Vitamin D: Benefits, Risks Of Deficiency, And Best Sources
While we know that the sunshine vitamin has a lot to offer, are we getting enough of it?
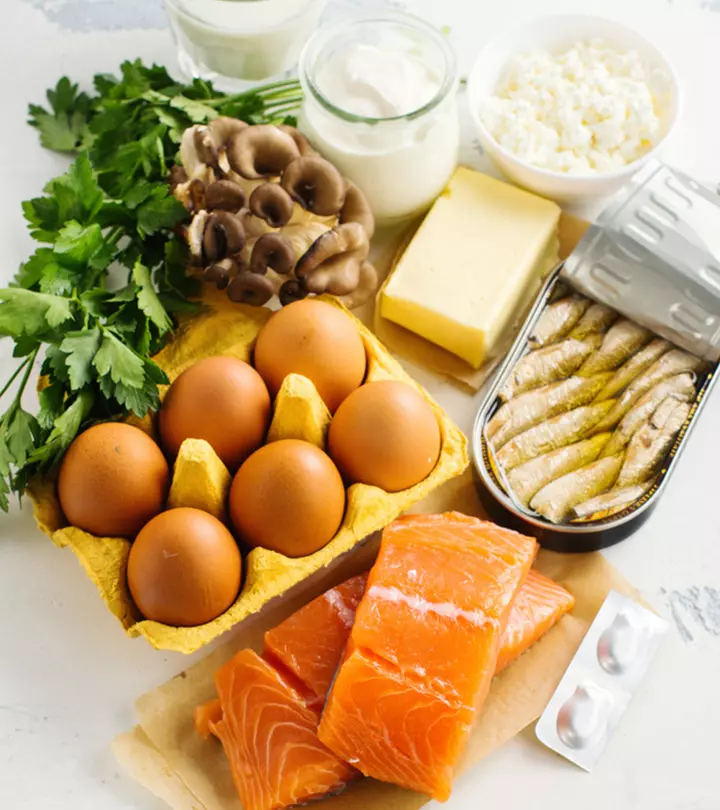

Image: Shutterstock
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that your body needs to perform many functions. Sunlight is the major source of this vitamin, and you also can get it through diet and supplements. However, vitamin D deficiency is turning out to be a major health concern worldwide as it weakens your bones, muscles, and immune system. It also impairs cognitive function, causes severe hair loss, and induces fatigue.
In this article, you will learn about the health benefits of vitamin D, the potential risks of its deficiency, and the best sources to obtain it. Keep reading.
In This Article
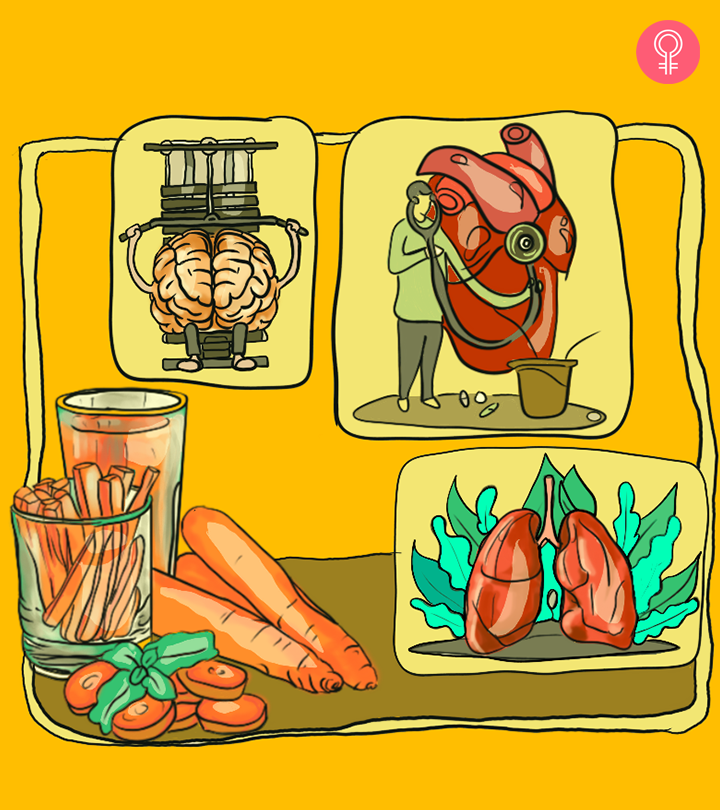
The Role Of Vitamin D In Your Body
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble prohormones (the precursor of hormones, which do not have any inherent hormonal activity until the body turns them into hormones). This vitamin helps promote the health of bones, teeth, skin, and vital organs through various mechanisms (1).
The skin has a compound called 7-dehydrocholesterol, which absorbs UV-B rays from the sun and gets converted into previtamin D3. This is then converted into vitamin D3 (2). In a way, sunlight is an incentive for your body to produce the vitamin.
Vitamin D is essential for (3):
- Calcium absorption for bone and muscle health
- Helping the immune system fight diseases
- Nerve signaling
- Maintaining heart health
- Maintaining brain health
- Regulating blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes
- Preventing or regulating symptoms of multiple sclerosis
 Trivia
TriviaThe lack or excess of vitamin D can affect bodily functions. So, what is the right amount of vitamin D for you? Keep scrolling to find out.
The Right Amount Of Vitamin D
You can get vitamin D from food and supplements apart from sunlight. Your body cannot produce this vitamin on its own.
The optimal requirements of vitamin D are (3):
| Stage Of Life | Recommended Amount |
|---|---|
| Birth to 12 months | 10 mcg (400 IU) |
| Children (1–13 years) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| Teens (14–18 years) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| Adults (19–70 years) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| Adults (71 years and older) | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
| Pregnant and breastfeeding teens and women | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
What are the best sources of vitamin D? When do you need to take supplements? Let us discuss this further in the following section.
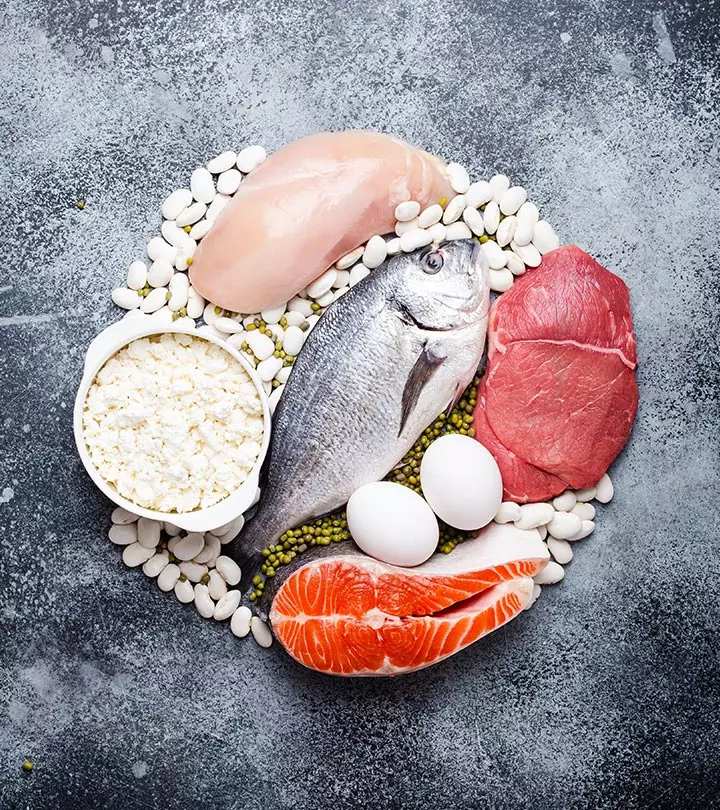
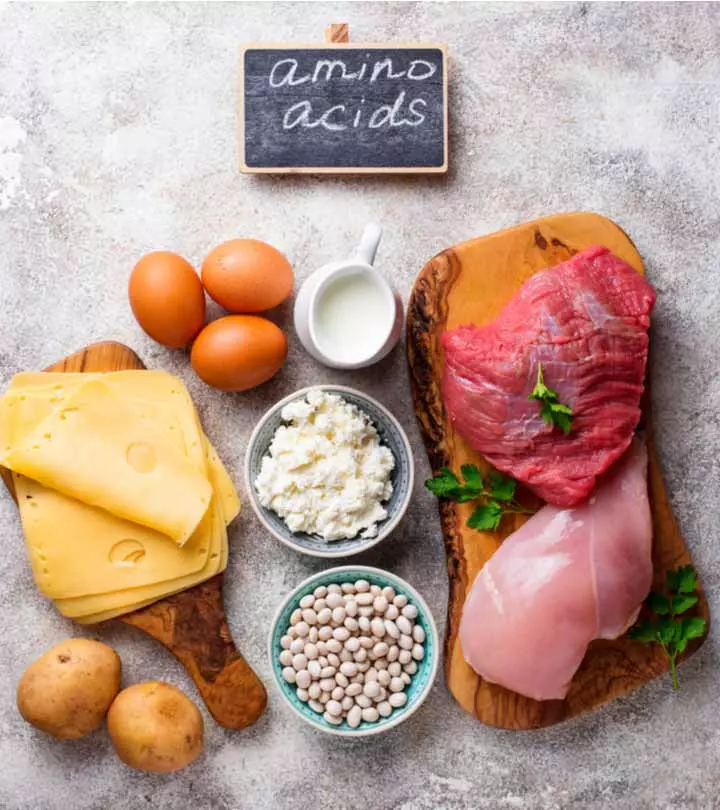
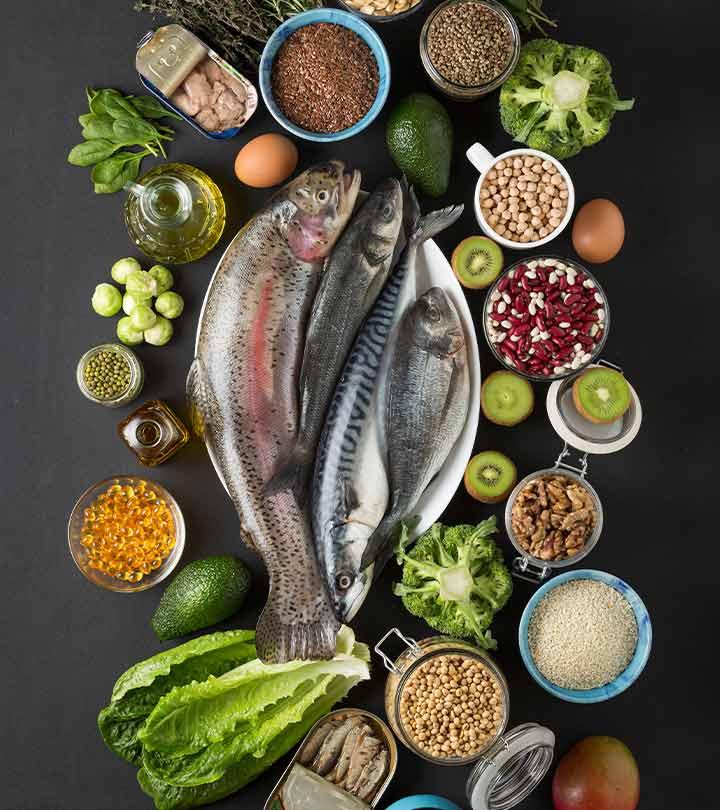
The best source of vitamin D is sunlight. Other sources of vitamin D include salmon, red meat, herrings, cod liver oil, egg yolks, and supplements. The body cannot make enough vitamin D during winters and the rainy seasons due to reduced sun exposure. Hence, supplements with 10 micrograms of vitamin D should to be taken during these seasons (4).
 Trivia
TriviaA lack of any essential vitamin can impact your health. What happens if you are deficient in vitamin D? Keep reading to know.
Vitamin D Deficiency: What It Could Cause
1. Osteoporosis
Vitamin D deficiency can affect calcium absorption in the body. Low levels of calcium lead to loss of bone mineral density and brittle, weak bones. This effect and oxidative stress may cause osteoporosis in older people (5). Research suggests that about 9 million fractures are reported worldwide every year due to osteoporosis (6).
2. Rickets Or Osteomalacia
Inadequate vitamin D causes brittle, weak, and soft bones in children. This condition is called rickets, which manifests in infancy. It causes frequent fractures in babies, stunted growth of limbs, and frequent pain in the bones. Besides, affected kids develop a curved leg structure when they start walking because of the weak bones (7). Osteomalacia (softening of bones) is a similar condition reported in adults due to a prolonged vitamin D deficiency (8).
Note: Osteoporosis and osteomalacia are often confused. While osteoporosis weakens once-strong bones, osteomalacia does not let the bones harden.
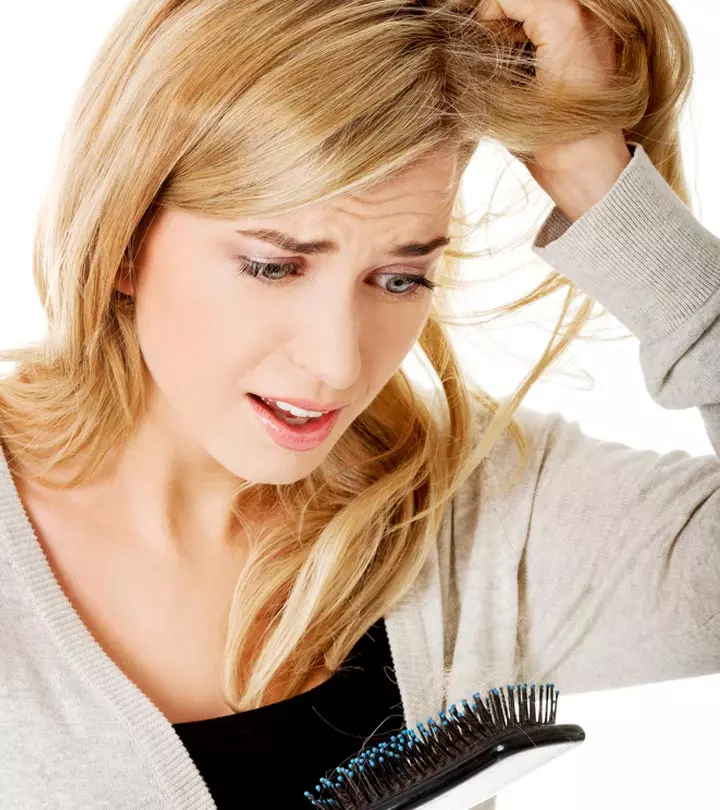
3. Hair Loss
Insufficient vitamin D levels may cause hair loss. The deficiency may trigger an autoimmune disease called alopecia areata, which weakens the immune system and causes inflammation of the hair follicles (9).
4. Depression And Anxiety
A study suggests that low vitamin D levels may cause late-life depression. Similarly, another study indicated that serum vitamin D levels are inversely associated with clinical depression. However, both studies highlight the need for more evidence to draw definitive conclusions (10), (11). Besides, more extensive research is warranted to determine whether supplementing vitamin D helps improve the symptoms of depression.
These are some of the downsides of vitamin D deficiency that you may not be able to detect on your own. However, this deficiency may also cause a few other conditions with notifiable symptoms. Keep reading to find out what they are.
How Can You Know If You Are Vitamin D Deficient?
1. Impaired Wound Healing/Falling Sick Often
The vitamin D receptors are expressed on immune cells. Hence, vitamin D can influence the innate immune system (12). People with impaired immunity are more susceptible to frequent illnesses and recover slowly from wounds (13).
A study was conducted on 4.6 million to analyze the effect of two vitamin D supplements on COVID-19 severity and morality. The participants were divided into three groups – the supplement groups (108,343 and 134,703) and the control group. The two groups showed 0.6% and 0.5% cases of severe COVID-19 infection and mortality caused by it compared to 1.3% in the control group.
2. Muscle And Bone Pain
Studies link vitamin D deficiency with muscle pain, especially in the legs (14 ). The deficiency may also weaken bones(due to improper calcium absorption) and muscles, leading to frequent falls and fractures in elderly people (15 ).
3. Fatigue
Studies suggest that inadequate vitamin D affects sleep patterns and induces fatigue. A study on Iranian nurses reporting tiredness showed that 89% of them were deficient in vitamin D (16). Another study on children found that vitamin D deficiency may result in poorer sleep efficiency and decreased sleep duration (17). Hence, normalizing vitamin D levels may help reduce fatigue (18).
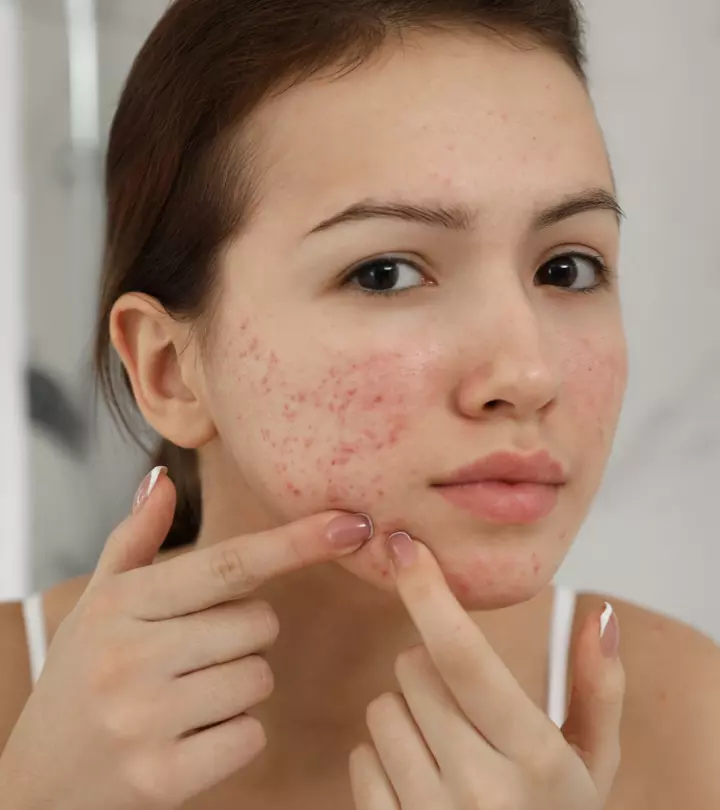
4. Acne Breakouts
Vitamin D deficiency is directly linked to inflammatory skin disorders like acne. According to a study, serum vitamin D levels were found to be low in acne patients compared to non-acne subjects. Besides, these levels were also inversely correlated to the severity of acne (19).
Consult a doctor immediately if you notice these symptoms and get yourself tested for blood vitamin D levels.
How do you know if you are at risk of developing vitamin D deficiency?
Groups At Risk Of Developing Vitamin D Deficiency
People who are more prone to this deficiency include (3):
- Breastfed infants
- Older adults
- People who do not get enough exposure to sunlight
- People with dark skin
- People who are obese or have undergone gastric bypass surgery
- People with conditions that limit fat absorption
Vitamin D benefits the bone, tooth, skin, and crucial organ health and is required for various physiological actions in the body. A deficit can cause your muscles and bones to deteriorate and your immune system to be compromised. Acne, hair loss, and exhaustion are also possible side effects of vitamin D deficiency. Sunlight is the best source of vitamin D. Salmon, herrings, red meat, egg yolks, cod liver oil, and supplements are also good sources. Enough sunshine exposure can aid in the treatment of this deficit. However, remember to use sunscreen to protect your skin from other harmful UV radiation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What drinks contain vitamin D?
Soy milk, orange juice, buttermilk, and cow’s milk are good sources of vitamin D (20).
Are bananas high in vitamin D?
No, bananas are not high in vitamin D.
Can too much vitamin D be harmful?
Yes, too much vitamin D may cause nausea, weakness, kidney problems, and bone pain.
Does low vitamin D cause migraines?
Yes, low vitamin D levels might cause migraines. Adequate vitamin D levels may play a role in migraine prevention, but more research is needed to establish a definitive connection between the two (21).
Can low vitamin D cause neuropathy?
Yes, it may. As per a study, not having enough vitamin D in your body, especially at severe levels, might be connected to experiencing more pain in diabetic nerve problems (22). High levels of certain markers in the body suggest that low vitamin D could play a role in causing this pain. It is important to keep your vitamin D levels in check, especially if you have diabetes.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin D helps promote the health of bones, teeth, skin, and vital organs.
- The best source of vitamin D is sunlight. Other sources include salmon, red meat, herrings, cod liver oil, egg yolks, and supplements.
- Vitamin D deficiency may trigger alopecia areata, which weakens the immune system and causes inflammation of the hair follicles.
Vitamin D deficiency is a widespread phenomenon, causing issues like bone pain and mood swings. While sunlight is a good source, sometimes symptoms show a need for food options that can act as supplementation. Check out this video for more.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Vitamin D and Cancer Prevention
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/diet/vitamin-d-fact-sheet - Sunlight and Vitamin D
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3897598/#:~:text=Vitamin%20D%20is%20the%20sunshine - Vitamin D – Consumer
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-Consumer/ - Vitamins and minerals – Vitamin D
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-d/ - The effect of vitamin D on bone and osteoporosis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21872800/ - Osteoporosis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441901/ - Vitamin D-dependent rickets
https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/vitamin-d-dependent-rickets/ - Osteomalacia – StatPearls
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551616/ - Vitamin D deficiency in alopecia areata
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24655364/ - The role of vitamin D in the prevention of late-life depression
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26998791 - Vitamin D and Depression: A Critical Appraisal of the Evidence and Future Directions
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6970300/ - Vitamin D and the Immune System
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3166406/ - Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses in Wound Epithelialization
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4086194/ - Vitamin D Deficiency Promotes Skeletal Muscle Hypersensitivity and Sensory Hyperinnervation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3319727/ - Recognizing the musculoskeletal manifestations of vitamin D deficiency
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3188408/ - Fatigue and Vitamin D Status in Iranian Female Nurses
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26755458 - Vitamin D and sleep in children
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7954071/ - Correction of Low Vitamin D Improves Fatigue: Effect of Correction of Low Vitamin D in Fatigue Study (EViDiF Study)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25210673/ - The impact of active vitamin D administration on the clinical outcomes of acne vulgaris
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31868550/ - Vitamin D Sources, Metabolism, and Deficiency: Available Compounds and Guidelines for Its Treatment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8074587/ - Vitamin D Deficiency and Its Correlates in Migraine Patients
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7061508/ - Severe Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated With Increased Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines in Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7987807/
Recommended Articles
- 15 Best Benefits Of Beta Carotene For Skin, Hair And Health
- 27 Amazing Benefits Of Vitamin C For Skin, Hair, And Health
- B-Complex: The 12 Powerful Benefits Of The Vitamin Group
- 15 Benefits Of Antioxidants – And How They Keep Us Healthy In A Polluted World
Read full bio of Dr. Sandeep Jassal
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan