Mangosteen: 7 Unexpected Side Effects Of The Tropical Fruit
Eating too much of this delicious fruity treat can sometimes do more harm than good.

Image: iStock
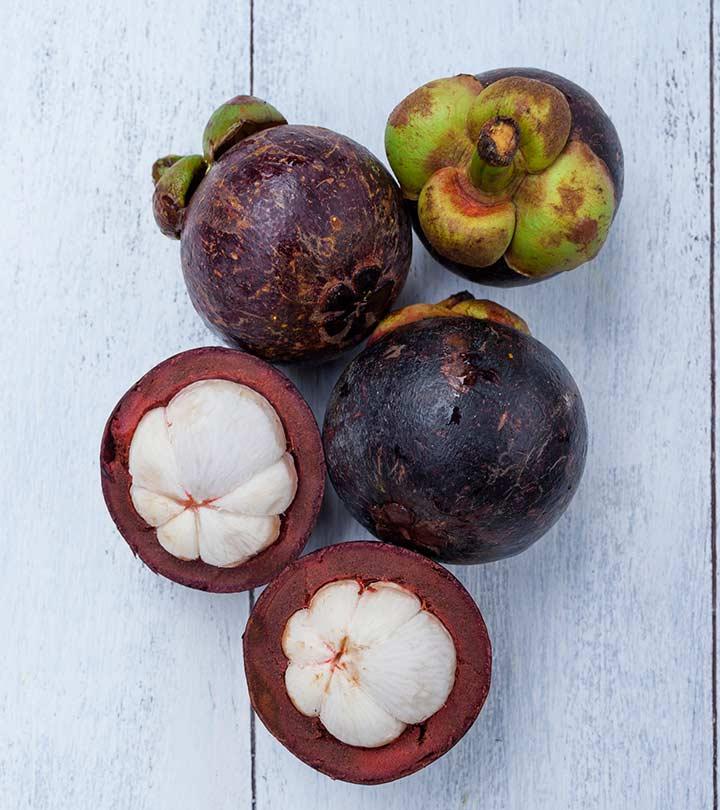
Mangosteen is a tropical fruit known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It is native to the Southeast Asian regions. It is used to treat many health ailments. However, there also are certain side effects of mangosteen recognized by the scientific communities.
Traditionally, mangosteen is used to treat many health ailments. However, recent studies show that it may negatively affect some individuals. It may cause complications in people with gastrointestinal and central nervous system issues. Hence, caution is advised while consuming the fruit. Learn more about the other side effects of mangosteen in this article. Continue reading.
 Know Your Ingredient: Mangosteen
Know Your Ingredient: MangosteenShort-Term Effects
May increase the risk of bleeding and cause gastrointestinal issues like bloating, and constipation, and allergies.
Long-Term Effects
May cause lactic acidosis leading to shock and death if left untreated, depression, sedation, and complications during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Drug Interactions
It may interact with chemotherapy and blood-thinning medications.
When To See A Doctor
If you experience excessive bleeding, stomach discomfort, diarrhea, and allergic reactions.
In This Article
What Are The Side Effects Of Mangosteen?
1. May Slow Down Blood Clotting

Mangosteen has been found to slow down blood clotting. It can increase the risk of bleeding in susceptible individuals (1). This is especially true when the fruit is taken along with certain drugs that increase the risk.
Consuming mangosteen may also increase the risk of bleeding during or after surgery. Avoid taking it at least two weeks before a scheduled surgery.
 Fun Fact
Fun Fact2. May Cause Lactic Acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a medical condition characterized by the build-up of lactate within the body. This happens due to the formation of excessively low pH in the bloodstream. This indicates the accumulation of excess acid within the body’s system.
A study highlights severe lactic acidosis that occurs due to the use of mangosteen juice as a dietary supplement (2). As per anecdotal reports, the symptoms associated with this condition may include weakness, dizziness, fatigue, vomiting, and nausea. If left untreated, this condition can lead to an acid build-up in the body to dangerous levels – leading to shock and death (3).
3. May Interfere With Chemotherapy
Animal studies have shown the anticancer effects of mangosteen (4). But studies on humans are yet to be conducted. Mangosteen products are often marketed to cancer patients as dietary supplements.
Some research shows that these supplements may interfere with cancer treatment and adversely affect blood sugar levels (5). In another report, certain antioxidant supplements were found to reduce the effectiveness of conventional radiation therapies (6).
As mangosteen supplements are often marketed for their antioxidant potential, it is important to exercise caution.
4. May Cause Gastrointestinal Issues

Some research has shown subjects experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms after consuming mangosteen for over 26 weeks. Some of these symptoms included bloating, diarrhea, gastric reflux, and constipation (7).
5. May Cause Sedation
The derivatives of mangosteen caused depression and sedation in rats. The effects had also resulted in decreased motor activity (8). However, more studies in humans are required to establish these effects.
6. May Cause Allergies
There is limited evidence if mangosteen can cause allergies. But anecdotal evidence suggests that it may cause reactions in people sensitive to the fruit. If you experience any reaction after consuming mangosteen, stop intake and visit your doctor. Mild symptoms are a skin rash and stomach upset.
7. May Cause Complications During Pregnancy
The safety of mangosteen during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not yet established. Hence, stay safe and avoid use. You may consult your doctor regarding the same.
Most of the adverse effects of mangosteen are yet to be established by concrete research. If you are usually susceptible to allergies or reactions, you may want to talk to your doctor before taking the fruit.
Why Is Mangosteen Banned?
Mangosteen was banned in the US by the FDA because it could be a host to import Asian fruit flies into the country. The ban was lifted owing to precautionary irradiation of the fruit, which was a treatment done to disinfect it. The method of irradiation is still under controversy despite its claims that it does not compromise with the taste and nutrition of the fruit (9).
However, food supplements containing mangosteen continue to be banned by the US FDA. Such supplements are mostly unregistered, and not much is known if they may cause any adverse effects (10).
Can the adverse effects of mangosteen be prevented if the fruit is taken in the right dosage? We have explored it in the following section.
Dosing Considerations For Mangosteen
The dosage of mangosteen is dependent on several factors, such as age, health, and medical conditions of the consumer. The composition of dietary supplements, such as mangosteen-based proprietary health drinks, is unavailable. There is no authentic literature available on the appropriate dosage of mangosteen that is to be consumed for preventing the adverse effects. More research is warranted in this regard. Hence, please talk to your doctor regarding the dosage.
The term “mangosteen” is commonly used interchangeably with “kokum”. However, the two are different. Learn more about the differences in the next section.
Kokum Vs. Mangosteen
Mangosteen and kokum are often confused with each other due to their uncanny resemblance. This also is likely due to the fact that they belong to the Clusiaceae family. However, they differ in taste and usage.
Mangosteen has a delicious sweet flavor with a hint of tanginess and is consumed fresh. On the other hand, kokum has a sour and tangy taste and is used as a flavoring agent in Indian dishes to add a zesty touch. Plus, kokum is not consumed fresh.
 Fun Fact
Fun FactInfographic: 5 Major Side Effects Of Excessive Mangosteen Consumption
It is possible to suffer serious health consequences if you overindulge in mangosteen. Although we have compiled all the potential side effects associated with excessive consumption of mangosteen above, we have narrowed them down to some of the most serious ones that need to be addressed.
Check out the infographic below to learn more about the adverse effects of having too many mangosteens. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Mangosteen is a tropical fruit with deep purple color and a slightly sweet or sour flavor. Its high antioxidant content is responsible for its benefits. However, the nutraceutical industry is marketing mangosteen juice as a dietary supplement with misleading claims. Excess consumption of mangosteen causes several side effects and adverse drug interactions. It may slow down blood clotting, cause lactic acidosis (build-up of lactate within the body), interfere with chemotherapy, and cause bloating, headache, diarrhea, acid reflux, and constipation. Excessive may result in liver toxicity and liver damage, so it is better to be cautious when taking herbal medication. Since there is limited evidence available, it should be consumed in moderation and only after consulting your doctor along with proper food contraindications.
Frequently Asked Questions
When is mangosteen not healthy?
Mangosteen may not be healthy when taken in excess. In a few, it may trigger allergies, constipation, bloating, and acid reflux.
Does mangosteen raise blood pressure?
No, mangosteen doesn’t raise blood pressure. In fact, it has hypotensive properties that can effectively manage high blood pressure.
Is mangosteen high in uric?
No, anecdotal evidence suggests that mangosteen has a low purine content, which are substances that are broken down into uric acid.
Can the skin or rind of the mangosteen fruit cause any adverse reactions when consumed or applied topically?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that topical application of the skin or rind of mangosteen may cause allergic reactions in some people, especially those with sensitive skin. Also, excess consumption of the mangosteen rind may upset your stomach. However, limited data is available to prove these claims.
Key Takeaways
- Bleeding, lactic acidosis, and interference with chemotherapy are a few side effects of consuming mangosteen.
- It may also cause gastrointestinal issues, sedation, and allergic reactions.
- Mangosteen should be avoided during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- It is banned in the US due to fear of Asian fruit fly infestation.
Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Get a better understanding of mangosteen, and why you should incorporate this fruit into your diet. Watch this video to learn about its origin, types, nutritional value, and various health benefits.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.),Chapter 3.29, Nonvitamin and Nonmineral Nutritional Supplements, Sciencedirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012812491800045X - Severe lactic acidosis associated with juice of the mangosteen fruit Garcinia mangostana.,Am J Kidney Dis.,US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18436094 - Lactic Acidosis, National Center for Biotechnology Information.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470202/ - Anti-Cancer Effects of Xanthones from Pericarps of Mangosteen, International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/9/3/355 - Mangosteen for the cancer patient: facts and myths., J Soc Integr Oncol., US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19442348 - Use of antioxidants during chemotherapy and radiotherapy should be avoided, CA Cancer J Clin. US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16166076 - Mangosteen Extract Shows a Potent Insulin Sensitizing Effect in Obese Female Patients: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Pilot Study, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986466/ - α-Mangostin from Garcinia mangostana Linn: An updated review of its pharmacological properties, Arabian Journal of Chemistry,
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1878535214000392 - Phytosanitary Applications of Irradiation, Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety.
https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/30200530/pdf/10552_2011.pdf - FDA Advisory No. 2019-541 || Public Health Warning Against the Purchase and Consumption of the following Unregistered Food Products and Food Supplements,“Food and Drug Administration Act of 2009”
https://www.fda.gov.ph/fda-advisory-no-2019-541-public-health-warning-against-the-purchase-and-consumption-of-the-following-unregistered-food-products-and-food-supplements/ - Science in Liquid Dietary Supplement Promotion: The Misleading Case of Mangosteen Juice, Hawai’i Journal of Medicine & Public Health, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3313772/?
































