Does Smoking Cause Hair Loss? Hair Loss Treatments For Smokers
Unveil the link between smoking and hair loss and discover the path to healthier choices!
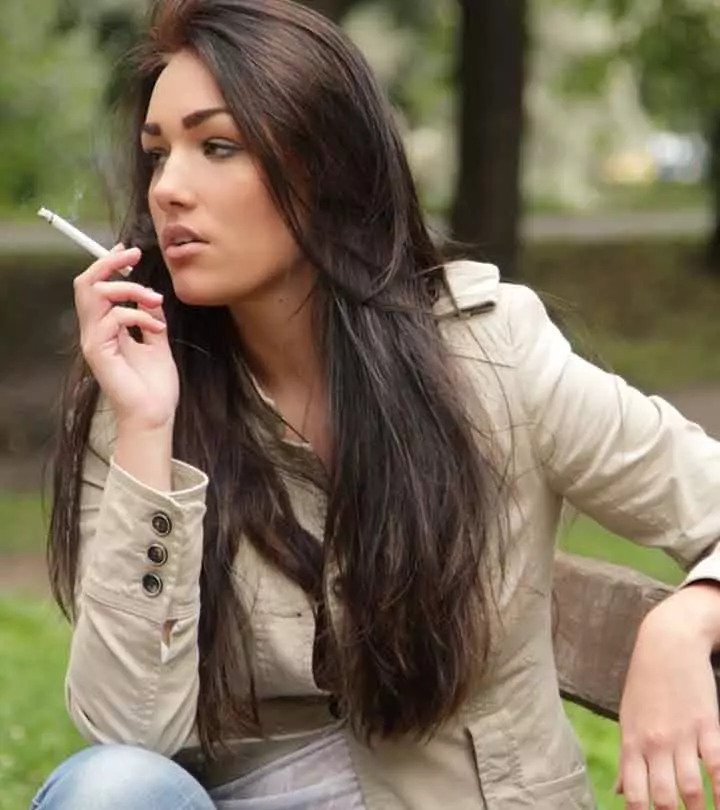

Image: ShutterStock
Most of us are aware of the side effects of tobacco smoking, which can lead to many life-threatening diseases. But are you aware of the link between smoking and hair loss? This is one lesser-known side effect of smoking. Some scientific studies have even proved this claim, and people with hereditary or genetic hair loss are at a higher risk.
Here, we explore the link between smoking and hair loss and the possible treatment options available. Keep reading.
In This Article
Smoking And Hair Loss: What Is The Link?
Studies are limited regarding the effects of smoking on hair loss. However, a few studies found some possible connections between the two. Here is how smoking may trigger hair loss:
1. It May Cause DNA Damage
Animal studies have found that tobacco contains genotoxic components that can damage the hair follicle’s DNA (1). This can trigger hair loss. However, this study is not conclusive and needs further research.
2. It May Cause Heavy Metal Toxicity
Smoking may cause cadmium toxicity and interrupt the hair cycle. Cadmium can cause oxidative stress to the hair and trigger hair loss. It may also disrupt the formation of the hair shaft and cause telogen effluvium (2).
3. It May Aggravate Alopecia
Although smoking and alopecia’s link needs further research, a study found that smoking status and intensity were among the key factors responsible for aggravating androgenic alopecia and considered potential risk factors (3). However, further studies are needed to establish an association.
4. It May Affect The Immune System
Research suggests that cigarette smoke may affect your body’s defenses. It can either increase the risk of developing allergies, cancer, and cardiovascular and respiratory diseases or make your immune system attack our own body (4). In the context of hair loss, this may lead to a condition like alopecia areata. This is a severe condition where the immune system targets the hair follicles. This process interferes with the normal growth cycle of hair, which may increase the risk of hair loss (5). However, the specific mechanism behind this matter is still not entirely clear and requires further detailed clinical research.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?This explains the question “How does smoking cause hair loss?” However, other than smoking, several other factors may also trigger hair loss.
Other Factors Triggering Hair Loss
Smoking, along with other underlying factors, may contribute to hair loss. They include:
- Psychological stress (6)
- Pregnancy (7)
- Hormonal imbalances (thyroid issues) (8)
- Nutritional deficiencies (9)
If you smoke and are experiencing hair loss, these factors too might be contributing. Often, smoking, along with some underlying factors, may trigger hair loss. Smoking also increases free radicals in the body and can deplete the body of nutrients, thus leading to hair loss. Consult a doctor to find out the exact reason behind your hair loss. Meanwhile, you may quit smoking and try to improve your hair health.
Can My Hair Grow Back If I Quit Smoking?
It depends on a lot of factors.
If you quit smoking, your hair fall may improve as your hair and body will not be exposed to the toxins released by tobacco. It may also improve your overall health. However, if an underlying condition is responsible for your hair loss, it may not improve unless you treat it.
A systematic review of 32 studies on the relation between smoking and hair health involving a total of 23,685 patients revealed that smoking is associated with a higher prevalence of alopecia and premature hair graying (PHG). Adults with alopecia areata consisted of 56.5% smokers compared to 42.6% nonsmokers.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipHence, it is better to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis. Let us explore the possible treatments to repair the hair damage caused by smoking in the next section.
Possible Hair Loss Treatments For Smokers And Ex-Smokers
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
Low-level laser therapy
(LLLT) is a popular method for stimulating hair growth. This non-invasive treatment is performed under the supervision of a doctor and has no side effects. However, the long-term consequences of LLLT still need more empirical backing (10).
- Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery has become a highly sought-after way of achieving a natural appearance. However, the doctor needs to evaluate your scalp and determine whether you are a good candidate for a hair transplant or not. Consult a dermatologist for a detailed analysis.
- Prescription Medications
Smokers looking to stop hair fall may consult a doctor who may prescribe medications like topical minoxidil and finasteride or a combined dose of both for treating hair loss. These medications block DHT (a type of androgen) that triggers hair loss (11).
These are some treatment options you may try to manage hair loss. However, if you are considering hair transplant surgery and wondering if you can restart smoking after that, here is what you need to keep in mind.
How Soon Can I Restart Smoking After A Hair Transplant Surgery?
Wait for at least two weeks before you start smoking.
Hair transplant surgeries can yield a high success rate, provided you adhere to certain precautions. As smoking can expose your body to an influx of toxins, give your scalp some time to heal. Otherwise, you may be more susceptible to infections on the open wound. Besides, it may lead to scar tissue formation.
While smoking can lead to the development of many diseases, limited scientific studies have found a link between smoking and hair loss. Some studies indicate that it may damage the hair follicle’s DNA and aggravate androgenic alopecia. Additionally, hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, or stress may contribute to hair loss. To combat this issue, you can quit smoking and, in turn, reduce hair fall. However, if there is an underlying symptom of a medical condition, consult your doctor immediately. They may offer treatment options such as low-level laser therapy or hair transplant surgery to treat hair loss.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is hair loss from smoking reversible?
In some cases, hair loss from smoking may be irreversible if there is any blood vessel damage underneath the scalp. However, if hair loss due to smoking is diagnosed early, it may be reversible with professional intervention.
How long after quitting smoking does hair grow back?
The hair generally takes 6 to 8 months to grow back after quitting smoking. However, this period varies from person to person and is dependent on the extent of damage caused by smoking.
Will quitting smoking stop gray hair?
Yes, smoking, in a few, may trigger premature graying of hair and hair thinning. Quitting smoking slows down this premature graying and stops hair graying after 6 – 8 months.
Does smoking dry your hair?
Yes, smoking makes hair dry and brittle. This is because of the various toxins in cigarettes that negatively affect hair health.
How can I protect my hair from cigarette smoke?
Headwraps and covers are the best ways to protect your hair from cigarette smoke.
Does cigarette smoke stick to hair?
Yes, the smoke from cigarettes sticks to the hair and causes hair damage.
Key Takeaways
- Smoking may lead to hair loss by likely causing DNA damage, aggravating alopecia, affecting the immune system, and by interrupting the hair cycle.
- Apart from smoking, several other underlying factors, such as nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalance, and psychological stress, may contribute to hair loss.
- Quitting smoking alone may not stop hair loss unless the underlying causes are addressed. Also, treatments such as laser therapy, hair transplant surgery, and taking prescription medications may help to some extent.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Induction of alopecia in mice exposed to cigarette smoke
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10713476/ - Possible Relationship between Chronic Telogen Effluvium and Changes in Lead, Cadmium, Zinc, and Iron Total Blood Levels in Females: A Case-Control Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4639951/ - Association of androgenetic alopecia with smoking and its prevalence among Asian men: a community-based survey
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18025364/ - Impacts of cigarette smoking on immune responsiveness: Up and down or upside down?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5352117/ - Autoimmunity: alopecia areata
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14870990/ - Hair and stress: A pilot study of hair and cytokine balance alteration in healthy young women under major exam stress
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5397031/ - Telogen effluvium: a comprehensive review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6709511/ - Telogen Effluvium: A Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4606321/ - Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315033/ - A Critical Assessment of the Evidence for Low-Level Laser Therapy in the Treatment of Hair Loss
https://journals.lww.com/dermatologicsurgery/Abstract/2017/02000/A_Critical_Assessment_of_the_Evidence_for.3.aspx - Topical minoxidil fortified with finasteride: An account of maintenance of hair density after replacing oral finasteride
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4314881/
Read full bio of Dawn Hilton
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Swathi E


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.