What Is Head Lice Life Cycle? How Long Do They Survive?
A timeline of the stages in the life of this parasitic insect and when to intercept it.

Image: Shutterstock
Head lice infestation causes pain, irritation, and often, embarrassment. The rapid head lice life cycle and quick reproduction ability allow these blood-sucking parasites to multiply easily on the human scalp. A distinct form marks each stage of louse development, and it is possible to strategize how to treat lice based on their stage. Knowing how head lice live and grow is important if you want to get rid of them successfully. This article explores the life cycle of head lice, the signs and symptoms of lice infestations, and the available treatment options. Check it out.
In This Article
What Are Head Lice?
The head lice are scientifically known as Pediculus humanus capitis. These wingless parasitic insects feed on human blood several times a day (1). These tiny creatures and their eggs (known as nits) are usually found on the head, eyebrows, and eyelashes (1). Although they spread rapidly, they do not transmit any disease.
Wondering how these parasites look? Find out below.
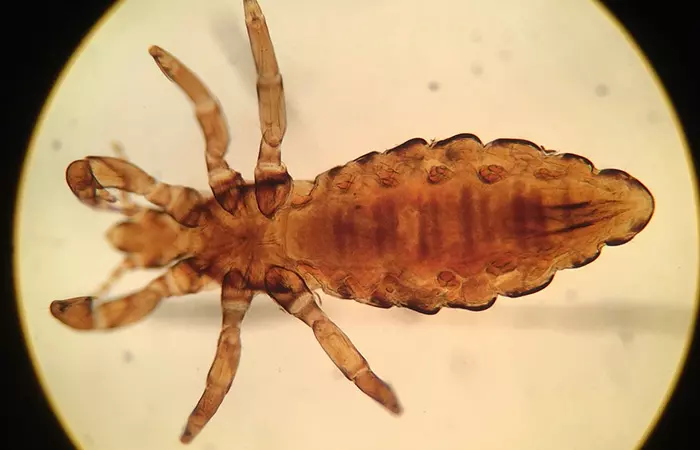
What Do Head Lice Look Like?
An adult head louse has six legs and a grayish-white or tan color (1).
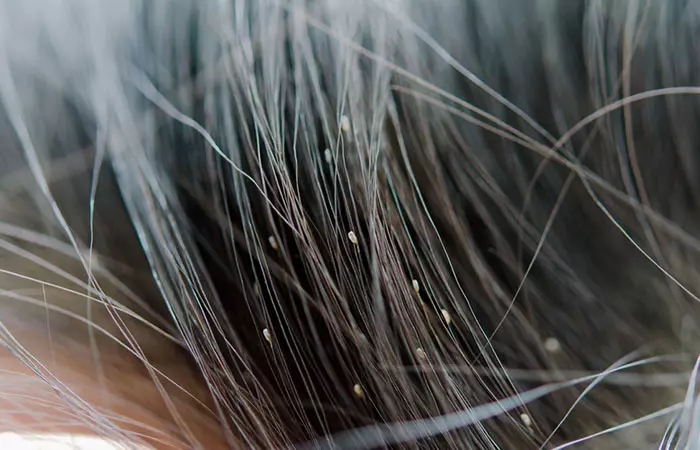
Nits are lice eggs that are usually white or yellow. They are often confused with dandruff, hair spray residue, or scalp buildup.
Keep reading to find out the telltale signs and symptoms of lice infestation.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Head Lice?
Lice infestation is characterized by intense itching and a feeling of something crawling in the hair or on the scalp (1). One may also experience the urge to scratch, irritation, and sleeplessness at night (1). Lice bites can trigger allergic reactions, prompting you to scratch your head often and resulting in sores or scabs.
You could have a lice infestation if you experience any of these symptoms. Lice may also spread from person to person. Let us see how.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?How Are Lice Transmitted?
Head lice are highly contagious and spread through physical proximity (2). Even sharing personal items like combs, hairbrushes, hair ties, hats, and headgear may cause the transmission. Close personal contact is the most likely way lice spread. Although lice cannot live long on inanimate surfaces, they can hitch a ride on towels or clothes. Sharing bedding and pillowcases with an infected person can also lead to lice infection.
We have learned that lice spread rapidly through personal contact. Keep reading to know more about their life cycle.
 Trivia
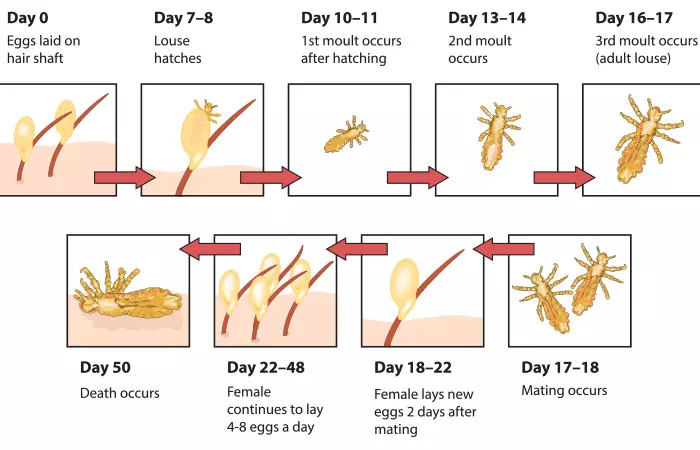
TriviaUnderstanding The Life Cycle Of Head Lice: The Three Stages
Head lice exist in three major forms:
- Nit: These are tiny, yellowish-white, oval-shaped lice eggs usually found near the scalp or the base of the hair shaft (1). They are often difficult to be viewed with the naked eye. These eggs take 8 to 9 days to hatch and move on to the next stage of the life cycle (1). They leave a hard shell or casing behind on the hair strands that are difficult to be removed.
- Nymph: This is a transitional stage of the head lice where they feed voraciously on the human blood for growth and development (1). The nymph takes about 9 to 12 days to develop into an adult head louse (1).
- Adult: This is the final stage in the life cycle where the adult lice are fully developed and thrives on blood (1). They usually lay 6 eggs every day (1).
These are the 3 major stages in the life cycle of the head lice. Wondering how long they live? Scroll down to find out.
Life Span Of Head Lice
The average life span of head lice is 30 days (1). They die 2 to 3 days after their life cycle is complete. However, they lay 6 eggs per day and quickly multiply. This makes eliminating them a challenge. In the following section, we discuss how lice survive.
How Do Lice Survive?
Head lice are parasitic in nature. They need to feed off a host for survival. They suck blood from the human scalp several times a day. Their bites can trigger allergic responses that may result in sores or scabs. The lice can grab onto the hair strands quite tenaciously. While this may make removing them a challenge, it is quite possible.
Treating Head Lice
Prescription or OTC medications such as pyrethrin and permethrin are popular for killing head lice. However, these kill adult lice but not their nits or eggs. Since head lice multiply rapidly, you need to use these treatments several times for the best results.
You may also use benzyl alcohol to treat head lice (3). Consult a doctor immediately in case of an allergic response.
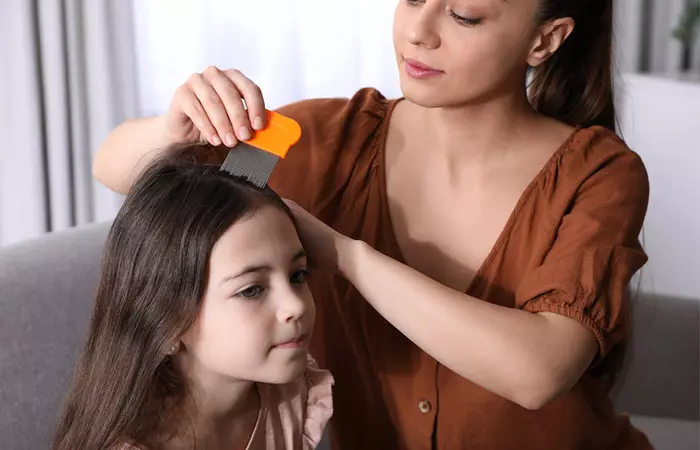
Natural remedies like olive oil and tea tree oil help kill lice and hinder their growth. Anecdotal evidence suggests these remedies are effective and safe. Wide-tooth combs or lice combs help remove nits and their casings.
Let’s dive a little deeper into home remedies that can help you combat this common lice issue. Scroll down.
Home Remedies For Lice Removal
- Coconut Oil
Apply 3-4 tablespoons of coconut oil to the scalp and hair, cover with a shower cap, and leave it on overnight. This helps suffocate the lice, which will make it easier to comb them out the following day.
- Vinegar
Mix 3 tablespoons of vinegar and water, apply the mixture to the scalp, cover your head with a shower cap, and leave it to rest for 2-3 hours. The acidic nature of the vinegar may help make the lice unconscious and loosen the nits, making it easy to comb them out.
- Mayonnaise
Apply 3 tablespoons of mayonnaise to the scalp and hair, wear a shower cap, and leave it on overnight. The mayonnaise helps suffocate the lice, making it easier for you to get rid of them with a lice comb.
These treatments may help remove your head lice. But what is more important is you prevent their recurrence.
Can You Prevent Head Lice?
You can limit or break the spread of lice by avoiding head-to-head contact with others. Limiting the use of personal items such as combs, hats, and bedding can also reduce the risk. Regularly clean your hairbrushes, and wash your clothes and upholstery.
Infographic: A Complete Guide To Head Lice
The constant need to scratch your scalp may indicate head lice. These parasites live on human blood and multiply easily, causing immense distress on a daily basis. But don’t worry, we have got you covered. The infographic below provides all the necessary information about head lice to help you tackle the menace easily. Check it out!

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Understanding the life cycle of head lice will help you get rid of them successfully. They are parasites that suck our blood for survival. They spread from one person to another within no time and are highly contagious. You can get rid of lice with medications and other remedies. With timely action and precautions, you can also prevent them from recurring. The methods and prevention tips mentioned above can help you know more about lice. However, consult a doctor if home remedies do not work, and the issue persists.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can lice live on bedding without a host?
Adult lice cannot survive longer than 1-2 days on bedding and pillows without a human host to feed on. However, if a human comes into close contact with the bedding, the lice can quickly latch onto the hair.
Do you need to wash pillows after lice?
Yes. You need to wash pillows and beddings used by the host as soon as the lice infestation has been discovered, as lice could live for up to 1-2 days, and nits could hatch in 8-9 days. In this time, they could easily transfer to the head of a different host.
How do I clean my house after lice?
You do not need to clean your entire house once you notice the lice infestation. Just wash personal beddings and clothes in hot water and dry on high heat. Other fabric surfaces can be cleaned as usual.
Does conditioner suffocate head lice?
Yes. A conditioner can suffocate and stun head lice for about 20 minutes, making it easier to comb them out.
Can head lice eggs live on clothes?
Lice eggs, or nits, can remain on clothes until a nymph hatches from it. It usually takes 8-9 days for them to hatch. Once it hatches, the nymph cannot live for longer than 24 hours without finding a human host.
Key Takeaways
- Head lice are parasitic insects that feed multiple times a day on human blood.
- Lice on the head are highly contagious and spread through close physical contact.
- The signs of lice infestation of lice include acute itching, irritability, and restlessness.
- Head lice are commonly treated with prescription or over-the-counter treatments such as pyrethrin and permethrin, as well as benzyl alcohol.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn about the life cycle of head lice from nit to adult in this informative video! Discover how long each stage lasts and how to prevent infestations from the video below.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- About Head Lice
https://www.cdc.gov/lice/about/head-lice.html - Head Lice,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5165061/ - The Clinical Trials Supporting Benzyl Alcohol Lotion 5% (UlesfiaTM): A Safe and Effective Topical Treatment for Head Lice (Pediculosis Humanus Capitis),
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1525-1470.2009.01059.x
Read full bio of Melissa Neubeck
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Swathi E