12 Health Benefits Of Milk Thistle, Nutrition, & Side Effects
A commonly used herbal remedy with many health-promoting medicinal properties
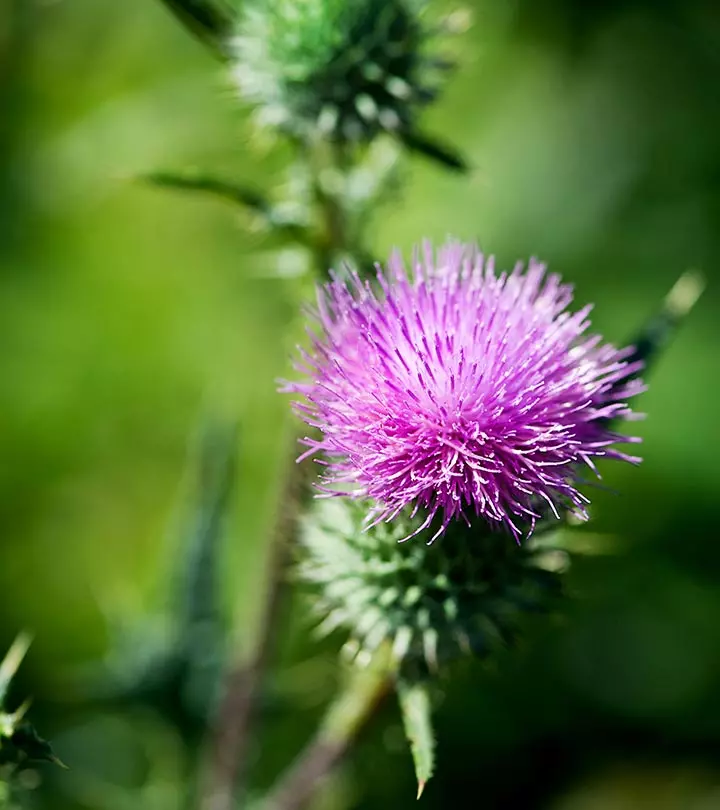

Image: Shutterstock
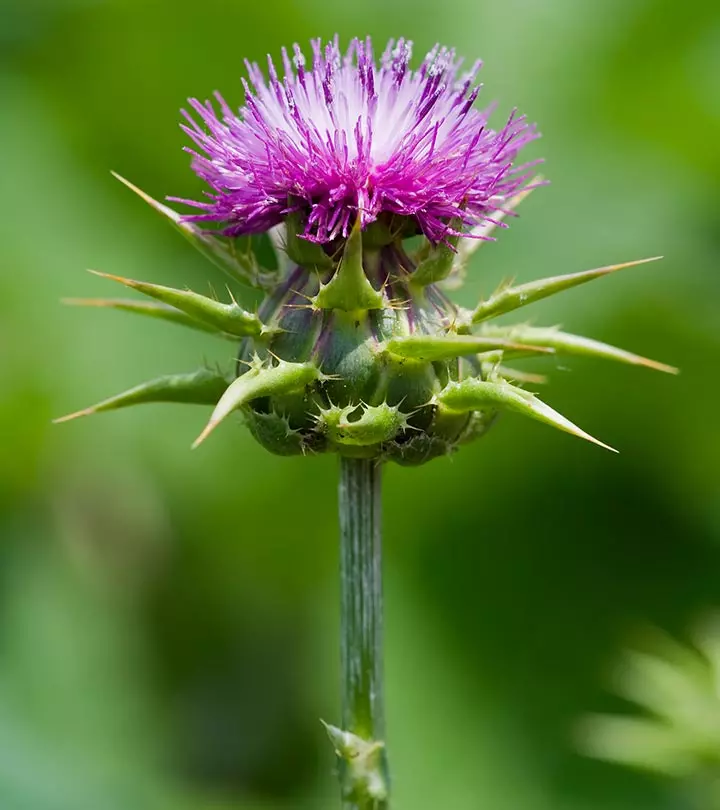
Milk thistle is a popular herbal remedy best known for its liver-protecting properties. This herb (also known as Silybum marianum) is native to the Mediterranean region. The benefits of milk thistle can be attributed to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. This flowering plant can help control blood sugar levels and enhance bone health. In this article, we have discussed how milk thistle benefits your health, its nutritional profile, and possible side effects. Keep reading to know more!
 Know Your Ingredient: Milk Thistle
Know Your Ingredient: Milk ThistleWhat Is It?
A plant native to the Mediterranean region containing seeds with medicinal value.
What Are Its Benefits?
It helps boost liver health, promote kidney health, brain function, weight loss, and improves immunity and digestive health.
Who Can Consume It?
Anyone can consume it except for people with low blood sugar levels.
How Often?
It can be consumed daily.
Caution
It may lower blood sugar levels too far and cause allergies and hormone-sensitive conditions and hormonal imbalances.
In This Article
How Does Milk Thistle Benefit You?
Milk thistle works by flushing out the toxins in the body, which can otherwise cause issues like liver cirrhosis, kidney stones, diabetes, ill effects of chemotherapy, etc.
The other important nutrients in milk thistle, like vitamin E, fight free radicals and can delay the signs of aging. These characteristics of milk thistle (along with a few others that we will discuss in a while) make it what it is – a simple herb bestowing us with its great benefits.
As per an Indian study, milk thistle has been used in traditional medicine to treat diseases of the liver and the biliary tract (1).
What Are The Health Benefits Of Milk Thistle?
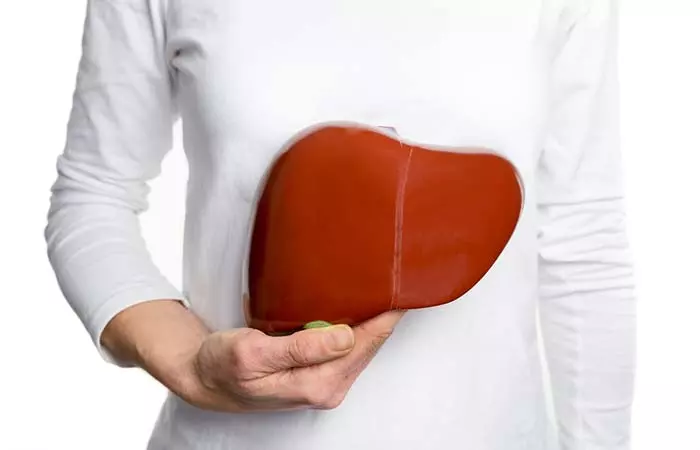
1. Milk Thistle Boosts Liver Health
Milk thistle contains silymarin, an active ingredient that protects the liver. The ingredient is a group of flavonoids that repair the liver cells that are damaged by alcohol and other toxins. Silymarin also protects the new liver cells from getting destroyed. Throughout history, this herb has been used to treat liver diseases (2).
“Silymarin in milk thistle reduces liver injury in animals. Hence, it can possibly be a treatment option for alcoholic liver disease in humans.”
– Abenavoli L and Co., Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University Magna Graecia, Catanzaro, Italy.
2. Protects The Kidneys And Gallbladder
As the kidneys work closely with the liver, and as milk thistle helps support liver health, it also promotes kidney functioning. The same goes for gallstonesi Small and firm crystalline masses that form unnaturally in the bile ducts or gallbladder. They are asymptomatic in many people. as well – studies have shown that this herb can help prevent gallstone formation. Milk thistle also protects the kidney cells, especially in the case of diabetic neuropathy (a condition in diabetes where kidney function is impaired) (3). It also supports the detoxification of the kidneys and gallbladder.
3. Aids Diabetes Treatment
Research suggests that when coupled with traditional treatment, milk thistle can improve diabetes. The herb can also improve insulin resistance and lower blood sugar levels. These effects of milk thistle can be attributed to silymarin (4).
Milk thistle also contains another compound called silibin, which was found to have positive effects on several diabetes complications (5). And another reason it could be good for diabetics is that it protects the liver – the liver also plays some role in releasing insulin into the bloodstream.
4. Milk Thistle Enhances Heart Health
Milk thistle may lower bad cholesterol and hence cut the risk of heart disease (6). It can also lower the cholesterol levels by lowering inflammation. It cleans the blood and prevents damage to the arteries due to oxidative stress. The herb also prevents glutathione depletion (we will discuss more of this in a bit), which is a master antioxidant that fights oxidative stress and prevents heart disease.
Other clinical studies have also proved that milk thistle has cardioprotective effects (7). A few other studies have shown how milk thistle can regulate blood pressure too.
5. Can Help In Cancer Treatment
The silybin in milk thistle can improve the functioning of certain chemotherapy drugs, especially in the case of ovarian cancer. The herb was also found to slow down the progression of prostate cancer cells. Some animal studies also found how milk thistle could reduce the side effects of chemotherapy (8).
Other studies state that milk thistle can induce cancer cell death in the case of colon and breast cancers. Though there is more research required in humans, this sure is an encouraging step (9).
6. Can Aid Weight Loss
There is some early research that shows how milk thistle can aid healthy weight loss. Mice fed with a high-fat diet lost weight after taking silymarin (10). And as milk thistle can regulate blood sugar, it may also help with weight loss – as research links steady blood sugar levels to improved weight loss.
7. Promotes Brain Health
Some early suggests that milk thistle can protect against multiple sclerosisi A pathological condition characterized by unnatural hardening of the body tissues, which results in nerve damage. and Parkinson’s disease. Silymarin was also found to suppress the formation of amyloid beta-protein, which is often linked to Alzheimer’s.
Several other studies also show how milk thistle can help prevent age-related brain ailments like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. Some research also talks about the importance of milk thistle in treating anxiety and depression – but we need more information on this before we come to conclusions.
A study jointly conducted by research teams from India, Australia, and Iran states that silymarin can be a potential treatment for a variety of neurodegenerative disorders and forms of neuroinflammation (11).
8. Milk Thistle Strengthens Bones
Studies confirm that milk thistle can be used as a potential treatment for osteoporosisi A medical condition characterized by fragile and brittle bones caused as a result of tissue loss. . The silymarin in milk thistle was found to be helpful in building bones and preventing bone loss (12).
Other studies talk about bone loss caused by estrogen, and how milk thistle might benefit in this aspect as well.
9. Delays Aging
The antioxidants in milk thistle fight free radical damage, and this eventually slows down the aging process, maintaining skin health. This is equally true with the signs of aging on the surface of your skin and within your internal organs.
Some research says that consuming milk thistle is one good way to reduce the signs of aging – which include wrinkles, dark spots, and fine lines (13). Internally, these antioxidants can delay aging by preventing joint pains and improving eye health.
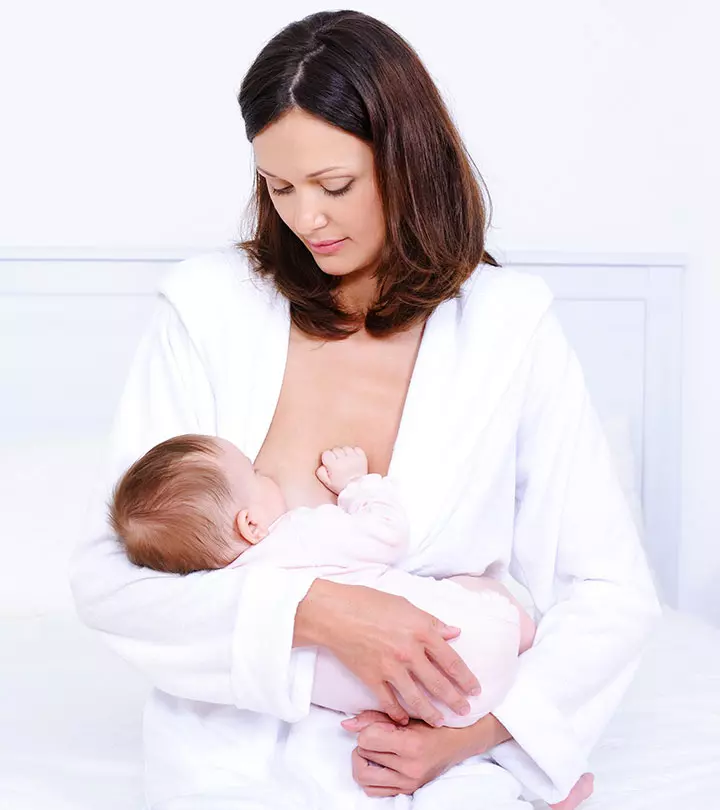
10. Might Be Beneficial During Breastfeeding
Historically, milk thistle was used to increase the supply of breast milk. Some preliminary studies show that it can increase the levels of prolactini A hormone produced by the pituitary gland, it is responsible for milk production in mammals. It is also known as lactotropin. in the body, which eventually stimulates milk production.
However, we suggest you take your doctor’s advice before using the herb in this regard.
11. Boosts Immunity And Prevents Allergies
Studies have shown that milk thistle can have immunostimulatory effects. It can boost immunity and improve the body’s ability to ward off infections and diseases (14). And since milk thistle improves liver function, this also benefits the immune system – as the two are closely interlinked.
The antioxidants in milk thistle also boost immunity and counter allergies. Skin rashes are one of the allergies that milk thistle can counter. More importantly, the herb might fight acne as well. As acne is also caused due to bodily toxins, the detoxifying effect of milk thistle can have desirable effects on it.
12. Improves Digestive Health
Milk thistle boosts enzyme formation and the production of bile – and this contributes to digestive health. And given its anti-inflammatory properties, the herb also soothes the mucus membranes in the gut.
Studies also show how milk thistle has been used for centuries to treat upper gastrointestinal issues and other digestive ailments (15).
 Fun Fact
Fun FactThose are the benefits of milk thistle. But there is another important aspect we need to know.
Milk Thistle And Glutathione (And Other Synergies)
We already discussed how milk thistle (silymarin) could protect against glutathione depletion. The herb, basically, preserves glutathione. This eventually strengthens the liver cell walls.
Glutathione is not the only compound milk thistle acts with in synergy. Other important ingredients like ashwagandha, curcumin, green tea extract, and gingko biloba extract powder also work in synergy with milk thistle and improve the antioxidant defense of the body.
 Trivia
TriviaThere are other important compounds in milk thistle that are responsible for its wonderful benefits.
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Milk Thistle?
Milk thistle contains a bio-flavanoid complex called silymarin. It is the primary ingredient of the plant. It is also the active compound that gives milk thistle its medicinal properties. Silymarin is made up of 3 flavanoids:
- Silybin, which is also known as silibinin.
- Silydianin, which is also known as silidianin.
- Silychristin, also known as silicristin.
The main flavanoid in silymarin is silybin, which makes up about 50-70% of milk thistle’s most important extract. Silybin has been studied clinically, and researchers have found it to be the most beneficial and biologically-active component of silymarin.
Before extraction, milk thistle’s fruits contain:
- Silymarin
- Silyhermin
- Neo-silyhermin A and B
- Protein
- Vitamin E
- Sterolsi A group of unsaturated steroid alcohols that occur naturally in plants and animals and play an important role in cell structure and function.
- Quercetin
- Apigenin
- Kaempferol
- Eriodyctiol
- Chrysoeriol
- Naringin
- Dihydroxychromone
The leaves contain:
- Luteolin
- Luteolin’s 7-0-Glucoside
- Triterpene acetate
- Fumaric acid
However, there are certain things about milk thistle that are not so good. Its overdose might lead to certain undesirable conditions.
What Are The Side Effects Of Milk Thistle?
- Might Lower Blood Sugar Way Too Much
Since milk thistle helps lower blood sugar, it might lower the levels way too much in case someone is already on diabetes medications. Hence, consult your doctor before using it.
- Allergies
Milk thistle can cause allergies in people who are sensitive to ragweed and other plants of the same family (Asteraceae).
- Might Aggravate Hormone-Sensitive Conditions
Since milk thistle extracts might mimic estrogen, it might aggravate hormone-sensitive conditions like breast and uterine fibroidsi Non-cancerous growths in the uterus that may develop during childbearing years in women. Common causes include obesity. and uterine cancer. Hence, it is best to consult a doctor before using it.
These are some potential health risks associated with excess intake of milk thistle. Let’s see its drug interactions in the following section.
What Medications Should Not Be Taken With Milk Thistle?
Milk thistle is a popular herbal supplement that may interact with certain medications. They are as follows:
- Antipsychotics: Anecdotal evidence suggests that milk thistle may reduce the effectiveness of antipsychotic medication, such as haloperidol.
- Anticoagulant Drugs: It may interact with blood thinners, such as warfarin. However, limited data is available in this regard.
- Anti-anxiety Drugs: Some anti-anxiety drugs such as diazepam, if taken with milk thistle, may have an additive effect that can induce drowsiness or sedation. However, more research is needed to support this claim.
Infographic: How To Use Milk Thistle
Milk thistle, a flowering herb, is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It has been used to manage many ailments since ancient times.
There are many ways to include milk thistle in your routine to reap its benefits, as elaborated in the following infographic. Check it out! Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Milk thistle is an herbal remedy known for its therapeutic properties. The many benefits of milk thistle can be attributed to its rich nutritional profile and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It may boost liver health, protect the kidneys and gallbladder, aid in diabetes treatment, enhance heart health, help in cancer prevention and digestion and weight loss. However, an overdose of milk thistle may lead to many side effects. It may lower blood sugar levels way too much, cause allergies, and lead to uterine cancer and uterine fibroids. Hence, use it in moderation to reap its maximum benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
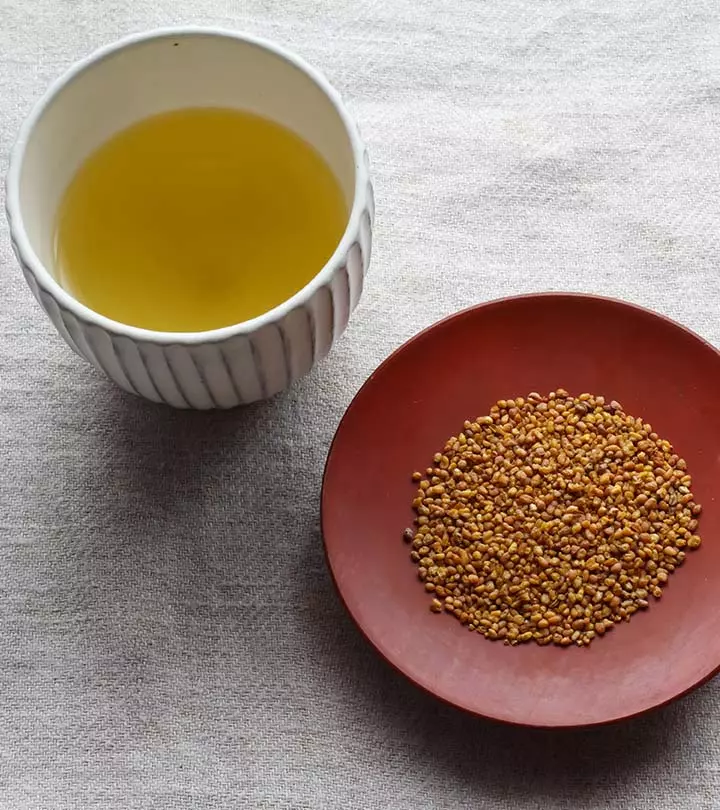
How to make milk thistle tea?
Crush a tablespoon of milk thistle seeds and add it to three cups of boiling water. Steep for about 20 minutes and then strain. You can take one cup at least 30 minutes before meals – once each in the morning, afternoon, evening, and before going to bed.
What is the ideal dosage of milk thistle?
The dosage is 150 milligrams per day – and this acts as a liver detox. For normal use, you can take between 50 and 150 milligrams daily.
Where to buy milk thistle?
You can get it from the nearest health store or online.
What is the best way to take milk thistle?
Though taking milk thistle the natural way may be better, it all boils down to your needs. Please check with your doctor.
Is it best to take milk thistle on an empty stomach?
Yes. Some sources say doing so makes it work faster. But do consult your doctor as well. This is because other reliable sources say that taking milk thistle on an empty stomach can lead to diarrhea.
What to avoid when taking milk thistle?
Milk thistle can inhibit the metabolism of certain drugs. Hence, ask your doctor if any of the medications you are taking could be metabolized by a liver enzyme called CYP3A4.
What is the best time to take milk thistle?
Ideally, it is suggested to consume milk thistle before taking meals. However, it is best to consult a physician before making any dietary changes.
Does milk thistle lower cortisol?
Animal studies suggest that milk thistle may help lower cortisol levels in the blood (16). Cortisol helps regulate stress, metabolism, and other vital functions (17). However, more studies are warranted to understand this theory further.
Is milk thistle good for arthritis?
Yes, milk thistle has potential anti-arthritic properties that may help manage the symptoms of arthritis and may decrease the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (18).
Key Takeaways
- Milk thistle detoxifies and helps regenerate liver cells by protecting the liver and promoting healthy one.
- Studies have shown that milk thistle is capable of lowering bad cholesterol and improving heart health.
- It may increase the supply of breastmilk and help during pregnancy by reducing oxidative stress.
- Excessive consumption may lower blood sugar levels more than desired.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn more about the amazing benefits of milk thistle for your liver. Watch this video to discover how this natural herb can help improve liver health and function. Hit play and get healthier!
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Protective effects of silymarin, a milk thistle (Silybium marianum) derivative on ethanol-induced oxidative stress in liver. Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17133738 - Milk thistle in liver diseases: past, present, future. Phytotherapy Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20564545 - Silymarin and diabetic nephropathy, Journal of Renal Injury Prevention, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4205984/ - Silymarin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Journal of Diabetes Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4908257/ - The Therapeutic Potential of Milk Thistle in Diabetes, The Review of Diabetic Studies, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4310066/ - The efficacy of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. (silymarin) in the treatment of type II diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Phytotherapy Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17072885 - Multitargeted therapy of cancer by silymarin, Cancer Letters, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2612997/ - Milk thistle, Cancer Research UK.
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/treatment/complementary-alternative-therapies/individual-therapies/milk-thistle-and-liver-cancer - Milk thistle: early seeds of potential, The Lancet. Oncology
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4116427/ - Silymarin improved diet-induced liver damage and insulin resistance by decreasing inflammation in mice. Pharmaceutical Biology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27387273 - A Mini Review on the Chemistry and Neuroprotective Effects of Silymarin. Current Drug Targets, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28025940 - Milk thistle: a future potential anti-osteoporotic and fracture healing agent. Current Drug Targets, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24093748 - Silymarin, a Flavonoid from Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L.), Inhibits UV-induced Oxidative Stress Through Targeting Infiltrating CD11b+ Cells in Mouse Skin, Photochemistry and Photobiology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2394725/ - Immunostimulatory effect of Silybum Marianum (milk thistle) extract. Medical Science Monitor, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12444368 - “Silymarin”, a Promising Pharmacological Agent for Treatment of Diseases, Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3586829/ - Influence of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Seed Cakes on Biochemical Values of Equine Plasma Subjected to Physical Exertion, Animals, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7590064/ - Physiology, Cortisol, StatPearls, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538239/ - Policosanol composition, antioxidant and anti-arthritic activities of milk thistle (Silybium marianum L.) oil at different seed maturity stages
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29661192/
Read full bio of Dr. Zeel Gandhi
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Payal Karnik