10 Natural Remedies For Diarrhea + Causes, Symptoms, And Prevention Tips
Explore simple and effective remedies to relieve diarrhea and improve your gut health.

Image: Shutterstock
Diarrhea is a common ailment that may aggravate fast if one does not take the right measures early on. While many prescribed medications and treatments can help improve the condition, you also can check out certain home remedies for diarrhea that can help you get rid of the problem.
Diarrhea is most often caused by a lack of basic hygiene or consuming contaminated food and water. Norovirus contamination, one of the most common causes of diarrhea, has been responsible for over 200,000 deaths in developing countries (1).
While most cases of diarrhea can be mild to start with, they often lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, cramps, bloating, and abdominal pain, among other symptoms. Therefore, it is important to keep yourself hydrated with oral rehydration solutions and take ample rest to help your body recover.
If your symptoms seem mild, you can make use of some of the home remedies listed here to keep things under control. However, if the symptoms last beyond a week, you must consult a doctor for the right diagnosis and medications. Read on to know how to stop diarrhea naturally at home.
In This Article
Home Remedies To Treat Diarrhea
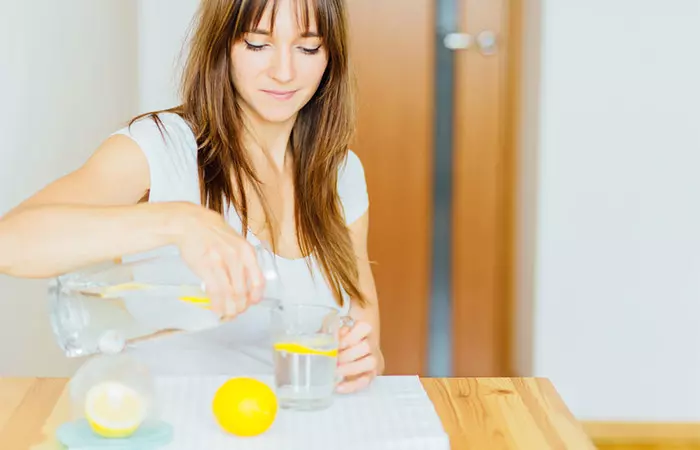
1. Lemon Water
The mixture of lemon juice, sugar, salt, and water is a popular remedy used by many to treat symptoms of diarrhea, like dehydration (2).
You Will Need
- ½ lemon
- 1 glass of water
- A pinch of salt
- 2 teaspoons of sugar
What You Have To Do
- Squeeze the juice from half a lemon into a glass of water.
- Add a pinch of salt and two teaspoons of sugar to it.
- Mix well and drink up.
How Often You Should Do This
Sip on this mixture every few minutes.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties (3), (4). It may help fight the microbes responsible for causing diarrhea and soothe the inflamed intestines.
You Will Need
- 2 teaspoons of apple cider vinegar
- 1 glass of water
- Honey (optional)
What You Have To Do
- Add two teaspoons of apple cider vinegar to a glass of water.
- Mix well and add some honey to it.
- Drink the mixture.
How Often You Should Do This
You can drink this mixture 2-3 times a day until the symptoms subside.
3. Almond Milk
Adults and infants who are lactose-intoleranti A condition in which the body can't digest lactose present in milk and dairy products, causing symptoms like diarrhea and bloating. tend to develop diarrhea on consuming dairy products, like buttermilk (5). Almond milk is a healthy and safe substitute (6).
You Will Need
Almond milk (as required)
What You Have To Do
Replace cow’s milk with almond milk in your cereals, smoothies, and other dishes.
How Often You Should Do This
You can make this a daily habit if you are lactose-intolerant.
4. Coconut Water
Coconut water can be used as a rehydration solution for people with mild symptoms of diarrhea. However, it should be used together with early refeeding (7).
You Will Need
1 glass of fresh young coconut water
What You Have To Do
Drink a glass of young coconut water daily.
How Often You Should Do This
You must preferably drink this concoction after every bout of diarrhea.
Caution: This remedy should not be used to treat symptoms of dehydration. It should also not be used for cholerai A bacterial infection caused by the consumption of contaminated food or drink, leading to dehydration and severe diarrhea. or renal impairmenti Commonly known as acute kidney failure, the state in which kidneys don’t function properly and fail to filter waste from the bloodstream. .
5. Peppermint Essential Oil
The active constituent of peppermint oil is menthol. Menthol can help relieve abdominal pain that accompanies diarrhea and other IBS symptoms. Two studies published in Digestive Diseases And Sciences and Mymensingh Medical Journal also confirmed the same post-sustained release of encapsulated peppermint oil in the small intestine (8), (9).
You Will Need
- 1 drop of food-grade peppermint oil
- 1 glass of warm water
What You Have To Do
- Add a drop of food-grade peppermint oil to a glass of warm water.
- Drink the solution.
How Often You Should Do This
You can drink this mixture 1-2 times daily.
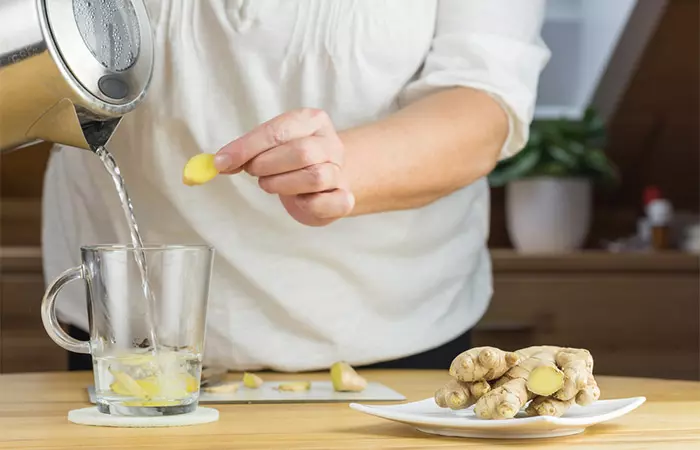
6. Ginger
According to a study published in Yakugaku Zasshi, Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, the acetone extract of ginger can help curb serotonini A chemical messenger and hormone responsible for carrying signals between nerve cells in the brain and body. -induced diarrhea (10).
You Will Need
- 1-2 inches of sliced ginger
- 1 cup of water
What You Have To Do
- Add an inch or two of sliced ginger to a cup of water.
- Bring the mixture to a boil in a saucepan.
- Simmer and strain.
- Drink the warm ginger tea.
How Often You Should Do This
You can drink this mixture 2-3 times daily.
7. Green Tea
Among the many benefits of green tea, one is its ability to treat diarrhea in the affected individuals (11).
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of green tea
- 1 cup of hot water
- 1 cardamom
What You Have To Do
- Steep a teaspoon of green tea in a cup of hot water with cardamom for 5-7 minutes.
- Strain and drink the tea.
How Often You Should Do This
You can drink green tea 1-2 times daily.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip8. Electrolyte Drinks (ORS)
Consumption of electrolyte drinks, such as sports drinks, as well as the ever-popular oral rehydration solution (ORS), may help alleviate the symptoms of dehydration that often accompany diarrhea (13).
You Will Need
- 6 teaspoons of sugar
- 1 teaspoon of salt
- 1 liter of boiled water
What You Have To Do
- Add six teaspoons of sugar to a liter of water. Mix well until it dissolves.
- Add a teaspoon of salt to the solution and mix well.
- Drink a cup of the solution.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this after every watery bowel movement you have.
9. Vitamin A
Vitamin A deficiency is often associated with an increased risk of diarrhea. Hence, restoring this deficiency can reduce the severity of the symptoms (14).
You Will Need
Vitamin A-rich foods or supplements
What You Have To Do
- Increase your intake of vitamin A-rich foods, like carrots, sweet potatoes, apricots, winter squash, cantaloupe, and spinach.
- You can also add vitamin A-rich spices, such as fennel, caraway seeds, cumin, fenugreek seeds, cinnamon, cloves, and nutmeg to the food you are cooking.
- You can also take additional supplements for this vitamin after talking to your doctor about the required dosage for you.
How Often You Should Do This
You can include small amounts of vitamin A-rich foods in your daily diet.
10. Rice Water
Rice water can cut down the number of stools without having any adverse effects on your health. It is especially great for treating diarrhea in infants that occurs as a result of infantile gastroenteritisi A condition in infants that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to severe diarrhea and nausea. in developing countries (15).
You Will Need
½ glass of rice water
What You Have To Do
- Strain the water from cooked rice.
- Consume half a glass of rice water after every bout of diarrhea.
- This remedy can also be used for children.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 2-3 times or more daily.
Other than these natural ingredients, you can also consume aloe vera juice, psyllium husk, slippery elm, and marshmallow root to relieve an upset stomach. While these remedies work their magic, you can also make some changes to your diet for a speedy recovery.
Senny Ong, an aesthetician and a blogger, shares how she treated diarrhea with a rice water remedy. After consuming spoiled food earlier, Senny got diarrhea and a sharp pain in her stomach. However, she remembered the rice water remedy that her friend had shared with her. She writes, “This simple recipe is quite easy to prepare. I quickly take a cup of brown rice and boil with 6 cups of water for 15 minutes, add a little bit of salt. Pour off the rice water only. Let it cool (i).” She adds that within an hour of consuming this drink the diarrhea stopped and she felt less pain as well
What Foods Help Stop Diarrhea?
Diarrhea can be quite uncomfortable. Hence, you must be a little careful about what you eat. This is where the BRAT diet comes into play.
BRAT is “bananas, rice, apple, and toast.” These bland foods will be quite easy on your stomach and will not aggravate your condition any further (1).
It is also necessary that you drink lots of fluids to keep yourself well-hydrated.
Foods To Eat
The foods that can help ease symptoms of diarrhea include:
- Clear broths
- Bananas
- Apples
- Toast
- White rice
- Mashed potatoes
- Yogurt
Foods To Avoid
Avoid these foods if you have diarrhea:
- Dairy products
- Fried or greasy foods
- Spices
- Raw vegetables
- Caffeine
- Citrus fruits
- Raw vegetables
- Pork
- Processed foods
- Alcohol
- Artificial sweeteners
These foods may either be too heavy for your recovering tummy or may further aggravate your condition if they are already contaminated, like in the case of raw vegetables. Hence, exercise caution.
Here are a few additional tips to prevent the recurrence of diarrhea.
How To Prevent Diarrhea
- Always wash your hands every time after using the washroom and also before you eat.
- Wash your hands if you come in contact with any contaminants or pets/animals.
- If you can’t get hold of water to wash your hands, use a sanitizer.
- Be careful when you are traveling to a new place. Do not eat or drink until you are sure the food and drinks are safe to be consumed.
- Wash your vegetables and fruits thoroughly before cooking them.
- Cook all meats well.
- Avoid eating uncooked or undercooked eggs.
- Avoid using dairy that is not pasteurized. If you are lactose-intolerant, avoid dairy altogether.
- Avoid handling food if you have diarrhea.
- Limit caffeine, alcohol, and other foods that have laxative potential.
 Trivia
TriviaIf you can think of any other possible hygiene tips that can help avoid diarrhea, add them to the above list and make sure you follow them religiously.
What causes diarrhea? Who is at risk of contracting this disease? Find out in the next section.
Causes And Risk Factors
Most cases of diarrhea are triggered by an infection in your gastrointestinal tract. Some common microbes that could be held responsible for triggering diarrhea are:
- Viruses like Norwalk virus, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis, and rotavirus.
- Bacteria like Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shigella, and Escherichia coli.
- Other parasitic organisms like Cryptosporidium, Giardia lamblia, and Entamoeba histolytica.
In some cases, especially in chronic diarrhea, a clear cause may not be found. Such cases of chronic diarrhea are referred to as “functional.”
Other factors that can increase your risk of developing chronic diarrhea include:
- Intestinal disorders like Crohn’s diseasei A rare inflammatory bowel disease that causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to diarrhea and abdominal pain. , Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), microscopic colitisi A type of chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes severe inflammation of the large intestine, leading to diarrhea. , or Celiac diseasei An autoimmune disease triggered by gluten-rich ingredients like wheat and barley that can cause a reaction in the body, such as diarrhea.
- Sensitivity to dairy products and/or artificial sweeteners
- Stomach or gallbladder surgery
- Hereditary or genetic conditions, like cystic fibrosisi A rare inherited disorder caused by a defective gene that results in damage to the digestive tract and lungs. or enzyme deficiencies
- Diseases of the pancreas or thyroid
- Radiation therapy treatmenti A form of cancer treatment that involves using high doses of intense radiation to eliminate cancerous cells in the body. of the abdominal or pelvic region
- Consumption of uncooked meats
- Swallowing water or swimming in contaminated water bodies
- Traveling to countries with poor hygiene
- Eating contaminated or unrefrigerated food
- Close contact with an individual with gastroenteritis
- Medications like laxatives and certain antibiotics can also trigger diarrhea.
According to a global survey by the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (US), diarrhea accounts for 1 in 9 child deaths worldwide. It is the second leading cause of death among children. HIV combined with diarrhea is more deadly and causes 11 times more deaths.
There are mainly three types of clinical diarrhea.
Types Of Diarrhea
- Acute Watery Diarrhea – It can last for several hours or even days. This type can also be caused due to cholera infection.
- Acute Bloody Diarrhea – Blood is also noticed in the watery stool. This type is also referred to as dysentery.
- Persistent Diarrhea – It lasts for 14 days or more.
Other than the characteristic watery stool, diarrhea may be accompanied by the following symptoms.
Signs And Symptoms
The common signs and symptoms associated with diarrhea include:
- Stomach ache
- Bloating
- Abdominal cramps
- Weight loss
- Increased thirst
- Fever
Other symptoms may include:
- Presence of blood in the stool
- Pus in the stool
- Dehydration
- Persistent vomiting
If you notice such symptoms along with chronic diarrhea, it could be an indication of a more severe illness. Most cases of diarrhea may ease on their own without treatment. However, in some cases, it is important to seek medical intervention.
When To See A Doctor
If your infant has had 6 bouts of watery bowel movements and 3 or more bouts of vomiting in 24 hours, do not waste any time in consulting a doctor. Children above 1 year should also be taken to a doctor if they have experienced 6 or more bouts of diarrhea in 24 hours.
You must also see a doctor immediately if you notice certain symptoms like:
- Continuous vomiting
- Persistent diarrhea
- Significant loss of weight
- Pus or blood in stool that may also turn the stool black
- Dehydration
Once you visit a doctor, they may do the following to diagnose diarrhea.
Diagnosis
Most often, doctors can diagnose diarrhea without having to carry out any additional tests as two or more watery stools a day indicates the condition without the need for any further diagnosis (1).
But, in severe cases, your doctor may suggest you take a stool test. This is done especially if the patient is very young or old.
For chronic and persistent cases of diarrhea, your doctor may ask you to take any of the following tests depending on the suspected cause:
- Full blood count – a low or raised blood count may indicate inflammation.
- Liver function test to test your albumin levels.
- Malabsorption tests to check the absorption of vitamin B12, calcium, and folate. Your iron status and thyroid functions may also be assessed.
- Testing for antibodies – as it can indicate Celiac disease.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein levels – Raised levels are usually an indication of inflammatory bowel disease.
If an underlying cause is responsible for causing diarrhea, the doctor may suggest further treatments accordingly.
Infographic: Foods That May Trigger Or Worsen Diarrhea
Diarrhea can not only be extremely uncomfortable but also life-threatening if not arrested at the earliest. Certain foods can trigger diarrhea or make it even worse. So it is important to know what to avoid when you are experiencing an upset stomach.
Check out the infographic to learn about what you shouldn’t eat when your digestive system is not in top shape. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Lack of basic hygiene and consuming contaminated food and water are the two most common causes of diarrhea. Most cases of diarrhea lead to electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, bloating, abdominal pain, and cramps, among other symptoms. Now that you know how to get rid of diarrhea, you can reduce the risk by taking a few precautions and maintaining basic hygiene. If you have mild diarrhea, you may follow the home remedies mentioned in this article for relieving the symptoms. However, consult your doctor immediately if the condition persists for several days.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do I get diarrhea after eating?
Experiencing symptoms of diarrhea every time after you eat something is known as postprandial diarrhea. The underlying causes of this kind of diarrhea may include infection, food poisoning, IBS, lactose intolerance, or certain medications.
What is the best thing to drink when you have diarrhea?
You should drink 8 glasses of fluids like fruit juices without pulp, broth, soda (without caffeine), and sports drinks to alleviate dehydration that often results from diarrhea.
How long does diarrhea usually last?
Diarrhea caused by an infection often lasts for no more than 3-5 days. If your symptoms last for more than 4-6 weeks, you most probably have an underlying gastrointestinal condition.
How do you know if your baby has diarrhea?
If your baby has 6 or more bouts of watery bowel movements in 24 hours, he/she has diarrhea and must be taken to a doctor immediately to prevent further health complications.
Can you have diarrhea in early pregnancy?
The shifting hormones, diet changes, and stress are all factors that contribute to many changes in your body during pregnancy, including diarrhea and constipation.
How to prevent traveler’s diarrhea?
Here are some tips that can help prevent traveler’s diarrhea:
• Drink only bottled water.
• Use bottled water even for brushing your teeth.
• Avoid consuming ice that may be made with tap water.
• Eat vegetables that are cooked. Avoid eating them raw.
• Make sure that all foods that you eat, including dairy, seafood, and meat, are properly boiled and/or cooked.
• If the area you are traveling to has had a recent outbreak of hepatitis, take the vaccination for the same before commencing your trip.
Can Coke stop diarrhea?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that intake of Coke may stop diarrhea. However, limited research is available in this regard.
Is it better to stop diarrhea or let it go?
It is best to let it run its course because diarrhea is your body’s way of flushing out bacteria or toxins. However, you may use some over-the-counter medicines (after getting prescribed by a doctor) to feel better.
How do you do a French mohawk braid?
Take some hair from the front of your head, just a bit away from the front hairline. Divide the hair into three sections and weave a stitch of a braid. Then add more hair to the side sections and weave another stitch. Keep braiding your hair in this manner. Fluff the hair in the end, and your French mohawk braid is set.
Key Takeaways
- Consuming green tea and electrolyte drinks may reduce diarrhea symptoms.
- To avoid dehydration brought on by diarrhea, drink lots of water and electrolyte-rich liquids like coconut water.
- The digestive tract may be soothed and diarrhea symptoms may be lessened by eating bland meals like rice, bananas, and boiled potatoes.
- Keeping away from irritants to the digestive system, such as spicy and fatty foods, will help lessen diarrheal symptoms.
- See a doctor if there’s continuous vomiting or blood in the stool.
The following video shares seven effective home remedies that can help you prevent diarrhea naturally. Watch it now and discover a few secrets to maintaining a healthy digestive system, from simple dietary changes to herbal remedies.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My diarrhea cure by Rice Waterhttps://sennyong.blogspot.com/2009/08/my-diarrhea-cure-by-rice-water.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Nemeth, Valerie. “Diarrhea.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 22 June 2019.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448082/ - Ahmed, A et al. “The use of ORS (Nimkol) in management of childhood diarrhoea by mothers in the suburbs of Rawalpindi-Islamabad.” JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association vol. 40,8 (1990): 178-82..
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2126298/ - Yagnik, Darshna et al. “Antimicrobial activity of apple cider vinegar against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans; downregulating cytokine and microbial protein expression.” Scientific Reports vol. 8,1 1732.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5788933/ - “STUDY ABOUT THE NUTRITIONAL AND MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF APPLE CIDER VINEGAR ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT.” Asian Journal of Science and Technology, ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322953260_STUDY_ABOUT_THE_NUTRITIONAL_AND_MEDICINAL_PROPERTIES_OF_APPLE_CIDER_VINEGAR_ARTICLE_INFO_ABSTRACT - “Lactose Intolerance in Adults: Biological Mechanism and Dietary Management”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4586575/ - Salpietro, C D et al. “The almond milk: a new approach to the management of cow-milk allergy/intolerance in infants.” Minerva Pediatrica vol. 57,4 (2005): 173-80.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16172596/ - Adams, W, and D E Bratt. “Young coconut water for home rehydration in children with mild gastroenteritis.” Tropical and Geographical Medicine vol. 44,1-2 (1992): 149-53.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1496708/ - Cash, Brooks D et al. “A Novel Delivery System of Peppermint Oil Is an Effective Therapy for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms.” Digestive Diseases and Sciences vol. 61,2 (2016): 560-71.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4729798/# - Alam, M S et al. “Efficacy of Peppermint oil in diarrhea predominant IBS – a double blind randomized placebo – controlled study.” Mymensingh Medical Journal : MMJ vol. 22,1 (2013): 27-30.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23416804/ - Huang, Q et al. Yakugaku zasshi : Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan vol. 110,12 (1990): 936-42. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.110.12_936
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2074539/ - Chacko, Sabu M et al. “Beneficial effects of green tea: a literature review.” Chinese Medicine vol. 5 13. 6 Apr. 2010, doi:10.1186/1749-8546-5-13
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2855614/ - Srivastava, Janmejai K et al. “Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future.” Molecular medicine reports vol. 3,6 (2010): 895-901. doi:10.3892/mmr.2010.377
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2995283/ - National Research Council (US) Subcommittee on Nutrition and Diarrheal Diseases Control. “THERAPY FOR DIARRHEA.” Nutritional Management of Acute Diarrhea in Infants and Children., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 1 Jan. 1985.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK219096/ - Briend, A. “Vitamin A and diarrhoea. Reducing the risk?.” Dialogue on Diarrhoea ,33 (1988): 4-5.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12342351/ - Wong, H B. “Rice water in treatment of infantile gastroenteritis.” Lancet (London, England) vol. 2,8237 (1981): 102-3.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6113434/
Read full bio of Dr. Millie Lytle
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Dipti Sharma