Female Pattern Baldness: Causes And Treatments To Minimize It
Your complete hair care guide to reclaiming your confidence right from the roots.
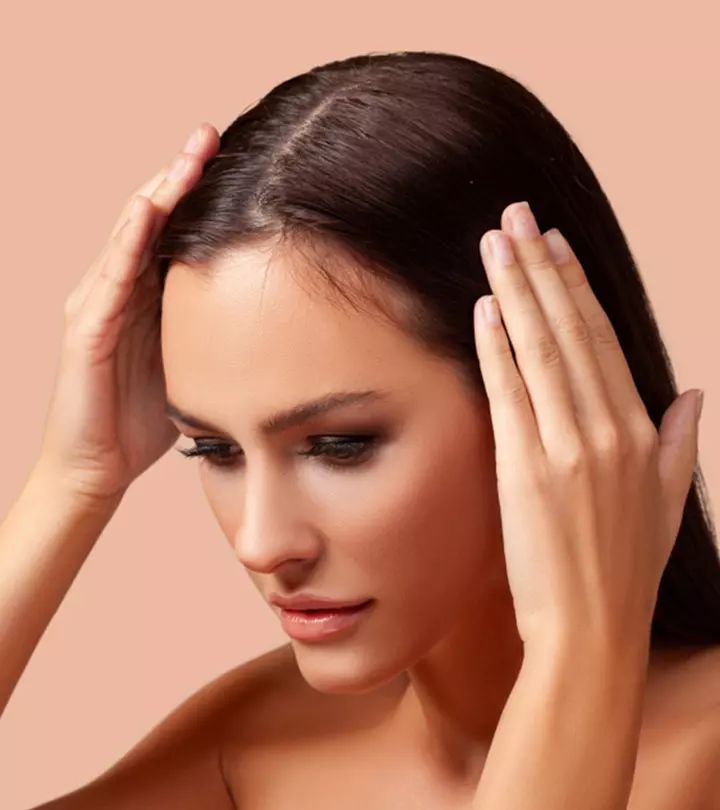

Image: Shutterstock
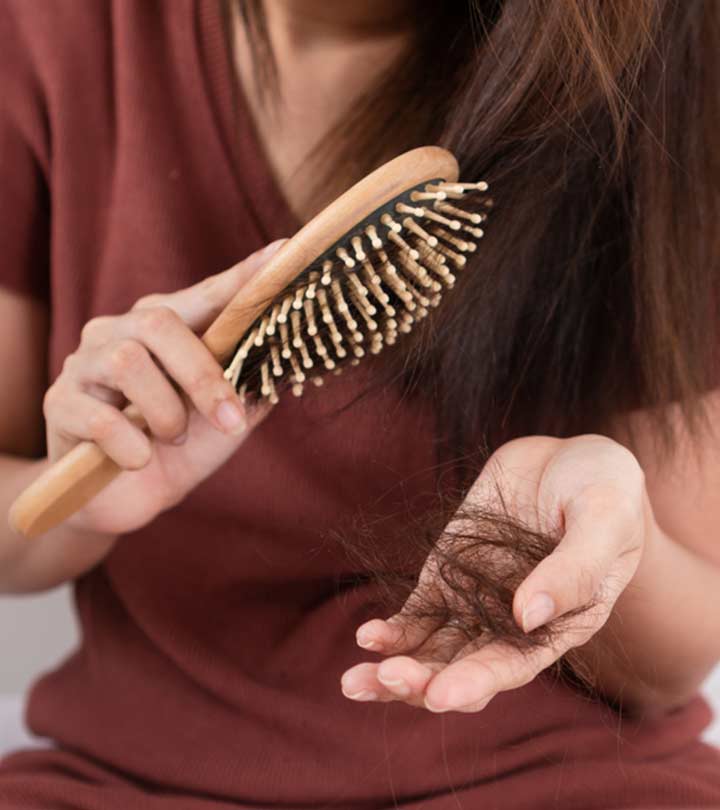
Losing over 100 hair strands a day is normal. These fallen hair strands are most likely to be in their hair growth cycle, and new hair will soon grow back in its place. But this doesn’t happen in the case of female pattern baldness – where one may notice bald patches on the scalp or clumpy hair fall. What causes this type of baldness? Is it reversible? Does it have any treatment options? Keep reading to know more.
In This Article
What Is Female Pattern Baldness?
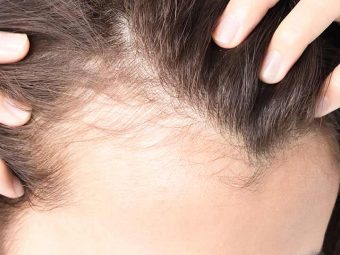
Female pattern baldness is characterized with excess hair loss and thinning. Although hair loss and balding is more common in males, females may also experience it. Women with female pattern baldness experience hair thinning that affects their hair volume. Although there will be no receding hairline, the scalp becomes visible.
A study conducted on 472 women with female pattern hair loss found that 8% had a reported diagnosis of PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome). Further tests and examination led to a diagnosis of PCOS in an additional 12 patients (2%).
Let us take a look at the various causes of female pattern baldness.
What Causes Female Pattern Baldness?
Genetics play a major role in female pattern baldness. Another cause could be an underlying condition that affects the production of androgen. A few other causes include:
- PCOS: Polycystic ovary syndrome may also cause hair loss or hair thinning in some women. This hair loss begins at the vertex of the head (1).
- Thyroid Disorder: Thyroid dysfunction may also cause hair loss and baldness in some women (2).
- Menopause: Some research shows women may experience hair loss during pre-menopause (3). Anecdotal evidence suggests that this may happen during menopause too.
- Medications: Certain medications may also cause hair loss (2). However, hair often regrows after you stop taking them.
- Illness: Severe infections and high fever may also cause hair loss (also called telogen effluvium).
There are several types of hair loss apart from female pattern baldness. Learn the symptoms of FPB to check if you have it or another hair loss type.
Symptoms Of Female Pattern Baldness
- Look for gradual shrinking of hair follicles that follow a specific pattern.
- The affected areas often include the crown region, upper parietal scalp, and, in some cases, the frontoparietal regions (4)
- Follow the Ludwig scale to check for FPB. First you may notice hair thinning at the crown, then hair begins to shed in the area with the preservation of the frontal hairline. Finally, there is heavy hair loss.
- You may notice a frontal midline recession, creating a central scalp thinning like a triangular-shaped figure resembling a Christmas tree
- Check for thinning associated with bitemporal recession (lateral-frontal part of the scalp and vertex), resembling male pattern baldness.
How To Diagnose Female Pattern Baldness
You can consult your doctor or dermatologist if you notice hair thinning or increased hair loss. They will examine your scalp to determine the hair loss pattern. If they suspect a different cause for your hair loss, they may conduct blood tests to arrive at a conclusion.
Treating female pattern baldness is important as it also may help reduce the chances of hair loss in the future. Some of these treatment methods are discussed in the next section.
What Are The Treatment options?
1. Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a popular over-the-counter medication used for treating hair loss in men and women. It is a topical medication applied to the scalp everyday. It may encourage new hair growth while preventing further hair thinning (4). It also can increase hair follicle size. However, this medication may not show the same results in all.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that the medication also may cause scalp dryness or itching. Hence, consult your doctor before using minoxidil.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip2. Spironolactone
One of the more popular oral medications that help treat female pattern baldness is spironolactone. This medication helps block the production of the androgen hormone – potentially preventing hair loss and helping with hair regrowth (4), (6). However, it may cause some adverse effects including dry mouth, nausea, and dizziness. More information is warranted in this regard. There is less information on the safety of spironolactone in pregnant or breastfeeding women. Avoid taking it without consulting your dermatologist.
3. Hair Transplant
You may opt for a hair transplant if medications are ineffective. Female pattern baldness usually affects some areas of the scalp. During the hair transplant procedure, doctors remove some of the hair follicles from the unaffected areas with healthy hair growth. They transplant these hair follicles to the affected areas.
4. Laser Treatment
Laser treatment involves low levels of laser lights that are emitted to stimulate hair growth (7). However, these treatments are usually expensive.
So, how long does it take for female pattern baldness to progress? Let’s find out.
How Long Does Female Pattern Baldness Take To Progress?
Female pattern baldness may affect women of any age group. However, it most commonly occurs in women after menopause. The hair loss may not be constant. You may see a slow increase in hair loss for 3 to 6 months, followed by stable hair growth for 6 to 12 months.
As it is primarily caused by genetics, it cannot be totally prevented. However, one can follow a few steps to reduce hair damage and breakage.
Minimizing Female Pattern Baldness
- Avoid perming, straightening, or dyeing your hair. These methods can damage your hair follicles.
- Eat a diet rich in protein, vitamins, and iron. These can promote healthy hair growth.
- Avoid excess sun exposure. UV rays may impair the hair shafts and lead to hair loss (8). Use a SPF spray or a hat while going in the sun.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipWhen To See A Doctor
Visit a dermatologist if you experience female pattern baldness. Women may experience hair loss for different reasons. The right diagnosis helps you understand the underlying causes and take the right measures.
Takeaway
Female pattern baldness can be managed with proper diagnosis and the right medical intervention. This hair thinning can be caused due to an underlying medical condition or the temporary side effect of a medication. Consult your healthcare provider if you notice significant hair loss to determine what is causing this hair trouble and what your next course of action should be. Do not lose hope and confidence; all you need to do is make incremental lifestyle changes to achieve the best results. Follow a balanced diet, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and drink plenty of water to promote healthy hair growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is female pattern baldness reversible?
Female pattern baldness is usually irreversible without treatment. However, there are medical treatments that can help in hair regrowth.
Does female pattern baldness happen suddenly?
It can occur suddenly or gradually over time. Diet, medications, illness, and childbirth are the main causes of sudden female pattern baldness.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Alopecia areata: an autoimmune disease?
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1600-0625.1999.tb00385.x - Drugs and hair loss
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23159177/ - Traction Alopecia
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/article-abstract/525588 - Female Pattern Hair Loss
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3968982/ - Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05785.x - Female Pattern Hair Loss
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3968982/ - Innovative use of spironolactone as an antiandrogen in the treatment of female pattern hair loss
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20510769/ - Low-Level Laser (Light) Therapy (LLLT) for Treatment of Hair Loss
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3944668/ - UV damage of the hair
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19138021/