10 Amazing Benefits Of Chicory Root, Nutrition & Side Effects
Be it steamed or in your coffee, consuming this nutty flower comes with its own set of perks.
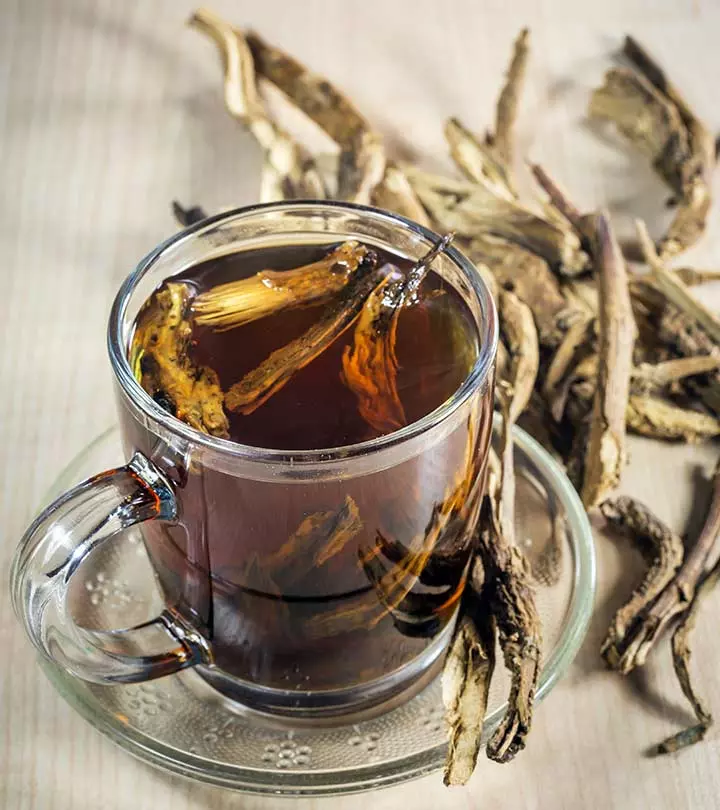

Image: Shutterstock
Chicory (Cichorium intybus) is a flowering plant whose root is popular as a coffee substitute. It is a perennial plant, and its roots are rich in fiber and other important nutrients.
Chicory root may boost digestive health, aid diabetes treatment, help fight inflammatory arthritis, aid detoxification and weight loss, and improve skin barrier function.
Now that we have answered ‘What is chicory?’, let us discuss the many benefits of chicory root as well as how you can use it in your diet. You can also check out the nutritional profile of the root.
 Know Your Ingredient: Chicory Root
Know Your Ingredient: Chicory RootWhat Is It?
Root of a perennial Mediterranean plant with edible leaves and roots rich in nutrients.
What Are Its Benefits?
It may help boost digestive health, liver health, and weight loss and aid diabetes management and skin barrier function.
Who Can Consume It?
Chicory is safe for most people to consume in moderation.
How Often?
It can be consumed daily.
Caution
Excessive consumption may cause gallstones and pregnancy complications.
In This Article
What Is Chicory Root? How Can It Be Good For You?
Chicory root comes from a plant of the dandelion family that bears bright blue flowers. It appears wood-like and is fibrous. This root has natural laxative effects on the body. It also contains inulin, which could promote bone health in rat studies (1).
In the following section, we will look at the benefits of the root in detail.
What Are The Benefits Of Chicory Root?
1. May Boost Digestive Health
The inulin in chicory works as a powerful prebiotic. It improves gut function by promoting the health of the gut bacteria. It also is well tolerated by individuals with gastrointestinal symptoms (2).
Inulin also works as a natural fiber and eases constipation (3). It promotes a smooth and regular digestive process, and this can potentially reduce the risk of colorectal canceri Development of cancer in the colon, the longest part of the large intestine or rectum. Initial symptoms include blood in the stool. (4).
2. May Aid Diabetes Treatment
Studies have shown that chicory root extract can increase the levels of adiponectin, a protein that regulates blood glucose levels. This can help delay or prevent the early onset of diabetes (5).
In a rat study, chicory extract was found to be useful as a natural dietary supplement for slowing down the progression of diabetes (6).
The C.intybus extract present in chicory root is known for its antidiabetic properties. It possesses antioxidant properties that can help improve insulin levels and diabetic neuropathy and enhance pancreatic beta cells. In this graph, the antioxidant activity of C.intybus extract is measured at different concentrations, in combination with C.sinensis extract, on normal rats and rats under diabetic control with catalase enzyme. The highest activity was noted at dose CI 100 μl and with CS extract.
Antidiabetic Activity Due To Antioxidant Potential In Chicory Extracts
Source: Phytochemical Compounds Of Cichorium intybus by Exploring its Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activities3. May Help Fight Inflammatory Arthritis
Preliminary studies show that bioactive extracts of chicory root can have a potential role in treating osteoarthritisi Inflammation in joints due to wear and tear of cartilage that connects them. It can lead to pain, stiffness, and difficulty walking. . More large-scale studies are needed to confirm these findings (7).
It is believed that plant polyphenolsi Naturally occurring micronutrients that are found in plants. They protect the body from heart diseases and cancer. have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that combat inflammation. If you have inflammatory arthritis, chicory root could be one natural remedy you can look at (after consulting your doctor).
Intake of chicory was found to enhance blood flow and the functioning of red blood cells (8). It is believed that this property of chicory could help combat inflammation, though more research is warranted. Chicory aids in the treatment of arthritis or gout, but more studies are needed in this regard.
4. May Aid Weight Loss
This could be attributed to the inulin in chicory root. Studies show that inulin can aid weight loss, especially in individuals with prediabetes (9).
Nicole Kistner, a vlogger, spoke about how she used chicory coffee to aid her weight loss. She said, “It gave me the same effects as the phentermine (weight loss drug). I wasn’t irritable. Whereas with phentermine, I had all those side effects (i).”
5. May Improve Skin Barrier Function
Studies have shown that chicory root extracts may improve skin barrier function. They may also treat the dryness that accompanies the aging process (10).
Chicory root extracts act as an active ingredient and can restructure the skin barrier. These extracts can effectively maintain homeostasisi The process by which an organism maintains chemical changes happening in the body while adjusting to external conditions. and prevent skin alterations (10).
6. May Reduce Stress
Whether chicory root directly reduces stress is yet to be studied. However, because of its flavor, it is often used to make a caffeine-free beverage that can be substituted for coffee. Studies show that excess coffee (caffeine) intake can aggravate stress. Repeated caffeine consumption, combined with stress, can increase one’s cortisol levels and further cause issues (11).
7. May Boost Liver Health
A rat study states that chicory extract can protect the liver from oxidative damage. However, excess (doses of 200 mg per kg of body weight) of the same may cause damage to the liver (12).
In an Egyptian study, chicory extract was found to reduce oxidative stress and prevent cell damage in rat livers. When taken along with celery leaves, the mixture could reduce the symptoms of liver diseases (13).
8. May Help Reduce Cancer Risk
Though we need more research in this regard, certain sources promote the anticancer activities of chicory. The root extract showed antiproliferative activity on skin cancer cells (14).
9. May Help Treat Kidney Disorders
Some research states that chicory can help prevent renal injury. In rats, the root lowered serum uric acid levels and prevented possible kidney damage. Chicory could be used as an alternative to alleviate kidney damage caused by high blood uric acid levels (15).
It is believed that chicory root also has diuretic properties, which may increase urine volume and eliminate toxins from your system.
If you have kidney issues, use chicory root only after consulting your doctor. The root is not a replacement for medications.
10. May Help Treat Candida And Eczema
Chicory extract was found to have antifungal properties that may help in the treatment of certain forms of Candida. The extract also has fewer side effects (16).
Replacing your regular coffee with chicory coffee may also help in treating Candida. Caffeine may stress your adrenal glands and weaken your immunity, further aggravating candida. Replacing it with chicory coffee may help, although there is no research to support this.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that chicory root may help treat eczemai A skin condition that causes dry, irritated, and itchy skin. It can be triggered by environmental factors as well as allergies. . You will need two teaspoons of ground chicory root and a glass of boiling water. Add the two to a steam bath for about 30 minutes, and allow the mixture to sit for another 30 minutes. Dip gauze bandages in the liquid and apply them to the affected areas. You can cover the bandage with a plastic wrap and leave it on for about 30 minutes. Repeat every morning and night for a week.
However, this procedure has not been validated by the medical community. Please check with your doctor before using chicory root for eczemai A skin condition that causes dry, irritated, and itchy skin. It can be triggered by environmental factors as well as allergies. treatment.
 Trivia
TriviaChicory root has long been used in jails in the United States as an alternative to coffee. When Union naval blockades sealed off the port of New Orleans during the American Civil War, Louisianans started to include chicory root in their coffee, starting a long-standing tradition.
Certain benefits of chicory root are yet to be studied extensively. However, the root does help promote health in a few ways. Let us learn how to prepare it in the next section.
How To Prepare Chicory Root
- Scrub the chicory roots under running water to remove dirt.
- Trim the side roots, leaving only the edible taproot.
- Peel the outer layer of the taproot with a vegetable peeler.
- Slice the chicory root into thin rounds, or dice it into smaller pieces, depending on the recipe you are following.
- Spread the diced roots on a baking sheet. Dehydrated them in the oven at 200°F for one and half hours.
- Once they are dehydrated, roast them at 300°F until they turn brown.
Use the dehydrated roots in soups and stews or use the roasted roots as a coffee alternative. You can store the whole or ground chicory roots in a tight glass jar, away from heat and moisture.
In the following section, we will look at the different ways you can include the root in your diet.
How To Use Chicory Root In Your Diet?
Some of the most popular methods include:
- Chicory Coffee
Wash and slice the roots. Roast them in an oven. Cook them until they turn dry and brown. Grind the roots in a food processor. The consistency must be similar to ground coffee. You can brew ground chicory alone or with coffee. Take a tablespoon of ground chicory and mix it with hot water.
- Grilled Chicory
You can cut chicory root and coat its sides with olive oil. Halved or quartered chicory heads work best on a grill. After setting the heads on the grill, they should be cooked in 10 minutes. You can have it on its own or drizzle it with lemon juice.
- Steamed Chicory
This method involves the leaves as well. Steam the leaves along with the chicory root in a steamer basket for about 5 minutes. You can add them to salads or pasta or make a herbal tea.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThese are the ways you can consume chicory and avail its wonderful benefits. In the next section, we will explore the nutritional profile of chicory root.
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Chicory Root?
| Nutrition Facts Serving Size 60g | ||
|---|---|---|
| Amount Per Serving | ||
| Calories 44 | Calories from Fat 1 | |
| % Daily Value* | ||
| Total Fat 0g | 0% | |
| Saturated Fat 0g | 0% | |
| Trans Fat | ||
| Cholesterol 0mg | 0% | |
| Sodium 30mg | 1% | |
| Total Carbohydrate 11g | 4% | |
| Dietary Fiber 0g | 0% | |
| Sugars | ||
| Protien 1g | ||
| Vitamin A | 0% | |
| Vitamin C | 5% | |
| Calcium | 2% | |
| Iron | 3% | |
| Vitamins | ||
| Amounts Per Selected Serving | %DV | |
| Vitamin A | 3.6IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 3.0mg | 5% |
| Vitamin D | ~ | ~ |
| Vitamin E (Alpha Tocopherol) | ~ | ~ |
| Vitamin K | ~ | ~ |
| Thiamin | 0.0mg | 2% |
| Riboflavin | 0.0mg | 1% |
| Niacin | 0.2mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.1mg | 7% |
| Folate | 13.8mcg | 3% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.0mcg | 0% |
| Pantothenic Acid | 0.2mg | 2% |
| Choline | ~ | |
| Betaine | ~ | |
| Minerals | ||
| Amounts Per Selected Serving | %DV | |
| Calcium | 24.6mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0.5mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 13.2mg | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 36.6mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 174mg | 5% |
| Sodium | 30.0mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.2mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.0mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.1mg | 7% |
| Selenium | 0.4mcg | 1% |
| Fluoride | ~ | |
*Values sourced from USDA, chicory roots, raw
Though the chicory root is nutritious, you should not consume it in excess. Over-consumption of the root or its extracts may lead to certain side effects. They are not scientifically proven and are based on anecdotal evidence.
What Are The Side Effects Of Chicory Root?
- May Cause Issues During Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
Chicory root may trigger menstruation and miscarriage. Hence, it is not recommended during pregnancy. There is not enough research in this regard. Hence, stay safe and avoid use.
- May Cause Allergies
If you are allergic to ragweed or related plants, you may be allergic to chicory as well. The root can cross-react with birch pollen and cause the associated oral allergy syndrome (17). If you are allergic to the marigold, daisies, chrysanthemums, etc., please consult your doctor before using chicory root.
- May Cause Gallstones
Chicory may stimulate bile production and cause issues in individuals with gallstones. Hence, it is imperative to consult your doctor.
Infographic: Must-Know Facts About Chicory Roots
Since ancient times, chicory root has extensively been for culinary and medicinal purposes. It is a good source of inulin, which has multiple health benefits. The following infographic takes you through some of the root’s historical uses as folk medicine and its safe dosage when consumed as a beverage. Check it out! Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Chicory roots are rich in dietary fiber and many other medicinal compounds. These roots have been used as food additives in cooking for centuries. The health benefits of chicory roots are numerous, and their intake may help improve digestive health, regulate blood glucose levels, and help fight inflammatory arthritis. You can include this root in many ways in your diet. However, overconsumption of chicory root may trigger miscarriage and menstruation, allergies, and gallstones in some people. Hence, limit its consumption and consult your doctor in any emergencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between chicory root and psyllium husk?
While chicory is a root, psyllium husk is a seed. The similarity between them, however, is that the two have fibrous characteristics.
Where to buy chicory root?
You can buy the root from your nearest supermarket or health food store. You can also get it online.
Does chicory root cause gas?
As per anecdotal evidence, chicory root fiber is broken down by bacteria in the intestine, which may lead to bloating and gas.
Does chicory root increase appetite?
No. The fiber in this root may decrease appetite and total calorie consumption. This, in turn, can lead to weight loss.
Is chicory root gluten-free?
Yes. Chicory root is gluten-free. Inulin, a fiber derived from this root has been used in many gluten-free cakes, bread, and pasta (18).
Does chicory root raise blood pressure?
No. Chicory root does not raise blood pressure. On the contrary, its regular consumption may lead to a decrease in systolic blood pressure (19).
Is chicory good for the heart?
There are no studies that link the consumption of chicory with improved cardiovascular health. However, as it is known to lower blood pressure and help with weight loss, it may exert a cardioprotective effect on the body (9), (19).
Does chicory give you energy?
No, chicory does not act as a stimulant the way coffee does. However, it is known to boost digestion and, hence, may help make more fuel from the food available for energy.
Is chicory root acidic or alkaline?
Chicory is considered to be an alkaline herb.
Key Takeaways
- Chicory roots may help regulate blood sugar and prevent your diabetes condition from progressing.
- They also contain polyphenols that battle inflammation. This can help relieve pain caused by osteoarthritis.
- They may also improve your skin’s ability to hold moisture and fight infections.
- A simple way to consume chicory is by adding it to your coffee.
- However, do not consume chicory root during pregnancy or lactation.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Watch this video for more details on the many health benefits and nutrient profiles of chicory root. Learn how this superfood can help improve your overall health and well-being.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Farmasi Chicory Coffee – 3 things I did to loose weight!https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hdT7c5nGweQ
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Dietary Chicory Inulin Increases Whole-Body Bone Mineral Density in Growing Male Rats, Journal of Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12468594-dietary-chicory-inulin-increases-whole-body-bone-mineral-density-in-growing-male-rats/ - Effect of Chicory-derived Inulin on Abdominal Sensations and Bowel Motor Function, Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5499961/ - Effect of consumption of chicory inulin on bowel function in healthy subjects with constipation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27492975 - Functional Effects of Prebiotic Fructans in Colon Cancer and Calcium Metabolism in Animal Models, BioMed Research International, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5331302/ - Effects of the extract from roasted chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) root containing inulin-type fructans on blood glucose, lipid metabolism, and fecal properties, Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26151029 - Effect of chicory seed extract on glucose tolerance test (GTT) and metabolic profile in early and late stage diabetic rats, DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3556018/ - Phase 1, placebo-controlled, dose escalation trial of chicory root extract in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee, BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2912794/ - Thrombosis preventive potential of chicory coffee consumption: a clinical study, Phytotherapy Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21425378 - A randomized controlled trial: the effect of inulin on weight management and ectopic fat in subjects with prediabetes, Nutrition & Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26500686 - Cichorium intybus root extract: A “vitamin D-like” active ingredient to improve skin barrier function, The Journal of Dermatological Treatment, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27161285 - Cortisol responses to mental stress, exercise, and meals following caffeine intake in men and women, Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2249754/ - Hepatoprotective Activity of Cichorium intybus L. Leaves Extract Against Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Toxicity, Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research.
https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download;jsessionid=6CD3F8457A3365D138CE98BC36CF8B45?doi=10.1.1.553.9404&rep=rep1&type=pdf - Hepatoprotective effect of feeding celery leaves mixed with chicory leaves and barley grains to hypercholesterolemic rats, Pharmacognosy Magazine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3113355/ - Cichorium intybus: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology, Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3860133/ - Effects of Chicory on Serum Uric Acid, Renal Function, and GLUT9 Expression in Hyperuricaemic Rats with Renal Injury and In Vitro Verification with Cells, Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6304617/ - Evaluation of the Antifungal Effect of Chicory Extracts on Candida Glabrata and Candida Krusei in a Laboratory Environment, The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29109313 - Oral Allergy Syndrome to Chicory Associated With Birch Pollen Allergy, International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12759485-oral-allergy-syndrome-to-chicory-associated-with-birch-pollen-allergy/ - Chicory Roots, Nutraceutical and Functional Food Components, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/chicory-roots - Effects of the extract from roasted chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) root containing inulin-type fructans on blood glucose, lipid metabolism, and fecal properties, Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4488567/
Read full bio of Anna Jones
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti