5 Amazing Benefits Of Lucuma Fruit, Nutrition Facts, & Risks
Keep your blood sugar levels in check with this vibrant and nutritious fruit.
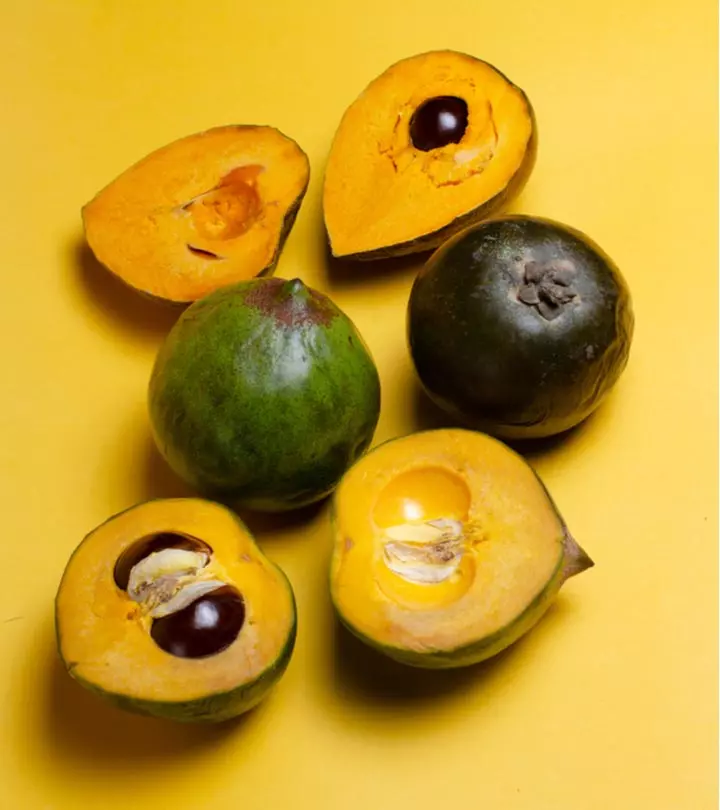

Image: Shutterstock
Lucuma is a delicious fruit loaded with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It is native to the highlands of Peru, Ecuador, and Chile and is used in various traditional recipes, such as Chilean Lucuma Dessert, for its distinct flavor and health benefits. The benefits of Lucuma fruit are many. It may reduce the risk of several diseases. It is also valued as a fertility fruit for the Incas. It is a staple in many parts of South America. This fruit can be consumed fresh or dried, and its powdered form can substitute table sugar.

 Know Your Ingredient: Lucuma fruit
Know Your Ingredient: Lucuma fruitWhat Is It?
A delicious, sweet fruit derived from the Pouteria lucuma tree.
What Are Its Benefits?
Boosts heart health, helps manage constipation, and may reduce the risk of cancer.
Who Can Use It?
All except those who are allergic to it.
How Often?
Typically around 1–2 tablespoons per day.
Caution
If consumed in excess quantities, it may spike blood sugar levels because it contains high sugar values. Hence, people with diabetes should be cautious about their intake of this fruit.
Here, we explore the health benefits of lucuma fruit, its nutritional profile, and how you can add it to your diet. We will also look at its potential side effects, if any. Keep reading.
In This Article
What Is Lucuma Fruit?
Lucuma fruit belongs to the Sapotaceae family that has a high nutrition content. The plant originates from the Andean valleys of Bolivia and Peru in South America, and is mostly cultivated during the summer. The fruits are small to medium and are oval-shaped. Their peel is very smooth and thin, and their color varies from dark to light green. Lucuma’s flavor is unique and sweet, and is best eaten fresh.
 Trivia
TriviaLet us look at the nutritional profile of lucuma in the following section. Keep reading!
Key Takeaways
- Lucuma is an exotic fruit with a unique sweet taste and numerous essential nutrients.
- It may help lower blood sugar levels, boost heart health, and protect against cancer.
- You can use lucuma as a flavoring agent or use it as a substitute for sugar.
Nutritional Profile Of Lucuma Fruit
100g of lucuma contain (1):
| Calories | 143.8 |
| Carbohydrate | 33.2g |
| Protein | 2.3g |
| Iron | 0.4 mg |
| Fat | 0.2g |
| Calcium | 16 mg |
| Fiber | 1.1g |
| Phosphorus | 26 mg |
Lucuma fruit offers an array of health benefits. Continue reading to know them.
Health Benefits Of Lucuma Fruit
1. May Help Control Blood Sugar Levels

Lucuma’s low glycemic index (it digests slowly) helps maintain steady blood sugar levels. The fruit contains soluble fiber that keeps blood sugar from rising. The fiber in the fruit may also improve insulin sensitivity (2). It inhibits enzymes like alpha-amylase, alpha-glucosidase, and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE). These enzymes break up carbohydrates and can significantly raise post-prandial (post-meal) blood glucose levels. Hence, inhibiting them helps manage hyperglycemia and hypertension linked to type 2 diabetes (3).
2. May Boost Heart Health

Lucuma is rich in antioxidants like polyphenols and carotenoids that may help improve heart health (4),(5). However, more research is warranted to understand the benefit of carotenoids. As stated, lucuma may significantly inhibit the production of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE). This enzyme may increase blood pressure by constricting blood vessels. It may also increase thirst and the desire for salt, which may significantly elevate blood pressure (3). Inhibiting this action of ACE may help manage blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
People with hypertension have a greater risk of developing heart disease. The phenolic compounds and potassium present in the fruit have properties that reduce hypertension and prevent heart disease (3), (6). This health condition may be managed to some extent by consuming juices or smoothies mixed with lucuma.
3. May Reduce Constipation

Lucuma contains significant levels of insoluble dietary fiber (that does not dissolve in water). This helps food move through your digestive system and prevents constipation (7). Intake of dietary fiber was also shown to increase stool frequency in patients with constipation. Besides, healthy-eating behaviors and timely intake of recommended levels of dietary fiber may help manage constipation among adults (8). However, dietary fiber may not improve stool consistency and painful defecation.
4. May Reduce The Risk Of Cancer
A variety of antioxidants in lucuma may contribute to its ability to fight certain cancers. β-sitosterol, a component found in lucuma, is an anticancer nutraceutical. Unlike chemotherapy, it turns out to be non-toxic (though it is less powerful too). Besides, β-sitosterol was proven to show anticancer activity in animals (9). The gallic acid in lucuma also acts as an antioxidant and may protect against cancer. The fruit also contains pectin and tannins. Pectin has anti-tumor activity while tannins may significantly combat the formation and development of tumor cells (10).
5. May Promote Skin Health
Lucuma contains vitamin C and beta-carotene (a vitamin A derivative), which contribute to skin health. Vitamin C improves collagen production and protects the skin from UVB rays. Beta-carotene is a highly effective antioxidant and has photo-protective properties (11).
 Trivia
TriviaYou can reap all these benefits by including lucuma in your diet. Here are a few ways to do it.
How To Add Lucuma To Your Diet?

- Substitute For Sugar: Lucuma has a sweet taste and is often used as a substitute for table sugar in various delicacies.
- Lucuma Ice Cream: Adding 1/4 cup of lucuma powder (as needed) to ice cream or any dessert enhances its flavor.
- Baked Foods: Substitute table sugar with lucuma powder in baking. It enhances the flavor of cakes, cookies, and pastries.
- Beverages: Mix lucuma powder with tea or coffee. Use 2 tablespoons of lucuma powder instead of regular sugar to make smoothies.
- Flavoring Agent: Lucuma powder can act as a sweet flavoring agent for yogurt and oatmeal. Add it to your favorite meals and enjoy the treat.
Since lucuma has a creamy texture and a thick consistency, it is one of the best options for preparing mousse. You may start with 1 tablespoon of lucuma powder and add more based on your taste preference. The powder gives the mousse a delightful caramel-like flavor, creating a unique and delicious treat. Check out the next section for a quick lucuma mousse recipe.
Lucuma Mousse Recipe
Ingredients
- 1-2 tablespoons of lucuma powder
- 1 can of condensed milk
- 1 cup of heavy cream
- 1 teaspoon of vanilla
- Pinch of salt
How To Prepare
- Mix the lucuma powder and condensed milk.
- Whip the cream until it is stiff and forms a peak.
- Fold in the lucuma mix.
- Add in the vanilla and salt.
- Chill the dish for 2-3 hours, then enjoy your lucuma mousse!
Lucuma may also exert a few undesirable side effects in a few people. Continue reading to know them.
Potential Side Effects And Allergies Of Lucuma Fruit
- Mild Hypoglycemia
Anecdotal evidence indicates that lucuma may cause hypoglycemia (blood sugar levels lower than normal) in some individuals. Consult a doctor if you have hypoglycemia and want to add lucuma to your diet. - Allergy

An itchy tongue, rashes, and headache were observed in a few people immediately after consuming lucuma. However, the medical literature has not shown any evidence for this. To be on the safe side, stop eating this fruit and consult your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Infographic: 5 Reasons To Add Lucuma To Your Diet
The lucuma fruit is used in various Peruvian and Bolivian dishes for its citrusy and caramel-like flavor. It is rich in iron and fiber, which may help boost your overall health and wellness. Check out the infographic below to know why you should add this delicious fruit to your daily diet.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxThe benefits of lucuma fruit are numerous. This fruit has a low glycemic index, and it helps maintain blood sugar levels. The antioxidants in this fruit help promote cardiovascular health. Lucuma reduces constipation, too, as it is rich in insoluble fiber. This fruit reduces cancer risk as well, and its vitamin C and beta carotene help promote skin health. Although the consumption of Lucuma is safe, it may cause mild hypoglycemia and allergies in a few. Hence, caution is advised.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is lucuma a superfood?
Yes, lucuma can be termed a superfood. It is loaded with nutrients like beta carotene, iron, zinc, vitamin B3, calcium, and proteins that can promote overall health if included as a part of the diet.
Does lucuma give you energy?
Yes, lucuma can give an energy boost. Its powder can also be mixed with juices or smoothies for boosting energy levels.
Is lucuma related to avocado?
No, lucuma is not related to avocado. However, it does resemble an avocado.
Is lucuma the same as monk fruit?
No. Monk fruit and lucuma are two different fruits. However, they are similar in taste and are loaded with many beneficial nutrients that promote overall health. Knowing everything about monk fruit and lucuma, including their benefits, nutritional profiles, and side effects, can help you make informed choices about your diet.
Is lucuma related to mango?
No, lucuma is not related to mango. However, its external appearance resembles that of an unripe mango, and its bright golden interiors resemble that of a ripe mango.
Is lucuma safe while breastfeeding?
Yes, lucuma is loaded with many beneficial nutrients and is known to promote lactation. However, it is advised to consult your doctor before consuming any new foods during breastfeeding.
Illustration: Amazing Benefits Of Lucuma Fruit, Nutrition Facts, & Risks
Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Discover the amazing benefits of lucuma fruit, an ancient Incan superfood! Learn how this fertility fruit can improve your health and well-being. Click on this video.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Lucuma (Pouteria lúcuma (Ruiz & Pav.) Kuntze)
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277816644_Lucuma_Pouteria_lucuma_Ruiz_Pav_Kuntze - Total Insoluble and Soluble Dietary Fiber Intake and Insulin Resistance and Blood Pressure in Adolescents
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6586511/ - Evaluation of antihyperglycemic and antihypertension potential of native Peruvian fruits using in vitro models
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19459727/ - The role of polyphenols in modern nutrition
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5601283/ - Carotenoids and cardiovascular health
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16762935/ - Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors 2012 – cardiovascular considerations and trial evaluation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22508699/ - Diets for Constipation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4291444/ - Dietary fibre intakes and reduction in functional constipation rates among Canadian adults: a cost-of-illness analysis
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.3402/fnr.v59.28646 - Anti-tumour effects of beta-sitosterol are mediated by AMPK/PTEN/HSP90 axis in AGS human gastric adenocarcinoma cells and xenograft mouse models
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323842715_Anti-tumour_effects_of_beta-sitosterol_are_mediated_by_AMPKPTENHSP90_axis_in_AGS_human_gastric_adenocarcinoma_cells_and_xenograft_mouse_models - Lucuma ( Pouteria lucuma ): Composition bioactive components antioxidant activity uses and beneficial properties for health
http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?pid=S2077-99172020000100135&script=sci_arttext - Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3583891/
Read full bio of Yvonne O’ Halloran
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi





















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.