What Are The Health Benefits Of Habanero Peppers?
From aiding in weight loss to relieving pain, these hot peppers can do a lot for you.

Image: Shutterstock
Habanero peppers, also called Capsicum chinense, are one of the hottest peppers recorded in history. The rich antioxidant and phenolic compounds explain the benefits of habanero pepper. It is a member of the capsicum family and has many benefits. Habanero pepper may reduce cancer risk, promote weight loss, lower cholesterol levels, and protect against cardiovascular disease. We discuss the health benefits of habanero peppers, how to use and handle them, and their possible side effects in this article. Keep reading.
What Is It? What Are Its Benefits? Who Can Consume It? How Often? Caution
Small fruit with a spicy taste, it is orange or yellow in color.
It may help in weight loss, reduce cancer risk, lower cholesterol levels, prevent cardiovascular diseases, reduce blood pressure, fight diabetes, and help relieve pain.
Anyone over the age of 18, if they can tolerate spice, can consume these peppers in moderation.
You can consume a little amount by adding it to your food every day.
Avoid consumption if you have high blood pressure, digestive issues, or a history of a heart attack.
In This Article
What Are The Benefits Of Eating Habaneros?
1. May Reduce Cancer Risk
The active component of habanero peppers, capsaicin, was found effective in cancer treatment. A study conducted at the University of California at Los Angeles School of Medicine (USA) showed that oral administration of capsaicin inhibited the proliferation of prostate cancer cells (1). Capsaicin may also slow down the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) doubling time (PSA is a protein present in small quantities in the semen of men (2). But this is not an indicator of prostate cancer). The phenolic compounds in habanero exhibit antioxidant activity and may act against cancer (3). A review published in Molecules suggests that the consumption of peppers may offer antioxidant benefits as they are rich in vitamins C, A, and E (4).
In another study, capsaicin was found to inhibit the growth of human breast and leukemia cancer cells (5).
2. May Aid Weight Loss
As per the World Health Organization, approximately 13% (600 million people) of the world population is dealing with obesity (6). The capsaicin in habanero peppers may possess anti-obesity potential. Studies suggest that the consumption of capsaicin may increase thermogenesis (the process of heat production) in the body (7). This, in turn, may improve lipid metabolism and help in the treatment of obesity. Capsaicin may also make you feel full for longer and decrease your appetite. Dietary capsaicin intake may improve metabolic health that helps in the prevention and treatment of obesity (6). However, more human studies are warranted to understand this benefit of habanero.
3. May Lower Cholesterol Levels
In animal studies, capsaicin intake was found to lower plasma cholesterol levels and decrease intestinal absorption of lipids and triglyceridesi A type of fat in the blood that the body need not convert into calories right away due to excess energy. (8). Administration of 8 mg of capsaicin per day for five weeks showed a significant decrease in cholesterol levels. A review published in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism suggests that the bioactive nutrients in hot peppers may help reduce inflammation, lower cholesterol, and reduce oxidative stress (9). Intragastric administration (inserting the needle through the abdominal wall into the stomach) of habanero peppers could also reduce total cholesterol levels (10).
4. May Prevent Cardiovascular Disease
Intake of foods rich in capsaicinoidsi A component found in pepper responsible for its pungency. It is determined by the Scoville heat units used to measure its concentration. may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) (11). The carotenoids in peppers are also potential cardioprotective agents that help decrease the prevalence of atherosclerosis (build-up fats in artery walls) and myocardial infarctioni A blockage of blood flow preventing the heart from receiving enough oxygen. Commonly known as heart attack. (12). In a study published in Preventive Nutrition and Food Science, oral administration of red pepper extracts could help prevent atherosclerosis in mice (13). However, more studies are warranted to understand this phenomenon of habanero in humans.
5. May Help Fight Diabetes
The capsaicinoidsi A component found in pepper responsible for its pungency. It is determined by the Scoville heat units used to measure its concentration. in habanero are said to reduce insulin resistance and help treat diabetes (11). A study conducted by the University of Tasmania found that capsaicin may regulate insulin levels following a meal in overweight individuals (14). Also, the polyphenolic compounds, flavonoids, carotenoids, and antioxidants in habanero peppers may help reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes (14 15). However, more studies are warranted to understand this phenomenon of habanero in humans.
6. May Reduce Blood Pressure
The bioactive compounds in red hot peppers, like capsaicinoidsi A component found in pepper responsible for its pungency. It is determined by the Scoville heat units used to measure its concentration. , may help lower blood pressure (11). Long-term capsaicin treatment was found to lower blood pressure in genetically hypertensive rats (16). However, limited studies are available in this regard.
7. May Help Relieve Pain
Capsaicin is a well-known ingredient in many topical pain relief creams. It has been used clinically to relieve many painful conditions. The extracts of peppers have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce inflammation. Topical application of capsaicin creams was found to alleviate neurogenic pain (17). The gels and creams have analgesici A drug used to treat different kinds of pain experienced in minor ailments, such as headaches as well as major conditions, such as arthritis. and anti-inflammatory properties. They can inhibit the production of Substance P, a compound responsible for swelling and pain associated with inflammation (18).
Anecdotal evidence suggests that habanero peppers have antibacterial properties and may help treat respiratory issues.
 Trivia
TriviaThese are the potential health benefits of habanero peppers. If you love the flavor of salsa or enjoy the taste of Mexican cuisine or Caribbean cuisine, then you should know more about these peppers. It is interesting to note that these peppers are often confused with jalapeno peppers. How are the two different?
Habanero Peppers Vs. Jalapeno Peppers
| Habanero Peppers | Jalapeno Peppers |
|---|---|
| Habaneros range from 100000 to 350000 on the Scoville heat scale. | Jalapeno range from 2500 to 8000 on the heat scale. |
| These peppers have a slightly sweet taste. | These peppers taste crisper and are similar to green bell peppers. |
| They are available in bright orange color with smooth skin. | They are usually available in deep green color with tapered ends. |
| They exists in a oblong, round, and lantern shape. | They exist in a slim and oblong shape. |
These are a few differences between habanero and jalapeno peppers. The spiciness of the habanero makes them unique among hot chili varieties. Hence, one should be very careful while handling this type of chili that ranks high on the Scoville scale. Here are some important tips to keep in mind.
Tips For Cooking With Habanero Peppers
- Wearing gloves is a good idea while you handle habanero peppers. They are high in capsaicin, and working with them without wearing gloves can lead to burns on your hands. Also, avoid rubbing your eyes until you wash your hands.
Rene, a vlogger, shared his experience of consuming a red habanero pepper in his video. He said, “ My mouth is on fire, my tongue don’t really feel it anymore. I could feel it going down my neck. It is making my tongue burn more (i).”
- A little amount of habanero pepper goes a long way. Hence, add little amounts of this spicy pepper to your food items.
- The spiciness of habaneros may burn your mouth if you consume large amounts at a time. Hence, know the remedy for pepper burn in advance (drink milk or eat sugar or chocolate).
- Use cold milk for treating topical pepper burns. Do not use cold water as it may spread the burning sensation
- Remove the skin of the habanero pepper before you start using it. Peeling the habanero pepper will be easier this way. Though the skin of habanero is thin, you can’t break it easily with your teeth.
Easy Habanero Recipes
1. Habanero Salsa
Ingredients
- 3-4 fresh habanero peppers
- 2 ripe tomatoes
- 1 small onion
- 2 cloves garlic
- 1/4 cup of fresh cilantro
- Juice from 1 lime
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Roast the habanero peppers, tomatoes, onion, and garlic until slightly charred.
- Remove the skin from the tomatoes and garlic.
- Blend the roasted ingredients with cilantro and lime juice.
- Season with salt and pepper to taste.
- Serve with tortilla chips.
2. Habanero Guacamole
Ingredients
- 2 ripe avocados
- 1 habanero pepper, finely minced
- 1/4 cup of red onion, finely chopped
- 1/4 cup of fresh cilantro, chopped
- Juice from 1 lime
- Salt to taste
How To Prepare
- Cut the avocados in half, scoop the flesh into a bowl, and mash.
- Add the habanero, red onion, and cilantro to the mashed avocados.
- Squeeze lime juice over the mixture and stir.
- Season with salt to taste.
- Refrigerate for 20 minutes before serving.
- Serve with tortilla chips.
 Trivia
TriviaIntake of habanero peppers in excess amounts may cause some side effects. Scroll down to know in detail.
Are There Any Side Effects Of Eating Habanero Peppers?
Habanero peppers are very high in capsaicin. Eating it for the first time may cause pain in most. The spicy hot sensation can stay on your tongue for 20 minutes or more. Your stomach and intestines may also experience the heat. One may also experience stomach ache and digestive discomfort in some cases. A high dose of capsaicin may temporarily raise blood pressure and body temperature. Hence, those with high blood pressure or a history of heart attacks must practice caution while eating habanero peppers. However, these effects are based on anecdotal evidence. More research is warranted.
Infographic: Top 6 Reasons To Add Habanero Pepper To Your Diet
Habanero pepper is an extremely hot variety of chili that is widely used in Mexican cuisine for its flavor. It also has several health benefits, such as lowering blood pressure and insulin levels in the body. Check out the infographic below to learn the top 6 reasons to add it to your regular diet.
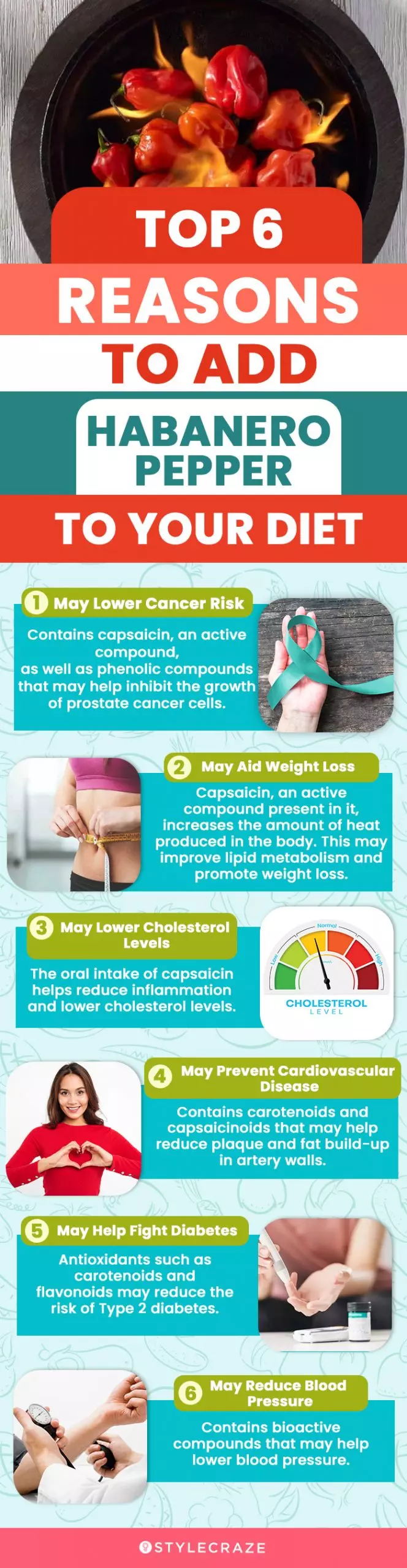
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Habanero peppers are a popular ingredient in hot sauces. They are rich in nutrients and plant compounds with many medicinal properties. They may help to relieve pain, reduce cancer risk, and may offer other benefits too. However, they also can cause heat and other side effects if consumed in excess. Gradually including them in your diet is ideal.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I eat habanero raw?
Yes, you can eat habanero raw.
Is habanero good for the immune system?
Yes, habanero contains polyphenols, which aid immune system functioning.
Is a habanero a natural antibiotic?
Yes, habaneros have antibacterial and antifungal properties that prevent bacterial and fungal infections.
Can habaneros make you sick?
Yes, habaneros are extremely spicy, which may make you feel nauseous.
Key Takeaways
- Capsaicin, the active component in habanero peppers, has anti-cancer and anti-obesity potential.
- Scientific evidence suggests that it increases satiety, reduces appetite, and improves lipid metabolism.
- Studies suggest that it may also regulate insulin levels and reduce type-2 diabetes risk.
- Make sure to wear gloves while processing or cooking these peppers to avoid burns. Their hot sensation can linger around on the tongue for about 20 minutes.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Unleash the fiery health benefits of Habanero peppers in this captivating video. Discover the incredible advantages of incorporating these spicy peppers into your diet, from boosting metabolism to supporting immune health. Watch the video below to know more.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My First Hot RED Habanero Experience – OMGhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WsSCX36GBjo
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “Capsaicin” “a component of red peppers” inhibits the growth of “androgen-independent” p53 mutant prostate cancer cells
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16540674/ - Capsaicin may slow PSA doubling time: case report and literature review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2825034/ - Phytochemical Characterization of By-Products of Habanero “Pepper Grown in Two Different Types of Soils from Yucatán” Mexico
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8071551/ - Capsaicin: From Plants to a Cancer-Suppressing Agent
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6274000/ - Tumor cell growth inhibition is correlated with levels of capsaicin present in hot peppers
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21240831/ - Dietary capsaicin and its anti-obesity potency: from mechanism to clinical implications
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5426284/ - Proteomic analysis for antiobesity potential of capsaicin on white adipose tissue in rats fed with a high fat diet
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20359164/ - Capsaicin lowers plasma cholesterol and triglycerides of lagomorphs
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4051752/ - Capsaicinoids Modulating Cardiometabolic Syndrome Risk Factors: Current Perspectives
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4893589/ - Systemic and local effects of intragastric administration of the habanero fruit (Capsicum Chinense Jacquin C.V.) in rats
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275360475_Systemic_and_local_effects_of_intragastric_administration_of_the_habanero_fruit_Capsicum_Chinense_Jacquin_CV_in_rats - Capsaicinoids Modulating Cardiometabolic Syndrome Risk Factors: Current Perspectives
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4893589/ - Carotenoids of Capsicum Fruits: Pigment Profile and Health-Promoting Functional Attributes
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6827103/ - Ethereal Extract of Pepper: Preventing Atherosclerosis and Left Ventricle Remodeling in LDL Receptor Knockout Mice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8027052/ - “Effects of chili consumption on postprandial glucose” “insulin” and energy metabolism
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16825682/ - Understanding glycaemic control and current approaches for screening antidiabetic natural products from evidence-based medicinal plants
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6731622/ - Dietary Capsaicin Protects Cardiometabolic Organs from Dysfunction
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4882656/ - Influence of Capsaicin on Inflammatory Cytokines Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Myoblast Cells Under In vitro Environment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5407112/ - Capsaicin: Current Understanding of Its Mechanisms and Therapy of Pain and Other Pre-Clinical and Clinical Uses
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6273101
Read full bio of Dr. Pallavi Srivastava
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi
































