Anti-acne Diet: What To Eat For Clearer And Healthier Skin
Consuming a healthy and balanced diet may be the solution to your acne woes.

Image: Shutterstock
Acne is a complex condition influenced by multiple health and lifestyle factors, and diet is one of them. Therefore, following an anti-acne diet and controlling your food choices are crucial in managing the symptoms. Many health professionals suggest that adopting a low-glycemic diet can greatly decrease acne flare-ups. Foods with high glycemic index are known for raising insulin levels, resulting in increased oil production and breakouts. While healthy food choices may not make the inflammation and zits go away overnight, they will benefit your skin in the long run. Keep reading to understand how diet influences acne and what foods can help you keep the breakouts in check.

In This Article
What Causes Acne?
If you are thinking that not taking proper care of your face gave you that ugly acne, dump that thought. Because your hormones influence the occurrence of acne. They make your skin produce excess oil. And when a layer of dead skin cells accumulates on the pores, you get acne. Apart from this, other factors, like stress, may also cause this condition (also called stress acne).
For a few people, acne diminishes with age, and for some, it gets severe, and this is due to the function of your immune system and other genetic factors (1).
According to the Canadian Dermatology Association (CDA), more than 80% of people with acne fall between 12 to 24 years of age. It is estimated that 99% of the cases are affected by face acne. Furthermore, 25% of all teenagers will still have acne at 25 years of age.
Key Takeaways
- You should include proper foods in your diet to manage acne.
- Omega-3, omega-6, and low-glycemic index foods are helpful in controlling acne.
- Vitamin and mineral-rich foods help to achieve healthy skin.
- Avoid dairy products as they can worsen acne breakouts.
Diet And Acne: The Link
Research doesn’t deny the link between acne and your diet. What you eat shows up on your face, and a healthy diet helps you get rid of acne. A review of several studies found that specific diets like a low-carb diet, plant-based diet, Mediterranean diet, Paleo diet, and food items can aggravate or reduce acne (2). High glycemic index foods like sugar, white bread, and white rice cause rapid carbohydrate absorption, raising glucose and insulin levels (3). This increases sebum production and causes acne (4). Also, milk, sugary beverages, and fatty products are prominent foods that cause acne in adults (5). However, there are a few misconceptions regarding the link between oily food and acne. A survey conducted on 49 participants with acne found that 71% of them believed it was caused by greasy foods (6). It is important to note that there are currently no studies that support this claim and more research is warranted.
Brandon William, a YouTuber, spoke about his experience of eliminating sugar and gluten from his diet to combat acne. He saw amazing results after 60 days. He said,” My skin has almost completely cleared up with only faint red remnants of the previous acne healing. Alos, the red itchy eczema that I had in the inside of my arm at the beginning of the challenge is completely gone (i).”
Now, let’s see how you can control your acne breakouts with an anti-acne diet.
The Acne Diet: Diet For Acne-free Skin
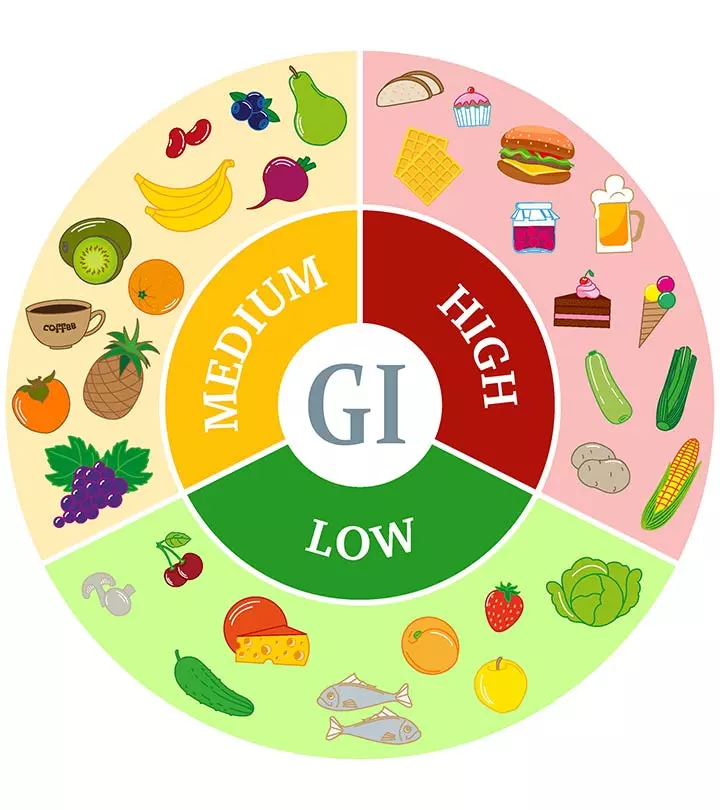
- Low Glycemic Index (GI) Diet
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Foods Containing Vitamins A, D, And E
- Antioxidant-rich Foods
- Diet Enriched With Zinc-containing Foods
- Controlled Dairy Intake
- Chocolate And Acne
- Other Best Supplements To Clear Up Acne
1. Low Glycemic Index (GI) Diet

What Does Research Say?
Several studies were conducted to find out the effectivity of a low glycemic index diet. Glycemic index (GI) is a measure where food items are ranked as per their effect on your blood sugar levels. In other words, foods that do not escalate your blood sugar levels have a low glycemic index. Clinical studies and controlled trials found that a low glycemic load diet reduced the free androgen index (i.e., controlled the release of a hormone called androgeni Group of male sex hormones that regulate the development and maintenance of male traits and the reproductive system. , which is one of the primary causes of acne), thus reducing the severity of acne (7), (8).
Food Items With Low GI
- Oat bran and rolled oats
- Whole wheat
- Brown rice
- Sweet potatoes
- Nuts and raisins
- Peanuts
- Lentils (red and green)
- Carrots (raw and boiled)
- Eggplant (aubergine or brinjal)
- Broccoli
- Tomatoes
- Mushroom
- Red peppers
- Coconut
- Kiwifruit
- Oranges
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids

What Does Research Say?
These fatty acids are mostly found in protein sources, such as eggs, fish, and a few plant sources. A study published in Lipids in Health and Disease reveals that omega-3 fatty acids are anti-inflammatory, and those who included omega-3s in their diet experienced reduced levels of acne severity (9).
Food Items High In Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Fish such as mackerel, herring, sardine, and salmon
- Cod liver oil
- Oyster
- Caviar
- Flaxseeds
- Walnuts
- Chia seeds
- Soybeans
- Grass-fed dairy products and meat
3. Foods containing Vitamins A, D, And E

What Does Research Say?
Vitamin A (retinol) fights acne when applied topically. A study conducted on both men and women showed that retinol was highly effective in treating acne inflammation (10).
A 2014 study published in Dermato Endocrinologyi The branch of medicine dealing with the endocrine system and related conditions and diseases. found that people who suffered from acne-prone skin had low levels of vitamin D (11). Another study found that the people suffering from acne experienced an improvement in their symptoms after they started taking oral vitamin D supplements (12).
Also, vitamin E, along with vitamin C, helps in preventing the formation of sebumi A waxy substance produced by sebaceous glands that keeps skin moist and prevents dryness. , and bacteria. ” ] and the growth of acne-causing bacteria (13).
Food Items High In Vitamins A, D, And E
- Sweet potato
- Carrots
- Egg yolk
- Raw whole milk
- Tuna
- Salmon
- Caviar
- Mushrooms
- Spinach
- Avocado
- Olive oil
- Tomatoes
4. Antioxidant-rich Foods

What Does Research Say?
Oxidative stress is one of the main reasons for acne. Your body has an antioxidant defense system, such as catalase (CAT) and the enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) that regulates the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus maintaining the redox balance of the cells. High levels of ROS and low levels of antioxidants causes oxidative stress. So, consume foods that are rich in antioxidants to avoid acne (14).
Food Items High In Antioxidants
- Dark chocolate
- Berries (cranberry, mulberry, goji berry, blackberry, and wild blueberry)
- Pecan nuts
- Kidney beans
- Cilantro
- Artichokes (boiled ones)
- Raisins
- Green tea
- Broccoli
- Tomatoes
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip5. Diet Enriched With Zinc-containing Foods

What Does Research Say?
According to studies, this micronutrient is crucial for the development of the skin and to maintain its proper function.
Also, zinc is effective against acne-causing bacteria. Several studies concluded that people who were suffering from acne (both men and women) had significantly low levels of zinc in their bodies (15), (16). When consumed orally, it reduces acne inflammation significantly. Therefore, it is wise to eat zinc-rich foods and use products infused with zinc for acne.
Food Items High In Zinc
- Spinach
- Chicken
- Mushrooms
- Yogurt or kefir
- Lamb
- Cashew
- Chickpeas
- Cocoa powder
- Sesame seeds
- Pumpkin seeds
6. Controlled Or No Dairy Intake

What Does Research Say?
Researchers suggest that dairy products can aggravate your acne (17). Why? It’s because the dairy cows are often given hormone injections to increase their milk production. And when you consume the milk or dairy products made from it, it causes hormonal imbalance in your body, which triggers acne (2).
Moreover, cow milk is intended for the calves to help them grow, and it is loaded with hormones and other steroids that are certainly not suitable for acne.
Milk Alternatives To Try To Avoid Acne
- Rice milk
- Soy milk
- Almond milk
- Coconut milk
- Tiger nut milk
- Macadamia milk
7. Chocolate And Acne

What Does Research Say?
A 2013 study found that chocolate could increase the severity of acne (18). Another study conducted in 2014 suggested that cocoa consumption could increase the acne symptoms (19). However, the evidence proving chocolate’s involvement in aggravating acne is very limited (20).
And it’s more likely that the sugar and other ingredients in the chocolate are to be blamed for your breakouts. If you are in a dilemma whether to eat chocolate or not, opt for dark chocolate and check the sugar and other carbohydrate content before consuming it.
8. Other Supplements To Clear Up Acne
- Selenium: A study published in Advances in Dermatology and Allergology states that people suffering from acne vulgaris have low levels of selenium in their body (21). So, to boost your selenium levels, you can take supplements.
- Vitamin C: This antioxidant is a savior for your skin. If you are wondering how to get clear skin, use Vitamin C-infused products and consume more and more citrus foods. It not only boosts cell regeneration but also clears acne and minimizes breakouts (22).
- Vitamin B3 Or Niacin: This essential vitamin is very efficient in treating acne (23).
These are the foods you can include in your diet to reduce the risk of getting acne breakouts. In addition to adding healthy foods to your diet, it is also crucial to cut out those that are causing your acne-probe skin harm. We have curated a list of foods you should keep away from to prevent acne. Keep reading.
Foods To Avoid To Prevent Acne
Here are the top foods that you should avoid indulging in if you wish to achieve clear skin, all free from embarrassing acne!
- Snacks with high sugar content like chips, cookies, etc.
- Drinks with high sugar content like sodas
- Foods that contain refined carbohydrates like white bread and pasta
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Fried foods
- Processed foods that contain additives and preservatives
- Chocolate with high sugar content
Infographic: A 7-Day Sample Anti-acne Diet Plan
Acne can be annoying and painful. Factors like poor skincare regimen, diet, and lifestyle can contribute to acne and skin irritation. The good news is cutting out sugar and processed foods and eating a healthy and balanced diet are key to combating acne. We have provided a 7-day sample diet plan to help you manage acne. Check out the infographic below to know more!
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Our food choices impact our skin health. However, diet and acne have a complex relationship. Only a doctor and nutritionist can guide you on how certain food choices may impact your internal health and acne. It is because diet can impact your hormones and other underlying factors, which may trigger or soothe hormonal acne flareups. The best acne diet includes consuming healthy and nutrient-dense foods and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Self-care through stress management, proper hydration, and meal planning can not just help with acne but also promote better functioning of the digestive system. You may follow the suggestions in the article and work with your doctor to determine how you may manage acne through your diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What foods cause the most acne?
Refined grains, sugar intake, gluten, fast foods, dairy products, whey protein, chocolate, and processed foods are the common foods that can trigger acne.
How do you detox for acne?
Detoxification for acne works best when you include whole foods like lots of vegetables and fruits in the diet. Sip on detox tea, apply exfoliating masks, and clean your face twice or thrice a day.
Is coffee bad for acne?
Yes, coffee is bad for acne. Although it might not cause acne, it may aggravate acne.
Are bananas good for acne?
Yes, bananas are good for acne. They help reduce skin inflammation thanks to their vitamin A content.
Illustration: Anti-Acne Diet: What To Eat For Clearer And Healthier Skin

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn what to eat and avoid to keep your skin clear and acne-free! Discover the best anti-acne diet to help you get rid of breakouts and maintain healthy skin in the video below.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. No Sugar, Dairy, and Gluten for 60 Days. Heres What Happened.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6BlPfnp85S8
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Acne: Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279211/ - Diet and Dermatology
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4106357/ - Glycemic Index (GI) or Glycemic Load (GL) and Dietary Interventions for Optimizing Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Patients with T2 Diabetes: A Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8971946/ - Diet and acne: A systematic review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8971946/ - Association Between Adult Acne and Dietary Behaviors: Findings From the NutriNet-Santé Prospective Cohort Study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32520303/ - Diet and acne: an exploratory survey study of patient beliefs
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27222768/ - ACNE CLINICAL GUIDELINE
https://www.aad.org/member/clinical-quality/guidelines/acne - The effect of a high-protein, low glycemic-load diet versus a conventional, high glycemic-load diet on biochemical parameters associated with acne vulgaris: a randomized, investigator-masked, controlled trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17448569/ - Acne vulgaris, mental health and omega-3 fatty acids: a report of cases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2577647/ - Oral vitamin A in acne vulgaris. Preliminary report
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6453848/ - Preliminary evidence for vitamin D deficiency in nodulocystic acne
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4580068/ - Comparison of Vitamin D Levels in Patients with and without Acne: A Case-Control Study Combined with a Randomized Controlled Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4999291/ - Vitamin E in dermatology
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4976416/ - Antibacterial and antioxidant strategies for acne treatment through plant extracts
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352914817302010 - Serum zinc in acne vulgaris
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6217164/ - Serum zinc and retinol-binding protein in acne
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/139912/ - High school dietary dairy intake and teenage acne
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15692464/ - Chocolate consumption modulates cytokine production in healthy individuals
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23465690/ - Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study Assessing the Effect of Chocolate Consumption in Subjects with a History of Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4025515/ - The relationship of diet and acne
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2836431/ - Significance of diet in treated and untreated acne vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4884775/ - Vitamin C in dermatology
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3673383/ - High dose niacin in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a pilot study
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/314425582_High_dose_niacin_in_the_treatment_of_acne_vulgaris_a_pilot_study
Read full bio of Dr. Enrizza Factor
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Krati Darak



























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.