How To Get Rid Of Back Acne: 17 Effective Home Remedies
Learn ways to treat those inflamed pores and tender cysts on your back in natural ways.

Image: Shutterstock
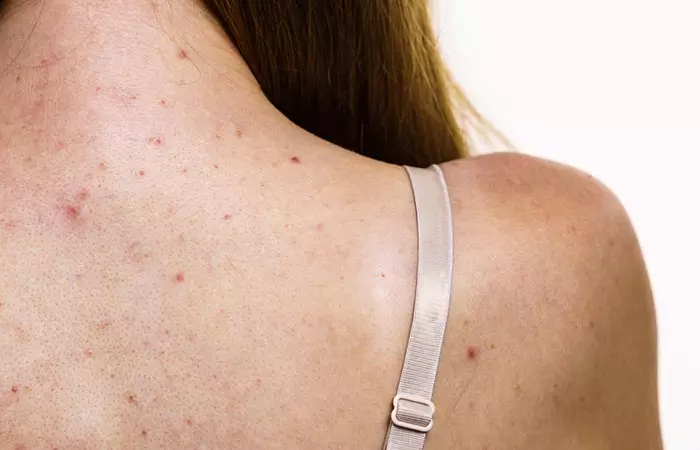
Back acne is challenging and annoying since it is difficult to see and hard to reach. Just like acne on any part of your body, back acne may be a result of clogged pores or a medical condition. Depending on the severity of the acne, your doctor may recommend medications along with a few home remedies to treat your back acne. In this article, we take a look at the causes and home remedies you can try to get rid of back acne.
In This Article
What Is Back Acne?
Back acne includes large tender cysts that develop on the back.
Just like our face, the skin on our back also has sebaceous glands. These glands excrete sebum. When the sebum gets built-up along with bacteria and dead cells, it leads to inflamed pores and breakouts.
A study was conducted on 1309 respondents from the US, Canada, Brazil, France, and Italy were allocated into 2 groups- F+T (facial and truncal acne= 694) and F (facial acne= 615). The study found that 54.3% of the first group had acne on the face and back while 10.6% of the second group reported acne on their face.
The severity of this acne may vary. A mild acne breakout results in few blemishes and may include whiteheads, blackheads, and pimples. Meanwhile, a severe acne breakout results in more spots and cysts.
People with back acne may experience low self-esteem and feel self-conscious about exposing their backs in public. This may result in avoiding particular situations or activities, which may impact one’s self-esteem and well-being. It can also influence the quality of their social interactions.
Hence, it is important to recognize the early signs of back acne and treat them promptly. Back acne can manifest in various forms. Check out the symptoms in the next section.
Key Takeaways
- Back acne, like facial acne, is usually caused due to clogging of pores.
- The common causes are oily skin, dandruff, bacterial action, laser treatments, or hormonal issues.
- Whiteheads and blackheads are non-inflammatory acne. Papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts are inflammatory acne lesions.
- You can treat back acne with home remedies, such as honey and tea tree oil.
- Proper hygiene, exfoliation, and sun protection can help prevent back acne.
Symptoms Of Back Acne
- Back acne typically presents as red or white bumps, similar to facial acne. These can be pustules (containing pus) or papules (small red bumps without pus).
- Comedones (pores), including blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones), may also appear on the back.
- In more severe cases, back acne can form deep, painful cysts or nodules. These are larger and may lead to scarring.
- The affected areas of the back may become red and swollen due to inflammation caused by bacterial infection or irritation.
- Cystic acne and severe inflammation can cause pain and discomfort.
- Some people with back acne may experience severe itching in the affected areas.
Understanding the causes of back acne can help you choose the right treatment option. Learn more in the next section.
What Causes Back Acne?
Factors that contribute to the development of back acne are:
- Oily skin due to overactive glands
- Dead skin cells
- Acne-causing bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes)
- Dandruff
- Hormonal issues polycystic ovarian disease)
- Previous laser treatments
- Shaving and waxing
- Ingrown hair
- Friction or heat
Understanding the different types of back acne helps deal with them better. Check the following section.
Types Of Back Acne
Acne is widely classified into two types – non-inflammatory and inflammatory.
Non-Inflammatory acne lesions include:
- Blackheads – Open comedones that occur when your skin pores are clogged with dead skin and sebum.
- Whiteheads – Closed comedones that result from a build-up of sebum and dead skin cells.
Inflammatory acne lesions include:
- Papules – Acne caused due to the inflammation of walls around skin pores.
- Pustules – Acne caused due to inflamed skin pores that are filled with pus.
- Nodules – Acne caused by irritated and clogged pores.
- Cysts – Acne caused by clogs occurring deep within your skin, resulting in white or red bumps that are painful to touch.
 Trivia
TriviaWe have listed some well-known home remedies that may help treat back acne. Continue reading.
Home Remedies To Treat Back Acne
1. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil exhibits anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties
(1). Hence, tea tree oil may reduce acne. It also can have fewer side effects when compared to other treatment options (2).
You Will Need
- 7 drops of tea tree oil
- 1 teaspoon of coconut oil
What You Have To Do
- Mix seven drops of tea tree oil with a teaspoon of any carrier oil (like coconut oil).
- Apply the mixture all over your back.
- Leave it on overnight and wash it off the next morning.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this daily for at least a week.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel possesses natural anti-inflammatory properties that may help relieve inflammatory acne
(3). It also exhibits anti-acne activity and enhances the effect of other popular acne medications, like tretinoin (4).
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of aloe vera gel
What You Have To Do
- Extract a teaspoon of aloe gel from an aloe vera leaf.
- Apply it to the affected areas.
- Leave it on for 30 minutes before washing it off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 2 to 3 times daily.
3. Epsom Salt
Epsom salts have excellent anti-inflammatory properties due to the presence of magnesium
(5). These properties may help reduce acne as well as the redness and inflammation that accompany it.
You Will Need
- 1 cup of Epsom salts
- Water
What You Have To Do
- Add a cup of Epsom salts to a tub filled with water.
- Soak in this for a good 20 to 30 minutes.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this daily or every alternate day.
4. Lemon Juice
Lemon juice possesses bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties (6), (7). Hence, it may help in reducing inflammation around the acne-affected area.
You Will Need
- ½ a lemon
- Cotton swabs (optional)
What You Have To Do
- Squeeze the juice from half a lemon.
- Soak a cotton swab in it and apply it to your acne lesions.
- You can also scrub half a lemon directly all over your back.
- Leave the lemon juice on for about 30 minutes and wash it off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this once daily.
5. Vitamin D

Acne-prone individuals may also be deficient in vitamin D (8). Therefore, restoring the levels of this vitamin may help treat the symptoms of acne lesions.
You Will Need
- 1000-4000 mcg of vitamin D
What You Have To Do
- Consume foods rich in vitamin D, including poultry, meat, eggs, fish, and almonds.
- You can also take supplements for vitamin D after consulting your physician.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this regularly.
6. Apple Cider Vinegar
has anti-inflammatory properties (9). It may not only reduce acne inflammation but also soothe the lesions.
You Will Need
- 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar
- 1 cup of water
- Cotton balls
What You Have To Do
- Add a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to a cup of water.
- Mix well and soak a cotton ball in it.
- Pat the soaked cotton ball gently all over your back, concentrating on the acne-prone areas.
- Leave it on for 20 to 30 minutes.
- Rinse it off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this multiple times daily.
7. Baking Soda
Anecdotal evidence suggests that baking soda may help relieve acne. However, there is no scientific evidence in this regard. Baking soda is thought to exfoliate your skin and soothe swelling and redness. It also absorbs excess oil from the skin and may dry out acne and help it heal faster.
You Will Need
- 1 tablespoon of baking soda
- Water (as required)
What You Have To Do
- Add some water to a tablespoon of baking soda and make a thick paste.
- Apply an even layer of the baking soda paste to your back.
- Allow the mixture to dry on your skin for at least 20 minutes.
- Wash it off your back while gently scrubbing it off your skin.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 2 to 3 times daily, but make sure you only scrub once.
8. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil contains medium-chain fatty acids, including lauric acid. Lauric acid exhibits anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that combat Propionibacterium acnes, the bacteria responsible for causing acne (10).
You Will Need
- 1 tablespoon of virgin coconut oil
What You Have To Do
- Take a tablespoon of virgin coconut oil in your palms.
- Massage it evenly on your back before you take a bath.
- Allow the oil to work for 30 minutes before rinsing it off.
- You can also consume a tablespoon of virgin coconut oil every morning for added benefits.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this once or twice daily.
9. Oatmeal Bath
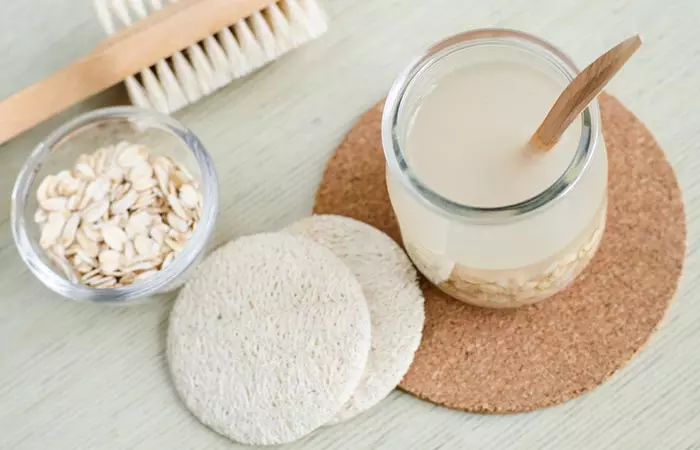

Oatmeal has powerful anti-inflammatory properties. It is a sought-after ingredient in dermatology to treat inflammatory conditions like acne (11), (12).
You Will Need
- 1-2 cups of oatmeal
- Water
What You Have To Do
- Pour one or two cups of oatmeal in a tub filled with water.
- Soak in the oatmeal bath for around 20 to 30 minutes.
How Often You Should Do This
Taking an oatmeal bath daily can help reduce back acne with time.
10. Vicks VapoRub
Vicks contains many anti-inflammatory compounds like camphor, menthol, and eucalyptus oil. These compounds treat back acne by reducing inflammation and redness (13), (14).
You Will Need
- Vicks VapoRub
What You Have To Do
- Apply Vicks VapoRub directly to the affected areas.
- Reapply as and when required.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this multiple times daily.
Note: Do not apply Vicks VapoRub to broken skin or lesions.
11. Yogurt
Yogurt is rich in probiotics, which are the good bacteria that live in your gut. These can help reduce inflammation within your body and may help treat acne (15).
You Will Need
- 1 bowl of plain yogurt
What You Have To Do
- Have a bowl of plain yogurt daily.
- You can also apply yogurt to the affected areas on your back.
How Often You Should Do This
Include yogurt in your daily diet.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip12. Garlic
Garlic contains allicin, which exhibits powerful anti-inflammatory activity(16). It not only helps reduce the inflammation and itching caused by back acne but also reduces their recurrence.
You Will Need
- A few garlic cloves
What You Have To Do
- Mince the garlic cloves.
- Extract the juice and spread it over your back.
- Allow it to sit for around 30 minutes and then wash it off.
How Often You Should Do This
You must do this at least twice daily.
13. Green Tea
Green tea
is beneficial for treating acne – whether it is taken orally or applied topically. This is due to the presence of polyphenols that help reduce sebum secretion and acne (17).
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of green tea
- 1 cup of water
- Cotton pads
What You Have To Do
- Add a teaspoon of green tea to a cup of hot water.
- Steep for 5 to 7 minutes and strain.
- After the tea cools down a bit, dip a cotton pad in it.
- Spread it gently on your back.
- Leave it on for 15 to 20 minutes and then wash it off with water.
- For added benefits, you can also drink green tea regularly.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 2 to 3 times daily.
14. Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is known to reduce acne lesions (18). It may also be used to exfoliate your skin and treat acne breakouts.
You Will Need
- 3% hydrogen peroxide solution
- Cotton pads
What You Have To Do
- Take hydrogen peroxide solution on a cotton pad.
- Apply it all over your back.
- Allow it to dry.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 1 to 2 times daily.
15. Honey
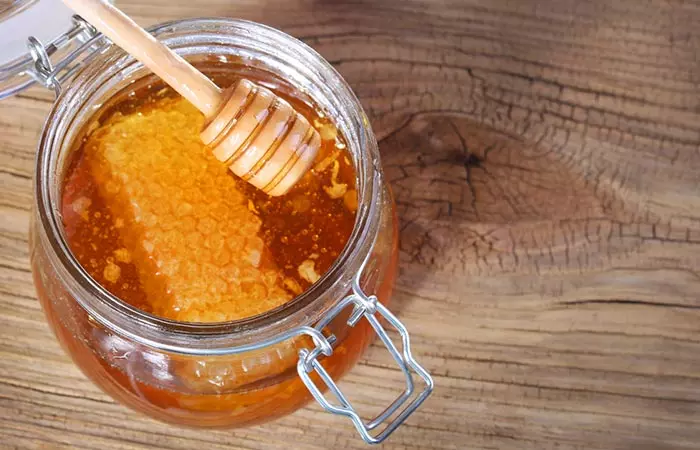

Raw honey is especially helpful in treating inflamed and pus-filled acne. Honey has natural anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that may help reduce acne (19).
You Will Need
- Raw honey (as required)
What You Have To Do
- Take some raw honey and apply it all over your back.
- Leave it on for 20 to 30 minutes before washing it off.
How Often You Should Do This
You must do this 2 to 3 times daily.
16. Sugar Scrub
The coarse texture of sugar may be used to exfoliate your back gently. Exfoliation may help remove accumulated dead skin cells in your pores that may otherwise be causing back acne.
You Will Need
- ½ a cup of sugar
- ½ a cup of coconut or olive oil
What You Have To Do
- Add half a cup of coconut or olive oil to half a cup of sugar.
- Use the mixture as a scrub to gently exfoliate your back while bathing.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this once daily or every alternate day.
17. Turmeric
The major component of turmeric is curcumin (20). This compound has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that may help treat acne lesions (21).
You Will Need
- 2 teaspoons of turmeric powder
- Water (as required)
What You Have To Do
- Mix two teaspoons of turmeric powder and a little water to form a thick paste.
- Apply the paste to your back evenly.
- Leave it on for 20 to 30 minutes.
- Wash it off with water.
How Often You Should Do This
You must do this once daily.
In addition to trying out these remedies, you need to take some precautions to prevent the recurrence of back acne.
Prevention Tips For Back Acne
- Shower immediately after an intense workout – The sweat and dirt accumulated after exercising can settle in your pores, which can aggravate acne.
- Exfoliate regularly – Use a mild, non-comedogenic exfoliator with salicylic acid. It helps remove excess oils and dead skin cells from the pores.
- UV rays from the sun may darken the acne and result in acne scarring. Hence, avoid sun exposure while you have back acne.
- Slather oil-free sunscreen daily – Sunscreen helps repair damaged skin and absorbs excess oil from the pores.
- Choose non-comedogenic skin care products.
- Keep your hair off your back.
- Wear loose-fitting clothes that do not irritate your skin. Tight clothes may push oil and bacteria deeper into the pores.
- Clean your gym clothes and towels regularly.
- Laser therapy can remove excess oils from your pores and may reduce acne. Even though the treatment is slow, it is quite effective in keeping back acne at bay.
- Avoid processed meals and high sugar, which may cause acne, and eat a well-balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Drink plenty of water to help flush out toxins and keep your skin hydrated.
- Practice stress-reduction exercises like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing as stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that may worsen acne.
A skincare and cosmetics blogger claims using a back brush helped him greatly in exfoliating his skin and getting rid of his back acne. Over time, he also discovered the best way to use a back brush for better results, “I used to always apply my soap and shower gel by hand onto my back first and then later scrub with my back brush. I didn’t know pouring the shower gel onto the back brush bristles first would make that much of a difference but it did (i)!” He also says how he later started adding his facial scrub to his shower gel and noted drastic improvements.
The type of food you take plays a vital role in combating back acne. The following diet tips can help.
Diets Tips For Back Acne
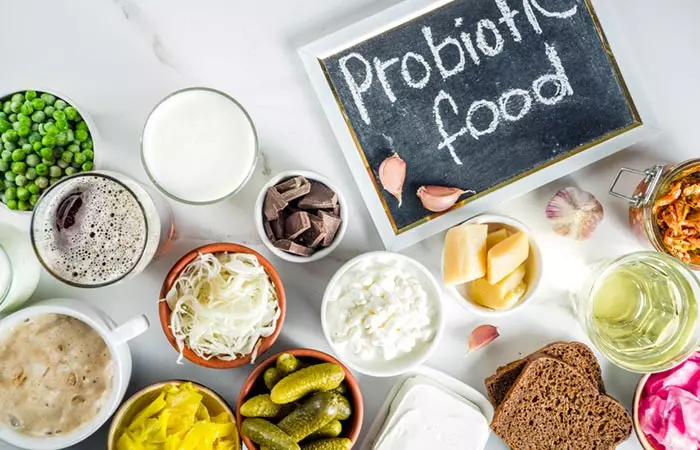

- Follow a healthy diet that includes fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Consume foods that are rich in vitamins A and D.
- Avoid foods like ice cream, cheese, and chocolates as they may aggravate acne.
- Stick to a low-glycemic diet to prevent the occurrence of acne (22).
- Eating probiotic-rich foods helps boost skin health and keeps acne at bay. Foods like kimchi, miso, yogurt, and kefir are rich in probiotics.
- Instead of an extreme or restrictive eating plan, try to follow a well-balanced diet.
Over-The-Counter Medicines For Back Acne
The following OTC acne products can help clear mild back acne. However, we suggest you consult a dermatologist to assess the severity of your acne and take the prescribed medications.
- Benzoyl Peroxide (emollient foam wash) (22): Use a product that contains 5.3% Benzoyl Peroxide. If you need a stronger dose, purchase foaming face washes that contain 10% benzoyl peroxide.
- Retinoid (adapalene 0.1% gel) (23): Retinoid can help unclog the pores. Using it along with benzoyl peroxide can reduce the severity of acne.
Infographic: 7 Home Remedies To Treat Back Acne
Back acne is as problematic as acne occurring on any other part of the body. However, what makes it more annoying is that it is difficult to reach and, hence, difficult to possibly treat. But fret not – while consulting your doctor is critical, you also can follow some simple remedies to aid the treatment. Here are 7 such home remedies to cure back acne. Take a look.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxBack acne can result from clogged pores or any other medical condition. However, a few home remedies can also help manage back acne effectively. Tea tree oil, baking soda, Epsom salt, coconut oil, lemon juice, vitamin D, aloe vera, oatmeal bath, apple cider vinegar, and yogurt help combat back acne. In addition, following prevention tips like showering after a workout, exfoliating regularly, and applying a sunscreen lotion reduces the risk of developing back acne. Maintaining a balanced diet also helps in combating back acne.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is back acne normal?
No, acne is caused due to an accumulation of sweat, dead cells, sebum, and bacteria under the skin. However, it is quite common.
What age does back acne go away?
Teenage acne usually clears up by the age of 20-25 years. However, adult acne that occurs after the age of 25 years can also present as back acne and require self care, treatment or, home remedies to go away.
When should I see my healthcare provider about back acne?
While mild acne can be treated by simple home remedies, severe acne will require proper medical attention. If you experience painful lumps, severe pain, inflammation, infection, or fever, consult your doctor immediately.
How common is back acne?
While back acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages and skin types, it is commonly seen in teenagers. It is the 8th most common skin disease with an estimated global prevalence of 9.38% (24).
Does back acne mean PCOS?
PCOS may trigger the ovaries to produce excess androgen hormone, increasing skin oil (sebum) production. This may lead to acne on the face, neck, and back (25).
Can stress cause back acne?
Yes, increased stress may lead to the excessive production of cortisol, which, in turn, may increase oil production. Stress also suppresses the immune system, which impairs the body’s ability to fight bacteria. These two processes may lead to back acne (26).
Can back acne scars be treated?
Yes, back acne scars can be treated using topical creams, chemical peels, micro-needling, laser therapy, and cryotherapy. Consult your dermatologist to find a suitable treatment for you.
How long does it take to clear up back acne?
Most OTC medications and home remedies for back acne show visible results in six to eight weeks. However, it might take up to three to four months to clear completely.
Is back acne contagious?
No, back acne is not contagious as it results from factors like excess oil production, clogged pores, and stress.
Illustration: How To Get Rid Of Back Acne Using Home Remedies

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn how to get rid of chest and back acne with simple tips and tricks. Get clear skin in no time! Check out this video now.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Tips on How to Get Rid of Back Acne aka Bacnehttps://bestmensskincare.wordpress.com/2012/10/29/tips-on-how-to-get-rid-of-back-acne-aka-bacne/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Carson, C. F., K. A. Hammer, and T. V. Riley. “Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil: a review of antimicrobial and other medicinal properties.” Clinical microbiology reviews 19.1 (2006): 50-62.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/cmr.19.1.50-62.2006 - Bassett, Ingrid B., Ross St C. Barnetson, and Debra L. Pannowitz. “A comparative study of tea‐tree oil versus benzoylperoxide in the treatment of acne.” Medical Journal of Australia 153.8 (1990): 455-458.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2145499/ - Surjushe, Amar, ReshamVasani, and D. G. Saple. “Aloe vera: a short review.” Indian journal of dermatology 53.4 (2008): 163.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2763764/ - Hajheydari, Zohreh, et al. “Effect of Aloe vera topical gel combined with tretinoin in treatment of mild and moderate acne vulgaris: a randomized, double-blind, prospective trial.” Journal of dermatological treatment 25.2 (2014): 123-129.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23336746/ - Rudolf, R. D. “The use of Epsom salts, historically considered.” Canadian Medical Association Journal 7.12 (1917): 1069.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1584988/ - Maria Galati, Enza, et al. “Anti-inflammatory effect of lemon mucilage: in vivo and in vitro studies.” Immunopharmacology and immunotoxicology 27.4 (2005): 661-670.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16435583/ - DE CASTILLO, Marta Cecilia, et al. “Bactericidal activity of lemon juice and lemon derivatives against Vibrio cholerae.” Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 23.10 (2000): 1235-1238.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11041258/ - Lim, Seul-Ki, et al. “Comparison of vitamin D levels in patients with and without acne: a case-control study combined with a randomized controlled trial.” PLoS One 11.8 (2016): e0161162.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27560161/ - Beh, Boon Kee, et al. “Anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects of synthetic acetic acid vinegar and Nipa vinegar on high-fat-diet-induced obese mice.” Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 1-9.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5532206/ - Yang, Darren, et al. “The antimicrobial activity of liposomal lauric acids against Propionibacterium acnes.” Biomaterials 30.30 (2009): 6035-6040.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19665786/ - Michelle Garay, M., M. Judith Nebus, and B. MenasKizoulis. “Antiinflammatory activities of colloidal oatmeal (Avena sativa) contribute to the effectiveness of oats in treatment of itch associated with dry, irritated skin.” J Drugs Dermatol 14.1 (2015): 43-48.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25607907/ - Pazyar, Nader, et al. “Oatmeal in dermatology: a brief review.” Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology 78.2 (2012): 142.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22421643/ - Juergens, U. R., M. Stöber, and H. Vetter. “The anti-inflammatory activity of L-menthol compared to mint oil in human monocytes in vitro: a novel perspective for its therapeutic use in inflammatory diseases.” European journal of medical research 3.12 (1998): 539.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9889172/ - Silva, Jeane, et al. “Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of essential oils of Eucalyptus.” Journal of ethnopharmacology 89.2-3 (2003): 277-283.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14611892/ - Kober, Mary-Margaret, and Whitney P. Bowe. “The effect of probiotics on immune regulation, acne, and photoaging.” International journal of women’s dermatology 1.2 (2015): 85-89.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5418745/ - Arreola, Rodrigo, et al. “Immunomodulation and anti-inflammatory effects of garlic compounds.” Journal of immunology research 2015 (2015).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4417560/ - Saric, Suzana, Manisha Notay, and Raja K. Sivamani. “Green tea and other tea polyphenols: Effects on sebum production and acne vulgaris.” Antioxidants 6.1 (2017): 2.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5384166/ - Milani, Massimo, Andrea Bigardi, and Marco Zavattarelli. “Efficacy and safety of stabilised hydrogen peroxide cream (Crystacide) in mild-to-moderate acne vulgaris: a randomised, controlled trial versus benzoyl peroxide gel.” Current medical research and opinion 19.2 (2003): 135-138.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12740158/ - McLoone, Pauline, et al. “Honey: A therapeutic agent for disorders of the skin.” Central Asian journal of global health 5.1 (2016).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5661189/ - ZorofchianMoghadamtousi, Soheil, et al. “A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin.” BioMed research international 2014 (2014).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4022204/ - Jurenka, Julie S. “Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research.” Alternative medicine review 14.2 (2009).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19594223/ - Kawashima, Makoto, ToshitakaNagare, and MasaharuDoi. “Clinical efficacy and safety of benzoyl peroxide for acne vulgaris: comparison between Japanese and Western patients.” The Journal of Dermatology 44.11 (2017): 1212-1218.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5697687/ - Leyden, James, Linda Stein-Gold, and Jonathan Weiss. “Why topical retinoids are mainstay of therapy for acne.” Dermatology and Therapy 7.3 (2017): 293-304.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5574737/
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
Read full bio of Sucharita Mishra
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.