8 Health Benefits Of Honeydew Melon + Nutrition Facts
Add this low-calorie, low-sodium melon to your shopping list to get a plethora of positive health effects.

Image: Shutterstock
Honeydew melon (Cucumis melo) is a low-calorie fruit. It is a yellowish and oval-shaped with a smooth rind and a pale center with a distinct aroma. The many benefits of honeydew melons can be attributed to their fiber, carotenoids, and plant compounds. They may help reduce blood pressure, prevent dehydration, promote eye health, and improve heart health. This article explores the nutrition facts of honeydew melons, health benefits, side effects, and some delicious recipes. Keep reading.
 Trivia
TriviaIn This Article
What Do Honeydew Melons Taste Like?
Honeydew melons have a sweet, subtle fruity-floral taste. Their degree of sweetness depends on the variety. A fully ripe honeydew melon is sweeter, juicier, and has a soft texture (not mushy). On the other hand, an unripe honeydew melon may taste a bit bland, has a crunchy texture, and a strong musky aftertaste, which reduces a bit when the fruit is fully ripe. It is perfect for snacking and is loaded with nutrients. Let’s take a look at its nutrient profile.
Kassie, a Youtuber, shared her personal experience with tasting a honeydew melon for the first time and how much she relished the sweet flavor. She states in her video, “That is candy, this is nature’s candy (i).” She further shares, “But this is very very good and it is so sweet and sugary that my fingers are getting sticky the way that they get when I’m eating a mango, like when I’m eating a good mango.”
Honeydew Melon Nutrition Facts
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, 100 grams of raw honeydew melon contain (1):
- Calories: 36
- Protein: 0.54 g
- Fat: 0.14 g
- Carbohydrate: 9.09 g
- Fiber: 0.8 g
- Sugar: 8.12 g
- Calcium: 6 mg
- Iron: 0.17 mg
- Magnesium: 10 mg
- Phosphorous: 11 mg
- Potassium: 228 mg
- Sodium: 18 mg
- Zinc: 0.09 mg
- Copper: 0.024 mg
- Manganese: 0.027 mg
- Selenium: 0.7 µg
- Vitamin C: 18 mg
- Riboflavin: 0.012 mg
- Folate: 19 µg
Honeydew melon is also rich in carotenoids and polyphenolsi Organic compounds of the phenol group that naturally occur in plants and provide defense against ultraviolet radiation. , making it a healthy food option. Scroll down to learn more about its health benefits.
8 Health Benefits Of Eating Honeydew Melon
- May Lower Blood Pressure
Honeydew melon is low in sodium and high in potassium (1). A review published in Plants suggests that the high water and mineral content in melons can help reduce blood pressure (2). From studies, a high intake of fruits and vegetables is linked with a reduced risk of high blood pressure (3). In addition, reduced sodium consumption and increased potassium intake can help control blood pressure (4).
- May Help Prevent Dehydration
Your body can become dehydrated when you lose more water than you consume. Honeydew melon contains about 90 percent of water (1). Studies suggest that the high potassium in honeydew melon helps with electrolyte balance in the body (5). The water and potassium content in honeydew melon helps in maintaining hydration.
- Promotes Eye Health
Honeydew melon is rich in carotenoids such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which help promote vision health (1). Lutein plays a key role in vision performance and reduces the risk of age-related macular degenerationi A disease that causes damage to the retina of the eye and results in blurred or reduced vision in people between the age of 50 and 60. , which is a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness (6), (7). A review published in nutrients suggests that these carotenoids act as blue light blockers and prevent damage by free radicals (8).
- Improves Heart Health
The carotenoids and polyphenols in honeydew melon possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They help reduce cholesterol levels, and blood pressure, and help treat and prevent cardiovascular disease (9). In addition, the folate and other vitamins in the melon offer protection against stroke (10).
- Supports Healthy Skin
Honeydew melon is rich in vitamin C and carotenoids that boost skin health. Vitamin C can stimulate collagen production and offer protection against UV-induced photodamage (11). This potent antioxidant can help prevent photoagingi Premature aging of the skin that is characterized by dark spots and fine lines due to prolonged exposure to solar radiation. and aid in the treatment of hyperpigmentationi A condition in which the skin produces excess melanin and causes darkened spots and patches on the skin. (12). However, more studies are needed to understand the benefit of honeydew melon in humans.
Insufficient Evidence For
- May Enhance Bone Health: Honeydew melon is rich in vitamins K and B complex and minerals like magnesium that are essential for maintaining bone mineral density and bone health (13), (14), (15).
- May Boost The Immune System: The vitamin C in honeydew melon helps prevent many infections like the common cold and pneumonia. The nutrient also plays a key role in supporting immune system function (16).
- May Support Fetal Development: Honeydew melon can be a refreshing and nutritious choice during pregnancy. A study found that nutrients like lutein and zeaxanthin play a crucial role in pre-natal development and may aid in a baby’s vision and brain development. Honeydew melon is a rich source of these nutrients (18). Consuming this fruit during pregnancy may support the health of both the mother and the child.
In addition, the carotenoids in honeydew melon may help reduce the risk of cancer (18).
Are there any adverse effects associated with excess intake of honeydew melon? Scroll down to find out.
Side Effects Of Honeydew Melon
Intake of honeydew melon in moderation is considered safe. However, excess consumption may lead to several side effects. These include digestive issues like diarrhea or elevated blood sugar levels.
Honeydew melon may also cause allergic reactions in a few people. However, little research is available on these side effects. If you develop mouth itching, rash, hives, cramps, trouble breathing, and nausea after consumption of honeydew, stop intake and consult your doctor. In general, symptoms will develop right after eating honeydew.
Are honeydew melon and cantaloupe the same? If not, how are the two different? Learn more in the next section.
Honeydew Melon Vs. Cantaloupe
While honeydew melon and cantaloupe have many similar qualities, they have some differences too. Honeydew melon has a smooth, light-colored rind with green flesh. Whereas cantaloupe is dark and netted with orange flesh.
Honeydew is sweeter with firm flesh, while cantaloupe has softer flesh. Cantaloupe is more likely to get contaminated due to its netted rind.
Cantaloupe is a richer source of vitamins A and C than honeydew (1), (19).
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?You should handle honeydew melon carefully to avoid spoilage. So, how do you store it?
How To Store Honeydew Melon?
Honeydew melons will last for about two weeks if stored at room temperature. Leftovers, if stored in the refrigerator, can look fresh for four to five days. You can also store them in the freezer where they may stay fresh for ten to twelve months.
Are you wondering how to eat this oval-shaped fruit? Check out the next section to learn how to prepare honeydew melon.
How To Prepare Honeydew Melon?
You can prepare honeydew melon in the following ways.
- Remove the ends with a knife and halve the melon.
- Remove the seeds with a spoon and cut the melon into wedges.
- Hold each wedge, remove the melon skin from the flesh, and cut it into cubes.
- Serve on a plate.
(Or)
- It is also possible to remove the skin first.
- Slice lengthwise and cut into small cubes.
- To make melon balls, use a measuring spoon and scoop out small balls.
You can also try this method:
- Cut honeydew melon lengthwise into wedges and then into chunks.
- The melon is ready to be served or used as an ingredient in a dish.
You can prepare delicious yet simple honeydew melon recipes at home. Scroll down to find out more.
Honeydew Melon Recipes
1. Honeydew Melon Sorbet
What You Need
- Honeydew Melon – 1
- Honey – ¼ cup
Process
- Cut honeydew in half and remove the seeds.
- Cut into slices and remove fruit from the skin.
- Transfer melon pieces to a parchment paper-lined baking sheet and freeze until hardened.
- Add the frozen melon and honey to a food processor and combine until evenly mixed.
- Transfer to a loaf pan and then to the freezer until completely frozen.
2. Honeydew Melon Smoothie
What You Need
- Chopped honeydew melon – 2 ½ cups
- Coconut milk – 1 cup
- Matcha – 1 teaspoon
- Cinnamon – 1/8 teaspoon
- Lime zest and lime juice – ¼ teaspoon, each
Process
- Add 2 cups of honeydew melon to a blender along with the coconut milk, cinnamon, matcha, lime juice, and zest.
- Blend until all the ingredients are well incorporated.
- Pour into serving glasses. Cut another ½ cup of honeydew into very small pieces and top the smoothie with the chunks of honeydew.
3. Honeydew Melon Jam
What You Need
- Honeydew melon – 1
- Sugar – 2 tablespoons
- Pure lime juice – 2 tablespoons
Process
- Scoop out and discard the seeds from the melon, slice and remove the peel, and chop the flesh into small pieces.
- Chop the flesh of the melon into very small chunks (about a quarter inch).
- Add all the ingredients to a medium-sized pot.
- Cook and stir constantly on high/medium-high heat for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Let it bubble and boil for the full amount of time.
- Either boil the excess liquid or drain after cooking.
- Store in airtight jars or containers in the refrigerator.
Infographic: Top 7 Amazing Benefits Of Honeydew Melon
Honeydew melons are perfect for quenching your thirst on hot summer days. Additionally, their ample health perks are good for the rest of your body too! Check out the following infographic to learn the top health benefits of this refreshing superfruit.
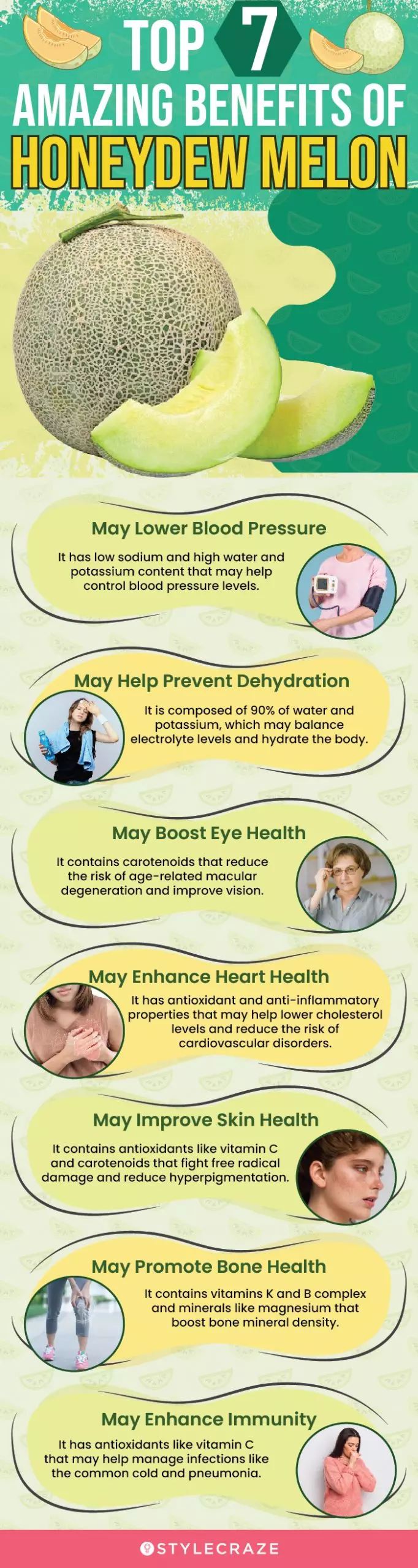
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Conclusion
Honeydew melon is a pale green fleshed sweet fruit with white or yellow rind. It is rich in a wide variety of vitamins and minerals, fiber, and plant compounds. The presence of these nutrients in honeydew melon benefits your health in a multitude of ways. From reducing blood pressure to supporting healthy skin, honeydew melon helps maintain optimal health. It can be eaten alone or as an ingredient in salads, soups, or smoothies. However, excess intake of honeydew melon has some side effects. Hence, consume it in moderation and consult your doctor in case of any emergencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is honeydew good for your stomach?
The presence of water in honeydew melon helps facilitate smooth and easy bowel movements. It also eliminates acidity and improves digestion (19). In addition, the presence of fiber in this melon may help improve digestive health and constipation.
Does honeydew help with bloating?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that the fiber and other nutrients in honeydew melon help with bloating. Being low in calories it is also weight loss friendly food. However, limited data is available in this regard.
Is honeydew melon acidic or alkaline?
Honeydew melon is mildly acidic.
Key Takeaways
- Honeydew melon is high in water content, which can help tackle dehydration.
- Honeydew melon can help curb free radical damage in the body. It is also good for vision.
- It can help promote skin health due to its high antioxidant and vitamin C content.
- Consuming honeydew melon in large quantities may cause diarrhea and increase blood sugar levels.
Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Uncover the incredible health benefits of honeydew in this enlightening video. From hydration to digestive health, this delicious fruit has much to offer. Watch now and incorporate honeydew into your healthy lifestyle today.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Tasting a fruit that grew up listening to musichttps://youtu.be/XudONVFXXDg?feature=shared
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Melons honeydew raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169911/nutrients - Nutritional Composition and Health Benefits of Various Botanical Types of Melon (Cucumis melo L.)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC8469201/ - Associations between dietary patterns and hypertension among Korean adults: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2008-2010)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3679332/ - Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio and Blood Pressure Hypertension and Related Factors
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4224208/ - Potassium Modulates Electrolyte Balance and Blood Pressure through Effects on Distal Cell Voltage and Chloride
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4332769/ - Lutein and Zeaxanthin Isomers in Eye Health and Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5611842/ - The Effect of Lutein on Eye and Extra-Eye Health
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30231532/ - The Role of Lutein in Eye-Related Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3708350/ - Carotenoids: potential allies of cardiovascular health?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4321000/ - Folate
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/ - The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5579659/ - Vitamin C in dermatology
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3673383/ - Vitamin K and Bone Metabolism: A Review of the Latest Evidence in Preclinical Studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6040265/ - B Vitamins Homocysteine and Bone Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4425139/ - Magnesium intake bone mineral density and fractures: results from the Women\’s Health Initiative Observational Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3953885/ - Vitamin C and Immune Function
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29099763/ - Potential Role of Carotenoids as Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3942711/ - Lutein, zeaxanthin and mammalian development: metabolism, functions and implications for health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5949277/ - Melons cantaloupe raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/746770/nutrients - Melon and Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334670049_Melon_and_Glucose-6-Phosphate_Dehydrogenase_Gene
Read full bio of Nilofar Pendhari
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi