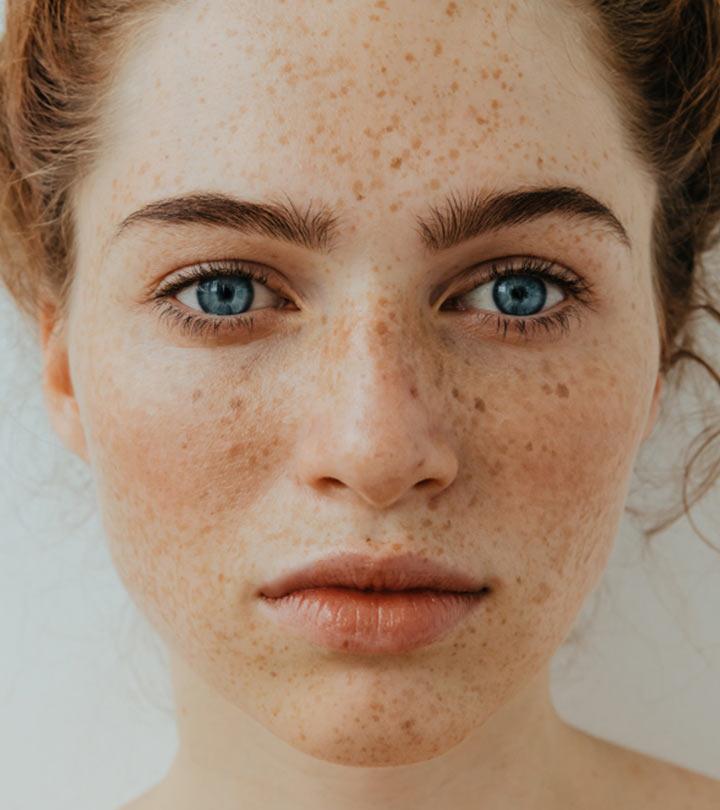
Before we get to the home remedies for skin pigmentation, let’s learn about skin pigmentation issues. Skin pigmentation disorders affect the melanin levels (natural pigment) in your skin and your natural skin color. Any changes in skin pigmentation may lighten or darken your skin color. Melasma, freckles, vitiligo, pigmented birthmarks are a few examples of pigmentation issues.
Hyperpigmentation is mostly caused by sun damage. However, it may also indicate underlying conditions or caused due to medication side effects. If you have developed hyperpigmentation due to improper skin care and sun damage, you may try some home remedies to fade these skin pigmentation issues. While they may not be as effective as medical treatments, you may see the results gradually. Scroll down.
In This Article
What Is Skin Pigmentation?
Pigmentation is discoloration of the skin. This common problem in which you develop dark patches on your skin is faced by both men and women. It is caused by excess melanin – the pigment that gives you your natural skin tone. When this pigment forms a deposit in the skin, it causes pigmentation (or hyperpigmentation).
Note: Not all pigmentations are harmless. Some may be a sign of an underlying disease. Consult a doctor if you notice any skin discoloration.
Researchers at the University of California argued that hyperpigmentation and pigmentation are one of the most common skin conditions in a 2018 study in Informatics that focused on female patients who had various skin conditions. Some of the other common skin issues they found were rosacea, melasma, and actinic keratosis. Check out the graph below to find out more.
Distribution Of Patients At UCSF For Each Skin Condition
Source: Large Scale Advanced Data Analytics on Skin Conditions from Genotype to PhenotypeThere are several types of skin pigmentation – some may respond to treatment, and some may not. The most common types of skin pigmentation are discussed in the following section.
Types Of Skin Pigmentation
- Age Spots Or Solar Lentiginosis (Liver Spots): These are the most common type of skin pigmentation and are formed due to sun damage. They are found in the areas frequently exposed to the sun.
- Melasma Or Chloasma: This is characterized by spots similar to age spots but covering a large area on the skin. These spots mostly appear due to hormonal changes. For instance, during pregnancy, the hormones may trigger the overproduction of melanin and cause skin darkening.
- Freckles (Ephelides): These are caused by sun exposure. They appear as tiny dots and specks on your face and shoulder areas.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): It is a condition in which your skin develops marks or spots as a result of an injury, burns, acne, or aggressive chemical treatment. It is also called hypopigmentation.
You may also face skin pigmentation disorders like:
- Vitiligo: It is an auto-immune condition, and the causes are still unknown. The melanocytes (melanin-producing cells) stop working and cause light patches on your skin. This condition can affect any or all of your body parts.
- Albinism: This is a genetic disorder. and People with albinism do not produce enough melanin, resulting in little or no pigments in their bodies.
A study of 9118 participants in the United States found that 1.52% of children and 2.16% of adolescents reported vitiligo. Expert dermatologists found a clinician-adjudicated prevalence of 0.84% in children and 1.19% in adolescents. These findings suggest over 591,000 cases of vitiligo among children and adolescents in the US in 2020, emphasizing the need for further research.
There are several causes behind skin pigmentation issues.
What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
UV rays are the biggest culprits that trigger the overproduction of melanin. However, the damage caused by UV rays is not visible immediately. Hence, if you have developed pigmentation on your face recently, it is most likely a result of the damage caused to your skin about a decade ago.
If you have been using sunscreen all your life but are still experiencing skin pigmentation, do not get baffled. The other factors that may cause skin pigmentation are
- Skin damage caused by injury (also called post-inflammatory pigmentation)
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy (melasma)
- Skin rashes (rosacea, psoriasis, eczema, contact dermatitis)
- Skin infections (acne, ringworm, tinea versicolor, candidiasis)
- Medical conditions ( Lupusi XAn inflammatory condition in which the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues and organs. , cyanosisi XA skin condition wherein the skin or mucous membrane turns bluish-purple due to oxygen shortage in the blood. Actinic keratosisi XA disorder in which the skin turns scaly, rough, or crusty due to excessive exposure to UV rays. , untreated or undiagnosed diabetes)
Certain skin cancers can also cause skin pigmentation, such as actinic keratosis, squamous cell carcinomai XA type of skin cancer caused by the excess production of squamous cells found on the skin’s surface. , basal cell carcinomai XA type of skin cancer where basal cells in the lower epidermis divide to form new cells and cause skin flaking. , and melanomai XA type of skin cancer develops in melanin-producing cells and can spread to other body parts. .
It is important to consult a doctor if you notice any changes in your skin color. Although most spots and hyperpigmentation are harmless and occur mainly due to age, sun exposure, or negligence, they may also indicate a medical issue. Before opting for home remedies for skin pigmentation and spots, you need to know what type of hyperpigmentation it is and what caused it.
If your skin pigmentation and spots are harmless, and you want to reduce their appearance quickly, your doctor may suggest chemical peels with acids, such as lactic, glycolic, salicylic, or citric acid. You can also try home remedies for skin pigmentation that can help fade the blemishes.
Note: These home remedies might not fade the pigmentation and spots completely. However, they can help improve their appearance and make them less apparent. These remedies take time to show results, so be patient. If your pigmentation and spots are not caused by medical issues, try these home remedies.
Home Remedies For Skin Pigmentation
1. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar contains polyphenolic compounds that offer various health benefits (1). These compounds may also be beneficial for the skin. Anecdotal evidence suggests that ACV may be beneficial in managing pigmentation and other skin issues. However, there is no scientific proof to prove these effects.
How To Use: Mix a tablespoon each of apple cider vinegar and water in a container (take equal parts of both depending on the treatment area). Dip a cotton swab into the mixture and apply it to the affected area. Leave it on for 3 minutes or until it dries completely. Wash it off with lukewarm water. Repeat twice daily.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera contains an active ingredient called aloin that has skin lightening properties (2).
How To Use: Mix 2 tablespoons of fresh aloe vera gel and 1 teaspoon of honey in a bowl. Let the mixture sit for 5-10 minutes. Apply it to the affected area and let it dry. Wash with lukewarm water.
3. Green Tea
Tyrosinase is an enzyme found in your body that is responsible for pigmentation. Green tea extracts have been found to inhibit mushroom tyrosinase (in vitro), which may have a depigmenting effect (3). However, more studies are required to establish its efficacy.
How To Use: Steep a green tea bag in a cup of hot water and wait for it to cool down. Rub the tea bag on the affected area. Repeat this treatment twice daily.
A beauty blogger shared how green tea with honey and rice flour helped her manage her acne and acne scars. She said, “I do this once or twice a week and this is one of my favourite home-made masks. As well as being super easy, my face feels so smooth and refreshed after (i)!”
4. Lemon
Lemon is considered one of the effective home remedies for skin pigmentation. Lemon is a potent bleaching agent and has skin lightening properties. It is used in many skin lightening formulations, such as Lucederm, Meladerm, and Skin Bright (4). However, lemon juice can irritate sensitive skin, so do a patch test on your arm before using it. Also, make sure to apply sunscreen after using this remedy because lemon juice can make your skin photosensitive.
How To Use: Mix a tablespoon of diluted lemon juice with a teaspoon of organic honey. Apply the mixture on the affected area and wait for 15 minutes before washing it off with lukewarm water.
5. Red Onion
Red onion is often used in scar lightening creams. A study done on mushroom tyrosinase found that the skin of red onion contains ingredients with potential for skin-whitening cosmetics (5).
How To Use: Rub a slice of red onion on the affected area. Let it stay for 10 minutes and then wash it off. Repeat the treatment twice daily.
6. Licorice Extract
Licorice contains glabridin, a polyphenolic flavonoid that helps prevent UV-induced pigmentation and has an anti-inflammatory effect. However, further studies are required to establish the depigmenting property (3).
How To Use: Boil 4-5 licorice roots in water. Let the liquid cool down and strain it into a spray bottle. Apply it as a mist twice daily.
Note: Store the licorice extract in the refrigerator and use it within 8-10 days.
7. Milk
Milk contains lactic acid, which is used in chemical peels to brighten and whiten skin. It has also been found that lactic acid could be used to treat melasma (6).
How To Use: Apply fresh milk with a cotton swab on the affected area and let it dry. Wash it off with lukewarm water. Do this twice daily.
8. Tomato
Tomato contains lycopene that can reduce the long-term effects of photodamage (7). Since spots and pigmentation are also long-term consequences of photodamage, tomato may help lighten them.
How To Use: Slice a tomato and rub it on the spots. Let it dry. Wash it off with lukewarm water. Follow this twice daily.
9. Black Tea
Black tea extract is said to have a skin-whitening effect. A study found that when applied to pigmented spots on guinea pigs, black tea inhibited the development of melanocytes and reduced hyperpigmentation (8).
How To Use: Boil a tablespoon of tea leaves in water. Let the water cool down and strain it into a bowl. Apply it to the affected area with cotton balls. Use it twice daily.
10. Orange Peel
Orange peel extracts can reduce melanin deposits, fade dark spots, and brighten your skin. The study was done on humans, and none of the subjects developed skin irritation (9).
How To Use: Dry and powder the orange peels. Mix the powder with a teaspoon of diluted lemon juice and honey and apply it as a face mask. Do this three times a week.
11. Potato
Potato juice contains azelaic acid that may help reduce blemishes and hyperpigmentation caused by acne and acne scars (10).
How To Use: Slice a potato and rub it on the spots. Wash it off after it dries. Repeat the process daily.
12. Sandalwood Oil
Sandalwood oil contains alpha-santalol that helps in hibits tyrosinase and UV-induced and age-related pigmentation (11).
How To Use: Mix 2-3 drops of sandalwood oil with a carrier oil (such as jojoba or sweet almond oil) and apply it to the affected area. Use this once daily.
13. Mulberry Extracts
Mulberry extracts derived from mulberry leaves can help with hyperpigmentation. In-vitro studies found that Mulberroside F, the active component present in mulberry inhibits tyrosinase activity, melanin production, and transfer. It also functions as a Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) scavenger. In a randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 75% of mulberry extract oil was found to be effective in reducing melasma (12).
How To Use: Steep mulberry leaves in jojoba or sweet almond oil for 3-4 days and then apply the oil to your skin. You can also apply crushed mulberry fruit on your skin. You may notice the results over time.
14. Orchid Flower Extract
The orchid extract has a similar effect as vitamin C for improving hyperpigmentation. A study involving 48 women between the ages of 30 and 60 for eight weeks found that it helped improve melasma and lentigo senilis and also had skin-whitening effects (13).
How To Use: You may buy products that contain orchid extracts, or you can seep orchid petals in hot water for half an hour, store it in a spray bottle and use it as a face mist.
15. Rice Water
Rice water is commonly used in Asian countries to reduce blemishes and brighten the skin. Anecdotal evidence suggests it contains enzymes that enhance skin brightness and hydrolysates that can prevent aging signs. This makes it a good remedy to prevent pigmentation issues, enhance skin radiance, and maintain hydration levels.
How To Use: Apply some rice water with a cotton pad on the affected areas. Massage it properly on the darker areas. Rinse if desired.
16. Soy
Soy and soy-based products may have positive effects on your skin health. Soy-derived compounds may impact skin color by preventing cells from absorbing pigment-containing particles. Thus, soy may be an effective solution in treating as well as preventing skin pigmentation (15).
How To Use: You may use a soy-based serum to hydrate and even out your skin tone.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThat was all about considering home remedies for skin pigmentation relief. Natural ingredients usually do not have major side effects unless you are allergic to them or have hypersensitive skin. They are safe but may take time to show results. If your condition is severe and you want quick results, talk to your doctor for more effective medical treatment options.
Medical Treatment Options For Pigmentation And Spots
The treatment you undergo depends on the cause of your hyperpigmentation. If it is due to other health-related issues, treating the underlying problem can help reduce pigmentation. Some of the common treatments options include:
- Microdermabrasion
- Intense pulsed light (IPL) treatment
- Chemical peel
- Laser resurfacing
- Cryotherapy
- Topical creams (corticosteroids, hydroquinone, retinoids, and vitamin C)
Preventing unwanted skin darkening is the first step to avoid hyperpigmentation in the future. You need to take good care of your skin and limit sun exposure. Here are a few tips you can follow to prevent skin pigmentation.
Tips To Prevent Skin Pigmentation
1. Use Sun Protection Every Day
Exposure to UV rays triggers sun spots, age spots, dark patches, and hyperpigmentation. Do not forget to apply sunscreen lotion on the exposed areas. Excessive sun exposure activates the melanin production system, and a good sunscreen helps to prevent that.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip2. Apply Anti-Inflammatory Skin Care Products
Whether it is acne or dermatitis, skin inflammation leaves marks that are tough to erase and make your skin look dark and pigmented. Let your skin heal by using anti-inflammatory skin care products.
3. Eat Healthy
A healthy and balanced diet keeps your skin and body healthy. Your body can use the vitamins and nutrients derived from the diet to trigger healing.
Infographic: 5 Effective Home Remedies To Reduce Skin Pigmentation
Changes in melanin levels affect your natural skin color, causing skin pigmentation disorders like freckles and melasma. This hyperpigmentation can result from increased sun exposure or any underlying condition. However, you can reduce skin pigmentation methodically by resorting to some effective home remedies. Read the infographic to learn about them.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Various factors trigger skin pigmentation. But home remedies for skin pigmentation make this issue less apparent and improve the appearance of pigmented spots. You can use aloe vera, apple cider vinegar, red onion, green tea, lemon, milk, tomato, black tea, licorice extract, orange peel, sandalwood oil, mulberry, or orchid flower extract to treat this skin problem. Turmeric, papaya, baking soda, yogurt, cucumber, rose water, fenugreek, carrot juice, and calendula are some of the other home remedies used to reduce dark spots and pigmentation. In addition, following a few preventive tips, like using sun protection, maintaining a healthy diet, and using anti-inflammatory skin care products, help reduce the risk of skin pigmentation. Try any of the home remedies mentioned above to make your skin glow!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to get rid of hyperpigmentation permanently?
If the pigmentation has affected the skin on deep levels, it may not be easy to get rid of it completely. However, with constant care and treatment, you can fade it to a great extent.
How do you get rid of pigmentation overnight?
It is not possible to get rid of pigmentation overnight. You can try home remedies and medical treatment options to improve its appearance over time.
What is the best treatment for hyperpigmentation?
A combination of medical treatment and home remedies is the best way to treat hyperpigmentation. Also, minimize sun exposure to ensure the issue does not aggravate.
How long does it take to clear up hyperpigmentation?
It may take anywhere between 3 months and 2 years, depending on the extent of your pigmentation and the treatment method. Ensure to take proper care of your skin.
What food causes pigmentation?
Overindulgence in dairy, spicy food, and fried food may cause inflammation in the body, which may result in post-inflammatory pigmentation (16), (17).
What should we eat to remove pigmentation?
You should follow an anti-inflammatory diet to reduce the signs of aging such as pigmentation. Anti-inflammatory diets usually include foods like fish and other seafood, legumes, whole grains, vegetables, soy products, seeds, fruits, and nuts (18).
Does drinking water reduce pigmentation?
Dehydrated skin that has low levels of water can develop dark spots and uneven skin tone. Increasing water intake has been found to be beneficial for skin health and in reducing skin pigmentation (19), (20).
Can rubbing ice on your face remove pigmentation?
While there is a lack of scientific research to support this claim, anecdotal evidence suggests that applying ice regularly on the face can improve circulation and lighten dark spots and pigmentation.
Does vitamin D help with skin pigmentation?
Usually, vitamin D is associated with melanin formation, which imparts colored pigment to the skin. However, preliminary studies have also linked darker pigmentation with vitamin D deficiency (21), (22). Therefore, results may be inconclusive in this regard. However, it is recommended to get adequate amounts of vitamin D through diet/supplementation and safe exposure to sunlight every day as it is an essential nutrient for the body.
Key Takeaways
- Changes in skin pigmentation alter melanin levels which can lighten or darken the skin color and cause conditions such as melasma, vitiligo, or dark patches.
- Aloin in aloe vera possesses skin-lightening properties.
- Black tea and green tea extracts have skin-lightening and depigmenting properties.
- Certain medical treatments, such as microdermabrasion, chemical peel, and cryotherapy, treat skin pigmentation.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Wondering how to manage skin pigmentation? Discover natural home remedies to effectively remove pigmentation and achieve a more even skin tone in this insightful video. Say goodbye to pigmentation and hello to radiant skin!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. DIY green tea and honey mask for acnehttps://thebeautyhack.wordpress.com/2015/04/10/diy-green-tea-and-honey-mask-for-acne/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Atik, Derya et al. “The Effect of External Apple Vinegar Application on Varicosity Symptoms, Pain, and Social Appearance Anxiety: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM vol. 2016 (2016): 6473678.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4735895/ - Sharique, A Ali et al. “On The Novel Action of Melanolysis by a Leaf Extract of Aloe vera and Its Active Ingredient Aloin, Potent Skin Depigmenting Agents.” Biological and Pharmacological Activity Original Papers: Thieme E-Journals, Planta Med Vol. 78,8 (2012): 767-771.
https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-0031-1298406 - Sarkar, Rashmi et al. “Cosmeceuticals for Hyperpigmentation: What is Available?.” Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery vol. 6,1 (2013): 4-11. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3663177/
- Smit, Nico et al. “The hunt for natural skin whitening agents.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 10,12 5326-49. 10 Dec. 2009.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2801997/ - Arung, Enos Tangke et al. “Tyrosinase inhibitory effect of quercetin 4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from dried skin of red onion (Allium cepa).” Natural product research vol. 25,3 (2011): 256-63.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20635304/ - Singh, Rashmi et al. “Effect of 82% Lactic Acid in Treatment of Melasma.” International Scholarly Research Notices vol. 2014.
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/isrn/2014/407142/ - Rizwan, M et al. “Tomato paste rich in lycopene protects against cutaneous photodamage in humans in vivo : a randomized controlled trial.” British Journal of Dermatology vol. 164, 1 (2010): 154-162.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.10057.x - Choi, So-Young, and Young-Chul Kim. “Whitening effect of black tea water extract on brown Guinea pig skin.” Toxicological research vol. 27,3 (2011): 153-60.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3834380/ - Wuttisin, N. et al. “Anti-tyrosinase activity of orange peel extract and cosmetic formulation.” International Food Research Journal vol. 24,5 (2017): 2128-2132.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329831595_Anti-tyrosinase_activity_of_orange_peel_extract_and_cosmetic_formulation - Umadevi, M. et al. “Health Benefits and Cons of Solanum tuberosum.” Journal of Medicinal Plants Studies vol. 1,1 (2013):16-25.
https://www.plantsjournal.com/vol1Issue1/Issue_jan_2013/3.pdf - Moy, Ronald L, and Corey Levenson. “Sandalwood Album Oil as a Botanical Therapeutic in Dermatology.” The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology vol. 10,10 (2017): 34-39.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5749697/ - Hollinger, Jasmine C et al. “Are Natural Ingredients Effective in the Management of Hyperpigmentation? A Systematic Review.” The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology vol. 11,2 (2018): 28-37.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5843359/ - Tadokoro, Taketsugu et al. “Whitening efficacy of plant extracts including orchid extracts on Japanese female skin with melasma and lentigo senilis.” The Journal of Dermatology vol. 37, 6 (2010): 522-30.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20536665/ - Chen HJ, Dai FJ, Chen CY, Fan SL, Zheng JH, Huang YC, Chau CF, Lin YS, Chen CS. “Evaluating the Antioxidants, Whitening and Antiaging Properties of Rice Protein Hydrolysates.” Molecules.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8231118/ - Leyden J, Wallo W. “The mechanism of action and clinical benefits of soy for the treatment of hyperpigmentation.” International Journal Of Dermatology.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21332714/ - Davis, Erica C, and Valerie D Callender. “Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color.” The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology vol. 3,7 (2010): 20-31.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2921758/ - Keewan, Esra’a et al. “Are Fried Foods Unhealthy? The Dietary Peroxidized Fatty Acid, 13-HPODE, Induces Intestinal Inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo.” Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 9,10 926.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32992618/ - Stromsnes, Kristine et al. “Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Diet: Role in Healthy Aging.” Biomedicines vol. 9,8 922.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8389628/ - Nguyen, Bach-Cuc, and Irene E Kochevar. “Influence of hydration on dihydroxyacetone-induced pigmentation of stratum corneum.” The Journal of investigative dermatology vol. 120,4 (2003): 655-61.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12648231/ - Palma, Lídia et al. “Dietary water affects human skin hydration and biomechanics.” Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology vol. 8 413-21.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4529263/ - AlGhamdi, Khalid et al. “The role of vitamin D in melanogenesis with an emphasis on vitiligo.” Indian journal of dermatology, venereology and leprology vol. 79,6 (2013): 750-8.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24177606/ - Kaushik, Shivani. “Skin pigmentation and vitamin D status: A single-center, cross-sectional study Bridget Kaufman, MD, Mount Sinai St. Luke’s and Mount Sinai West; Alex Luna, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons.”
https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(17)31404-4/fulltext