Boysenberry: Health Benefits And Side Effects
Rich in essential vitamins and minerals, this dark and juicy berry does more good than you know.

Image: iStock
Berries are a delight every summer, all over the world. While most grow naturally and are found in the wild, there are also a few hybrid varieties developed meticulously by crossbreeding over the years. Boysenberry is one such hybrid berry that’s usually found freshly harvested in your nearby farmer’s market. Rich in vitamins and antioxidants, boysenberries help improve your health in several ways. Read on to know about their nutrient facts, health benefits, flavor profile, and various ways to include them in your diet.
In This Article
What Is Boysenberry?
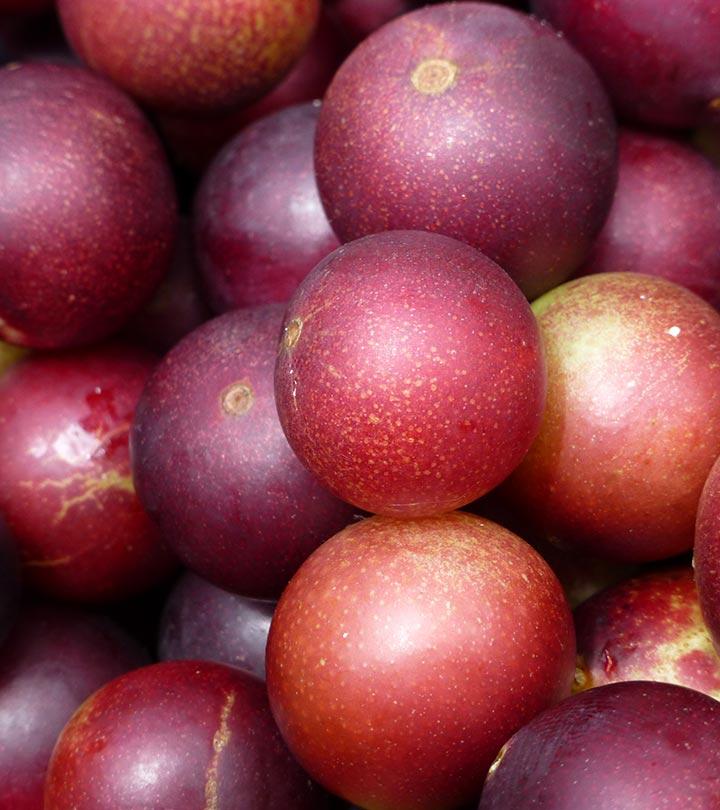
Boysenberry fruit is a large, juicy, dark purple berry that looks like a cluster of small grapes. It is a hybrid fruit developed by cross-breeding loganberry, dewberry, raspberry, and blackberry by Rudolph Boysen in Anaheim, California, in the 1920s. These berries are soft and fragile and don’t transport well. These also tend to get spoiled very quickly, so need to be harvested and consumed soon. With their somewhat sweet yet tangy taste, you can enjoy them fresh as a healthy snack or turn them into delectable jams, jellies, sauces, syrups, and pie fillings.
 Trivia
TriviaLet’s take a deeper look at its nutrient content in the next section.
Nutritional Information
According to the USDA, one cup of frozen, unthawed boysenberries has the following nutrition content (1).
| Water | 113 g |
| Energy | 66 kcal |
| Protein | 1.45 g |
| Total lipid (fat) | 0.343 g |
| Carbohydrate | 16.1 g |
| Fiber | 7 g |
| Sugars | 9.1 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 35.6 mg |
| Iron, Fe | 1.12 mg |
| Magnesium, Mg | 21.1 mg |
| Phosphorus, P | 35.6 mg |
| Potassium, K | 183 mg |
| Sodium, Na | 1.32 mg |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.29 mg |
| Copper, Cu | 0.106 mg |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.722 mg |
| Selenium, Se | 0.264 µg |
| Vitamin C | 4.09 mg |
| Thiamin | 0.07 mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.049 mg |
| Niacin | 1.01 mg |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.33 mg |
| Vitamin B-6 | 0.074 mg |
| Folate | 83.2 µg |
| Choline | 13.5 mg |
| Vitamin B-12 | 0 µg |
| Vitamin A, RAE | 3.96 µg |
| Carotene, beta | 52.8 µg |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | 10.3 µg |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg |
Boysenberries are a good source of vitamins A and C, iron, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and dietary fiber. It also contains vital B vitamins and folate that play an important role in cellular mechanisms and brain development. Additionally, a cup of berries has about 200 mg of potassium and just 1.3 mg of sodium which is essentially good for your cardiovascular health.
Further ahead in the article, we understand how these nutrients translate into some important health benefits for you.
Potential Health Benefits Of Boysenberry
- May Help Promote Lung Health
The polyphenols and antioxidants in boysenberry may have a positive effect on lung health. Research states that regular consumption of boysenberry juice might help moderatechronic lung fibrosisi A lung condition wherein damaged and scarred lung tissue makes it difficult for the organs to function, causing shortness of breath. in asthma and other chronic pulmonary conditionsi Any lung disease that prevents normal functioning of airflow to and from the lungs over a long period of time. (2). A recent study in 2021 also suggests that drinking boysenberry and apple juice concentrate might help reduce lung inflammation and tissue damage (3).
- May Help Support Your Heart Health
Boysenberries are rich in anti-inflammatory polyphenols that may help reduce the risks of cardiovascular disease (4). A few animal studies suggest that consumption of boysenberry juice might help lower blood pressure and serum triglyceride levelsi It refers to the amount of fat in the blood. Increased levels can cause a stroke, heart attack, or pancreatitis. significantly (5), (6). Another study suggested that boysenberry juice can help maintain the thickness of endothelial cell walls, thereby enabling normal blood flow and pressure (7).
- Rich In Antioxidants
Boysenberry is also packed with anthocyanins, the pigmented flavonoids with antioxidant properties that give them their rich vibrant color.
Research has shown that anthocyanins might help prevent neurodegenerativei Diseases caused due to the continuous degradation of nerve cells responsible for mobility and cognition. and cardiovascular diseases associated with oxidative stress (8). These flavonoids may also help strengthen your vision and help reduce the risks of cancer (9).
As per another study, boysenberry seed oil was reported to have the strongest oxygen radical absorbance capacity compared to blueberry, red raspberry, and marionberry seed oils (10).
- May Help Improve Your Bone Health
Boysenberries contain important vitamins and minerals that help support bone health. One cup of frozen boysenberries contains about 36 mg of both calcium and phosphorus. It also has a good amount of vitamin K and manganese, which are vital for bone metabolism (11). The deficiency of these vitamins and minerals could lead to an increased risk of developing osteoporosisi This condition hampers the formation of new bone cells to replace old ones which makes bones weak and more prone to fracture. (12), (13).
- May Help Boost Your Immunity
Like most berries, boysenberries are a rich source of immune-boosting vitamin C. One cup of boysenberries contains more than 4 mg of vitamin C which helps fight infections and strengthen your immune system (14).
Now, with the above boysenberry benefits, you might be keen to include them in your diet and wonder what they taste like. If you find blackberries bitter for your taste, you may actually like the sweet and bold flavor of boysenberries. With their bigger size, they are also quicker to harvest and easier to incorporate into various dishes. Let’s see next what you can make with these clustered berries.
How To Add Boysenberry To Your Diet
Boysenberries are most often seen in the nearest farmers markets around May or early June all through the summers. Boysenberries are typically not found in grocery stores or supermarkets as they are thin-skinned and fragile to transport. These berries don’t last long and should ideally be processed into jams and jellies as soon as harvested.
Boysenberries may last around a week in the fridge, or you can choose to freeze them for later use. The best way to freeze them is to line them out on a baking sheet with enough space in between two berries. Once completely frozen, you can transfer them into a freezer-safe sealed container suitable for long-term storage.
Tue Nguyen, a chef and YouTuber, went to the Boysenberry Festival to try different boysenberry dishes and summed up her experience as follows: “Honestly, all I gotta say about this boysenberry adventure is that food coma is real (i).”
Boysenberries are a balanced mix of sweet raspberries and tart blackberries in taste. A few common ways to include boysenberries in your diet are as follows:
- Bake them into a variety of cakes, pies, and crumbles.
- Blend them into smoothies or add them to a fruit salad.
- Add them to your favorite desserts such as crisps, cobblers, and cakes.
- Make them into jams, jellies, and syrups.
- Add them as a topping or flavoring in ice cream, yogurts, and cheesecakes.
- Make them into syrups and drizzle over pancakes or waffles.
- Blend them into sauces that complement savory dishes like roasted pork or beef.
- Pair them with other berries, coconuts, apricots, peaches, honey, raisins, hazelnut, cinnamon, chocolate, fino sherry, and rum to enhance the flavor of any dish to your liking.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipIn addition to these, you also can prepare a scrumptious dish with boysenberry. We have listed a recipe in the next section. Check it out.
Boysenberry Recipes
Boysenberry Pie
Ingredients
- 1 double-crust pie dough
- 5 cups of boysenberries
- ½ to ¾ cup of sugar
- 3 tablespoons of instant tapioca
- 1 teaspoon of lemon juice
- A pinch of nutmeg
- 1 egg, beaten
Instructions
- In a bowl, combine boysenberries, lemon juice, sugar, tapioca, and nutmeg and make a berry mixture.
- Now, roll out one portion of the pie dough on a floured surface into a 12-inch circle. Line the bottom of a 9-inch pie pan with the dough, then refrigerate.
- Roll out the second portion of the pie dough.
- Fill the dough-lined pie dish with the berry mixture.
- Place the second rolled-out pie dough on top of the pie. Press the edges to seal it and make small air vents. Brush the top with egg.
- Bake at 400° F for 30 minutes.
- Cover the edges and top with aluminum foil to prevent burning. Reduce the heat to 350° F and continue baking for another 30 minutes.
Before including boysenberries in your diet, you should be aware of its possible side effects as well.
Side Effects And Allergies
Since boysenberry is a hybrid berry, people who have prior allergies to raspberry, blackberry, loganberry, or dewberry might have a possibility of allergic reactions to boysenberries as well. They may experience mild allergic reactions like itching, swelling, or stomach discomfort after eating these berries. If you suspect any such allergic symptoms, you should discontinue eating boysenberries and consult a doctor.
Consumption of berries might increase the possibility of kidney stone formation and other renal complications due to their high potassium and oxalate content.
To Sum Up
Boysenberry is a hybrid berry rich in antioxidants, flavonoids, vital vitamins, and minerals. This makes these vibrant berries beneficial to your health in several important ways. They help reduce oxidative stress, promote cardiovascular health and digestion, and may help in weight management and boost your immunity as well. They have a sweet, tart, and bold taste that lends well to making smoothies, salads, jams, jellies, cakes, pies, tarts, and other baked goods.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a marionberry and a boysenberry?
Marionberry is a cultivar of blackberry while boysenberry is a hybrid of four berries.
Is boysenberry a tree or a bush?
It is a bush. Like most berries, boysenberry grows on low, trailing bushes.
How do you know when boysenberries are ripe?
As boysenberries mature, they develop a reddish-dark purple color and develop a distinctive aroma.
Key Takeaways
- Boysenberries are a hybrid fruit developed by cross-breeding loganberries, blackberries, raspberries, and dewberries.
- These sweet and tangy berries are consumed soon after harvesting as they rot quickly.
- Boysenberries offer various health benefits with their vitamin, mineral and antioxidant contents. These berries boost the immune system, reduce the risk of chronic diseases and promote healthy skin.
- Some people may experience itching, swelling, or stomach discomfort after eating these berries.
- Due to their high potassium and oxalate content, excess consumption of these berries may increase the risk of kidney stones and other renal complications.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Discover the amazing health benefits of boysenberries! Learn from this video why nutritionists recommend adding them to your diet for improved health.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. I HAD BOYSENBERRY ON EVERYTHINGhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WO_AiQfNbzQ
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Boysenberries frozen unsweetened
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171713/nutrients - Boysenberry ingestion supports fibrolytic macrophages with the capacity to ameliorate chronic lung remodeling
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27371734/ - Boysenberry and apple juice concentrate reduced acute lung inflammation and increased M2 macrophage-associated cytokines in an acute mouse model of allergic airways disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33747463/ - Acute and chronic flow-mediated dilation and blood pressure responses to daily intake of boysenberry juice: a preliminary study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23848379/ - Effects of acute and chronic boysenberry intake on blood pressure and endothelial function in spontaneous hypertensive rats
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24759259 - Boysenberry Polyphenols Suppressed Elevation of Plasma Triglyceride Levels in Rats
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26440637 - Boysenberry polyphenol inhibits endothelial dysfunction and improves vascular health
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30106986/ - Anthocyanins: A Comprehensive Review of Their Chemical Properties and Health Effects on Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32825684/ - Anthocyanins and Human Health: An In Vitro Investigative Approach
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1082894/ - Fatty acid composition and antioxidant properties of cold-pressed marionberry boysenberry red raspberry and blueberry seed oils
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15686403/ - The role of nutrients in bone health from A to Z
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17092827/ - Osteoporosis: the role of micronutrients | The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | Oxford Academic
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/81/5/1232S/4649817 - The health benefits of vitamin K
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4600246/ - Vitamin C and Immune Function
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29099763/
Read full bio of Nilofar Pendhari
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Payal Karnik