Cinnamon Benefits For Skin: How To Use And Side Effects
From healing wounds to soothing acne, reap the benefits of this spice and calm your skin issues.

Image: Shutterstock
Cinnamon is a spice known for its culinary use and medicinal benefits for good health. However, you may also use cinnamon for skin care issues and improve skin quality. Every part of the tree, including the leaves and roots, has amazing skin care benefits.
Cinnamon has antiviral, antimicrobial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties (1). These properties, along with its sweet fragrance, make it a wonderful ingredient to add to your daily skin care routine. There are several DIY cinnamon remedies to improve your skin. This article discusses the benefits of cinnamon, how to use it, and its side effects. Keep reading
 Know Your Ingredient: Cinnamon
Know Your Ingredient: CinnamonWhat Is It?
A light brown spice obtained from an aromatic tree bark.
What Are Its Benefits?
It is claimed to treat wrinkles, acne, inflammation, and skin damage and brighten the skin.
Who Can Use It?
It can be used by people of all skin types of all age groups to treat different skin problems.
How Often?
Skin care products containing cinnamon can be used every day.
Caution
Cinnamon should be diluted before applying directly on the skin. It may cause irritation, discoloration, or burning sensation.
Benefits Of Cinnamon For The Skin
Cinnamon extracts can help improve common skin conditions and have numerous benefits. They include:
- Has Antimicrobial Properties: Cinnamon oil has antibacterial, antimicrobial, and antifungal properties against some bacteria and fungi, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans(2 ). Staphylococcus aureus causes skin infections, such as abscesses (boils), furunclesi An inflamed, painful, under-the-skin boil that develops when one or more hair follicles become infected. , and cellulitisi A prevalent bacterial skin infection that makes the skin around the infection red, swollen, and painful. (3). Candida albicans cause skin infections, erythemai Redness of the skin, possibly due to sunburn or excess friction, that may be widespread or localized. , skin thickening, and hyperkeratosisi A condition characterized by the thickening of the keratin-based outer layer of the skin, which may be brought on by chronic inflammation. (4).
Cinnamon is often used in skincare and in the treatment of wounds due to its powerful antimicrobial properties. A 2019 study in the International Wound Journal shows that preparing bandages with cinnamon extract can effectively control fungal infections caused by fungi species, such as C. albicans. Hence, the use of such natural ingredients in wound healing can help reduce concerns about the long-term side effects of topical treatments.
Antifungal Activity Of Cinnamon Bandages
Source: Anti-fungal bandages containing cinnamon extract- Promotes Wound Healing: Cinnamon contains cinnamaldehyde, an antimicrobial compound active against against P.aeruginosa strains commonly found in skin wounds and infections. An animal study found that cinnamaldehyde inhibited the growth of P. aeruginosa in skin wounds and accelerated healing (5 ).
- Soothes Pain: Cinnamon bark essential oil extracted from Cinnamomum zeylanicum is commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine to soothe aching joints. It works as an anti-inflammatory agent. However, further research is required to determine its clinical efficacy (6).
- Reduces Acne: Topical cinnamon gel can soothe mild to moderate acne (7). It decreases the number of inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions and reduces other associated symptoms like redness and excess sebum production. Cinnamon contains eugenol, cinnamaldehyde, and coumarin, which can reduce acne blemishes. A study showed that using a herbal soap containing cinnamon oil reduced acne scars and pigmentation (8).
- Prevents UV Damage: Cinnamon also contains vitamin C that protects the skin from UV damage and premature aging (8).
- Brightens The Skin: Cinnamaldehyde is a tyrosinase inhibitor (reduces melanin production) and can be used as a skin-whitening agent in cosmetics (9). Cinnamon also contains p-coumaric acid, a compound used as a skin-lightening ingredient in cosmetics (10). Both the agents may help reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Treats Infections: The Central Council For Research In Ayurvedic Sciences states that a mixture of cinnamon powder and honey can treat cuts, skin infections, and wounds (11), (12).
- Minimizes Wrinkles: Cinnamaldehyde may increase collagen production and effectively reduce signs of aging like wrinkles and fine lines (13).
- Prevents Oxidative Damage: Cinnamon contains beta-carotene, vitamin B, eugenol, cinnamaldehyde, coumarin, vitamin A, potassium, polyphenols, cinnamic acid, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, lycopene, lutein, zeaxanthin, iron, and other nutrients (11). Vitamin A prevents skin damage caused by UV exposure and may even be useful in minimizing psoriasis, ichthyosis (scaly skin), and acne (14). Coumarin helps reduce inflammation, and polyphenols prevent oxidative damage (15), (16).
- Works As Larvicidal: Cinnamon essential oil extracted from Cinnamomum cassia is larvicidal and can repel mosquitoes (11). You can use it as a topical mosquito repellent to prevent mosquito bites.
- Boosts Collagen Production: Ceylon cinnamon extracts can stimulate collagen synthesis and prevent skin sagging and wrinkles (13).
 Fun Fact
Fun FactNow that you know the advantages of using cinnamon for your skin, let’s learn how to use it to reap its benefits.
In This Article
How To Use Cinnamon For Your Skin
You can use cinnamon oil, powder, and other extracts in homemade face masks and DIY remedies or use skin care products with cinnamon extract for its moisturizing and exfoliating properties. Here are a few possible ways to use cinnamon for the skin:
- Mix a drop of cinnamon essential oil with petroleum jelly, olive oil, or coconut oil and use it to moisturize dry lips. You can apply petroleum jelly and a pinch of ground cinnamon to plump your lips.
- Mix a pinch of cinnamon powder with salt, olive oil, almond oil, and honey and use it as a scrub to manage dry skin.
- Make a paste with a teaspoon of cinnamon and three tablespoons of honey and use it as a spot treatment to manage acne. It may also reduce redness and moisturize the skin.
- Mix a pinch of cinnamon, aloe vera gel, a pinch of turmeric, licorice powder, and apply it as a face mask to boost skin elasticity, firmness, and hydration.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Note: Do not apply cinnamon essential oil directly to your skin, as it may cause irritation and a burning sensation. Instead, dilute it with other carrier oils like olive, coconut, jojoba, argan, and castor oils.
While you can apply cinnamon to your skin, there are some adverse effects you need to be aware of before using it.
Side Effects Of Using Cinnamon
Applying cinnamon to your skin is clearly beneficial. However, it may irritate the skin and cause allergic reactions like:
- Redness
- Rashes
- Burning sensation
- Discoloration
Marmie, a blogger, shared her cautionary tale about a honey, cinnamon, and milk combination mask that led to burning her face. She writes. “BEWARE of CINNAMON!!! It can chemically BURN you. My face was so red. I put aloe on it immediately. It settled down after about 30 minutes. And fortunately, after several hours most traces of redness are gone (i).”
Ingesting excess cinnamon can cause:
- Tingling sensations
- Itching,
- Cough
- Breathlessness
Make sure you perform a patch test before using cinnamon for the skin.
Infographic: 6 Ways Cinnamon Benefits The Skin
While cinnamon is relished in desserts and other recipes, its various properties have made it popular in the beauty industry as well. This potent spice can easily be incorporated into your daily skin care routine. But before going ahead, take a look at its benefits that has everyone going gaga over it. Check out the infographic below for more information. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team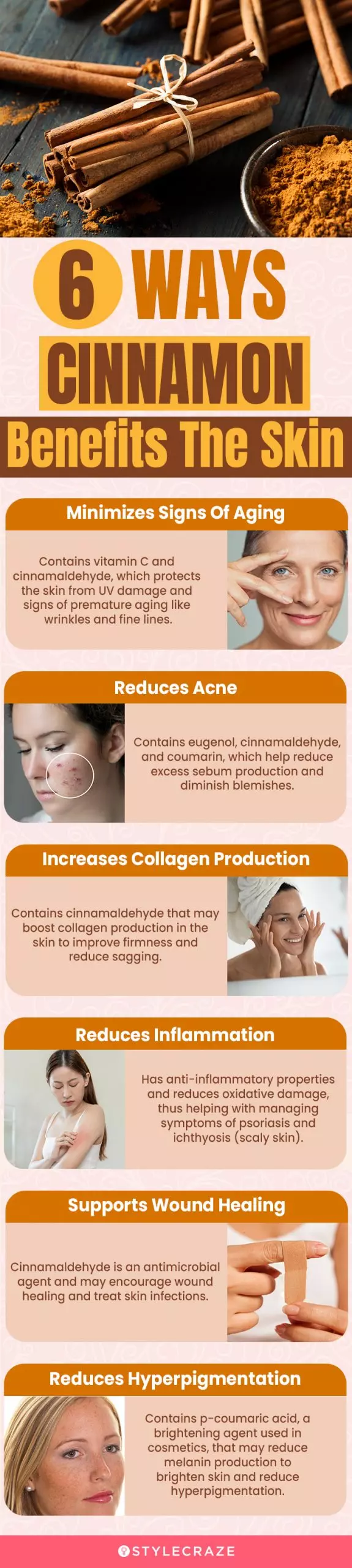
The antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties of cinnamon make it an excellent ingredient to incorporate into your daily skin care routine to enhance your beauty. Using cinnamon for skin care issues helps heal skin issues, soothes pain, reduces wrinkles, manages acne, and brightens your skin. You can use cinnamon powder, oil, and other extracts to make natural remedies like DIY face masks for exfoliation. However, it may cause skin irritation if you are allergic to cinnamon. Therefore, perform a patch test before adding it to your skincare routine. Consult a doctor if you notice any side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is cinnamon good for oily skin?
Yes, cinnamon is good for oily skin. Cinnamon has anti-inflammatory and anti-fungal properties that can help treat breakouts and inflammation (17). It also helps control excess oil production.
Can we leave cinnamon on the face overnight?
Yes, we can leave cinnamon on the face overnight. Cinnamon possesses anti-fungal, antioxidant, and antibacterial qualities, which could help reduce acne. In addition, cinnamon reduces skin oiliness when left on the face overnight. It also promotes blood flow to the skin.
Can cinnamon cause skin damage?
Cinnamon belongs to the spice family and can cause reactions like rash, redness, irritation, and burning due to hypersensitivity. To prevent harsh reactions, you should always use cinnamon powder and essential oil in a diluted mixture.
Is cinnamon good for combination skin?
Yes, cinnamon is a natural exfoliator and is safe for all skin types. Yet, you must use it diluted with a carrier oil. The combination skin type has dry skin areas that may be cinnamon sensitive.
Does cinnamon tighten skin?
Yes, cinnamon increases blood circulation, oxygen, and nutrient supply to the skin surface. This, in turn, increases collagen and elastin production, which plumps the skin and tightens it.
Is cinnamon good for pores?
Cinnamon has astringent properties and helps in unclogging and tightening the pores.
Is cinnamon good for blackheads?
A cinnamon and lemon juice mask is an effective home remedy for blackhead removal. Cinnamon unclogs and tightens the pore, while lemon has antibacterial properties.
Key Takeaways
- Cinnamon has antimicrobial properties, and it promotes wound healing.
- You can scrub your skin by mixing a pinch of cinnamon powder with salt, olive oil, almond oil, and honey.
- Redness, burning sensation, rashes, and discoloration are allergic reactions caused by cinnamon.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Cinnamon is a great spice that can help improve your skin texture. Check out this video to learn about its amazing benefits and how it can help improve your complexion and skin health.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. The burning cinnamon mask – beware,http://www.amarmielife.com/2013/01/the-burning-cinnamon-mask-beware.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Cinnamon Overview of Health Benefits
https://www.mccormickscienceinstitute.com/content/msi/assets/Singeltary%20Nutr%20Today%2043 - Cinnamon: a Multifaceted Medicinal Plant
https://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2014/642942.pdf - About Staphylococcus Aureus
https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/staph/basics.html - Interaction of Candida Species With the Skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5488103/ - Topical Application of Cinnamaldehyde Promotes Faster Healing of Skin Wounds Infected With Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6515316/ - Anti Inflammatory Activity of Cinnamon (cinnamomum Zeylanicum) Bark Essential Oil in a Human Skin Disease Model
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ptr.5822 - Efficacy of Topical Cinnamon Gel for the Treatment of Facial Acne Vulgaris: a Preliminary Study
http://bmrat.org/index.php/BMRAT/article/view/515 - Influence of the Addition of the Essential Oil of Cinnamon (cinnamomum Burmanii) in Soap Against Skin Care
https://knepublishing.com/index.php/KnE-Social/article/view/4129/8497 - Chemical Composition and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity of Cinnamomum Cassia Essential Oil
https://as-botanicalstudies.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/1999-3110-54-10 - P-Coumaric Acid as an Active Ingredient in Cosmetics: a Review Focusing on Its Anti Melanogenic Effects
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/8/8/275 - Cinnamon: a Clinical Approach as 2 Multifarious Natural Remedy With 3 Absolute Immunity
http://ccras.nic.in/content/important-uses-dalchini - Important Uses of Dalchini
http://ccras.nic.in/content/important-uses-dalchini - Cinnamon Extract Promotes Type I Collagen Biosynthesis Via Activation of Igf-I Signaling in Human Dermal Fibroblasts
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22233457/ - Role of Micronutrients in Skin Health and Function
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4428712/ - Coumarin: Chemical and Pharmacological Profile
https://www.japsonline.com/admin/php/uploads/538_pdf.pdf - Discovering the Link Between Nutrition and Skin Aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3583891/ - Cinnamon: A Multifaceted Medicinal Plant
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4003790/
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty