12 Health Benefits Of Flaxseeds, Nutrition, And Side Effects
Good for your gut and heart, don't miss out on these delightful nourishing packets.

Image: Shutterstock
Flax is a fiber crop native to Egypt. It has been part of Ayurvedic medicine for centuries in Asia. The benefits of flaxseeds are equally impressive, as they are rich in fiber, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids.

Flaxseeds also possess powerful antioxidants in the form of lignans. They may help manage diabetes and reduce the risk of several cancers. That’s not it! They are also thought to induce weight loss and improve heart and digestive health.
In this article, we have discussed the health benefits of flaxseeds, their nutritional breakdown, side effects, recipes, and how to select and store them. Keep reading!
 Know Your Ingredient: Flaxseeds
Know Your Ingredient: FlaxseedsWhat Is It?
Small seeds with a nutty flavor that are high in fiber.
What Are Its Benefits?
It can help manage body weight, diabetes, skin and hair health, and menstrual symptoms and also improve digestive and heart health.
Who Can Consume It?
Anyone except individuals with hormone-sensitive cancers or health conditions can consume it in moderation. It may also react to certain medical supplements and drugs.
How Often?
1-2 tablespoons a day is considered a healthy amount.
Caution
High dosages can cause bloating, gas, stomachache, and nausea.
In This Article
What Is Flaxseed?
Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) is one of the oldest crops, which has been cultivated since the beginning of civilization. This is also known as linseed, which has gained popularity as a healthy food. These small oil seeds have a mild, nutty flavor and can be easily incorporated into the diet. In addition, this plant-based food source is loaded with many healthy fats and plant compounds that offer many health benefits.
Flaxseed has a rich nutritional profile with a wide variety of vitamins, minerals, and other healthy nutrients. Scroll down to know its nutritional breakdown.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Key Takeaways
- Flaxseeds are plant-based food sources with a rich nutritional profile. The antioxidants, plant compounds, and high protein in flaxseeds offer many health benefits.
- They may help minimize cancer risk, manage diabetes, enhance digestive health, and aid in weight loss.
- Excess intake of flaxseeds may lower blood sugar and blood pressure levels way too much. They also may slow down blood clotting in some cases.
Flaxseed Nutrition Facts

According to the United States Department of Agriculture, 1 tablespoon of flaxseeds (7 grams) contains (1):
- Calories: 37.4
- Protein: 1.28 g
- Fat: 2.95 g
- Carbohydrates: 2.02 g
- Fiber: 1.91 g
- Calcium: 17.8 mg
- Iron: 0.401 mg
- Magnesium: 27.4 mg
- Phosphorus: 44.9 mg
- Copper: 1.22 mg
- Potassium: 56.9 mg
- Sodium: 2.1 mg
- Folate: 6.09 mg
Flaxseed is considered a functional food and contains bioactive compounds like lignans and alpha-linolenic acid. In addition, flaxseed contains many plant compounds such as phenolic acids (ferulic acid, gallic acid, and chlorogenic acid) and flavonoids (2).
Flaxseeds and chia seeds are nutrient-dense food sources with many similar benefits. So what is the difference between these two seeds? Scroll down to find out.
Flaxseeds Vs. Chia Seeds – How Do They Compare Nutritionally?

Flaxseeds and chia seeds are both nutrient-dense with some similar health benefits. However, from their nutritional point of view, flax seeds have more copper and potassium than chia seeds (1), (3).
Flaxseeds contain more omega-3 fats and are more effective at reducing hunger and appetite than chia seeds. Whereas chia seeds have slightly more calories and fiber values than flaxseed.
In addition, they have slightly more carb and fiber values per serving than flaxseeds.
Though they differ in their nutritional values, both these seeds offer numerous health benefits. Scroll down to find the health benefits of flaxseeds in the following section.
Health Benefits Of Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds are a powerful superfood packed with essential nutrients that can positively impact various aspects of your health. Understanding these benefits is key to making informed choices about your health and wellness. Here are the benefits of flaxseeds:
1. May Help In Cancer Prevention
Several studies on postmenopausal women showed that supplementing diets with flaxseeds could reduce the risk of breast cancer (4). The seeds may also reduce tumor growth in patients with breast cancer. In addition, the omega-3 fatty acids in the seeds have anti-inflammatory properties that help in this regard.
Lignans were also found to reduce the growth of cancerous tumors (5). Research also shows that flaxseeds may help prevent prostate cancer (6).
2. May Aid Diabetes Treatment
Studies showed that flaxseed supplementation lowered fasting blood sugar levels by 20%
(7). More importantly, the seeds contain mucilage, which is a gel-forming fiber that can slow digestion and the resultant release of glucose into the blood.
Preliminary studies have also shown that flaxseeds can delay the onset of diabetes mellitus. They contain a compound called SDG, which could reduce the risk of type 1 diabetes and delay the onset of type 2 diabetes (8).
3. May Aid Weight Loss
As flaxseeds are rich in fiber, they can aid weight management
(9). The seeds also contain omega-3s. Studies show that omega-3s may suppress appetite and improve satiety – and this may help in weight loss (10).
The lignans in flaxseeds are also believed to boost metabolism, which may aid weight loss. However, more research is needed to understand the mechanism.
Studies also showed that flaxseeds could increase fat excretion, thereby decreasing the amount of fat content in the body. This may promote weight loss (9). You can explore ways to use flaxseeds for weight loss in case you want to give it a try.
4. May Enhance Digestive Health
Animal studies showed that flaxseed supplementation in the diet could promote the health of gut flora (11). The soluble fiber in flaxseeds could aid digestion as well, although supporting research is limited. Ground flaxseeds are believed to work better as eating them whole can ake them pass through your system without getting digested.
The most common use of flaxseeds involves their laxative properties. This means the seeds can make you poop. They can also help treat constipation or diarrhea but ensure you drink enough water after consuming them (5).
The omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseeds can help reduce inflammation and protect the lining of the GI tract. In people with healthy digestive systems, the seeds promote the beneficial gut flora (12). Further research is needed to understand the benefits of omega-3s and their connection to gut flora.
5. May Protect The Heart
The omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseeds have been found to cut the risk of coronary heart disease. They also help improve the functioning of the arteries (13). A Costa Rican study showed that individuals consuming more of ALA (the type of omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseeds) had a lower risk of heart attack (14).
6. May Fight Inflammation
Two tablespoons of ground flaxseeds contain over 140% of the daily value of omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to fight inflammation. The alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) in the seeds was found to decrease pro-inflammatory compounds in the body (15).
The omega-3s in flaxseeds can also help treat inflammatory arthritis (16).
7. May Treat Menstrual Symptoms
Consuming flaxseeds may regularize ovulation. Women who regularly ate flaxseeds were found to ovulate during every menstrual cycle because of hormone balance (17). Adding flaxseeds to your diet may also help reduce menstrual cramps, though more research is required to support this effect.
Another important piece of research tells us that flaxseeds may help ease menopause symptoms, like hot flashes. some other studies state otherwise, and more research is warranted to understand how flaxseeds work in this regard (18).
8. Flaxseeds Are Gluten-Free
Flaxseeds work as a great replacement for all those gluten-containing grains in your diet (5). In case you are gluten-intolerant, most grains could be hard to digest. This is where flaxseed can be a good choice for anyone with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity (19).
9. May Be Beneficial During Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
Flaxseeds are a rich source of fiber and omega-3s and a good source of protein – and a pregnant woman requires all these nutrients. Fiber could help treat constipation that often occurs during pregnancy. The protein and omega-3s are critical for the child’s health. However, there is no direct research stating the benefits of flaxseeds during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
As per an animal study, flaxseeds can promote retina and optic nerve development in the offspring (20).
However, we recommend you talk to your doctor before taking flaxseeds for this purpose as there is some conflicting evidence in this regard.
10. May Lower Cholesterol Levels
Consuming flax seeds may have beneficial effects on cholesterol levels. They may have lipid-lowering effects in animals and humans. A study found that the lignans present in the seeds could significantly reduce plasma cholesterol and glucose concentrations in the body (21).
Another study shows that milled flaxseed lowers total and LDL cholesterol in people with peripheral artery disease. It also has an additional LDL-cholesterol-reducing capability when used along with cholesterol-lowering medication (22). So, it may be good to include flaxseeds in your daily diet if you have cardiovascular issues or high cholesterol. However, please consult your doctor before use.
11. May Make Your Skin Glow
The omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseeds may contribute to skin health and appearance. They can keep your skin hydrated and make it smooth. Studies show that dietary supplementation of flaxseeds can balance the anti- and pro-inflammatory compounds and promote healthy aging (11).
The oil of flaxseeds may also help. It may prevent everyday irritants and pollutants from entering your skin pores (23). It also prevents water loss from the skin. Improving the skin’s moisture levels can also help reduce wrinkles.
Keeping your skin moisturized prevents it from drying out, and this makes it glow. While we need more research to determine if flaxseeds can directly influence growth, some evidence states that flaxseed oil could improve skin barrier function (23).
Flaxseeds may also aid the treatment of ailments like psoriasisi A non-contagious autoimmune disorder where skin cells accumulate and develop into scales and dry, itchy areas. and eczemai A chronic skin disorder that may flare up occasionally and result in dry, irritated, and inflamed skin. , though direct evidence is lacking in this regard.
You can either rub plain flaxseed oil gently into your skin or consume the seeds on a daily basis. The anti-inflammatory properties of flaxseeds can also treat skin inflammation. As per animal studies, the antioxidants in the seeds may also help reduce the risk of skin cancer (24).
You can also try a flaxseed facial. Mix two tablespoons of raw honey, a teaspoon of fresh lime juice, and a tablespoon of flaxseed oil. Apply the mixture directly to your face. Leave it on for 15 minutes and wash with normal water. Do it in the mornings, every day.
12. May Strengthen Hair
Brittle hair is often attributed to a lack of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet. As flaxseeds are rich in these fatty acids, as per animal studies, they were found to strengthen hair, improve hair coat quality, and combat hair fall (25). They can also help prevent a condition called cicatricial alopecia, which is a permanent hair loss condition caused by inflammation.
Joy O, a blogger, shared her experience of using flaxseed gel for hair. She said, ” This gel gave my hair an amazing shine. It softens and made my curls pop (ⅰ).”
You can prepare a hair gel using flaxseeds. Boil two cups of water. As the water begins to boil, add four tablespoons of flaxseeds to it. Cover the pot with a lid and let it simmer for 15 to 20 minutes. Turn the heat off and strain the infusion. Apply the resultant gel to your scalp every morning and then wash as usual after 20 minutes.
Ensure you do not consume an excess of flaxseeds as they may cause certain undesirable side effects.
What Are The Side Effects Of Flaxseeds?
Flaxseeds may cause adverse effects in some people. Excess consumption of these seeds may cause some adverse effects, such as nausea, constipation, bloating, and pain in the abdomen. It is essential to speak with a healthcare professional before adding flaxseeds to your diet, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are on medication, as flaxseeds may interfere with other medications. Want to know more about the side effects of flaxseeds? Keep reading.
- May Lower Blood Sugar Levels Way Too Much
Since flaxseeds may lower blood sugar levels, individuals who are already on diabetes medication may experience alarmingly low blood sugar levels if they consume an excess of the seeds. However, limited research is available in this area. Consult your doctor.
- May Lower Blood Pressure
Flaxseeds help lower blood pressure (26). However, if taken along with medications for treating high blood pressure, the seeds may cause hypotension (excessively low blood pressure). Hence, people on blood pressure medications should exercise caution.
- May Slow Down Blood Clotting
Studies show that omega-3 fatty acids can reduce blood clotting and increase bleeding (27). As the seeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and may show a significant decrease in blood clotting, people with bleeding disorders must not take them. Also, don’t consume flaxseeds at least two weeks before surgery.
- May Aggravate Hormone-Sensitive Conditions
Flaxseeds can mimic the hormone estrogen, and this can aggravate hormone-sensitive conditions like cancers of the breast, uterus, and ovaries and uterine fibroidsi Non-cancerous growths in the organ that originate from the muscle and connective tissue of the uterus wall. (28).
- May Cause Issues During Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
Since the seeds can mimic estrogen, they may cause issues in pregnant and breastfeeding women (28). Please consult a doctor before using them.
Interactions
Limited research is available in this area. Individuals with diabetes should always check with their doctor before consuming flaxseeds. Omega-3s, the essential fatty acids in the flaxseeds, may interact with the blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin (Coumadin), which, in turn, can increase bleeding (29).
Avoid the consumption of these seeds while taking diabetes medication.
Though flaxseeds possess a vast array of nutrients, they are not magic pills. Therefore, it’s important to be aware of all side effects of flaxseeds before consuming them. Moreover, remember there are no one-food-for-all-ailments when it comes to good health. Consistently making the right dietary choices is key. In the following section, we have discussed how you can add flaxseeds to your diet.
Tips For Adding Flax Seeds To Your Diet
There are a few ground rules:
- The best way to consume flaxseeds is in their sprouted form. Soaking and sprouting them removes phytic acid and also enhances mineral absorption. You can soak the seeds for 10 minutes in warm water or for 2 hours in cold water.
- Flaxseeds are best-consumed ground. This is because our bodies cannot receive the nutrients if they are taken in the whole form.
- Ensure you consume the seeds with plenty of water.
- You can add the seeds to your morning cereal or breakfast smoothie. You can also add them to salads.
- Ensure you don’t heat flaxseed oil as its composition might change, and it may not be useful. But surprisingly, the nutrients in whole flaxseeds are heat-stable. Hence, you can roast flaxseeds and enjoy the benefits as the nutrients won’t be destroyed.
- You can also add flaxseeds to your Paleo diet. The seeds are technically Paleo because they are seeds.
- The best time to eat flaxseeds is early in the morning, along with your breakfast.
These are some important tips for adding flaxseeds into your diet. You can prepare some delicious flaxseed recipes at home. Scroll down to know more.
Flaxseeds Recipes

1. Vegan, Gluten-Free Flaxseed Pudding
What You Need
- Ground flaxseeds – 1 cup
- Almond milk – 2 cups
- Sweetener – optional
- Pinch of salt
Process
- Combine the ground flaxseeds and milk in a bowl.
- Add a pinch of salt and your sweetener of choice (optional).
- Store in the fridge for 30-60 minutes or overnight to attain a pudding-like consistency.
- Alternatively, you could blend whole flaxseeds and all other ingredients in a blender for 30-60 seconds, then portion and refrigerate until set.
2. Flaxseed Oatmeal Recipe
What You Need
- Instant oats – ½ cup
- Flaxseeds – 1 ½ teaspoons
- Water – 1 cup
- Brown sugar or honey – To taste
- Milk – to taste
Process
- Take oats, water, and 1 tsp of flaxseeds in a saucepan and heat.
- Stir to combine. Cook for 7 to 8 minutes or until most of the liquid is soaked up.
- Now add any sweetener you like, milk to taste, and mix well.
- Spoon this into a serving bowl and top with ½ tsp of flax seeds.
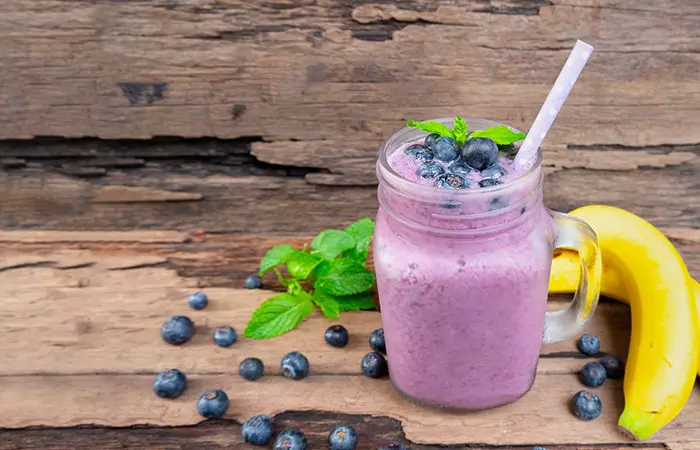
3. Blueberry Banana Flaxseed Smoothie
What You Need
- Ground flaxseed – 2 tablespoons
- Blueberries – 1 cup
- Banana – 1
- Fat-free Greek yogurt – ½ cup
- Milk – ¾ cup
- Honey – 2 teaspoons
- Ice cubes – 6
Process
- Place all the ingredients in a blender and blend until smooth.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipFlaxseeds are sensitive to heat and sunlight. So, they should be carefully stored to avoid spoilage. Scroll down to know how to select and store flaxseeds carefully.
How To Select And Store Flaxseeds?

Flax seeds are available whole or ground in the grocery or online stores. If you buy whole flaxseeds, make sure there is no moisture content and no sign of insects. If you keep them in the refrigerator, they will last for four months. Whereas, if you store them in the freezer, they will last up to a year.
If you are buying ground flaxseeds, make sure they are packed in an airtight container.
The Bottom Line
The benefits of flaxseeds are numerous. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein. These seeds help reduce cancer risk and aid diabetes treatment and weight loss. They also promote digestive, cardiovascular, hair, and skin health.
Infographic: DIY Flaxseeds Face Masks
You have read about the many benefits of flaxseeds for your skin, from keeping your skin hydrated and smooth to preventing irritation, water loss, and wrinkles. But how do you use flaxseed for your skin, especially if you have greasy or dry skin?
Check out the below infographic to learn how to make face masks with flaxseeds for dry and oily skin.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Additionally, they are gluten-free and are beneficial during pregnancy and breastfeeding. While they can be consumed ground or sprouted, excess intake may lower blood sugar and blood pressure levels way too much. They also may slow down blood clotting and aggravate hormone-sensitive conditions. Hence, caution is advised. Moderate consumption of flaxseeds, if you are not allergic to them, can help you enjoy long-term health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many flaxseeds can you take in a day?
You can limit the serving size to less than 5 tablespoons (or 50 grams) a day.
Can you substitute flaxseeds with chia seeds?
Yes, chia seeds are also equally nutritious and beneficial. They look similar too.
How to store flaxseeds?
Whether you purchase ground flaxseeds or grind them at home, you can store them in a tightly sealed container in the refrigerator. Whole flaxseeds can also be stored this way, and they can last for 6 months.
Where can you buy flaxseeds?
You can get the seeds from your nearest departmental or online stores.
Can you eat flaxseeds raw?
Yes, it is fine to eat the seeds raw. Some believe ground flaxseeds can help your body better absorb the nutrients. Also, store raw flaxseeds in the fridge, or the oils in them might make them go rancid.
Do flaxseeds cause acne?
In some cases, yes. This happens if your body doesn’t accept the seeds. Stop using them and consult your doctor.
In general, flaxseeds may aid acne treatment. The omega-3s in the seeds fight inflammation, which is one major cause of acne. The same goes for flaxseed oil as well, though no studies support the link between the oil and acne. However, if your body doesn’t accept the oil, it may react through acne breakouts.
What are flaxseeds called in different languages?
Flaxseeds are called semillas de lino in Spanish, budhur alkitaan in Arabic, alsee ka beej in Hindi, avise ginjalu in Telugu, ali vidai in Tamil, and agasi in Kannada.
Does flaxseed help with belly fat?
The seeds are rich in dietary fiber that may suppress appetite. This may help reduce belly fat, though there is no research to support this.
What is flaxseed oil? How is it made? What are its benefits?
Flaxseed oil is made by cold-pressing flaxseeds. This oil is rich in omega-3 fats and helps reduce cancer cell growth, promote heart health, treat constipation, and improve skin health.
Does ground flaxseed have more health benefits than whole flaxseed?
Ground flaxseeds are easy to digest compared to whole flaxseeds and benefit your health in more ways.
Can I use flaxseed oil in cooking or on a salad?
Yes. You can use it for cooking, without heating. This is because heating may degrade this oil and turn it into a potentially harmful form. So, it is best to add to already prepared dishes. (Note: avoid reheating it in the microwave). In addition, you can make salad dressings with flaxseed oil.
How long does flaxseed take to lower cholesterol?
In a study, those who consumed flaxseed drink and flaxseed bread observed a reduction in their cholesterol (bad cholesterol) levels in 7 days (9). However, this effect may vary among individuals.
Illustration: Health Benefits Of Flaxseeds, Nutrition, And Side Effects

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Seeds, flaxseed
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169414/nutrients - Flaxseed—a potential functional food source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4375225/ - Seeds, chia seeds, dried
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170554/nutrients - The Effect of Flaxseed in Breast Cancer: A Literature Review, Frontiers in Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5808339/ - Flax and flaxseed oil: an ancient medicine & modern functional food, Journal of Food Science and Technology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152533/ - Pilot Study Of Dietary Fat Restriction And Flaxseed Supplementation In Men With Prostate Cancer Before Surgery: Exploring The Effects On Hormonal Levels, Prostate-Specific Antigen, And Histopathologic Features
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11445478/ - An Open-Label Study on the Effect of Flax Seed Powder (Linum Usitatissimum) Supplementation in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus, Journal of Dietary Supplements, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22432725/ - Flaxseed and Diabetes, Current Pharmaceutical Design, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26561065/ - Flaxseed dietary fibers lower cholesterol and increase fecal fat excretion, but magnitude of effect depend on food type, Nutrition & Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3307491// - Dietary Supplementation With Long Chain omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Weight Loss in Obese Adults, Obesity Research and Clinical Practice, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23697585/ - Dietary Flaxseed as a Strategy for Improving Human Health, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6567199/ - Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5751248/ - Does alpha-linolenic acid intake reduce the risk of coronary heart disease? A review of the evidence
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15945135/ - Alpha-linolenic acid and risk of nonfatal acute myocardial infarction, Circulation, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18606916/ - Effect of L. Usitatissimum (Flaxseed/Linseed) Fixed Oil against Distinct Phases of Inflammation, ISRN Inflammation, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3767321/ - Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man, Biochemical Society Transactions, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28900017/ - Effect of Flax Seed Ingestion on the Menstrual Cycle, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8077314/ - A Phase III, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Trial of Flaxseed for the Treatment of Hot Flashes1:NCCTG N08C7, Menopause, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3246070/ - Gluten-free products in celiac disease: Nutritional and technological challenges and solutions, J0urnal of Research in Medical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6327684/ - Flaxseed used since pregnancy by the mother and after weaning by the offspring benefits the retina and optic nerve development in rats, The Journal of Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28282776/ - Dietary flaxseed lignan extract lowers plasma cholesterol and glucose concentrations in hypercholesterolaemic subjects
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18053310/ - Dietary flaxseed independently lowers circulating cholesterol and lowers it beyond the effects of cholesterol-lowering medications alone in patients with peripheral artery disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25694068/ - Supplementation of Flaxseed Oil Diminishes Skin Sensitivity and Improves Skin Barrier Function and Condition, ResearchGate.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21088453/ - Dietary Flaxseed Supplementation and Experimental Metastasis of Melanoma Cells in Mice, Cancer Letters, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9500208/ - Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) supplementation associated with reduced skin test lesional area in horses with Culicoides hypersensitivity, Canadian Journal of Comparative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC227015/ - Potent Antihypertensive Action of Dietary Flaxseed in Hypertensive Patients, Hypertension, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24126178/ - There’s something fishy about this bleeding, NDT Plus, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4421441/ - The pros and cons of phytoestrogens, Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3074428/ - Expert Opinion: omega-3 Fatty Acids and Bleeding-Cause for Concern?, The American Journal of Cardiology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17368278/
Read full bio of Anna Jones
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi




























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.