9 Health Benefits Of Pineapple, Nutrition, And Side Effects
Let the nutritional profile of this vibrant, refreshing fruit brighten up your diet.

Image: Shutterstock
Pineapples are a tropical sweet and sour fruit that is juicy and a rich source of antioxidants and some key enzymes; hence, the benefits of pineapples start with better digestion. Besides, they have also been associated with inducing weight loss and treating inflammation.
Pineapples are also linked with improving children’s nutritional status (1), thanks to their rich nutritional profile. They are especially abundant in vitamins A and C.
In this article, we look at the benefits of this delicious fruit, its potential side effects, how to add it to your diet, and more. Keep scrolling!
 Know Your Ingredient: Pineapple
Know Your Ingredient: PineappleWhat Is It?
A tropical oval fruit with a spiky green outer skin,a crown of leaves and yellow flesh.
What Are Its Benefits?
Pineapple contains bromelain that aids digestion, exhibits anti-cancer properties, helps combat inflammation, and treats osteoarthritis.
Who Can Consume It?
Everyone can eat pineapple as long as they are not allergic.
How Often?
1 cup of pineapple can be consumed daily.
Caution
Pineapples must be avoided by individuals on blood thinner medications to circumvent drug interactions.
In This Article
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Pineapples?
A cup (165 grams) of fresh pineapple chunks contains 82 calories. It has 22 grams of carbs and 2.3 grams of fiber. Following are the other nutrients present:
- 79 mg of vitamin C
- 95 IU of vitamin A
- 21 mg of calcium
- 19 mg of magnesium
- 12 mg of phosphorus
- 180 mg of potassium
- 29 mcg of folate
*Values sourced from USDA National Nutrient Database, pineapple, raw
So, what is pineapple good for? Over the years, science has heavily researched on pineapples and the health benefits they offer. The following section talks about them in detail.
What Are The Health Benefits Of Pineapples?
Pineapple contains bromelain, a digestive enzyme that offers most of its benefits. Bromelain has been found to combat cancer and fight inflammation and associated ailments. The fruit also boosts your immunity and strengthens bones. Let us check out the other benefits of eating pineapple.
1. May Aid Weight Loss
Studies show the possible anti-obesity effects of pineapples. Rats fed on a high-fat diet showed a reduction in body weight, body mass index, body fat accumulation, and liver fat accumulation after the intake of pineapple juice (2).
Pineapple juice was observed to decrease lipogenesis (formation of fat) and increase lipolysis (the breakdown of fats to release fatty acids) (2).
Pineapple may appear to be the ideal food to burn belly fat, although we need more research in this regard.
2. May Aid Digestion
The most important component of pineapple is bromelain, a potent digestive enzyme. Studies show that bromelain (Digestive enzyme) supplementation may help in the breakdown of proteins (3).
It can help treat pancreatic insufficiency, a digestive disorder in which the pancreas doesn’t produce enough of certain enzymes the body uses to digest food in the small intestine (3).
A formula with bromelain as one of the primary ingredients could relieve excess flatulence and diarrhea (3).
A fruit enthusiast blogger explored the role of pineapples in weight loss, emphasizing their nutritional richness. They mention, “When I started inviting pineapple to my daily food fiesta, I noticed my tummy didn’t feel like a bloated balloon at a kid’s party anymore. It was more like a beach ball, light and more manageable (i).” Advising on incorporating pineapples in balanced meals, the blogger cautions against relying on pineapple detox diets, promoting sustainable harmony in dietary choices for effective weight management.
3. May Help Reduce Cancer Risk
Studies have stated that bromelain in pineapples may have anti-cancer properties, thereby promoting cancer prevention. The enzyme may have a direct impact on cancer cells and their environment (4).
Bromelain exhibits anti-cancer effects on colon cancer cells. Foods containing bromelain are considered good candidates for reducing the risk of colorectal cancer (5).
Bromelain can also hinder cancer progression by fighting inflammation, a primary contributor to cancer. It prevents the further generation of cancer cells by exposing them to the immune system. Various traditional and clinical reports indicate the anti-cancer properties of pineapple’s bromelain. Further studies may offer more promising results in this area (6).
In mouse studies, bromelain was also found to inhibit the growth and spread of breast cancer cells. It also could reduce the survival of these cells (7).
4. May Help Combat Inflammation
In animal studies, bromelain has been reported to have therapeutic effects on various inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory bowel syndromei A spectrum of illnesses that lead to gastrointestinal pain and swelling caused due to chronic inflammation. . Bromelain exposure could remove a number of cell surface molecules that contribute to inflammation (8).
Bromelain in pineapples also achieves this by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (9). These are compounds in the human system that promote inflammation, more so in the case of inflammatory bowel disease.
Pineapple extract was also found to treat other issues related to inflammation, including allergic airway disease. The fruit’s enzyme could alter the activation and expansion of specific cells of the immune system. The study was conducted on mouse cells (10).
5. May Help Treat Arthritis And Promote Bone Health
Bromelain may also aid in the treatment of osteoarthritisi A form of arthritis that develops as the pliable tissue at the ends of bones ages and wears down. . The enzyme exhibits analgesic properties, especially in inflammatory pain in humans. It achieves this by directly influencing bradykinin, a pain mediator that causes the contraction of smooth muscle and dilation of blood vessels (11).
Pineapples also contain manganese, a mineral important in bone formation. They also contain vitamin C that supports the formation of collagen in bones. Pineapples can promote the growth of bones in the young and strengthen bones in older people (12).
The anti-inflammatory properties of pineapple’s bromelain may also help treat rheumatoid arthritisi A condition that causes persistent inflammation and affects several joints, especially those of the hands and feet. pain (13).
6. May Improve Cardiac Health
Bromelain in pineapples was found to reduce the aggregation of blood platelets. This may help treat acute thrombophlebitis (a condition characterized by blood clots). However, more studies on human populations are needed to conclude the beneficial effects of bromelain on cardiovascular disease (14).
Bromelain may also break down cholesterol plaques, further promoting heart health (15). Its efficacy in the treatment of other cardiac diseases, including coronary heart disease, rheumatic heart diseasei A disorder when rheumatic fever (a condition brought on by untreated strep throat) irreparably damages the heart valves. , congenital heart diseasei A collective term for a group of birth defects that impair the heart's ability to beat normally, potentially affecting blood flow. , and heart attack is yet to be proven.
7. May Promote Immunity
Bromelain in pineapples can modulate the immune system and potentially accelerate wound healing (16).
Children consuming pineapple juice also had a lower risk of contracting microbial infections. The fruit was found to increase the concentrations of the disease-fighting white blood cells by four times (1).
In another study, children with sinusitis showed faster recovery with a bromelain supplement (17).
Another study sheds light on bromelain’s potential to treat asthma symptoms. It may exert a therapeutic effect on various allergic airway diseases, including allergic asthma (18).
8. May Enhance Recovery
The anti-inflammatory properties of pineapple’s bromelain can aid recovery. This is especially true in case of a much-needed recovery after surgery. More studies are needed to establish bromelain’s effectiveness in post-surgery recovery (19).
In a study, bromelain intake significantly reduced pain in patients undergoing dental surgery. The enzyme offered similar relief as other anti-inflammatory drugs (20).
Bromelain was also found to reduce feelings of fatigue. It reduced muscle damage and improved recovery across consecutive days of cycling (21).
9. May Improve Skin Health
There is limited research in this aspect. The vitamin C in pineapples may benefit the skin. The vitamin promotes collagen production and may protect the skin from damage (1).
Pineapples are amazing-looking fruits with equally amazing benefits. There is no reason you shouldn’t add them to your diet. But how do you do it?
How To Add Pineapples To Your Diet
Pineapples are affordable and easy to eat. In addition to their goodness, they taste delicious too. You can enjoy pineapples in the following ways:
- Add a sliced pineapple to your morning smoothies.
- Chop pineapple and add it to your evening salad.
- Add the fruit to your homemade pizza.
- Pineapple is a versatile fruit and can be easily incorporated into most dishes.
 Trivia
TriviaThus, you can incorporate pineapple into your diet in many ways. However, it can be a challenge to properly cut the fruit. Learn how you can cut this tropical fruit easily below.
How To Cut A Pineapple
The following steps will help you cut a pineapple effortlessly:
- Wash the pineapple and let it dry.
- Lay it on its side and slice off the crown and the base.
- Stand the fruit upright, and carefully carve away the pointy skin, following the curve from the top to its base.
- Once the skin is completely removed, examine the fruit for any remaining ‘eyes’ (small, prickly brown spots).
- Remove them by making diagonal cuts in a V-shape along their lines.
- Cut the smooth pineapple crosswise into rounds or lengthwise into spears, depending on your preference. You can also choose to cube it by slicing it into bite-sized pieces.
Having a pineapple may not be the only way to enjoy the beneficial effects of bromelain. You may also check out supplements.
A Note On Bromelain Supplements
Your health care provider may recommend bromelain supplements, depending on your requirements and health condition. A standard dose of bromelain hasn’t been established yet. We recommend you check with your doctor before taking a supplement. They would also make the appropriate suggestions on the dosage.
You can get a bromelain supplement from your nearest health food store or online.
Pineapple is a tropical fruit with a myriad of benefits. But like any food out there, it has its share of potential adverse effects.
What Are The Side Effects Of Pineapples?
- May Cause Allergies
In some cases, pineapples may cause allergic reactions and diarrhea. The allergies include intense itching, rashes, abdominal pain, and vomiting (22). - May Aggravate Asthma Symptoms
Though some research shows that pineapple may treat asthma symptoms, in certain individuals, the fruit may have an opposite effect (23). - May Increase The Risk Of Bleeding
Bromelain may inhibit platelet aggregation and prevent blood clots. This can increase the risk of bleeding in certain individuals. It may also increase menstrual bleeding. Avoid pineapples right after surgery (24). (Pineapple may enhance recovery post-surgery, but its intake must be supervised by your doctor.)
Also, avoid using bromelain along with prescription blood thinners (25).
- Might Cause Miscarriage During Pregnancy
Anecdotal evidence suggests that pineapples may cause miscarriage (26). Hence, stay on the safe side and avoid intake of pineapples during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Please consult your doctor.
 Fun Fact
Fun FactInfographic: 5 Reasons To Consume Pineapples
The sweet and tangy pineapple is a must during summer. The exotic fruit not only scores with your tastebuds but also offers a plethora of health benefits. It contains bromelain, a digestive enzyme that aids in better digestion, fights inflammation, and improves your overall health. Let’s take a look at some of the health benefits of pineapple in the infographic below. Keep reading!
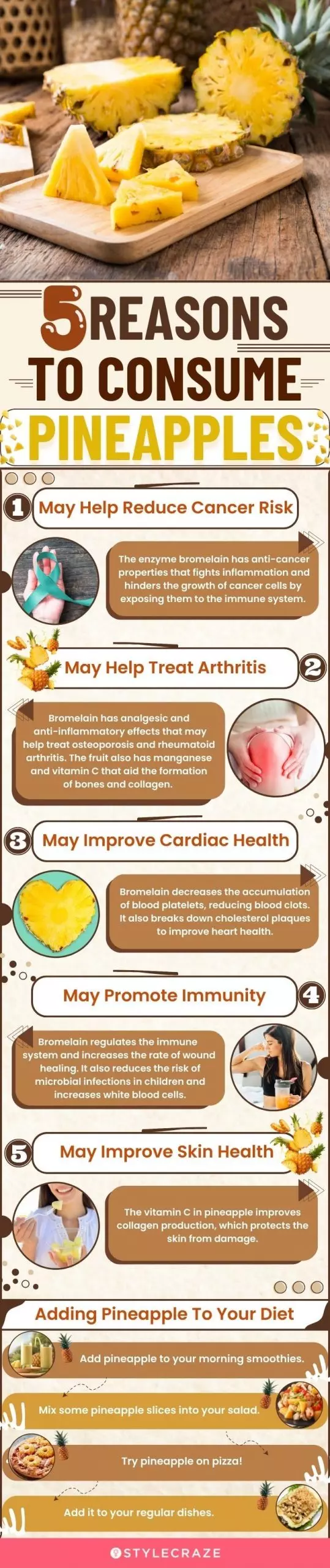
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Though pineapple is a wonder fruit with its own benefits and side effects as memtioned above, its composition, including thiamin, riboflavin, vitamin B6, and niacin, makes it comparatively more advantageous to consume (27).
Pineapple benefits you in numerous ways. They can effectively aid in providing energy, weight loss and digestion and improve bone, cardiac, and skin health. Some other pineapple health benefits include improved immunity, hydration levels, and enhanced recovery. The fruit can also combat inflammation and reduce cancer risk. However, if you are allergic to pineapple, it is better to avoid its consumption. It may also aggravate asthma symptoms and increase the risk of bleeding and miscarriage in some. If you are pregnant or have any specific health condition, consult your doctor before including pineapple in your diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much pineapple can you eat in a day?
A cup of pineapple contains about 80 milligrams of vitamin C, which is more than the recommended dietary allowance of the vitamin. Though there is not enough information on how much of this fruit you can eat in a day, having a cup (166 grams) of it should suffice to enjoy all the wondrous pineapple benefits.
Is pineapple good for diabetes?
Pineapple is relatively low in sugar, so it can be good for people with diabetes. But moderation is key. Hence, please check with your doctor.
Is it good to eat pineapple at night?
Yes. Some experts believe that pineapple may also boost sleep.
Is pineapple good for your liver and kidneys?
The fruit seems to be good for both the organs. Though more extensive research is required, consuming the fruit may help boost the health of your liver and kidneys.
What is the best time to eat pineapple?
Pineapples are best consumed on an empty stomach or in the afternoon.
Is pineapple good for constipation?
Yes. Pineapple is rich in fiber, which makes bowel movements regular and helps treat constipation (28).
Is pineapple good for anti-aging?
Yes. Pineapple core extract was found to exhibit higher antioxidant and anti-aging properties, which can act against the signs of aging (29).
Is watermelon or pineapple better for you?
Pineapple is better because watermelon contains lesser vitamin C, manganese, and copper than pineapple (30), (31).
Key Takeaways
- Pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain, which has anti-inflammatory properties that aid in digestion and combat arthritis.
- Consumption of pineapple also improves heart health, promotes weight loss, and boosts immunity.
- You can add pineapple to your smoothies, salads, or pizzas.
- Excess consumption of pineapple may cause miscarriage, allergies, and asthma.
Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Pineapple is a delicious and nutritious fruit with many health benefits. Click on this video to know more about why you should include this delicious tropical fruit in your diet.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How To Loss Weight With Pineapple: The Juicy Truthhttps://medium.com/how-tos/pineapple-and-weight-loss-the-juicy-truth-f8b3657b9c0d
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Effects of Canned Pineapple Consumption on Nutritional Status, Immunomodulation, and Physical Health of Selected School Children, Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4258310/ - Physiological and molecular study on the anti-obesity effects of pineapple (Ananas comosus) juice in male Wistar rat, Food Science and Biotechnology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30319853 - The Role of Enzyme Supplementation in Digestive Disorders, Alternative Medicine Review.
http://archive.foundationalmedicinereview.com/publications/13/4/307.pdf - Bromelain’s activity and potential as an anti-cancer agent: Current evidence and perspectives, Cancer Letters, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19700238/a> - The chemopreventive action of bromelain, from pineapple stem (Ananas comosus L.), on colon carcinogenesis is related to antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24123777 - Potential role of bromelain in clinical and therapeutic applications, Biomedical Reports, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4998156/ - Evaluation of the Radiosensitizing Potency of Bromelain for Radiation Therapy of 4T1 Breast Cancer Cells, Journal of Medical Signals and Sensors, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6419564/ - Bromelain treatment decreases neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation, Clinical Immunology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18482869 - Dietary Supplementation with Fresh Pineapple Juice Decreases Inflammation and Colonic Neoplasia in IL-10-deficient Mice with Colitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2991605/ - Bromelain limits airway inflammation in an ovalbumin-induced murine model of established asthma
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22894886/ - Bromelain as a Treatment for Osteoarthritis: a Review of Clinical Studies, Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC538506/ - Nutritional Value and Medicinal Benefits of Pineapple, International Journal of Nutrition and Food Sciences.
https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.872.9571&rep=rep1&type=pdf - Efficacy of proteolytic enzyme bromelain on health outcomes after third molar surgery. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, Medicina oral, patología oral y cirugía bucal, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6344017/ - A review of the use of bromelain in cardiovascular diseases, Journal of the Chinese Integrative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21749819 - Properties and Therapeutic Application of Bromelain: A Review, Biotechnology Research International, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3529416/ - Bromelain: biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/PL00000936 - Therapeutic Use, Efficiency and Safety of the Proteolytic Pineapple Enzyme Bromelain-POS® in Children with Acute Sinusitis in Germany, International Journal of Experimental and Clinical Pathophysiology and Drug Research.
https://iv.iiarjournals.org/content/19/2/417.short - Bromelain limits airway inflammation in an ovalbumin-induced murine model of established asthma, Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22894886 - Therapeutic uses of pineapple-extracted bromelain in surgical care – A review, The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28065968 - Perioperative bromelain reduces pain and swelling and improves quality of life measures after mandibular third molar surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24589242 - Acute protease supplementation effects on muscle damage and recovery across consecutive days of cycle racing, European Journal of Sports Science, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25604346 - Systemic allergic reaction and diarrhoea after pineapple ingestion, Tropical and Geographical Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8511816 - Allergic reactions, including asthma, to the pineapple protease bromelain following occupational exposure, Clinical Allergy, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/498486 - Therapeutic uses of pineapple-extracted bromelain in surgical care – A review, The Aga Khan University, Department of Surgery.
https://ecommons.aku.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1532&context=pakistan_fhs_mc_surg_surg - Bromelain has paradoxical effects on blood coagulability: a study using thromboelastography, Blood coagulation & fibrinolysis, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25517253 - Causal explanations of miscarriage amongst Qataris, BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5532791/ - The impact of raw and differently dried pineapple (Ananas comosus) fortification on the vitamins, organic acid and carotene profile
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844020320764#:~:text=In%20case%20of%20pineapple%20several,all%20%5B25%2C%2026%5D - Benefits and Uses of Pineapple, Researchgate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306017037_Benefits_and_uses_of_pineapple - Comparison of Antioxidant and Anti-hyaluronidase Potentials of Pineapple Core Extract (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) and Luteolin, Researchgate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337340357_Comparison_of_Antioxidant_and_Anti-hyaluronidase_Potentials_of_Pineapple_Core_Extract_Ananas_comosus_L_Merr_and_Luteolin - Pineapple, raw, all varieties, FoodData Central.
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169124/nutrients - Watermelon, raw, FoodData Central.
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167765/nutrients
Read full bio of Dr. Geeta Dharmatti
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli






























