Gum Boil: Symptoms, Natural Remedies, And Medication
Heal the painful, pus-filled lump with some readily available natural ingredients.
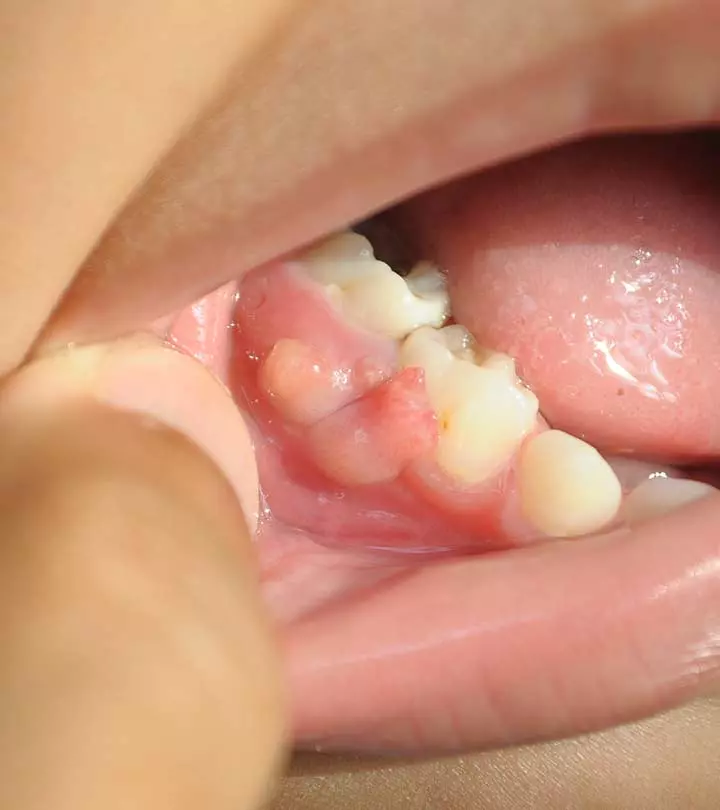
Image: Shutterstock
Do you sometimes feel a tender bump on your gum that makes you uncomfortable? This could be a gum boil. Gum boils are painful and distressing to look at. Simple acts of chewing and eating can be painful due to the boils. If left untreated, gum boils may lead to potential health complications such as septicemiai A serious, often life-threatening case of blood poisoning caused by bacterial infections. Also known as sepsis. (blood infection) and shock (1). In this article, we will be discussing a few gum boil remedies and treatment options that are available.
In This Article
What Is A Gum Boil?
Also known as parulisi A painful oral lesion or abscess that develops on the gumline, especially at the base of a decayed tooth due to an acute infection. or gum abscesses, gum boils are swollen, pus-filled bumps that develop on your gums. Gum boils are a sign of a bacterial infection and they form when there is a bacterial build-up in the gum area. Factors such as food stuck in your teeth, plaques, decaying teeth, or gum disease can lead to the overgrowth of bacteria in gum pockets. There are two types of gum boils:
- Periodontal Abscess –A type of abscess characterized by collection of pus inside the gum tissue called the periodontal pocket. Periodontal abscess is one of the most common forms of boils that require a trip to the dentist every year (2). Caused by gram-negative anaerobic bacteria, a recurrent untreated periodontal abscess may lead to oral cancer cell formation (3).
- Periapical Abscess– Caused by Streptococcusi A genus of parasitic gram-positive bacteria that causes dental infections, pneumonia, pharyngitis, cellulitis and other diseases. and Bacteroides species, these dental abscesses form at the root of the tooth (4). Due to the buildup of bacteria at the root, it results in tooth and bone pain.
While pain in your gum may be the first sign of a gum boil, it may be accompanied by a few other symptoms as well.
Symptoms Of A Gum Boil
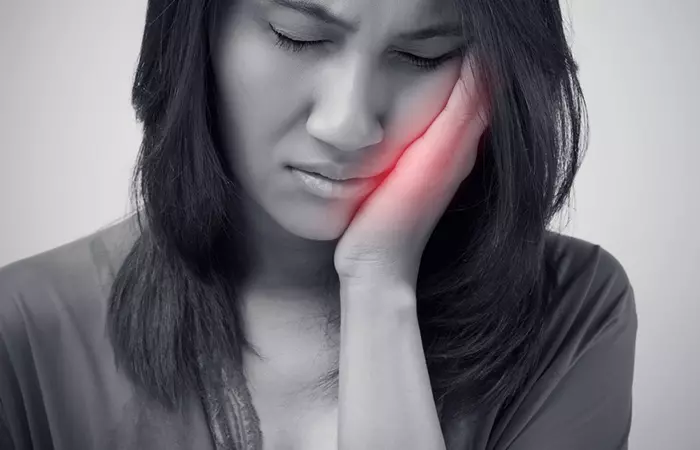

The common symptoms of gum boil are (1), (5):
- Swollen gums
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Sore and tender gum
- Facial erythemai A skin condition that causes reddening of the skin in patches due to increased blood flow due to stress, injury or inflammation. – facial redness
- Trismusi A condition in which the jaw muscles suddenly and painfully contract and cause the mouth to be locked temporarily, or even permanently. – locked jaw
- Dysphagiai Difficulty in swallowing due to dental or neurological problems or blockages in any part of the swallowing process. – trouble swallowing
- Discolored teeth
- Hoarse voice
- Drooling
MsFoy, a blogger, shared their painful experience of gum boils. They said, “The roof of my mouth swelled to an astonishing size and shape, and everything hurt – my jaws, my tongue, my nose, my sinuses, my left eye, my head – and my neck became very stiff and I had difficulty swallowing (i).”
These symptoms can have certain underlying causes. Learn more about them in the next section.
Causes Of Gum Boils
Here are some common causes of this condition (5):
- Gum diseases (gingivitis or periodontitis)
- Tooth decay
- Trauma or injury
- Gum surgery
- Weak immunity
- Bacterial infection
- Poor oral hygiene
- Impacted teeth
- Dental procedures (extractions or root canals)
- Tobacco use
Identifying a gum boil is the first step towards treating it. Know more in the next section.
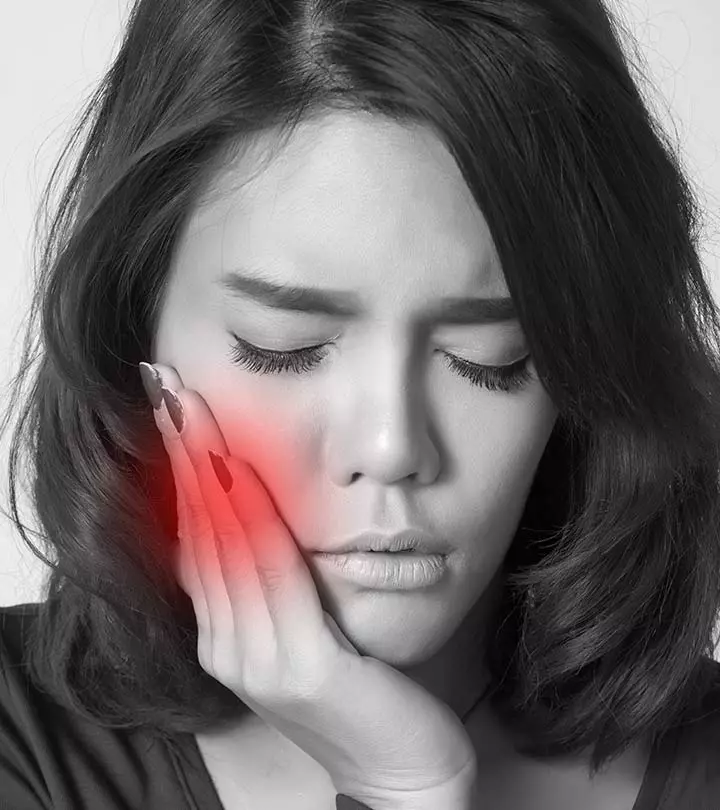
What Does A Gum Boil Look Like?
A gum boil appears as a swollen bump on the gums that are closer to a tooth. It is often red, pus-filled, and tender to touch. The size of the boil can range from a small pimple-like bump to a larger, more noticeable swelling.
In the next section, we talk about a few gum boil remedies you can try at home to help alleviate the symptoms.
Home Care And Natural Remedies For Gum Boil
Following these simple home remedies may not only reduce the symptoms, but may even prevent you from developing gum boils in the future.
- Good Oral Hygiene

Taking good care of your teeth can go a long way in keeping gum boils, tooth decay, and gum disease at bay. A few tips to follow:
- Brush your teeth twice every day.
- Floss your teeth daily.
- Visit a dentist twice a year for a cleaning and checkup.
- Limit sugary drinks and foods.
- Stop Smoking
Studies suggest that smoking has been associated with the development of gum disease. This is because smoking changes the human microflora in the teeth which may lead to the destruction of the tissue. Smoking may also reduce the effectiveness of the treatment for gum disease (6). Cutting off the habit of smoking and chewing tobacco may reduce the risk of gum disease and help your gum heal after treatment.
- Gargle With Salt water

Salt is a natural antibacterial and disinfectant (7). Studies suggest that rinsing with salt water may help promote gum health and oral wound healing (8). You can mix 1 teaspoon of salt in 1 cup of lukewarm water. Gargle the mixture in your mouth for 30 seconds before spitting it out. Repeat this 2 to 3 times regularly.
- Rinse Your Mouth With Hydrogen Peroxide Mouthwash
Hydrogen peroxide is widely used as an antimicrobial agent and may help fight against different types of bacteria and microbes (9). A 2011 review suggested that hydrogen peroxide mouthwash along with daily oral hygiene may be instrumental in reducing gingival inflammation in the long run (10).
A study was conducted in 2017 to see the effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide on patients with moderate to severe periodontitisi A gum infection that causes damage to the soft tissues and bone that support the teeth and can lead to tooth loss. . The authors found that patients who had been given the hydrogen peroxide treatment exhibited fewer symptoms than the control group that did not receive the treatment (11). To make a hydrogen peroxide mouthwash, combine 1 part of hydrogen peroxide with 2 parts of water. Gargle with this mixture for 30 seconds before spitting out. Do this twice a day.
- Turmeric Paste

Turmeric has been used for centuries to treat various medical conditions. According to a study, turmeric may help treat periodontal diseases and may reduce dental pain (12). Another study reported that curcumin, the active compound present in turmeric, may be instrumental in preventing gum disease (13). To make a paste, combine 1 teaspoon of turmeric with ½ teaspoon of salt and 1⁄2 teaspoon of mustard oil. Brush your teeth with this paste twice every day. Let it sit for 2 to 5 minutes and then thoroughly rinse your mouth with water.
- Essential Oils
There are many essential oils that may inhibit antimicrobial activity. Research suggests that tea tree, thymei An aromatic herb that belongs to the mint family and yields a medicinal oil with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. , and peppermint oil may be as effective as a traditional antiseptic against oral microbes (14). To use essential oils for oral health, add 1 drop of essential oil to your mouthwash or regular toothpaste. For rinsing, you can mix 1 drop of essential oil with a quarter of water.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipEven after trying these gum boil remedies, gum boils may remain. In that case, seeking medical treatment is the next step.
Medication And Dental Procedures
To treat gum boils properly and effectively, your dentist may recommend one or a combination of the following treatments:
- Antibiotics – Since a bacterial infection is the cause of gum boils, administering antibiotics is the best way to kill the bacteria. Most of these boils form below the gumline where topical creams may not reach, antibiotics are the best way to treat them.
- Deep Cleaning – Gum disease and tooth decay are some of the common factors behind gum boils. Going for deep cleaning or scaling can remove plaques and heal the swollen gums. You may also try these home remedies for swollen gums for temporary relief.
- Drainage– In some cases, your dentist may drain the pus from the boil, relieving the pain and allowing faster healing.
- Surgical Procedures– If a person develops a boil at the root of the teeth (periapical abscess) due to tooth decay, a root canali A dental procedure to remove the infected pulp and clean the insides of a damaged or infected tooth to save it from further decay. is the way to treat the infection. If the infection has spread to the teeth, your dentist may surgically extract the teeth to prevent the tooth infection from spreading further.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipInfographic: Tips For Preventing And Soothing Gum Boils
Gum boils develop on the gums, mainly from a bacterial infection beneath the surface of the gums. In many cases, they are a result of poor dental hygiene and, if left untreated, may lead to serious complications. The infographic below focuses on home care and natural remedies you can use to prevent and get relief from them. Check it out to learn more!

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
To Sum It Up
Gum boils are swollen, pus-filled growths on your gum that can cause soreness and pain. Food stuck in your teeth, gum disease, and tooth decay allow the bacteria to build in the gums, resulting in gum boils. Gum boils may be prevented by practicing good dental hygiene and not smoking. However, if you still get gum boils, home remedies, such as washing your saltwater rinse, and brushing with essential oils may help alleviate the symptoms and reduce the risk of periodontal disease. If these home remedies fail to provide relief, you should consult your dentist for further treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause gum boils?
Stress may compromise the immune system, rendering it incapable of fighting off infections that lead to gum boils.
What antibiotics treat gum boils?
Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, Azithromycin, Cefixime, and Penicillin are some of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for the treatment of gum boils.
Can sugar intake cause gum boils?
Sugar intake may increase the incidence of gum diseases as sugar may promote oral bacterial growth.
Can apple cider vinegar get rid of gum boils?
Apple cider vinegar has mild antimicrobial properties which can help facilitate recovery from gum boils. However, it may not be able to completely cure it.
Are gum boils contagious?
No, gum boils are not generally contagious. However, severe infections may lead to a transfer of bacteria through the saliva.
Will gum boils bleed?
Yes, gum boils may bleed if it is severe or punctured.
Learn more about treating an abscessed tooth at home with simple, natural remedies. Watch this video for tips on finding relief from the pain and discomfort of the condition.
Key Takeaways
- Gum boils develop when the bacteria builds up in gum pockets owing to different reasons.
- If left untreated, periodontal or dental abscess (a type of gum boils) may even cause oral cancer.
- One should brush twice a day and rinse the mouth with antimicrobial and antibacterial agents.
Illustration: Gum Boil: Symptoms Natural Remedies And Medication

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Hooptedoodle #236 – Run Around Screaming until You Diehttps://prometheusinaspic.blogspot.com/2016/10/hooptedoodle-236-run-around-screaming.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Dental abscess: A microbiological review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3858730/ - Periodontal Abscess
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560625/ - Treponema denticola chymotrypsin-like proteinase may contribute to orodigestive carcinogenesis through immunomodulation
https://idp.nature.com/authorize?response_type=cookie&client_id=grover&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Farticles%2Fbjc2017409 - Prevalence of unculturable bacteria in the periapical abscess: A systematic review and meta-analysis
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0255485#sec005 - Dental Abscess
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493149/ - Smoking and Periodontal Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3633395/ - Gingiva teeth and sea salt
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12822103_Gingiva_teeth_and_sea_salt - Rinsing with Saline Promotes Human Gingival Fibroblast Wound Healing In Vitro
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0159843 - The Use of Hydrogen Peroxide for Disinfection and Sterilization Applications
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9780470682531.pat0885#:~:text=Hydrogen%20peroxide%20has%20been%20shown - The effects of hydrogen peroxide mouthwashes on the prevention of plaque and gingival inflammation: a systematic review
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1601-5037.2010.00492.x - Adjunctive antimicrobial chemotherapy based on hydrogen peroxide photolysis for non-surgical treatment of moderate to severe periodontitis: a randomized controlled trial
https://idp.nature.com/authorize?response_type=cookie&client_id=grover&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Farticles%2Fs41598-017-12514-0 - Role of curcumin in systemic and oral health: An overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3633300/ - Comparative evaluation of 0.1% turmeric mouthwash with 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate in prevention of plaque and gingivitis: A clinical and microbiological study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3498709/ - Antimicrobial efficacy of five essential oils against oral pathogens: An in vitro study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4054083/
Read full bio of Dr. Sandeep Jassal
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty
























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.