15 Best Remedies To Increase White Blood Cell Count At Home
Boost your immunity naturally with garlic, spinach, and citrus fruits.
Image: Midjourney/ StyleCraze Design Team
If you are searching for how to increase white blood cell count, you have landed on the right page. Leukocytes or white blood cells are formed in your bone marrow and are responsible for fighting infectious pathogens. The human body creates more than a million white blood cells every day that identify the different pathogens out there and get ready to fight it. If you experience any inflammation, it means that the white blood cells in your body are working hard to get rid of the infection (1). When you experience bouts of cold often, it could be an indication of low white blood cell count in the body. Don’t worry, we have got you covered. In this article, we take a look at the different types of white blood cells in your body and a few home remedies to help you increase the white blood count. Scroll down for more information on how to increase white blood cells!

Did You Know?
The number of leukocytes in the blood is an indicator of a disease. Hence, the white blood cell count is an important component of the complete blood count.
In This Article
What Are The White Blood Cell Counts?
- Average Normal Range Of WBCs – 4,000-11,000 white blood cells per microliter of blood (1).
- Low WBC Count – Less than 4,000 white blood cells per microliter of blood (1).
- High WBC Count – More than 11,000 white blood cells per microliter of blood (1).
WBCs are of different types.
Key Takeaways
- White blood cell fluctuation might indicate infections, autoimmune, cancer and congenital disorders, poor nutrition, or the effect of medicines.
- White blood cells help fight infections and produce antibodies to fight damaging cells.
- Some of the signs of a low white blood cell count are high fever and sweating.
- Lavender oil may help boost white blood cell count and overall immunity.
- To maintain white blood cell count, an optimal balance diet rich in vitamins, fatty acids, and zinc, and exercise is essential.
Types Of White Blood Cells
White blood cells are of numerous types. Here is all you need to know about them (1):
- Neutrophils: Fight infections by ingesting microbes like bacteria and fungi.
- Eosinophils: Fight large parasites like intestinal worms. These cells also secrete IgE antibodies to combat allergens.
- Basophils: Secrete histaminei A chemical found in the body cells of humans that triggers allergic reactions, like runny nose and sneezing. during allergic reactions.
- Lymphocytes: Lymphocytes consist of three cells – B cells, T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. B cells recognize viruses and release antibodies against them, while T cells and NK cells fight cells infected by viruses and cancer.
- Monocytes: Monocytes convert into macrophagesi Type of white blood cells that destroy harmful organisms, clear dead cells, and stimulate the cells of the immune system. and ingest cell debris.
Let us now understand how white blood cells protect the body from foreign body invasion.
How Do White Blood Cells Help Us?
White blood cells are the body’s first line of defense against infection. They protect our body from infections by fighting off bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and other foreign invaders. These cells also facilitate the production of antibodies and help destroy infectious agents as well as cancer cells (1).
Fluctuations in the number of white blood cells can occur due to several reasons. You may notice an increase in your white blood cell count during exercise, while the count may drop while you are resting (2).
Pregnancy and postpartum are two important stages of life where you may notice a fluctuating WBC count. A 2025 study in eBioMedicine noted the pattern of the typical white blood cell count in the first week following birth, depending on the mode of delivery. After the delivery of the baby, the WBC count significantly declines and attains a stationary stage. Elective cesarean birth shows the highest decline, while emergency cesarean birth shows the least. For further information, see the graph below.

Total white blood cells in the postnatal period
Source: White blood cells in pregnancy: reference intervals for before and after deliveryHowever, in some cases, the count might drop abnormally. There could be various factors at play, which we have discussed below.
What Causes Low White Blood Cell Count?
White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, the spongy tissue inside some of your larger bones. A drop in the WBC count could be a result of the following (3):
- Viral infections
- Congenital disorders
- Cancer
- Autoimmune disorders
- Severe infections that require a lot of white blood cells
- Medications like antibiotics
- Poor nutrition
- Alcohol abuse
A low WBC count that is ineffective in fighting infections results in a condition called leukopenia. Read on to know more about it.
What Is Leukopenia?
Leukopenia is when the number of white blood cells, especially a type called granulocytes, is lower than normal (3). This condition is often called neutropenia as well. It can happen due to the body producing fewer white blood cells or because the cells are being used up or destroyed faster. Common causes include infections, certain medications, cancer, and issues with the spleen or immune system. Primary neutropenia, where it happens on its own, is rare but can sometimes be inherited, especially in children, and may come with other health problems. The main concern with neutropenia is a higher risk of infections. Treatment focuses on finding the cause and using antibiotics when serious infections are present (3).
Let us learn more about its signs and symptoms. Keep reading!
Signs And Symptoms Of Low White Blood Cell Count
These include (4):
- High fever
- Chills
- Sweating
If your WBC count has dropped because of an infection, you may notice the following symptoms:
- Swelling and redness
- Mouth sores
- A sore throat
- Severe cough
- Shortness of breath
A low WBC count is not always critical unless it drops so low that the cells cannot protect your body anymore from infections. In such a situation, certain home remedies can help. Let us find out how to increase white blood cells quickly.
How To Increase White Blood Cell Count Naturally
There are many foods that increase platelet count naturally. Here are some commonly found food and ingredients that boost WBC count.

1. Lavender Essential Oil

Lavender oil is often used to treat stress and anxiety and promote sleep. It may also boost the WBC count, thus enhancing your overall immunity (5). However, the exact mechanisms behind its effects are still under research, and results may vary depending on the individual.
Essential oils like sweet almond oil, tea tree oil, and cypress oil also have similar effects in improving the production of white blood cells (5).
You Will Need
- 20 drops of lavender oil
- 60 mL of any carrier oil (sweet almond or jojoba oil)
What You Have To Do
- Add 20 drops of lavender oil to 60 mL of any carrier oil.
- Mix well and use it to massage your body.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this once daily.
2. Garlic

Garlic possesses immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties (thanks to the presence of allicini A yellow oily liquid found naturally in garlic and is responsible for its characteristic odor and bitter taste. ) It may increase your immunity by stimulating the production of various white blood cells, which include lymphocytes, eosinophils, and macrophages (6).
You Will Need
1-2 teaspoons of crushed or minced garlic
What You Have To Do
- Add crushed garlic to your favorite dish and consume it daily.
- If you can handle the strong flavor of garlic, you can have it raw.
How Often You Should Do This
Consume garlic regularly.
3. Spinach
Ever wondered what foods increase white blood cells? Here is the answer. Spinach is a rich source of vitamins and minerals. It also exhibits antioxidant properties (7). Spinach is also rich in folate, a nutrient that helps with DNA synthesis and cell division. These processes are crucial for producing blood cells, including WBCs in the bone marrow (8) (9). These properties can help in increasing the number of white blood cells.
You Will Need
A portion of cooked spinach
What You Have To Do
- Add a portion of cooked spinach to your daily diet.
- You can consume spinach directly or add it to your favorite salad or pasta.
How Often You Should Do This
Consume spinach daily.
4. Papaya Leaves

Papaya leaves contain acetogenins, which are important compounds that boost your immunity by increasing WBC count. Papaya leaf juice serves as an excellent remedy for dengue fever (10). A study published in the journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity examined the effects of mature papaya leaf concentrate on animals. It showed significant blood improvements after three days of administration. Researchers found that the treatment increased platelet counts by 76.5%, white blood cells by 30.51%, and red blood cells by 9.08%, without causing any toxicity. These results highlight the potential of papaya leaf concentrate as a safe and effective way to enhance blood cell production (10).
You Will Need
- A bunch of papaya leaves
- Water (as required)
What You Have To Do
- Take a bunch of washed papaya leaves and blend them.
- Add a little water to the mixture and blend again.
- Strain the mixture and consume one tablespoon of the juice.
- You can add some honey to the mixture if the juice is too bitter.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 1 to 2 times daily.
5. Vitamins
Vitamins A, C, E, and B9 play a major role in improving your white blood cell count. Vitamin A plays a special role in increasing lymphocytes, whereas vitamin C is known to boost your overall immunity (11), (12). Vitamin B9 is necessary for the production of neutrophils, and vitamin E promotes the production of natural killer cells (13), (14).
Consume foods, like spinach, carrots, cheese, meat, eggs, fish, sweet potato, and citrus fruits. You can also take vitamin supplements after consulting your doctor.
6. Yogurt

The probiotics in yogurt boost immunity. They also have stimulating properties that help increase WBC count (15), (16).
A study published in the Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism journal investigated how daily yogurt consumption affects cellular immunity in 33 young healthy women, comparing conventional and probiotic yogurt. The findings suggest that both types of yogurt increase the activity of T cells, which are a type of white blood cell (16).
You Will Need
1 bowl of probiotic yogurt
What You Have To Do
Consume a bowl of probiotic-richi Food rich in living microorganisms, like bacteria and fungi, that has good health benefits for the digestive system. yogurt.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this at least once daily.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip7. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3i Healthy fatty acids present in vegetable oils and nuts (especially walnuts) or supplements to maintain health. supplements have immunomodulatory properties that boost your immunity by increasing WBC count (17). A study shows omega-3 fatty acids may help improve the function of macrophages and neutrophils, specialized cells in the human immune system that fights infection. Due to this, they may help improve immune function (18).
You Will Need
1000 mg of omega-3 supplements
What You Have To Do
- Consume 1000 mg of omega-3 after consulting your doctor.
- You can also consume fish, like mackerel, sardines, salmon, and other foods, like walnuts and avocados, to increase your intake of omega-3s.
How Often You Should Do This
Take these supplements only once daily.
8. Zinc
Zinc can help restore the normal functioning of white blood cells, thereby boosting immunity (19). Zinc is also essential for the development and functioning of white blood cells called neutrophils and lymphocytes, which are important for fighting infections (20).
You Will Need
8-11 mg of zinc supplements
What You Have To Do
- Consume 8 to 11 mg of zinc supplements after consulting your doctor.
- You can also consume foods rich in zinc like oysters, red meat, beans, and nuts.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this daily.
9. Broccoli
The sulforaphanei Sulfur-rich compounds are generated when chewing vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and bok choy. (SFN) in broccoli can help regulate your white blood cell count and boost your immune system (21).
You Will Need
1 cup of cooked broccoli
What You Have To Do
- Consume a cup of cooked broccoli.
- You can sprinkle some salt and consume it directly or add it to your favorite salad.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this daily.
10. Selenium
Dietary intake of selenium has a positive effect on the production of white blood cells, especially lymphocytes and neutrophils. Selenium also enhances your immunity against infections and diseases (22). In a case study published in the Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, a patient with chronic neutropenia was found to have only a selenium deficiency after ruling out other causes. Treatment with a selenium supplement for two months led to a significant improvement in the patient’s white blood cell and neutrophil counts. When the selenium treatment was stopped, the counts gradually decreased to their previous low levels, indicating that selenium supplementation had effectively corrected the deficiency and improved the neutropenia (23).
You Will Need
200 mcg of selenium supplement
What You Have To Do
- Take 200 mcg of selenium supplements daily after consulting your physician.
- You can also meet your daily selenium requirement by consuming more of tuna, sardines, chicken, and turkey.
How Often You Should Do This
Consume the selenium supplement once daily.
11. Kiwi
Kiwis contain powerful antioxidants and are also rich sources of potassium and vitamins C and E. All these nutrients play an important role in enhancing your immunity and increasing the number of white blood cells (24).
You Will Need
1-2 kiwis
What You Have To Do
- Peel the kiwis.
- Cut them into pieces and eat immediately.
How Often You Should Do This
Have 2 to 3 kiwis daily for maximum benefits.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip12. Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits are rich sources of antioxidants and vitamin C, both of which enhance immune function (25). Vitamin C also supports the function of many types of immune cells, including lymphocytes, the natural killer cells (26). So, citrus fruits may also help increase the WBC count. Some citrus fruits that are easily available are oranges, kiwis, strawberries, lemons, and grapefruits.
13. Noni Fruit
One of the major nutrients in noni fruit is vitamin C, which is why this fruit works well in enhancing immunity. It exhibits stimulating properties that help increase the count of T and B lymphocytes (27).
You Will Need
30-60 mL of unsweetened noni juice
What You Have To Do
- Consume 30 to 60 mL of unsweetened noni juice.
- You can either drink store-bought organic juice or extract the juice directly from the fruit and consume it.
How Often You Should Do This
Have noni juice every day.
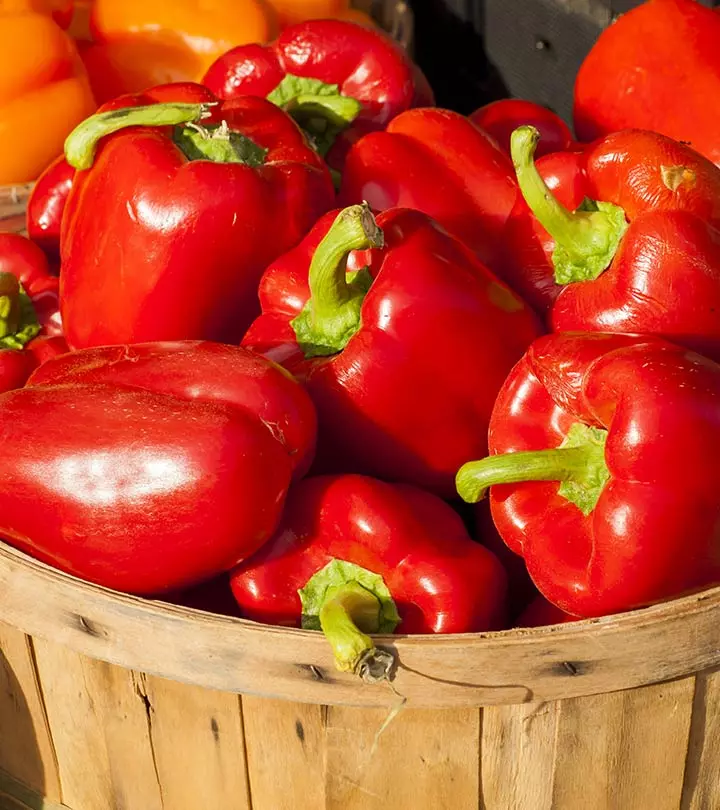
14. Red Bell Peppers
Red bell peppers are rich in vitamin C and have immunity modulation properties (28). Hence, they may help boost your immune system. A review published in the journal “Antioxidants” examined the role of Vitamin C in supporting the immune system, particularly in cancer patients who are often immune-compromised after treatments like chemotherapy. It highlighted that Vitamin C is crucial for the development and function of T lymphocytes, the type of white blood cells essential for immune responses (29).
You Will Need
1 red bell pepper
What You Have To Do
Cut it into small slices and toss them raw in your salad. Enjoy the crunch!
How Often You Should Do This
You can eat them on a daily basis.
15. Sunflower Seeds
Sunflower seeds contain phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin E, and vitamin B6. These nutrients and antioxidants boost white blood cells to fight infection and keep your body functioning properly (30).
You Will Need
A handful of raw or salted sunflower seeds
What You Have To Do
Toss them in your salad, or sprinkle on sautéed vegetables or munch on them.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this daily.
So these are some remedies that answer your “how to raise white blood cell count” query. We strongly recommend you begin treatment and also use the above remedies if you happen to notice a fall in your WBC count. Not restoring a low WBC count to its optimum levels can lead to complications.
Complications Of Insufficient White Blood Cells
- You become more prone to microbial and parasitic infections.
- If you have cancer, your treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be delayed because of your weak immune system.
- In severe cases, the condition may result in the death of the individual (31).
So, it is best to consult a doctor and diagnose the condition without delay. Read on to know more about it.
Diagnosis Of Leukopenia
To diagnose leukopenia, doctors usually start with a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test. This test measures the number and types of white blood cells in your blood. If the CBC shows a lower-than-normal white blood cell count, further tests might be needed to pinpoint the cause. These could include additional blood tests, bone marrow exams, or tests to check for infections or other conditions.
The goal is to understand why your white blood cell count is low and to guide appropriate treatment. Keep reading to learn more about the treatment options available.
Treatment Options
Treating low white blood cell counts depends on what’s causing the problem. If it is due to an infection, doctors might prescribe antibiotics or antiviral medications. For issues related to medications, adjusting or changing the drug could help. If the cause is a condition like cancer, treatment might involve chemotherapy or radiation, followed by medications to boost white blood cell production. In cases where the bone marrow is not producing enough cells, doctors might recommend treatments like growth factors or, in severe cases, a bone marrow transplant. Identifying the cause is key to choosing the right treatment and improving white blood cell counts.
Apart from consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients like vitamin C and zinc, some lifestyle changes may also help increase your WBC count. Learn more about them in the following section.
Lifestyle Tips On How To Increase White Blood Cell Count
Here are some lifestyle tips that may help you increase your white blood cell count:
- Exercise regularly, as moderate exercise may help increase WBC production by boosting the immune system (2). You may opt for activities like walking, jogging, or yoga.
- Sleep is essential for immune health and the proper functioning of white blood cells (32). Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Avoid smoking, as it may weaken the immune system and lower white blood cell count (33).
Limit alcohol consumption, as it may impair immune function and decrease white blood cells (34).
Low white blood cells may weaken your immunity but their excess may be an indication of an underlying issue. What causes high white blood cells? Learn more about it in the next section.
What Causes High White Blood Cell Counts?
Abnormally high white blood cell count is known as leukocytes. It can occur due to the following factors:
1. Infection
When your body is under attack from pathogens such as bacteria or viruses, it can trigger the production of white blood cells to build immunity against them. White blood cell count may also increase in response to stress, leukemia, or parasitic infections (1).
2. Autoimmune Response
Autoimmune disorders can cause your body to confuse between the pathogen and healthy tissues. This can raise the white blood cell count, resulting in them attacking the healthy tissues. This is seen in medical conditions such as rheumatoid diseases, cancer, and allergic reactions (35).
Infographic: Ways To Prevent Low White Blood Cell Count
White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. They defend your body against several diseases and infections. So, maintaining sufficient levels of WBCs is essential for proper body functioning. However, many factors can cause low WBC count in the body. You can prevent it by taking some precautionary measures. Check out the infographic below to learn some ways to minimize the chances of a low white blood cell count. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
A few natural remedies and healthy lifestyle changes are all you need if you are looking for how to increase your white blood cell count. Viral infections, cancer, autoimmune diseases, congenital disorders, poor nutrition, and antibiotics may cause low white blood cell count. You can treat the condition by using herbal supplements, lavender essential oil, garlic, spinach, sunflower seeds, red bell peppers, citrus fruits, noni fruit, and kiwi. You can opt for other treatments and remedies like acupuncture, meditation, yoga, massage therapy, blood transfusion, or stem cell transplant to help increase the white blood cell count and assist in stress management. In addition, selenium, broccoli, zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, yogurt, vitamins, and papaya leaves effectively improve low blood cell count. Try any of the remedies mentioned above that best suit you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to increase white blood cells?
It can take anywhere from a few days to weeks to increase white blood cells with proper treatment and remedies.
How many white blood cells are there in the human body?
In normal adult bodies, there should be about 4,000-10,000 white blood cells per microliter of blood. Any variation in this count is a sign of an underlying infection in your body.
What foods to avoid if you have a low white blood cell count?
Avoid uncooked food, raw meat and sushi, and unpasteurized beverages as they may increase your risk of contracting infections and further lower your white blood cell count.
What vitamin deficiency reduces white blood cell count?
Studies suggest that deficiency of vitamins B and D can be linked to a weaker immunity (and a low white blood cell count) (36), (37). Hence, consuming a diet (or supplements) rich in these vitamins can boost your immune function. Consult a doctor for more information on the right diet and supplements.
Does a low white blood cell count make you tired?
No, a low white blood cell count itself is not associated with fatigue. However, if you continue experiencing increased fatigue, it may be the symptom of an underlying issue that needs medical attention.
Illustration: Best Remedies To Increase White Blood Cell Count At Home

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Get a detailed insight into ways that will help you naturally increase the white blood cell count in the body to keep your immune system strong and fight off infections. Watch this video now!
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Histology, White Blood Cell, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563148/ - Effects of exercise on leukocytosis and blood hemostasis in 800 healthy young females and males, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3905589/ - The Etiology and Management of Leukopenia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2154209/ - Low white blood cell count, National Health Service.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/low-white-blood-cell-count/ - Immunological and Psychological Benefits of Aromatherapy Massage, Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1142199/ - Immunomodulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Garlic Compounds, Journal of Immunology Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4417560/ - Functional properties of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) phytochemicals and bioactives, Food & Function, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27353735/ - Folate, National Institutes of Health.
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/ - Bone Marrow, Blood Cells, and the Lymphoid/Lymphatic System, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7158316/ - Carica papaya L. Leaves: Deciphering Its Antioxidant Bioactives, Biological Activities, Innovative Products, and Safety Aspects, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9203216/ - Retinol (vitamin A) is a cofactor in CD3-induced human T-lymphocyte activation, Immunology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/9155646/ - Vitamin C and Immune Function, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29099763/ - In vitro immune response of human peripheral blood cells to vitamins C and E, Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/14711460/ - The effects of vitamin E on NK cell activity and lymphocyte proliferation in treated mice by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/19259883/ - Consumption of Dairy Yogurt Containing Lactobacillus paracaseissp. Paracasei, Bifidobacterium animalisssp.lactis and Heat-Treated Lactobacillus plantarum Improves Immune Function Including Natural Killer Cell Activity, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5490537/ - Daily intake of probiotic as well as conventional yogurt has a stimulating effect on cellular immunity in young healthy women, Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/16508257/ - Long chain omega-3 fatty acid immunomodulation and the potential for adverse health outcomes, Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3912985/ - Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6834330/ - Zinc in Human Health: Effect of Zinc on Immune Cells, Molecular Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2277319/ - Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9701160/ - Nrf2 activation by sulforaphane restores the age-related decline of Th1 immunity: Role of dendritic cells, The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3897785/ - Effect of Oral Supplementation of Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles on White Blood Cell Profile of BALB/c Mice and Mice Exposed to X-ray Radiation, Avicenna Journal of Medical Biotechnology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3732865/ - Microquantity for macroquality: case study on the effect of selenium on chronic neutropenia, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22042286/ - Effects of kiwifruit on innate and adaptive immunity and symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections, Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/23394995/ - Citrus fruits as a treasure trove of active natural metabolites that potentially provide benefits for human health, Chemistry Central Journal, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4690266/ - Effects of Citrus Fruit Juices and Their Bioactive Components on Inflammation and Immunity: A Narrative Review, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8264544/ - Immunostimulant activity of noni (Morinda citrifolia) on T and B lymphocytes, Pharmaceutical Biology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/20645768/ - Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Different Grafted Varieties of Bell Pepper, Antioxidants, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://dpi.wi.gov/sites/default/files/imce/school-nutrition/pdf/fact-sheet-bell-pepper.pdf - Influence of Vitamin C on Lymphocytes: An Overview, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29534432/ - Therapeutic Potential Of Sunflower Seeds: An Overview, International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences, ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275653985_THERAPEUTIC_POTENTIAL_OF_SUNFLOWER_SEEDS_AN_OVERVIEW - Leukopenia is Associated with Worse but not Prohibitive Outcomes Following Emergent Abdominal Surgery, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4805422/ - Sleep and immune function, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3256323/ - Effect of Cigarette Smoking on Haematological Parameters in Healthy Population, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5511531/ - Association of alcohol consumption with white blood cell count: a study of Japanese male office workers, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12603505/ - Leukocytosis, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560882/ - The influence of vitamin B12 supplementation on the level of white blood cells and lymphocytes phenotype in rats fed a low-protein diet
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4439950/ - Circulating Vitamin D levels status and clinical prognostic indices in COVID-19 Patients
https://respiratory-research.biomedcentral.com/counter/pdf/10.1186/s12931-021-01666-3.pdf
Read full bio of Reda Elmardi
Read full bio of Shaheen Naser
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Dipti Sharma



























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.