6 Health Benefits Of Lipedema Diet, Exercise, & What To Eat
Understand the ways diet and a healthy lifestyle can ease the symptoms of this condition.
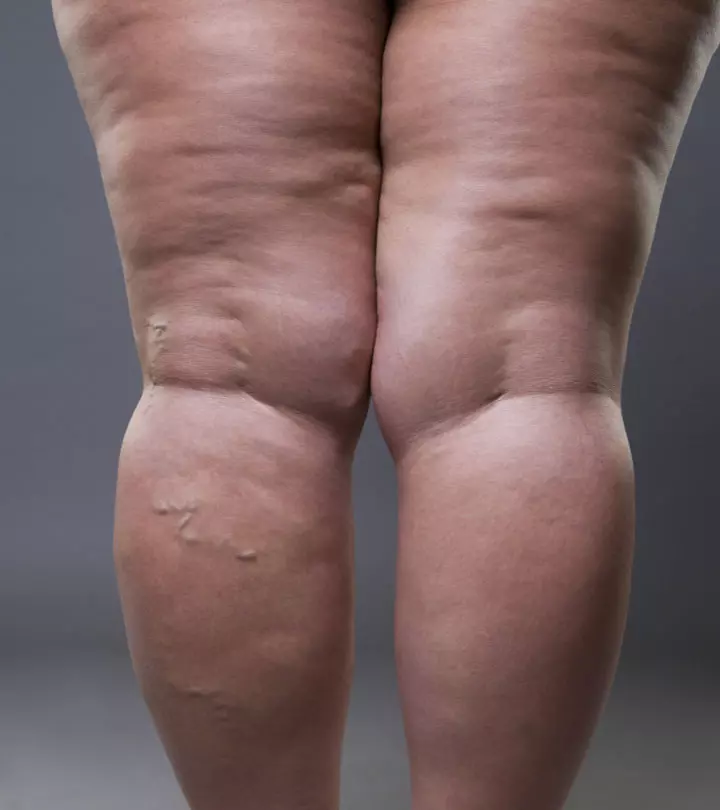
Image: Shutterstock
Lipedema, often misdiagnosed as obesity, primarily affects women. It is a progressive condition characterized by a disproportionate accumulation of fat in the lower limbs. Regular low-impact exercise and healthy eating have been shown to help you deal with lipedema better. Read on to know what food products you should avoid in the lipedema diet, and what kind of diet and exercise can help you reduce the pain and discomfort of lipedema.

 At A Glance: Lipedema Diet
At A Glance: Lipedema Diet- Principle: A diet restricting any form of carbohydrates, high fat, and highly processed junk foods
- Purpose: To reduce the symptoms and discomfort associated with lipedema
- Who It Is For: Individuals with lipedema
- Duration: Short-term
- Who Should Avoid: Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, children below the age of 18, and those with certain underlying chronic health conditions
- Cons: May make one feel dizzy and weak initially, cause sweaty palms and chills in the feet at night, and lead to mood swings, confusion, and poor brain function
In This Article
What Is Lipedema?
Lipedema or lipoedema is a disease of inflamed fat cells and disproportionate fat deposits, especially in the lower half of the body. It primarily affects women and causes a fat build-up in the tissues of the hips, pelvis, and legs. Strangely, it doesn’t affect the feet and hands. Women with lipedema have larger hips and legs in comparison to their upper bodies. While initially it might be mistaken as obesity, it can lead to unbearable pain and even immobility due to the swelling of the legs (1). Hormonal fluctuations during menstrual cycles or menopause could potentially make the symptoms worse.
Lipedema is classified into one of the following five types, based on the location of the fat deposits in the body (1):
Type 1 – buttocks, hips, and pelvis.
Type 2 – buttock to the knees.
Type 3 – buttocks to the ankles.
Type 4 – includes upper arms as well.
Type 5 – only the lower legs.
Currently, there are no particular lab tests or imaging exams to confirm the diagnosis of lipedema. It is usually done based on the woman’s medical and family history and physical examination of the symptoms of lipedema, as discussed below.
Key Takeaways
- Lipedema is a condition that causes the accumulation of fat in the lower part of the body.
- Easy bruising, cold skin, hard nodules, and fibrosis are the most common symptoms of lipedema.
- Pasteurized dairy products, simple sugars, and high-fat animal meat are good for the condition.
- Regular low-impact exercises may help weight management and reduce pain and inflammation.
Symptoms Of Lipedema
Most women with lipedema would have uneven deposits of adipose tissue or body fat in their lower bodies. There are some other common symptoms that might accompany lipedema, but not all women must have them. As per the Genetic And Rare Diseases Information Centre (GARD), these symptoms may include (1), (2)
- Painful Fat: The fat build-up in the hips and legs might become painful and tender to touch and any sort of pressure.
- Easy Bruising: The affected parts of your body might bruise easily. Tiny spider veins that run close to the skin surface might contribute to this bruising.
- Upper Arm Fat: About a third of women affected with lipedema might also have excess fat build-up in their upper arms.
- Hard Nodules: Pea-sized hard nodules or lumps of fat can be felt under the skin when massaged.
- Cuffing At Wrist Or Ankle: Since lipedema does not affect the hands and feet, the swollen legs and arms might look cuffed, especially in later stages of the disease.
- Cold Skin: The skin of the affected area of the hips and legs might seem cooler to touch than the rest of the body.
- Immobility: With the worsening of the condition, the increase in leg size, heaviness, and the associated pain might lead to joint damage and changes in your gait, making it difficult to walk at all.
- Fibrosis: Chronic inflammation in lipedema might also lead to fibrosis or the formation of scar tissue in the fat deposits, further hindering lymph circulationi The movement of lymph from the body tissues into the lymphatic vessels to help protect the body from foreign cells. .
- Lymphedema: With the progress of the condition, lymphedema (swelling due to lymph fluid blockage) might also occur in the lower limbs and hip area (3).
Another symptom might be weight loss. Shannon Ashley, a lifestyle blogger, was diagnosed with stage 3 lipedema, the cause of her weight gain. She writes, “The reason my weight has been increasing over the years so much is that somewhere around stage 2 of lipedema, my metabolism began to fail as the lipedema tissue grew (i).”
Apart from the above symptoms, women with lipedema have been found to be more vulnerable to higher rates of migraines, hypothyroidismi Deficiency of thyroid hormones that causes growth retardation, poor mental development, and weight gain. , depression as well (4). But, strangely enough, they may have lower risks of high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndromei A group of conditions that lead to an increased risk of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. since most of the fat is deposited in the legs and hips, and not around the visceral organs (5).
Lipedema, with its life-altering symptoms, might take a toll on your physical and mental well-being. However, with proper treatment, exercise, diet changes, and self-care, the above symptoms of lipedema can be managed to a certain extent. So, what kind of diet can help reduce fat deposits, pain, and fluid retention without affecting their metabolism?
What Is The Best Diet For Lipedema?
While you may not see an immediate improvement in your condition, there are a few food products that might cause lipedema to worsen. You should avoid the consumption of:
- Pasteurized dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)

- High-fat animal meat (bacon, red meat, sausage)
- Simple sugars and carbohydrates (white rice, pasta, potatoes, honey, or cereals)
- Highly processed and salty foods ( beef jerky, smoked meat, canned meat)
- Processed or refined flour products (white tortillas or bread)
Along with the right dietary choices, incorporating exercises that target swollen areas can also be beneficial. For instance, you may try exercises that are designed to treat cankles. By learning how to get rid of cankles, you can reduce the appearance of swelling around the ankles, an area often affected by lipedema.
Apart from these basic changes, you can also follow any anti-inflammatory diet for lipedema, a condition known to cause inflammation. Some popular dietary plans used to manage this condition include low-carb or ketogenic, vegetarian, and Mediterranean diets. Research shows that many women with lipedema have found considerable improvement in their symptoms following the ketogenic diet (6).
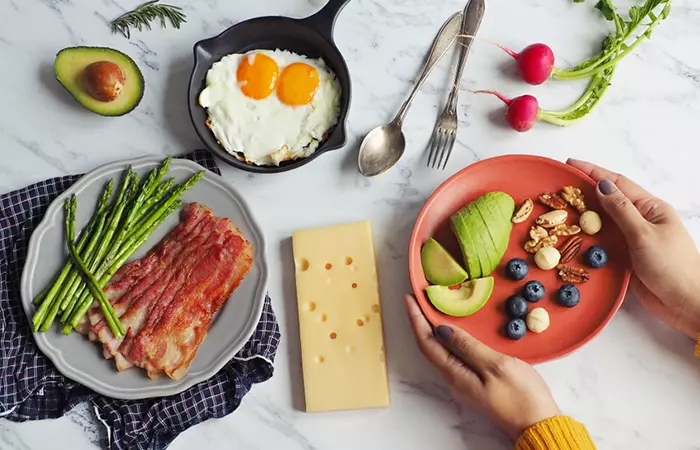

A ketogenic diet restricts the dietary intake of any form of carbohydrates such as sugar, rice, pasta, bread, potatoes, and most fruits. This results in a metabolic state called ketosis, wherein fat becomes the primary source of your body’s energy instead of glucose. But how does a ketogenic diet help improve the symptoms of lipedema? Is it really beneficial in dealing with stubborn fat, its associated pain, and fluid retention? Let’s find out.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipBenefits Of The Lipedema Diet
While direct evidence is scanty, a few small studies, clinical trials, and anecdotal evidence suggest that a ketogenic diet may help reduce the fat buildup, pain, and discomfort associated with lipedema (6).
Some of the research pieces of evidence that state the beneficial effects of the ketogenic diet for lipedema are mentioned below.
- Helps Lose Weight

When women with lipedema shift to a ketogenic diet, there is a resultant change in their metabolism. Their bodies are forced to metabolize fats instead of glucose to produce energy. This may lead to the burning up of some of the excess accumulated body fat. Many studies confirm that when people cut back on carbs completely and fill up on proteins and fats instead, they tend to eat less and lose weight (7), (8).
- May Help Reduce Fluid Retention
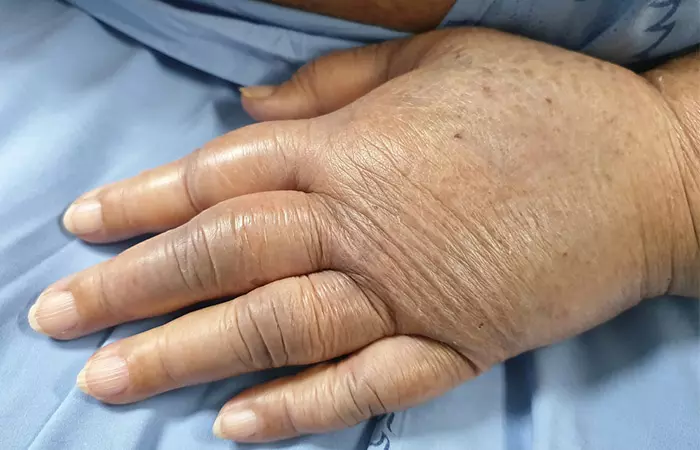
Progression of lipedema may result in lymphedema, a chronic condition that leads to swelling of the body part caused due to a compromised lymphatic system, over time. As per a study, the ketogenic diet can be potentially helpful in reducing lymph fluid retention and swelling of the limbs (9).
- May Help Reduce Pain And Inflammation
The pain associated with lipedema fat could be due to inflammation and allodynia (nerve pain) (10). A number of studies have shown that a ketogenic diet reduces inflammatory and chronic pain associated with weight and obesity (11). Few animal studies also suggest the beneficial effect of the ketogenic diet in reducing allodynia and inflammation (12), (13).
- Helps Remove Excess Fluid
Women with lipedema may benefit from the loss of water from their tissues that may help reduce water retention and the corresponding swelling of the limbs. The ketogenic diet has a diuretic effecti A state where the body gets rid of excess fluid and salt through urine. initiating loss of water weight in the first few days followed by fat-weight loss (14). As per a study on people with obesity and lymphedema, a ketogenic diet was found effective in reducing the amount of lymph fluid retention in their affected limbs (15).
- May Help Remove Excess Salt
Women with lipedema tend to have higher sodium concentrations in the accumulated fat tissue of their legs and hips (16), (17). A ketogenic diet, by lowering insulin and releasing water weight, also helps remove salt from your body (18), (19).
- May Help Improve Mental Health

Women diagnosed with lipedema have been found to feel low, demotivated, and depressed. Pain and lack of mobility affect their mental well-being as well (19), (20). The ketogenic diet has been found to help improve mental health conditions like depression and anxiety (21). This could help improve the quality of life for women suffering from the cumulative health effects of lipedema.
The lipedema diet may aid in weight loss and reduce pain. Check out this easy, wholesome, and delicious recipe you can try on this diet.
Easy Lipedema Diet Recipe
Grilled Salmon With Roasted Vegetables
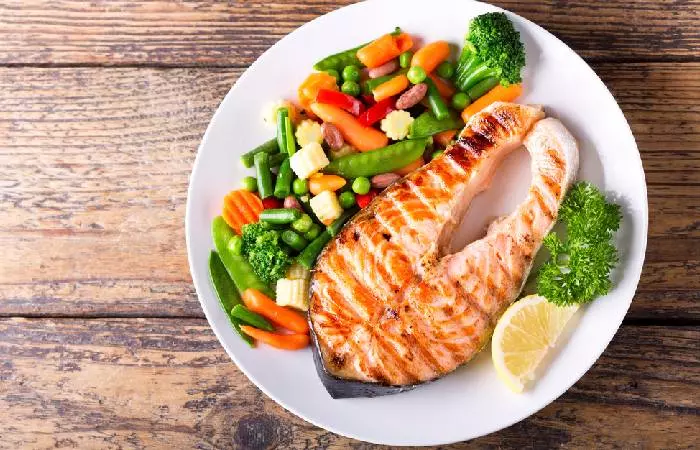

Ingredients
- 2 salmon filets
- 1 zucchini (sliced)
- 1 yellow bell pepper (sliced)
- 1 red onion (sliced)
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- 1 teaspoon of dried oregano
- Salt and pepper, to taste
- Lemon wedges, for garnish
Method
- Preheat the grill to medium-high heat.
- Brush the sliced zucchini, yellow bell pepper, and red onion with olive oil, dried oregano, salt, and pepper.
- Grill the vegetables for about 5-7 minutes on each side or until they are tender.
- Season the salmon filets with salt and pepper.
- Grill the salmon for about 3-4 minutes per side.
- Serve the grilled salmon and the vegetables on a plate and garnish with lemon wedges.
While a change in diet is needed to help facilitate metabolic changes from within, it needs to be supplemented with some amount of exercise to help mobilize the fluid and fat accumulated in lipedema. Let’s delve deeper into what forms of exercise are possible and best suited at different stages of lipedema.
What Is The Best Exercise For Lipedema?
While the painful build-up of fat might prevent you from performing any heavy exercise, maintaining a moderately active lifestyle is key to helping reduce the pain and symptoms. Even gentle walking and leg movements can help mobilize the fat deposits and lymph fluid, reducing the inflammation and pain thereof (22).
In the initial stages of lipedema, women should try and maintain an active lifestyle. Even light walking for 45 minutes, 4 to 5 times a week may be helpful. However, women diagnosed with lipedema in the later stages might find it difficult to move due to the pain associated with the fat buildup in the lower half of their bodies.
In such cases, light aquatic exercises like walking in water or low-impact water aerobics might help provide some relief. Water helps provide buoyancy to help move the body and some amount of compression as well to channelize the lymph circulation. Few women also use rebounders (small trampolines) or exercise on the vibration plates for lipedema (23). Here is a list of some simple exercises you can try for lipedema:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Arm and leg raises
- Cycling
- Yoga
- Pilates
- Stretching
Other treatments that might help improve the symptoms of lipedema include liposuction (surgical removal of subcutaneous fat), physical therapy, massage therapy, compression therapy (with or without vibration), and manual lymph drainage (24), (25).
Regular low-impact exercise and following the lipedema diet might help reduce some symptoms and manage this condition better.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipInfographic: Stages Of Lipedema
Lipedema is usually diagnosed by a physical examination of the skin and the amount of fat buildup underneath. Starting from small nodules, it could progress to fatty folds, changing the appearance of the legs altogether. Click on the infographic below to know what to expect during the various stages of lipedema.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Lipedema is a painful condition of uneven fat accumulation in the hips and legs of genetically susceptible women. While there are no tests or imagery exams to confirm it, the physical symptoms and family history can help diagnose the type of lipedema. Unlike obesity, lipedema is resistant to most diets and exercise. A lipedema diet requires you to avoid certain kinds of food. This might help provide some benefit and relief in living with lipedema better.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can exercise make lipedema worse?
Yes. High intensity or vigorous exercises may exacerbate lipedema.
Can you lose weight in your legs with lipedema?
No, you cannot lose weight in your legs with lipedema. However, in certain lipedema types, fat accumulation occurs only in particular body parts. If there is fat accumulation in the abdomen, hips, pelvis, and thighs, it can make your legs look smaller.
Is oatmeal good for lipedema?
Yes, whole grains like oats are good for lipedema.
Does fasting help lipedema?
Not really. You should eat a healthy diet (like a ketogenic diet). Your body needs nutrition to survive and be active. Eat foods that have a good amount of fiber and protein and also consume fruits and vegetables.
What happens if lipedema is left untreated?
Lipedema, if left untreated, can elevate the risk of hypertension, diabetes, heart failure, and certain eating disorders (27).
Is turmeric good for lipedema?
Yes. Turmeric functions as an antioxidant and may aid in lowering inflammation, enhancing blood vessels, and eliminating free radicals (28).
How does Mucinex help lipedema?
Mucinex is believed to reduce pain or thin out the extracellular proteins in lipedema tissue and act as an expectorant. However, there is not enough research supporting these beliefs.
What hormone causes lipedema?
Estrogen is the hormone that leads to the development of lipedema (29).
What is the pinch test for lipedema?
You can frequently identify if you have lipedema with a quick pinch test. Lightly pinch the skin in the potentially affected areas of the body to do this. If you have excessive pain, you might have lipedema.
Illustration: Health Benefits Of Lipedema Diet, Exercise, & What To Eat

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn how to eat right to help manage lipedema. Discover the best diet to help treat your lipedema symptoms and improve your overall health by clicking on this video.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. A Chronic Disease Made Me Very Fathttps://medium.com/honestly-yours/a-chronic-disease-made-me-very-fat-e827fdf3d562
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Lipedema: A Relatively Common Disease with Extremely Common Misconceptions
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5055019/ - Lipedema
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK573066/ - Lipedema and the Evolution to Lymphedema With the Progression of Obesity
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7714724/ - New Insights on Lipedema: The Enigmatic Disease of the Peripheral Fat
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31764671/ - Lipedema: friend and foe
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5935449/ - Ketogenic diet as a potential intervention for lipedema
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306987720333260?via%3Dihub - Effects of Low-Carbohydrate and Low-Fat Diets
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4428290/ - The role of energy expenditure in the differential weight loss in obese women on low-fat and low-carbohydrate diets
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15598683/ - Lifestyle Modification Group for Lymphedema and Obesity Results in Significant Health Outcomes
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33281522 - Cause and management of lipedema-associated pain
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33001552/ - Effects of a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet on reported pain blood biomarkers and quality of life in patients with chronic pain: A pilot randomized clinical trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34534353/ - Ketogenic diet effects on inflammatory allodynia and ongoing pain in rodents
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33436956/ - Reduced pain and inflammation in juvenile and adult rats fed a ketogenic diet
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20041135/ - Ketogenic Diet – StatPearls
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499830/ - Lifestyle Modification Group for Lymphedema and Obesity Results in Significant Health Outcomes
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33281522 - Tissue Sodium Content is Elevated in the Skin and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Women with Lipedema
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29280322/ - Upper and Lower Extremity Measurement of Tissue Sodium and Fat Content in Patients with Lipedema
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32270924/ - The effect of insulin on renal sodium metabolism. A review with clinical implications
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7028550 - The effect of lipedema on health-related quality of life and psychological status: a narrative review of the literature
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31062201/ - Depression and appearance-related distress in functioning with lipedema
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29614880/ - Exploring the mechanisms of action of the antidepressant effect of the ketogenic diet
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32406387 - The Effects of Complete Decongestive Therapy or Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Therapy or Exercise Only in the Treatment of Severe Lipedema: A Randomized Controlled Trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33297826/ - Physiotherapy and rehabilitation applications in lipedema management: A literature review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33190432/ - Lipedema | Stanford Health Care
https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-conditions/blood-heart-circulation/lipedema.html - Liposuction for the Treatment of Lipedema: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines [Internet]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31479212/ - Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Diseases: Dercum Disease Lipedema Familial Multiple Lipomatosis and Madelung Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK552156/ - Lipedema, a Rare Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3309375/#:~:text=If%20lipedema%20is%20not%20treated,%2C%20diabetes%2C%20and%20heart%20failure. - Increase in Leptin and PPAR-γ Gene Expression in Lipedema Adipocytes Differentiated in vitro from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7072543/#:~:text=Furthermore%2C%20clinicians%20recommend%20supplements%20such,removing%20free%20radicals%20%5B2%5D. - Lipedema and the Potential Role of Estrogen in Excessive Adipose Tissue Accumulation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8583809/#:~:text=Estrogen%2C%20a%20key%20regulator%20of,in%20the%20pathophysiology%20of%20lipedema.
Read full bio of Pallavi Jassal
Read full bio of Varsha Patnaik
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Payal Karnik



























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.