Egg Protein Chart – How Many Proteins Does Egg Contain?

Image: iStock
The king of all meals, breakfast is one of the most important meals of the day. The word breakfast is the literal meaning. You are having your first meal after “fasting” for say five to eight hours. Yes, sleeping not only rests your mind and your external limbs, but relaxes your internal organs as well.
Now, the all important question is, ‘if breakfast is the most important meal of the day, what should be included in it?’
A breakfast is never complete unless it has egg in it. Well, who does not like it sunny side up! Many among us like the savor the yolk at the end, some of us consider the white to be the special treat, but it’s safe to say that we all love having eggs.
Eggs are a great source of protein. They contain equal proportions of the nine amino acids necessary to fulfill the dietary needs of the human body. Studies have proven that having two to three eggs a day leads to a healthy lifestyle. However, consuming eggs on a daily basis has its own myths, here are all the answers regarding the myths and beliefs of having eggs on a daily basis.
Many individuals among us consider eggs to be a non-vegetarian food. For those vegetarian extremists’ foods like quinoa, buckwheat, spinach and fruits are the replacements for eggs. They might not be complete sources of proteins but they do provide the necessary energy the body needs to function. However, the catch here is vegetarians must cook these foods in a very methodical fashion so that the crucial vitamins do not get destroyed.
Non-vegetarians have no reason to worry! They can also get complete proteins from beef, chicken, fish and other meat products, beside eggs. They get the best of both-great taste and lot of proteins.
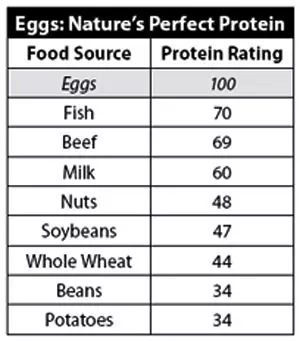
Now let us see what makes an Egg such a dependable source of proteins. This dietary chart given below depicts the protein content in eggs, and compares its protein content with other foods like beef, milk, fish, nuts etc.
In This Article
Egg Protein Chart
Here is the detailed breakdown of the protein levels present in various eggs:
- An egg contains about 6.3 grams of proteins – and about 3.6 grams of protein in egg white & 2.7 grams in Egg Yolk.
- Eggs even have calories which should be balanced with the complete diet calorie intake.
- An average boiled egg has about 6 grams of proteins.
- An omelet, which is a very common breakfast item made with eggs contain about 10 grams of proteins.
- A Duck’s egg has 15 grams of protein
- A Quail’s egg has 2 grams of proteins.
- Scrambled eggs made up from 2 eggs and milk together contain 14 grams of proteins
A. Apart from these, Eggs are also used in the following ways:
Eggs are a rich source of protein and are often used to make protein powders. These protein powders provide proteins to people who are nutritionally deprived. You may be aware of whey, casein and soy protein powders, but have you heard of egg-white protein powders? The two main benefits of the egg-white protein powders are:
- It is lactose free, so those who are lactose-intolerant and can’t have whey or casein protein powders can go for egg-white protein powder. The egg-white protein powder contains 25grams of proteins in a 30 gram serving. This protein content is similar to whey and casein, so one doesn’t have to compromise on their daily dose of protein from these supplements.
- Whey is a fast-digesting protein while caesin is a slow-digesting protein. Egg-white powder falls in between so it helps the muscle synthesis to go on for longer.
- Egg White powder is a complete protein because it has all the 10 essential amino acids. No other naturally occurring substance has the same amount of amino acids.
B. The amino acids available in the egg proteins are exhaustive and they give your body all the necessary amino acids. Adequate dietary protein intake is necessary. It should include all the essential amino acids your body needs daily. An egg has all the amino acids such as histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan and valine. These amino acids are present in a proportion that suits the needs of the human body. Hence the egg is often used as a yardstick to compare protein content of other foods. Eggs not only have nine essential amino acids, it also contains nine other amino acids.
According to the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) whole egg, whey protein and soy protein score 1 on the scale of 0 to 1. However, the Amino Acid Score (AAS) rates the egg at 1.21, which is above human needs. The Protein Efficiency Ratio of eggs is 3.8 and the Biological Value of eggs is rated between 88 and 100. So each large egg provides a total of 6.29 grams of high quality protein, that’s why eggs are classified with meat in the Protein Foods Group.
The egg yolk contains higher proportion of the egg’s vitamins than the white, like vitamins A, D, E and K. It also contains vitamin B6 and B12, folic acid, pantothenic acid, thiamine, calcium, copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, selenium and zinc. So don’t ignore the yolk because it is high on calories, after all you do need some calories for energy.
C. The egg protein chart is an effective guide. It keeps you informed about the proteins you gain from consuming eggs. It also informs you of other foods that you could consume in case you miss out on eggs. So any lapse in the consumption of these foods can be compensated.
Everyone knows who a vegetarian is but for those who do not know the technicalities here is the definition: A vegetarian is a person who doesn’t eat meat or any by-product from animal slaughter. There are some vegetarians who have limited themselves to certain foods that are considered non-vegetarian to have a wholesome diet. A well planned vegetarian diet can be healthy and nutritionally adequate. Here are some types of vegetarian diets:
- Vegans or Total Vegetarians: They eat only plant food like fruits, vegetables, seeds, legumes, nuts and grains.
- Lacto-Vegetarians eat plant foods as well as dairy products such as milk and cheese.
- Lacto-Ovo Vegetarians eat plant foods, dairy products and eggs. Most Americans follows this diet.
- Semi-Vegetarians don’t eat red meats but they do have chicken or seafood with plant foods, eggs and dairy products.
Vegetarians generally receive adequate amount of nutrients, however, they do have to cut back on some nutrients like these:
Protein: Protein is not only important for growth and maintenance of body tissues; it is an important component of enzymes and hormones. Protein helps in the production of milk in lactating women. An assortment of plant foods like tofu, tempeh, whole grains, legumes, vegetables, seeds and nuts provide the essential amino acids.
The proteins in egg whites can be easily digested by the body, so wrestlers and body builders swear by it. Athletes also have egg whites as a source of protein since it provides a high ratio of proteins to calories with very little or no fat. Eggs also contain abundant antioxidants that fight free radicals in the body and keep you safe from cancer. There are so many benefits of eggs that you can’t just ignore them. Eggs add flavor to many foods and make you strong from within.
Omega 3 Fatty Acids: Omega 3 Fatty Acids reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improves cognitive function and vision. The primary sources of Omega 3 Fatty Acids are fish, organ meats and DHA rich foods like eggs. Vegetarians cannot get Omega3 Fatty acids from vegetable sources alone, they have to take supplements.
Calcium: Though calcium deficiencies in vegetarians are rare, there are some vegetables that inhibit calcium absorption. So in that case dairy and poultry products are needed to make the diet balanced.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D helps in calcium absorption from the digestive tract and uses it for building strong bones and teeth. The best sources of vitamin D are derived from milk and eggs. So vegetarians lose out on vitamin D entirely.
Vitamin B 12: Vegetarians need to pay special attention to this nutrient. The body needs little amounts of vitamin B12 for red blood cell formation and normal nerve function. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause irreversible nerve damage. Vegans lack vitamin B12 in their diet and need to have dairy or soy products and vitamin B12 supplements.
Iron: Iron is found in both animal and plant foods, but iron from animal foods gets absorbed by the body easily. Iron from plant foods does not get absorbed by the body due to high fiber content. Fiber is not absorbed by the body and it ties up with minerals like iron and hinders its absorption as well.
Zinc: Zinc is a mineral that is present in plant food but better absorbed from animal sources. So some vegetarian diets do not provide the recommended amount of zinc. So they have to eat nuts, cheese and soy products along with vitamin C rich foods to enable a better absorption of zinc.
Vegetarians should follow the diet principles recommended in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. A well planned vegan diet can meet all the guidelines. The recommendations emphasize that 26 oz. per week of meat, poultry and eggs should be consumed.
D. The best part about eating eggs is that they are routinely consumed for breakfast and hence you don’t have to fit them forcibly into your daily diet schedule. Also they go very well as a complementary food with other dishes – so you don’t have to worry about eating them separately.
Best Ways to Cook Egg
Have you ever thought about the right way of cooking eggs to maximize nutrition? Here are some guiding principles for making the most of the eggs lying in your fridge:
- Generally applying heat to food is a naturally destructive process. If you heat egg whites the protein becomes denatured and more bioavailable. A protein called ‘avidin’ also gets destroyed in the process which is a good thing. So heating egg whites is beneficial. However, less heat should be applied to egg yolk as the fats and other nutrients tend to get damaged.
- Pastured egg yolks are best sources of fats and proteins. So you should eat the egg yolk and not keep it aside.
- Many good fats oxidize and become less beneficial, harmful even. This is true in case of egg yolks. It is best to leave egg yolks uncooked. If you plan to fry eggs make sure you do not heat it in the presence of oxygen for a long duration. The heat can curl up proteins in the egg whites and egg yolks and create sticky fats that your body cannot utilize. This happens because oxygen accelerates the process of destruction while heating.
Different Ways of Cooking An Egg Are:
- Soft boiled, is the optimum way to cook an egg as fats and nutrients in the yolk essentially have three protective layers from oxidation- the water, eggshell and egg white. This way all the nutrients in the eggs are preserved. The egg whites are cooked for the best protein utilization and the removal of avidin. In addition, making a soft boiled egg is faster and easier compared to a frying an egg in a pan. Also the yolk remains creamier and thicker.
- Poached eggs are loved by many for its pure taste. However, when the egg yolk remains submerged in water surrounded by the egg white, the protective shell layer is lost. Also it is very inconvenient to serve poached eggs.
- The thought of having raw eggs can make you scream but it is the best way to have eggs. Be careful not to have too much of raw egg whites because they have a protein called avidin that can combine with B vitamin called Biotin and can create serious health problems. If you can’t have raw egg yolks or raw whole eggs, then blend them in your morning smoothie. Make sure that you put the eggs at the end and fold it in for few seconds. By this way you can reduce the oxidative stress from chopping fats up to very small particles and exposing them to oxygen.
- When eggs are boiled the yolk reaches a higher temperature and thus the destructive process starts. However due to the presence of eggshells the contact with oxygen is not possible thus some amount damage is controlled. You can never replace entire meals with hard boiled eggs.
- While making the sunny side up the heat is given from the bottom of the pan so the yolk remains preserved but the protective water coating on the egg is lost. So it is advisable to have less of the world favorite ‘sunny side up’.
- To make an over, easy heat has to be applied on both sides’ thus precious nutrients and fats in egg yolks are completely lost.
- Scrambling the eggs is a way of chopping the fats and proteins to tiny particles and exposing them to heat and oxygenation. Avoid this method of cooking if you are using conventional feedlot eggs. The fats present in conventional feedlot eggs are pro-inflammatory and they don’t need to be oxidized further. Even if you are using pastured egg this method remains to be the worst way to cook eggs. The oxidation of fat and cholesterol makes it detrimental to your health.
Whichever way you prefer cooking an egg, make sure the egg yolk is preserved. Having an egg yolk is never bad.
Should You Eat Eggs Daily?
Whole eggs are high in calories, fat and cholesterol so consuming eggs every day can put you at the risk of heart disease by increasing the levels of blood cholesterol. So it is better to stick to egg whites and other egg alternatives to reduce health risks. Here is why you should limit your egg intake:
- Excess Calories: Large eggs provide 75 calories each. Would you believe that just a plate of scrambled eggs can fill you up with 225 calories? This high amount of calories will surely cause weight gain. Eating three eggs per day can lead to one pound of weight gain in less than three weeks.
- Increased Fat Intake: Consuming eggs on a daily basis increases your fat intake. While some fats are good as it helps to absorb fat soluble vitamins, saturated fat from eggs can be harmful as it increases your risk of heart disease. In fact, three scrambled eggs at breakfast can pack up 35% of calories for the entire day.
- High Cholesterol: Consuming eggs every day adds excessive amount of cholesterol to the diet. Cholesterol is a fatty and waxy substance that builds up on arterial walls when you have too much of them in your bloodstream. The cholesterol becomes hard and stiff resulting in blood clots. Your heart has to work harder to push blood through the arteries thus increasing blood pressure. The harmful effects of cholesterol increase the risk of heart attacks. So keep your daily cholesterol intake less than 200 milligrams. One large egg contains 185 milligrams of cholesterol and it takes up more than your daily cholesterol allotment. Having meat and seafood in your diet along with egg adds more cholesterol to your diet.
All the fat and cholesterol come from the egg yolk, so opt for plain egg whites or separate yolk from the whites before cooking. If you make three scrambled egg whites then your calorie count goes down to less than 60. The cholesterol and fat content in egg whites is far less than those present in whole eggs.You can also go for fat-free and cholesterol-free eggs.
Are you already planning to stop eating eggs after reading the demerits of whole eggs? Blood cholesterol levels are mainly responsible for cardiovascular diseases and eggs are considered the main culprits behind increasing the blood cholesterol levels. Well that is a myth; let us first clear the misunderstanding by showing you what exactly increases the cholesterol levels and the role fat plays in that process.
Previously, all dietary cholesterol was thought to increase the risk of heart disease. The truth is only certain types of blood cholesterol can line the arteries and indicate a potential risk of heart attack. Cholesterol is needed by the body for proper functioning and it is produced by liver and other organs.The amount of dietary cholesterol is of less significance compared to blood cholesterol caused due to saturated and unsaturated fat.
It is true that egg yolk contains high amount of fat, but it is unsaturated, which is associated with “good” or HDL Cholesterol (High-Density Lipoprotein). The HDL Cholesterol helps to remove the LDL Cholesterol (Low-Density Cholesterol) which lines the blood vessels causing blood clots and heart attacks. So having eggs instead of other sources of animal protein can decrease the amount of saturated fat intake.
Studies show that individuals who have already had elevated levels of LDL Cholesterol, the risk of heart disease did not increase when they started including eggs in their daily diet. However, fat in eggs does contain calories. Therefore limit your intake but never omit it from your diet. If you deny yourself a diet of eggs a week you are losing out on all essential nutrients.
So are you going to put back the egg in the refrigerator or eat it? Now that all your doubts are clear you can eat an egg without feeling guilty at all!
Chickens that are raised in a natural environment and fed with a proper diet that enhances the health of the chicken tend to provide eggs with higher nutritional value. Often the chicken feed is spruced up with chemicals or supplements that will make the chickens give eggs that have a longer shelf life. So always check the labels before you buy eggs, make sure they are ‘verified’ cage free or free-range eggs.
Proteins are the building blocks of life and every cell contain proteins. You need protein in your diet to help your body repair cells and make new ones. Protein is also important for the growth and development in children, teens and pregnant women. Lack of proteins can lead to skin and hair problems, indigestion, weak immune system and muscle related problems. The protein chart for eggs very well determines its use as a rich source of protein and makes everyone aware of how to use it in different forms providing different quantities of protein proportions.
I hope this article Proteins in Eggs helps you attain good health!
Editors notes:
- The start to the article was abrupt.
- The flow is good
- Need to refine the language by a bit.
- Few errors in the sentence formation and tenses.
- Tone is good, a tad bit informal in places.
- Overall a great article.
Nutrition Values
| Egg | Protein | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Raw | 6g | 75 calories |
| Boiled average | 6g | 80 calories |
| Fried in oil | 6g | 120 calories |
| Scrambled (2 eggs + milk) | 14g | 170 calories |
| Poached 1 egg | 6g | 80 calories |
| Scotch egg | 7g | 140 calories |
| Omelette | 10g | 128 calories |
| Quiche (egg & cheese) | 15g | 300 calories |
| Egg Fried Rice | 6g | 210 calories |
| Meringue | 7g | 360 calories |
| Duck egg | 15g | 170 calories |
| Quail egg | 2g | 20 calories |