Cupping Therapy: Benefits, Side Effects, And More
Deal with all sorts of aches and pains with this ancient healing method.
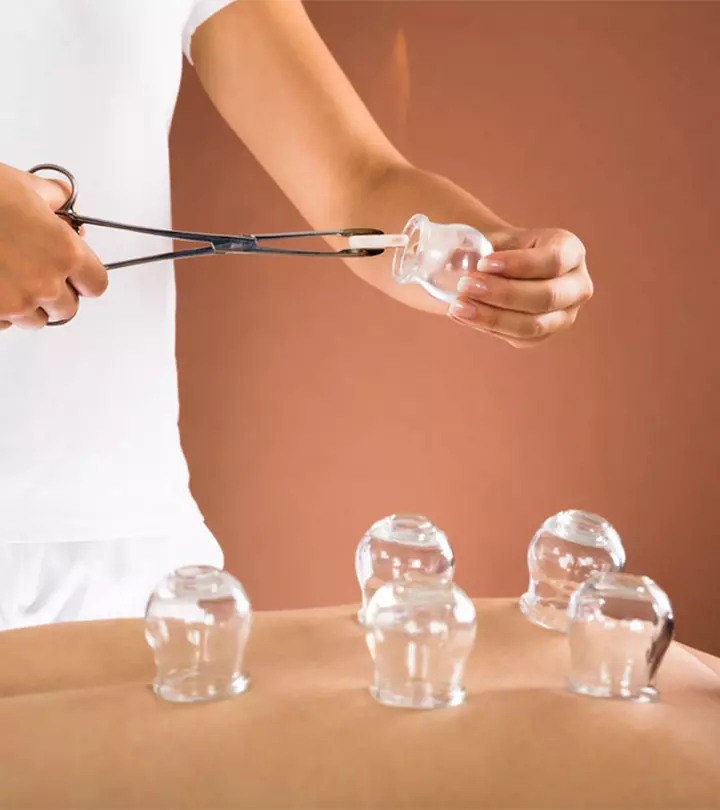

Image: Shutterstock
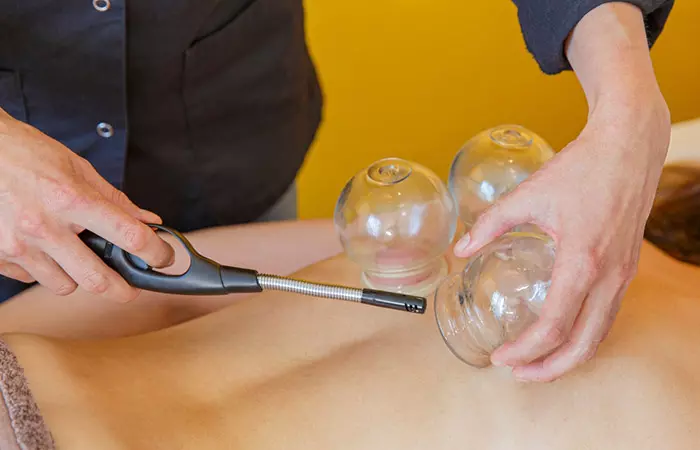
Cupping therapy is a healing method in alternative medicine that is currently used in the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions. This technique involves placing special suction cups on the person’s skin to create a pull or suction which helps facilitate increased blood flow and healing to the affected areas. Although cupping therapy has been practiced for centuries in many countries, it is not fully understood and well-researched today. In this article, we will take a closer and more detailed look at what cupping therapy is, the different types of cupping therapy, its potential health benefits, and how to do it.
In This Article
What Is Cupping Therapy?
Cupping therapy is an ancient healing practice that originated in China. Also known as Hijama cupping or vacuum cupping, cupping massage therapy has been practiced across different Asian, Middle Eastern, and Latin American cultures across the world. Proponents of the method believe that cupping stimulates the flow of “Qi” or life force in the body. They also claim that it restores the body’s balance between the positive (yin) and negative (yang), allowing the body to fight pathogens and reduce pain.
 Trivia
TriviaIn the next section, we explore the different types of cupping therapy practiced currently.
Types Of Cupping Therapy
Originally, suction cup therapy was performed using animal horns. As time went by, cupping techniques adopted the region’s local materials such as bamboo, ceramic, silicone, metal, and plastic. Modern cupping therapy uses round glass cups with one open end to perform the treatment. These are the two types of cupping therapy performed widely today.
- Dry Cupping
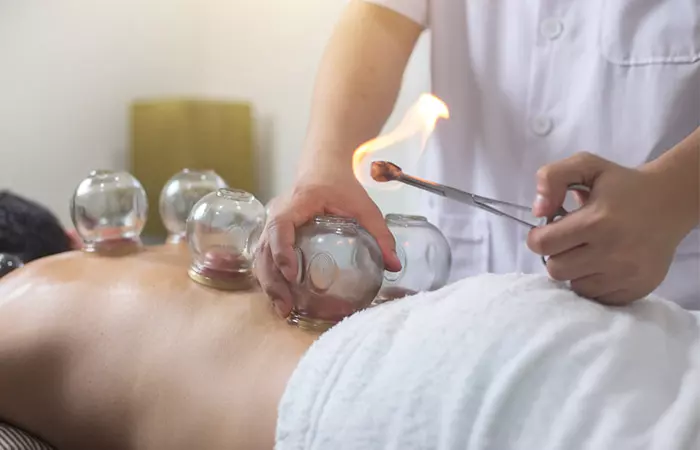
In this method, the medical practitioner heats the cups with fire and places them over several areas on the skin to create a vacuum. This suction lifts the skin and stretches the muscles upward, increasing blood flow and reducing muscle tension and pain.
- Wet Cupping
This technique involves using a scalpel or lancet to make light incisions on multiple areas of the skin, allowing a small amount of blood to be drawn into the cups during the suction process. Practitioners believe this method expels toxins and harmful substances from the body to promote overall healing.
How is cupping therapy done? Let us take a closer look at it In the next section.
How To Do Cupping Therapy
The number of sessions in cupping therapy is determined by the cupping therapist based on your physical health. If you have a history of medical conditions, let your therapist know before you opt for the treatment. Each session takes about 20 minutes and is conducted in the following order (1).
- The practitioner selects specific points for cupping and disinfects the areas.
- The therapist puts alcohol or herbs inside the cups and sets them on fire.
- Once the fire goes out, they are placed upside down on your skin.
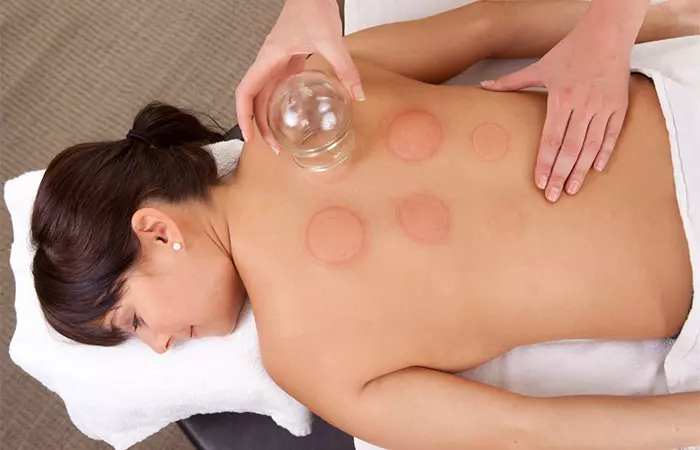
- As the air inside the cups cools, it creates a suction, causing the skin to rise and redden.
- The cups are left on your skin for a period of three to five minutes.
- In wet cupping, the therapist follows all the steps of dry cupping before making small cuts on the skin using a needle or blade.
- The cups are placed again on the skin for a second time and a small amount of blood is drawn.
- The cups are kept for a period of three to five minutes.
- After the removal of the cups, the specific sites are disinfected and dressed to avoid infection.
Emily Elizabeth, a lifestyle blogger, shared her experience of doing cupping therapy and found it to be an easy procedure. She said, “Taking them off was easy and painless too. It was actually a pretty cool feeling. I’m two days out now and have very light bruising on a couple of the spots. Basically, my back feels like I got a massage (i).”
Cup therapy comes with a host of potential benefits. Let’s delve deeper into what they are.
6 Potential Health Benefits Of Cupping Therapy
Modern research suggests that cupping therapy may be effective in treating the following medical conditions.
1. Pain-related Conditions – Cupping has been used as a pain relief treatment for years. A 2011 review suggests that dry cupping therapy may be effective in reducing lower back pain in comparison to conventional drug treatment (2). Other studies also indicate that cupping therapy may reduce neck pain, chronic back pain, and migraines, and improve the overall quality of life (3), (4), (5).
2. Skin Diseases – A 2012 review suggested that cup therapy may be essential in treating skin conditions such as acne, skin itch, hives, and herpes zosteri Also known as shingles, it is a painful rash due to the reactivation of the chickenpox virus, the reasons for which are unknown. (6), (7).
3. Fibromyalgia – Cupping therapy may be effective in managing fibromyalgia, a condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain and fatigue. A study was conducted to see the effect of cupping therapy on symptoms and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia. After administering cupping seasons for 18 days, the patients reported a significant decrease in pain and an improvement in their quality of life (8).
4. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – A 2019 study aimed to examine the effect of cup therapy on patients with carpal tunnel syndrome, a nerve condition that causes pain and tingling in the arm. The study indicated that cupping therapy was effective in reducing the severity of the symptoms in conjunction with physical therapy (9).
5. Arthritis – While cupping has been used to treat many pain-related conditions, it comes as no surprise that it may be essential in the treatment of arthritis. Studies indicate that cupping therapy may decrease inflammation and knee pain associated with rheumatoid arthritisi An inflammatory disease that usually affects joints in the body, but in severe cases, can also damage internal organs. and osteoarthritisi A disease in which protective tissues at the end of bones wear down gradually and worsens over the course of time. (10), (11).
6. Hypertension – Cupping therapy may help manage high blood pressure. Studies suggest that wet cupping may be successful in reducing blood pressure levels in patients with hypertension (12).
While current studies suggest that cupping therapy is a beneficial technique for relaxation, detoxification, and recovery, more studies are required to confirm and further understand its effect on different medical conditions. Does cupping therapy have any adverse effects on your health? Let’s find out in the next section.
Possible Side Effects
While cup suction is considered mostly safe under the care of a trained medical professional, the following side effects have been reported during or after the session (13).
- Bruises
- Scar formations
- Nausea
- Soreness at cupping site
- Burn
- Anemia
- Dizziness
- Possible infection at the sites of incisions
People with the following conditions should exercise caution or speak to a medical professional before opting for this treatment (13).
- Psoriasis
- Bone fractures
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Pregnancy
- Menstruation
- Chronic heart disease
- Ulcer
- History of stroke
- Hemophilia
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Asthma
- Suspicious lump
 Quick Tip
Quick TipDue to limited scientific research, it is difficult to know how common these side effects are. If you do experience these side effects, consult a doctor immediately.
Just like we learnt its possible side effects, it’s important to learn its aftercare too. Check out the tips in the next section.
Cupping Aftercare
- Stay Hydrated
Drink lots of water to assist the body in flushing out toxins and recovering from the heat of the treatment.
- Avoid Big Meals
Opt for lighter meals to aid digestion; big meals can slow down the digestive process and cause discomfort.
- Rest Up
Allow your body time to heal by taking a few hours of rest after cupping. Don’t rush into daily chores or activities.
- Keep Yourself Warm
After cupping, the pores open up, and exposure to cold air may be uncomfortable. Bring a shawl or blanket if
heading outdoors.
- Avoid Exercise
Avoid strenuous activities immediately after cupping. Light stretching and breathing exercises are a better option for a quick recovery.
- Skip Sunbathing
The sun’s heat can be harsh on the skin after cupping and might cause irritation.
To Sum It Up
Cupping therapy is an ancient healing method used in the treatment of various medical ailments. While modern research suggests that cup therapy may help with hypertension, skin conditions, arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and fibromyalgia, more studies need to be conducted to understand how it affects the body’s health. Cupping therapy is mostly safe under the guidance of a trained professional but you may experience certain side effects after the session. If you experience burns, dizziness, bruises, nausea, and soreness at the cupping site, consult a doctor immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is cupping therapy painful?
Cupping is not a painful procedure. You may experience a little tightness of the skin due to the suction of the cup. However, the therapist will make sure you are comfortable and not in any pain.
Does cupping release knots?
Yes, cupping helps release knots. It is an effective technique for relieving muscle tension, reducing swelling, and easing scar tissues.
What to expect after cupping?
You may experience some side effects, like tiredness, after cupping. You may also notice round bruise-like marks on the skin. These will fade away in a week or two.
Key Takeaways
- Cupping therapy is a practice from traditional Chinese medicine that uses cups to balance the body’s energy flow.
- The technique involves using a cup to create a suction on the skin to improve blood circulation and promote healing.
- Dry and wet cupping are the types of cupping therapy that help reduce chronic back pain and hives.
- Cupping therapy may cause soreness at the cupping site, nausea, dizziness, and infection.
Cupping therapy is an ancient healing technique used to improve circulation and reduce pain. Watch the video below to know more about this unique therapy in detail.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i Cupping- I Tried it & Survived to Recaphttps://smilesinthetrials.wordpress.com/2016/08/10/cupping-i-tried-it-survived-to-recap/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- The medical perspective of cupping therapy: Effects and mechanisms of action
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6435947/ - Cupping for Treating Pain: A Systematic Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3136528/ - Is cupping therapy effective in patients with neck pain? A systematic review and meta-analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6231582/ - Cupping therapy and chronic back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6248735/ - The effect of wet-cupping on the severity of migraine headaches: Randomized controlled clinical trial
http://bmrat.org/index.php/BMRAT/article/view/521 - An Updated Review of the Efficacy of Cupping Therapy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3289625/ - Cupping Therapy for Diseases: An Overview of Scientific Evidence from 2009 to 2019
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342081922_Cupping_Therapy_for_Diseases_An_Overview_of_Scientific_Evidence_from_2009_to_2019 - Efficacy of cupping therapy in patients with the fibromyalgia syndrome-a randomised placebo controlled trial
https://www.nature.com/articles/srep37316 https://idp.nature.com/authorize?response_type=cookie&client_id=grover&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Farticles%2Fsrep37316 - The effects of cupping therapy as a new approach in the physiotherapeutic management of carpal tunnel syndrome
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30697914/ - Effect of Cupping (Al-Hijama) therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A cohort study in Yemen
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351239786_Effect_of_Cupping_Al-Hijama_therapy_in_rheumatoid_arthritis_patients_A_cohort_study_in_Yemen - Cupping therapy a treatment modality in knee osteoarthritis pain management
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331211939_Cupping_therapy_a_treatment_modality_in_knee_osteoarthritis_pain_managemen - Effects of wet-cupping on blood pressure in hypertensive patients: a randomized controlled trial
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284282557_Effects_of_wet-cupping_on_blood_pressure_in_hypertensive_patients_a_randomized_controlled_trial - Cupping Therapy: An Overview from a Modern Medicine Perspective
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2005290117302042 - DRY CUPPING IN CHILDREN WITH FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION: A RANDOMIZED OPEN LABEL CLINICAL TRIAL
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5566148/
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan