Cordyceps Benefits For Health, Dosage, And Side Effects
Explore how this mushroom can naturally boost your energy and performance.
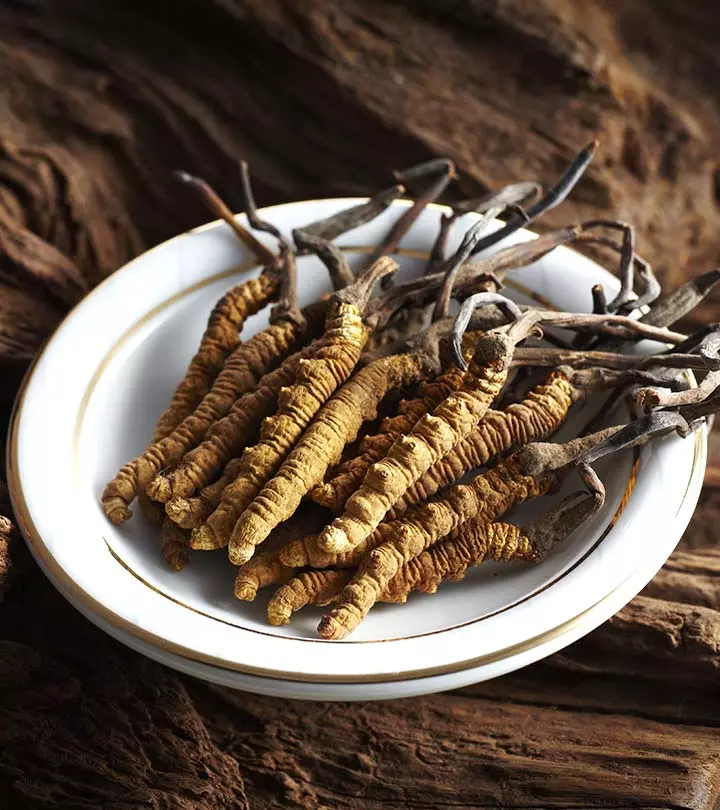

Image: Shutterstock
Cordyceps are mushrooms that grow as a parasite on insect larvae. The benefits of Cordyceps can be attributed to their rich antioxidants and many beneficial nutrients. These mushrooms can also combat inflammation. The remains of insects and fungi are formed as an outgrowth on host cells, which are later collected and dried. These dried remains are used as supplements. The benefits offered by Cordyceps range from enhancing exercise performance to reducing the risk of cancer. Cordyceps were used in many traditional medicines as well.
Know more about these medicinally valued mushrooms in detail, including their nutrition, benefits, and possible side effects. Read on.
In This Article
Types Of Cordyceps
There are more than 600 documented types of cordyceps, but only a few of them are edible. Among them, the following are commonly available.
- Cordyceps militaris: Grows on grains such as rice and is used in traditional Chinese medicine.
- Cordyceps sinensis: Also known as “caterpillar fungus”. Grows on ghost moth larvae in Nepal and China and is highly valued for its medicinal properties.
- Cordyceps cicadae: Grows on cicadas, has a crunchy texture with a mild, sweet flavor, and is hailed for its immunity-boosting properties.
- Cordyceps ophioglossoides: Grows on club molasses, has a bitter taste, and is medically used to relieve fatigue and respiratory issues.
The benefits of cordyceps are not limited to these. Dive deeper into them in the following section.
Health Benefits Of Cordyceps
1. Increase Exercise Performance
Polysaccharides (polycarbohydrates) are active components in Cordyceps and possess anti-fatigue properties (1). A study by the University of North Carolina, USA, found that acute supplementation of Cordyceps may improve tolerance to high-intensity exercise. It indicated greater benefits with consistent chronic supplementation (2). Cordyceps also boost the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecules and enhance the body’s oxygen consumption during exercise (3). These mushrooms are also found to increase oxygen uptake (VO2) and resistance to fatigue among older people during exercise (4). Another study by the University of California, USA, suggests that taking Cordyceps capsules thrice a day for 12 weeks boosts exercise performance. They may also contribute to wellness (5).
Shoshin Show, a YouTuber, shares her experience of testing Cordyceps mushroom for its effect on endurance and heart rate during physical activity. She ran a test for eight weeks alternating between supplement and control days. She measured the metrics to find the difference between Cordyceps and control. She said, “My biking performance on Cordyceps days was nice seconds faster on average. That’s about a five percent improvement (i).” She added, “I was also able to bike faster with improved heart efficiency.”
2. May Help Reduce Cancer Risk
Cordyceps
have an anti-cancer effect (6). Cordycepin, the first isolated drug from Cordyceps militaris, may help prevent the spread of cancer cells besides potentially inhibiting their growth. It works by suppressing tumor growth in different pathways (7). The polysaccharides and other bioactive compounds in Cordyceps also act as potent anti-cancer agents (8). A study suggests that the methanolic extract of C. militaris inhibits the growth of several tumor cells (9). Similarly, the ethanol extract of Cordyceps has a high cytotoxic (damaging or killing cells) activity that can prevent the growth of colon and liver cancer cells (10), (11).
3. May Have Anti-Aging Properties
The polysaccharides in Cordyceps have antioxidant and anti-aging properties that may slow down the signs of premature aging (12). As per a review published in the International Journal Of Molecular Medicine, Cordyceps sinensis oral liquid (CSOL) was found to improve the lifespan of fruit flies by inhibiting oxidative stress (13). C. sinensis has also been shown to reverse age-related changes in gene expression and prolong the lifespan of mice (14). However, more studies are needed to understand this phenomenon of cordyceps in humans.
 Pro Tip
Pro Tip4. May Help Manage Diabetes
A study by Chang-Jung Christian University, Taiwan, on diabetic rats suggests that the fruiting body of Cordyceps can serve as a functional food for those with diabetes (15). In addition, a combination of powders of fruiting bodies and the mycelia (the vegetative parts) of Cordyceps was found to protect the kidneys of those with diabetic nephropathy (16).
5. May Improve Heart Health
Cordycepin, a bioactive component in Cordyceps militaris, has lipid-lowering effects (17). Besides, Cordyceps have been approved to treat arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) in China (3). Oral administration of C. sinensis could also treat heart injuries in a rat model with chronic kidney disease (18). The extracts of mycelia of Cordyceps sinensis have cardioprotective and antioxidant properties. They were found to help reduce contracture (deformity due to tightness of muscles) in the heart (19). Also, a study on hamsters found that cordycepin can prevent hyperlipidemia (20). However, more human studies are needed to understand these benefits of Cordyceps.
6. May Help Fight Inflammation
Cordyceps militaris
is used in Chinese medicine to treat lung and bronchial inflammation. In a study, it could effectively reduce airway inflammation in mice with asthma (21). In addition, the methanol extracts of Cordyceps pruinosa were found to suppress the inflammation-causing genes (22). A review published in Oriental Pharmacy and Experimental Medicine suggests that Paecilomyces hepiali (a strain of Cordyceps spp) has anti-inflammatory effects that help reduce the expression of inflammatory genes (23). However, more studies are warranted to understand this benefit of Cordyceps in humans.
Insufficient Evidence For
7. May Increase Sex Drive
Ophiocordyceps sinensis has medicinal properties that can enhance sexual performance and libido (sexual desire). It is shown to increase sperm count, mobility, and serum testosterone levels (24).
8. May Help Treat Kidney Disease
A study by the Chinese University of Hong Kong, China, found that Cordyceps sinensis may be used to treat kidney disease (25). Cordyceps preparations, as an adjuvant therapy to conventional medicine, showed potential promise to alleviate complications of chronic kidney disease. However, evidence is too limited to arrive at any definitive conclusion.
9. May Improve Liver Health
Cultured Cordyceps sinensis mycelia may have the potential to improve liver function (26). However, limited studies are available to prove this claim.
Cordyceps are available in different forms. In the following section, we will discuss what to look for when buying its supplement form.
Cordyceps Supplements
Cordyceps
supplements are available as capsules, tablets, or powders. You can also buy dried Cordyceps mushrooms online. Dried forms are often used to make extracts while powdered Cordyceps can be blended into tea, smoothies, or protein shakes. Always look for NSF or USP seals on the labels while buying supplements. Ensure the product is yeast-free.
 Pro Tip
Pro TipWhat is the recommended dosage of Cordyceps? Read to know the answer.
Recommended Dosage Of Cordyceps
No recorded dosage recommendations of Cordyceps are available as most of the studies are limited to animals. However, most anecdotal studies suggest that taking 1 to 3 grams of Cordyceps per day is safe for most people and has no side effects.
In the following section, we understand how you can store Cordyceps.
How To Store Cordyceps?
Keep them in a cool and dry place. Store unsealed supplements in a refrigerator. Place them in the freezer if you want to consume them for a long time.
That said, consuming them for extended periods may cause side effects in some individuals. Let us understand more in the next section.
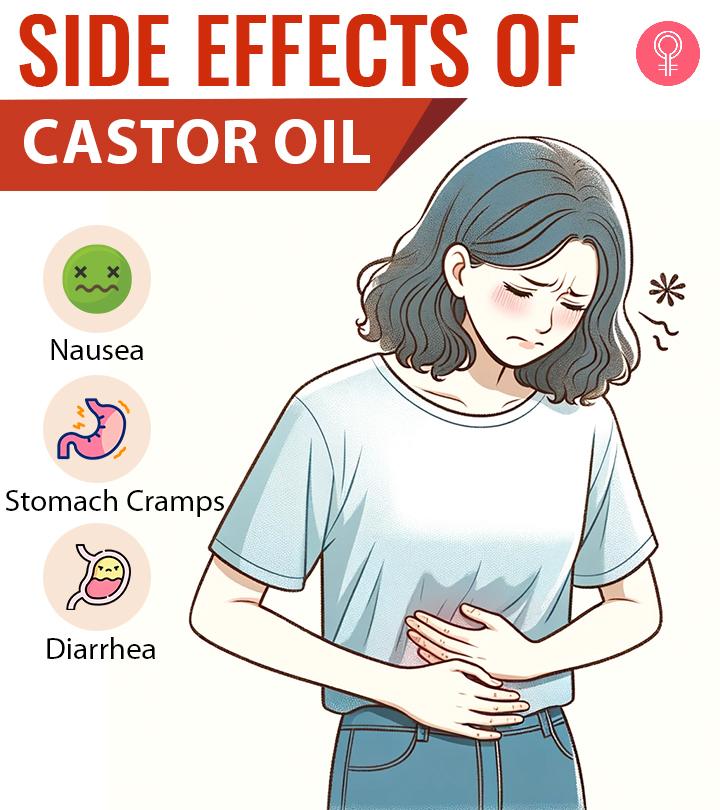
Possible Side Effects Of Cordyceps
Cordyceps
are generally considered safe if you use them in the short run. They are also considered non-toxic, but some people may experience nausea, diarrhea, and dry mouth. Avoid them if you have rheumatoid arthritis (chronic inflammatory disorder affecting many joints) (27). Pregnant and lactating women should avoid them due to limited data on their safety. Consult your doctor before using Cordyceps if you are on any medication.
In A Nutshell
Cordyceps are parasitic fungi with medicinal properties. They grow on the larvae of insects and exhibit several anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The benefits of cordyceps can be attributed to their rich nutritional profile. They may increase exercise performance, reduce cancer risk, slow down the signs of aging, help manage diabetes, and improve heart health. However, they may cause nausea and diarrhea in some people. In addition, people with rheumatoid arthritis should avoid the intake of these mushrooms. Consume them in the recommended dosages and avoid their intake if you are under any medication.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you take cordyceps every day?
Yes, cordyceps can be taken every day. However, their consumption should be limited to 3 – 6 grams a day.
When should I take cordyceps?
Cordyceps or their supplements are recommended to be taken during the day.
Do cordyceps boost the immune system?
Yes, cordyceps can boost the immune system. They stimulate the immune cells and improve immunity.
How long do cordyceps take to start working?
They take approximately 1- 2 weeks to show results.
Does cordyceps make you sleepy?
No, cordyceps cannot make you feel sleepy. Instead, they have an energizing effect and may often interfere with one’s sleep cycle. Hence, consuming them in the morning is generally recommended.
Key Takeaways
- Cordyceps improves the body’s oxygen consumption during exercise and helps increase exercise performance.
- This mushroom may prevent the growth of cancer cells, slow down the signs of aging, help manage diabetes, and improve heart health.
- You can take cordyceps supplements as capsules, tablets, or powders.
- Though it is considered non-toxic and safe, some people may experience diarrhea, nausea, and dry mouth upon eating cordyceps.
Take a look at the incredible benefits of Cordyceps and other medicinal mushrooms. This video also talks about ways to add them to your diet and how they can contribute to your overall wellness. Click on the play button now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
(i) Do Cordyceps mushrooms affect exercise and heart rate?https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KlhvEaB0hbw
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Effect of Polysaccharide from Cordycepsmilitaris (Ascomycetes) on Physical Fatigue Induced by Forced Swimming
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28094746/ - Cordycepsmilitaris Improves Tolerance to High-Intensity Exercise After Acute and Chronic Supplementation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27408987/ - Cordyceps as a Herbal Drug
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92758/ - Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial and assessment of fermentation product of Cordycepssinensis (Cs-4) in enhancing aerobic capacity and respiratory function of the healthy elderly volunteers
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02836405 - Effect of Cs-4 (Cordycepssinensis) on exercise performance in healthy older subjects: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20804368/ - Anticancer and antimetastatic effects of cordycepin, an active component of Cordycepssinensis
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272750546_Anticancer_and_antimetastatic_effects_of_cordycepin_an_active_component_of_Cordyceps_sinensis - Anti-tumor and anti-metastatic roles of cordycepin, one bioactive compound of Cordycepsmilitaris
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319562X1830127X?via%3Dihub - Cordyceps Mushroom: A Potent Anticancer Nutraceutical
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Cordyceps-Mushroom%3A-A-Potent-Anticancer-Khan-Tania/9157909cc7e8dceaccebb8e557a59848227e0bc5?p2df - Cordycepsmilitaris (L.) Link Fruiting Body Reduces the Growth of a Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line by Increasing Cellular Levels of p53 and p21
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26263965/ - Anti-cancer effect of Cordycepsmilitaris in human colorectal carcinoma RKO cells via cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial apoptosis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26141646/ - Anti-tumor effect of Cordycepsmilitaris in HCV-infected human hepatocarcinoma 7.5 cells
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26115996/ - Antioxidant and anti-aging activities of polysaccharides from Cordyceps cicadae
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32339570/ - Cordycepssinensis oral liquid prolongs the lifespan of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, by inhibiting oxidative stress
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4564082/ - Cordycepssinensis Cs-4 restores aging-associated changes in gene expression and extends lifespan in normal aged mice
https://faseb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1096/fasebj.25.1_supplement.1090.13 - The anti-hyperglycemic activity of the fruiting body of Cordyceps in diabetic rats induced by nicotinamide and streptozotocin
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15050427/ - Cordycepsmilitaris Treatment Preserves Renal Function in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy Mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27832180/ - Lipid-lowering effect of cordycepin (3-deoxyadenosine) from Cordycepsmilitaris on hyperlipidemic hamsters and rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21882527/ - Cordycepssinensis protects against liver and heart injuries in a rat model of chronic kidney disease: a metabolomic analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4814030/ - Cardiovascular protection and antioxidant activity of the extracts from the mycelia of Cordycepssinensis act partially via adenosine receptors
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23192916/ - Cordycepin prevents hyperlipidemia in hamsters fed a high-fat diet via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20724804/ - Effects of the immunomodulatory agent Cordycepsmilitaris on airway inflammation in a mouse asthma model
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19133568/ - Methanol extract of Cordycepspruinosa inhibits in vitro and in vivo inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-kappaB activation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12831777/ - Anti-inflammatory effects of Cordyceps mycelium (Paecilomyceshepiali, CBG-CS-2) in Raw264.7 murine macrophages
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4371127/ - Review of Naturopathy of Medical Mushroom OphiocordycepsSinensis in Sexual Dysfunction
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4791983/ - Cordycepssinensis (a traditional Chinese medicine) for treating chronic kidney disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25519252/ - Short-term curative effect of cultured Cordycepssinensis (Berk.) Sacc Mycelia in chronic hepatitis B
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1693509/ - Pharmacological and therapeutic potential of Cordyceps with special reference to Cordycepin
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs13205-013-0121-9
Read full bio of Tracy Tredoux
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi






















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.