Indian Diet Chart For Diabetic Patients: 4 Regional Meal Plans
Everything you need to keep in mind about this specialized diet plan, including sample charts.

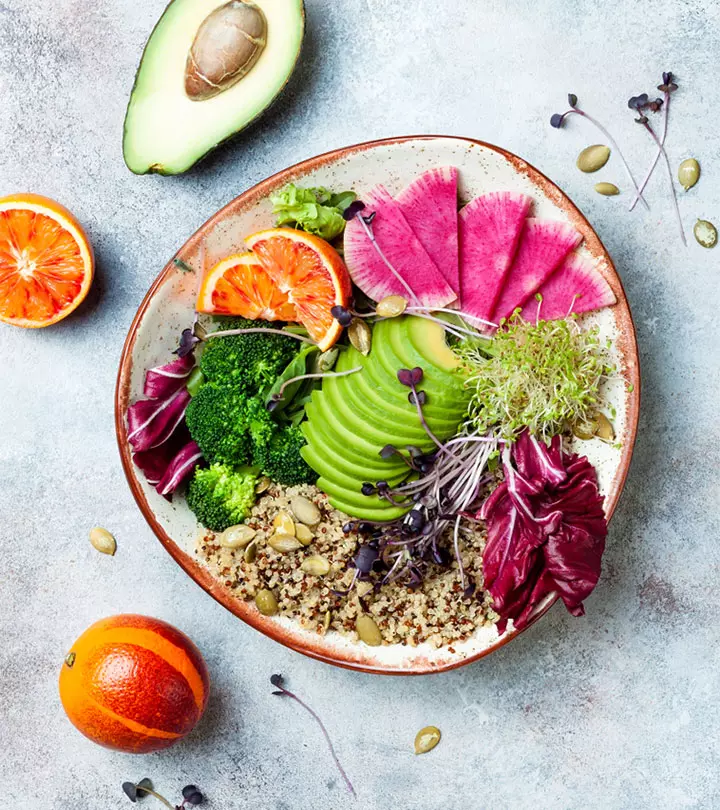
Image: ShutterStock
In India, over 41 million people have diabetes. It is estimated to increase to 70 million by 2025 (1), (2). No wonder India is called the diabetes capital of the world. But an Indian diet chart for people with diabetes may help reverse this trend to a great extent – as one of the root causes of diabetes type 2 is poor eating habits and a sedentary lifestyle. A well-planned diet is important for controlling blood sugar levels and promoting overall health. It helps lower the chances of complications related to diabetes. By encouraging mindful eating, it supports a healthier lifestyle, making it essential for managing diabetes effectively.

Of course, genes also may play an important part. But revamping your lifestyle can increase the chances of reversing diabetes type 2. Continue reading to know what to eat if you have diabetes and the lifestyle changes you need to make. We also have included a diet chart for you. Scroll down.
 At A Glance: Diabetes Diet For Indians
At A Glance: Diabetes Diet For Indians- Principle: A 1200-1600 calorie Indian diet with low carbs, healthy fats, and nutrient-rich, high-fiber vegetables.
- Purpose: To regulate blood sugar levels with Indian food options.
- Who It Is For: Indians with diabetes.
- Duration: Long-term
- Caution: Practice portion control and refrain from skipping meals as it may lead to fatigue, nutrient deficiencies, brain fog, medication imbalance, eating disorders, or brain fog.
In This Article
What Is Diabetes?

The WHO defines diabetes as a chronic metabolic disease that occurs when the body does not produce enough insulini A hormone produced in the pancreas that helps regulate sugar (glucose) levels in the blood. or does not use insulin (insulin resistance) that is produced, resulting in elevated blood glucose levels (3).
According to the study published in The Lancet journal, it was estimated that 8.4 million people had type 1 diabetes in 2025. Out of these, 1.5 million were younger than age 20 years, 5.4 million between 20-59, and 1.6 million were older than 60. It was further seen that 0.5 million new cases of diabetes were diagnosed in 2025.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?type 2 diabetes (the more common variant) is characterized by insulin resistance.
Key Takeaways
- Your diabetes diet should comprise fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, healthy proteins, good fats, and dairy.
- A North Indian diabetes plan may include food options like whole wheat parathas, vegetable moong chillas, vegetable curry, and chicken stew.
- A South Indian diet may include options like dosas with chutney and vegetable sambar, low-fat milk, buttermilk, and chicken soup.
- You may add diabetes superfoods like bitter gourd, oats, quinoa, turmeric, and flaxseeds to your diet for better control over blood glucose levels.
How Does A Diabetes Diet Help Manage Blood Glucose Levels?
Diabetes management needs a holistic approachi that involves lifestyle management, along with good glycemic control and balanced nutrition to manage blood sugar levels. The right food choices often help manage blood sugar levels, improve blood cholesterol, and keep you in a healthy weight range. Portion control also helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Keith Runyan, a Ketogenic diabetic athlete, shared his experience with managing his diabetes with diet and exercise on his blog. He said, “The low-carb ketogenic diet greatly reduced my glycemic excursions and halved my insulin requirements from 58 to 28 IU/day and markedly reduced (i).”
Sample Indian Diet Chart For Diabetes

The Indian diabetic diet plan will ensure you have 1200-1600 calories per day, which is based on age, sex, type of diabetes, physical activity, and type of medication you are on. It will also help with carbohydrate counting, which is a meal planning method to keep track of carbohydrate consumption. The activity level and insulin dose can be matched to the carbohydrate intake.
Note: The Indian diet charts for diabetic patients provided below are for general informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have diabetes, allergies, or any other medical condition, always consult a qualified healthcare professional and dietician before making any dietary changes. This will ensure that any adjustments made are safe and appropriate.
North Indian Diet Chart For Diabetic Patients
| MEAL | FOODS TO EAT |
|---|---|
| Early Morning | Options:
|
| Breakfast | Options:
|
| Pre-Lunch | Options:
|
| Lunch | Options:
|
| Evening Snacks |
|
| Dinner | Options:
|
| Before Bed |
|
East Indian Diet Chart For Diabetic Patients
| MEAL | FOODS TO EAT |
|---|---|
| Early Morning | Options:
|
| Breakfast | Options:
|
| Pre-Lunch | Options:
|
| Lunch | Options:
|
| Evening Snacks | Options:
|
| Dinner | Options:
|
| Before Bed |
|
South Indian Diet Chart For Diabetic Patients
| MEAL | FOODS TO EAT |
|---|---|
| Early Morning | Options:
|
| Breakfast | Options:
|
| Pre-Lunch | Options:
|
| Lunch | Options:
|
| Evening Snacks | Options:
|
| Dinner | Options:
|
| Before Bed |
|
West Indian Diet Chart For Diabetic Patients
| MEAL | FOODS TO EAT |
|---|---|
| Early Morning | Options:
|
| Breakfast | Options:
|
| Pre-Lunch |
|
| Lunch | Options:
|
| Evening Snacks | Options:
|
| Dinner | Options:
|
| Before Bed |
|
In addition to the foods mentioned in these sugar diet charts, you can consume the following:
Foods To Eat
- Healthy Fats
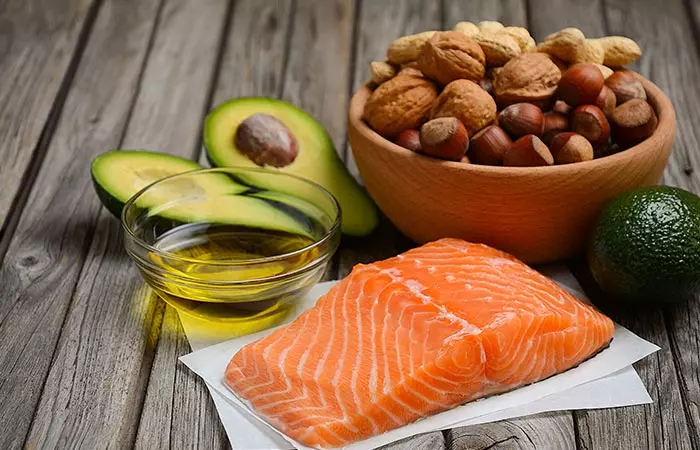

Not all fats are bad, and you do not have to stick to low-fat foods. Aim to limit your saturated fat intake and increase the intake of monounsaturatedi Unsaturated dietary fat (consisting of a single unsaturated carbon bond) that is good for human health. and polyunsaturated fatty acidsi Healthy dietary fat like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. They are usually found in oils and nuts. in your diabetes diet. A recent clinical trial showed a positive correlation between PUFA intake and improvement in glycemic control (4). Both the quality and quantity of fat matter in the regulation of blood sugar levels.
Foods To Eat – Fish, fish liver oil, flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, walnuts, avocados, and oysters.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip- Carbohydrates
Complex carbs with high fiber content are recommended for individuals with diabetes. A study on Chinese individuals with type 2 diabetes on a low-fat diet (LFD) and a low-carb diet (LCD) showed that LCD had better control over blood glucose levels as compared to LFD (5).
Whole grains are fiber-rich foods and help improve the glucose levels after a meal and maintain healthy insulin levels, according to a systematic review study (6). Avoid refined carbs with low to no fiber content.
Foods To Eat – Rye, oats, quinoa, millet, legumes, brown rice, wild rice, whole wheat, and low sugar bran flakes.
- Healthy Proteins

Consuming high-quality protein does not alter the post-meal increase in glucose levels. But a protein meal mixed with carbs increases insulin secretion, which can help regulate blood glucose levels (7). Include proteins with high biological value in each meal of the balanced diet plan.
Foods To Eat – Lentils, Brussels sprouts, soy, kidney beans, tofu, hummus, pumpkin seeds, chicken, turkey, fish (sardines, mackerel, tilapia, catla, rohu, singi, magur, pomfret, cod liver oil, hilsa, tuna, and trout).
- Vegetables
Vegetables are nutrient-rich foods and good sources of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. Having at least two servings of vegetables (cooked or raw) a day will help you lose weight, boost your immunity, and develop good control over blood glucose levels. A study on Japanese individuals with T2DM revealed that the ‘eat vegetables before carbohydrates’ approach had better glycemic control than an exchanged based meal (8).
Foods To Eat – Spinach, sweet potatoes, cauliflower, peas, capsicum, gourds, onion, garlic, celery, asparagus, beans, brinjal, lettuce, zucchini, tomato, broccoli, and kale.
- Dairy
Dairy proteins (casein and whey protein) in milk, yogurt, and cheese exert a beneficial role in the management of diabetes by increasing insulin secretion (9). A cohort study established an inverse relationship between dairy intake and the prevalence rate of diabetes (10).
Foods To Eat – Low-fat milk, egg whites, non-fat yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese, low-fat or non-fat sour cream, and unflavored soy milk.
Functional Foods For Diabetes
Functional foods with bioactive compounds can have a beneficial effect in managing blood glucose levels. The list of superfoods are:
- Fenugreek
- Bitter gourd
- Psyllium husk
- Millets
- Brown rice
- Legumes
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Cinnamon
- Turmeric
- Nuts and oilseeds – Walnuts and flaxseeds
Foods To Avoid On A Diabetic Diet
Certain foods that can negatively impact blood sugar levels include:
- Sugary Beverages: Sodas, sweet teas, and other beverages with added sugars can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pasta, and rice are stripped of beneficial fiber during processing, making them quickly digestible and raising blood sugar swiftly (11).
- Trans Fats: These are found in margarine, peanut butter, and processed snacks and can contribute to insulin resistance (12).
- Highly Processed Foods: Snack bars, pre-packaged meals, sugary cereals, and chips can be loaded with added sugars and unhealthy fats.
- Fried Foods: High amounts of unhealthy fats can contribute to heart problems, especially for people with diabetes (13).
- Fatty Meats: Avoid high-fat cuts of meat and processed meats like sausages to reduce saturated fat intake.
Keep reading to understand how certain lifestyle changes can positively impact blood sugar levels!
Lifestyle Changes For People With Diabetes
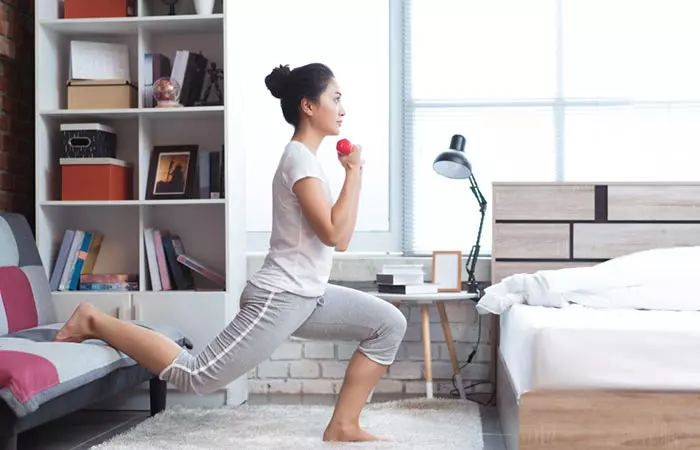

As per the American Diabetes Association, diabetes self-management education and support (DSMES), medical nutrition therapy (MNT), physical activity, smoking cessation counseling, and psychological care are the fundamental aspects to change blood glucose biomarkers (14).
Keith Runyan further added, “In 2019, in an effort to further reduce my hypoglycemic episodes, I added consistency of meals, exercise, and sleep to my blood glucose management strategy. As a result, I have had only 5 mildly symptomatic hypoglycemic episodes since 2019.”
Following a few practices, like waking up early, practicing yoga, working out, practicing healthy eating habits, getting proper sleep, meditating, taking out time for yourself, going to bed early, etc., are a few changes that will bring positivity and happiness in your life.
Scroll down for some additional meal prep, ingredient substitutions, and other tips you can follow for diabetes management. Keep reading!
Additional Tips For Diabetes Management
Here are a few additional tips to help ensure your health is on track:
- Use healthy cooking methods like steaming, grilling, roasting, air frying, or sauteing over deep-frying.
- Prep your ingredients beforehand. Chop vegetables, soak pulses, and marinate proteins in advance to save time and ensure healthy choices.
- Prepare and freeze healthy meals or ingredients in advance to avoid last-minute unhealthy choices.
- Avoid store-bought cooking sauces and spices with added salt and sugar. Instead, make them at home.
- Replace high glycemic index foods, like white rice and refined flour, with low GI foods, such as brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat flour, and chickpea flour.
- Substitute refined sugar with diabetes-friendly options, like stevia and monk fruit.
- Practice portion control to manage carbohydrate intake. You can use a smaller plate for it.
- Balance your meals by filling half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains.
Infographic: Indian Diabetes Diet Chart – Foods To Eat
Poor eating habits are one major cause of diabetes. Intake of nutrient-rich low glycemic index foods helps control blood glucose levels. While we have covered information about the right foods to eat, we want to reiterate a few specific ones. Click on the infographic below to learn more about the right foods to include in the Indian diabetes diet chart for curbing diabetes.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
This Indian diet chart for diabetic patients may help reverse the condition to a great extent. A holistic strategy that includes lifestyle management, effective glycemic control, and balanced nutrition is needed to control blood sugar levels. The appropriate meal choices can help monitor blood sugar levels, lower your cholesterol, and maintain a healthy weight. In fact, you can also follow a prediabetes diet plan to prevent or delay getting diabetes in the first place! Based on dietician recommendations, choose diabetes-friendly recipes for meals, which will lower the glycemic load and help reduce the risk of diabetes. Consult a doctor and a nutritionist for advice tailored to your health and other medical conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I balance my favorite foods with my diabetic diet?
You can balance your favorite foods with a diabetic diet by practicing moderation and portion control. Try to pair them with healthier options, like vegetables or whole grains, to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Plan meals ahead of time to avoid impulsive eating.
I am 24 years old, and I have been diagnosed with diabetes. Does this mean I have to follow a restricted diet for the rest of my life?
It is not a “restricted diet” but rather a “controlled diet.” You can have anything you want, but keep a check on your daily sugar and salt intake. Yes, you need to avoid certain foods that, in general, do no good to anybody. Be active, avoid a sedentary lifestyle, and practice yoga.
Will drinking bitter gourd juice or neem juice help to treat diabetes?
Yes. Doctors recommend bitter gourd juice and neem juice for individuals with diabetes. There is scientific evidence that bitter gourd and neem help in lowering blood glucose levels. You can either have boiled bitter gourd or chew three or four neem leaves first thing in the morning.
Bitter gourd contains an insulin-like compound called polypeptide-p or p-insulin. This compound can control diabetes naturally. Neem leaves contain flavonoids, triterpenoids, glycosides, and antiviral compounds that may help manage blood sugar levels. However, overeating may have hypoglycemici A condition where the blood sugar level hits lower than the required range. Usually caused by diabetes medication. effects.
I am 62 years old, and I cannot do heavy workouts. Please suggest any other alternative.
Start by going on long, lazy walks. Later, pick up the pace of your walks. You can also practice pranayama. Work with a yoga expert who will guide you.
How much weight will I lose?
Check with your doctor to know what your ideal weight should be according to your age, medical history, sex, current weight, bone mass, etc. Then, plan your daily diet accordingly to reach your ideal weight.
Is eucalyptus oil effective in treating diabetes? Where can I buy eucalyptus oil?
Yes, there is scientific evidence that eucalyptus oil helps reduce blood glucose levels. You can buy eucalyptus oil from various online stores. Mix four to five drops of eucalyptus oil in warm water or warm milk and drink it. Make sure not to add too much of eucalyptus oil as it might be toxic.
Which fruits should I eat?
Eat gooseberries, black plum (Jamun), apple, banana, guava (not ripe), raw papaya, etc. You can also eat fruits that have high fructose content such as mango, litchi, and grapes. But make sure not to overdo them.
Learn about five traditional Indian foods that can help you manage diabetes! Click on this video and discover how to incorporate these foods into your diet for better health.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. #111 December 2025 – Keith Runyan, MD – My T1D Managementhttps://ketogenicdiabeticathlete.wordpress.com/page/2/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- India – Diabetes capital of the world: Now heading towards hypertension, The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5995205_India_-_Diabetes_capital_of_the_world_Now_heading_towards_hypertension - Current scenario of diabetes in India, Journal of Diabetes, Wiley Online Library.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1753-0407.2008.00004.x - Diabetes, World Health Organization.
https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes - Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6566834/ - The Effect of Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29882884/ - Whole Grain Intake and Glycaemic Control in Healthy Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5537883/ - Plasma insulin responses after ingestion of different amino acid or protein mixtures with carbohydrate, The American journal of clinical nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10871567/ - A simple meal plan of ‘eating vegetables before carbohydrate’ was more effective for achieving glycemic control than an exchange-based meal plan in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes, Asia Pacific journal of clinical nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21669583/ - Dairy Foods and Dairy Proteins in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Evidence, Advances in Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4424779/ - Dairy consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of cohort studies, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21559046/ - Type 2 Diabetes and Dietary Carbohydrate Intake of Adolescents and Young Adults: What Is the Impact of Different Choices?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8537173/ - Trans-Fatty Acids Aggravate Obesity, Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis in C57BL/6 Mice, Possibly by Suppressing the IRS1 Dependent Pathway
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/21/6/705 - Dietary fats and mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes: analysis in two population based cohort studies
https://www.bmj.com/content/366/bmj.l4009 - 5. Lifestyle Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019, American Diabetes Association.
https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/42/Supplement_1/S46
Read full bio of Merlin Annie Raj
Read full bio of Priyanka Sadhukhan
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Payal Karnik

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.