Melasma: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Options
Unlock the secrets behind melasma and understand its origin and treatment options
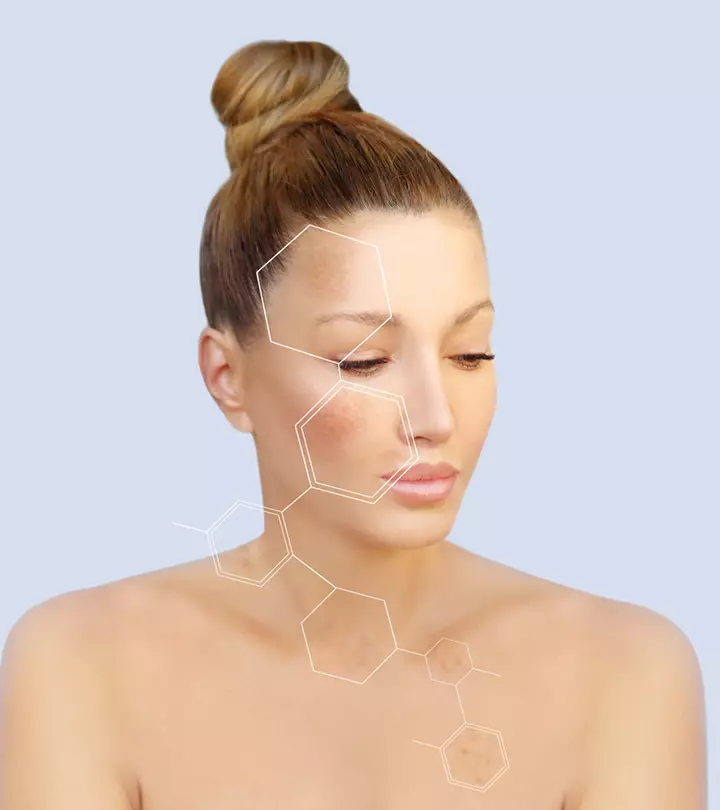
Image: Shutterstock
Melasma is a skin pigmentation disorder. If you have melasma, you may develop gray or brown patches on your skin. Though you can treat the condition, it can affect a person’s emotional well-being.

Melasma is not a permanent condition, and the right treatment and remedies can help minimize it. This article discusses the different causes of melasma, how it can be treated, and the preventive care you need to take. Keep reading to know more.
In This Article
What Is Melasma?
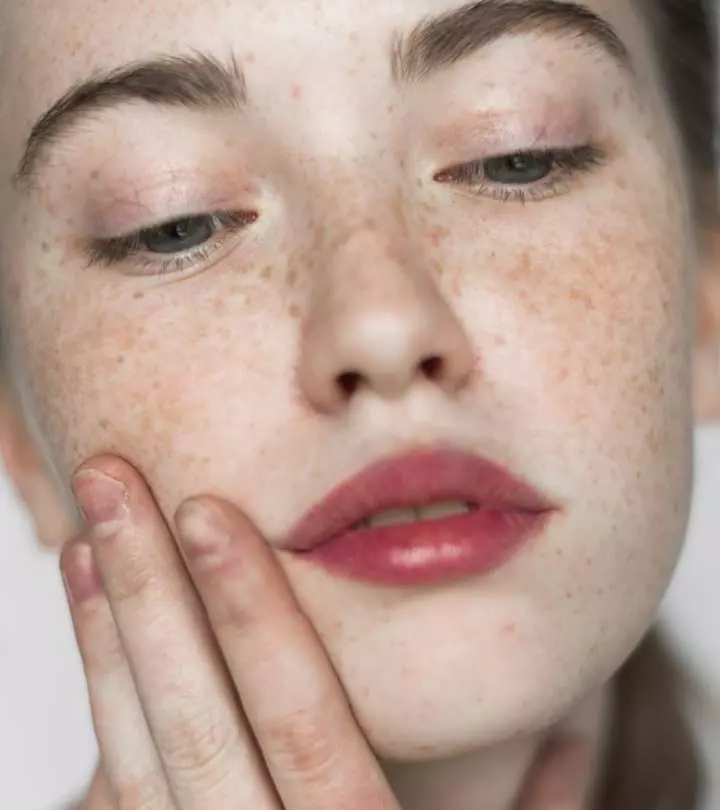
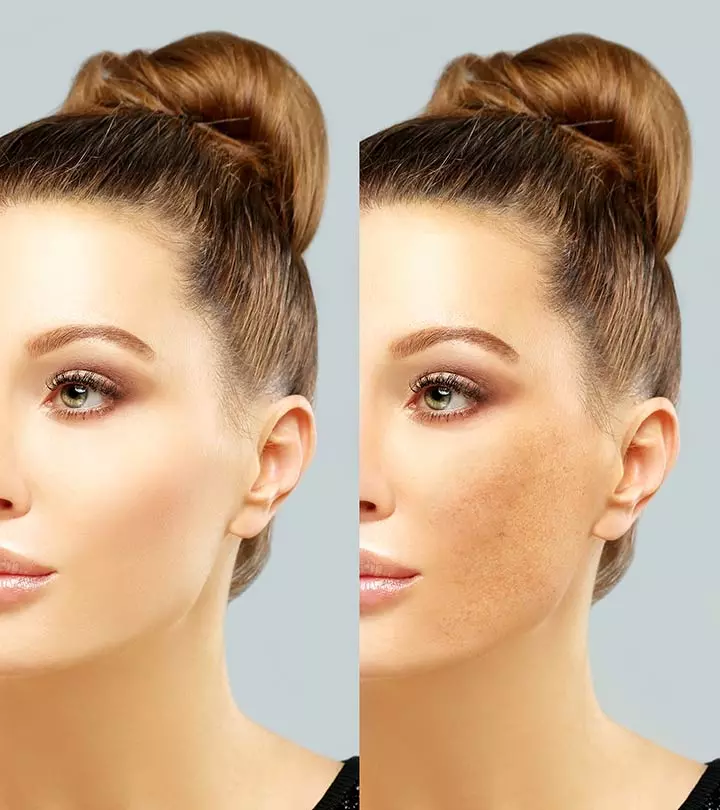
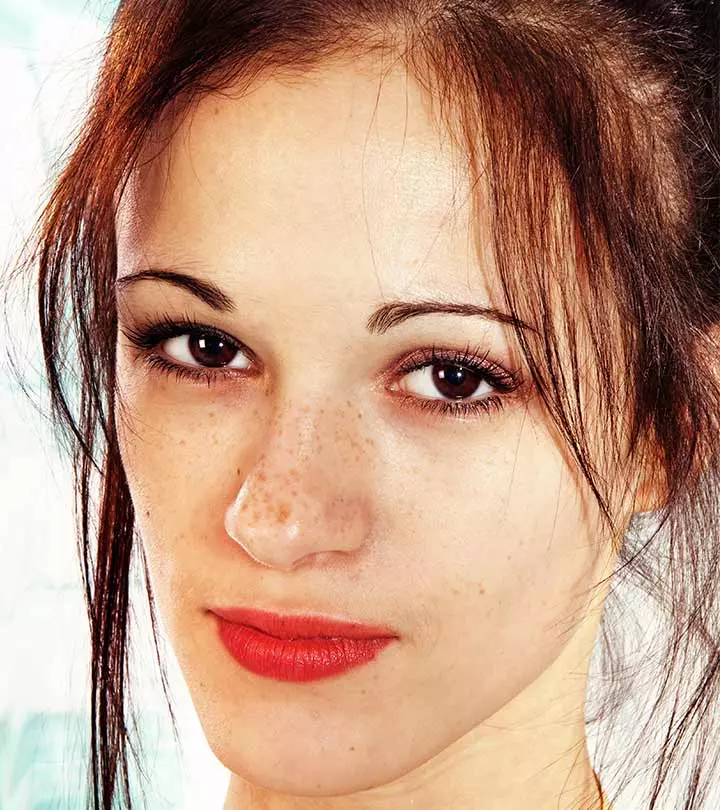
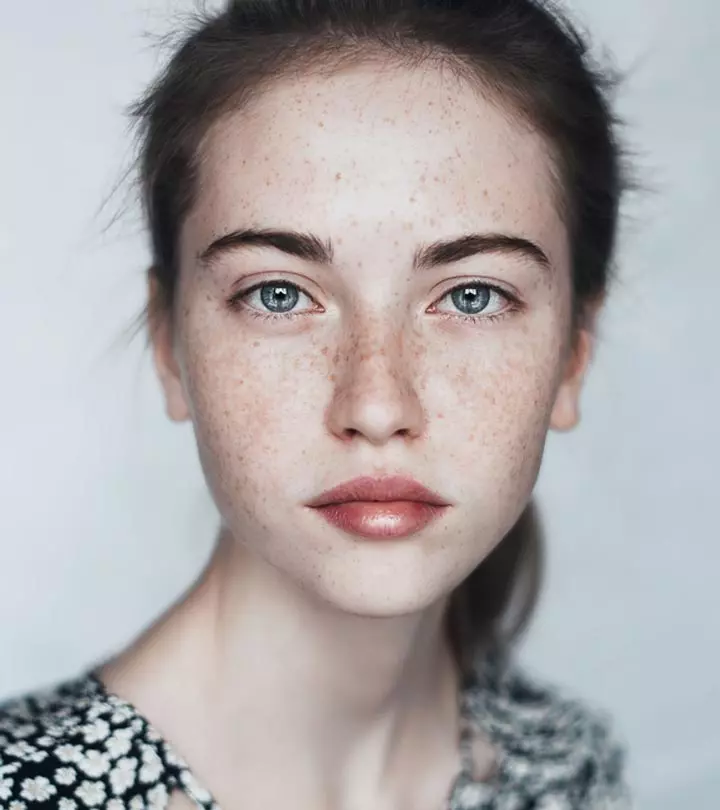
Melasma is a skin disorder that causes hyperpigmentation on the sun-exposed areas of your face and body. It leaves brown or blueish gray patches on your face and body and is especially common among individuals with brown skin living in tropical latitudes. The skin condition also affects mostly women.
Melasma is also called chloasma or mask of pregnancy. As it is, pigmentation during pregnancy is very common. Although it is painless and benign, it can hamper your social life by making you self-conscious.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Only a licensed medical practitioner or a dermatologist can examine your skin and diagnose the skin condition. We will now look at some symptoms of this skin disorder.
Key Takeaways
- Melasma is more common in women, and the pigmentation usually occurs on the nose, cheeks, chin, etc.
- It is classified into different types based on the type of patches, color, and amount of melanin present.
- Besides excess sun exposure and other reasons, a family history of melasma can also cause this condition.
Symptoms Of Melasma
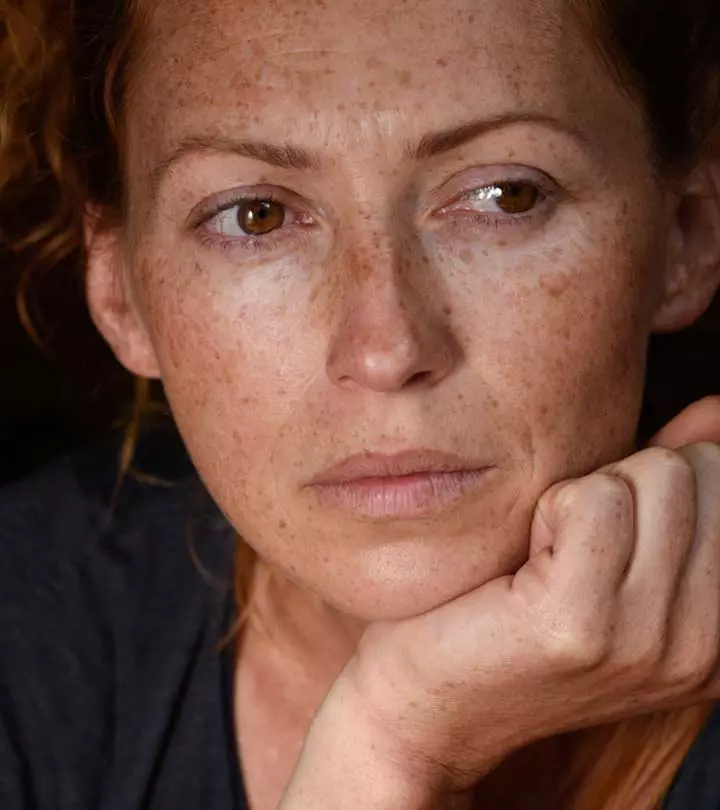
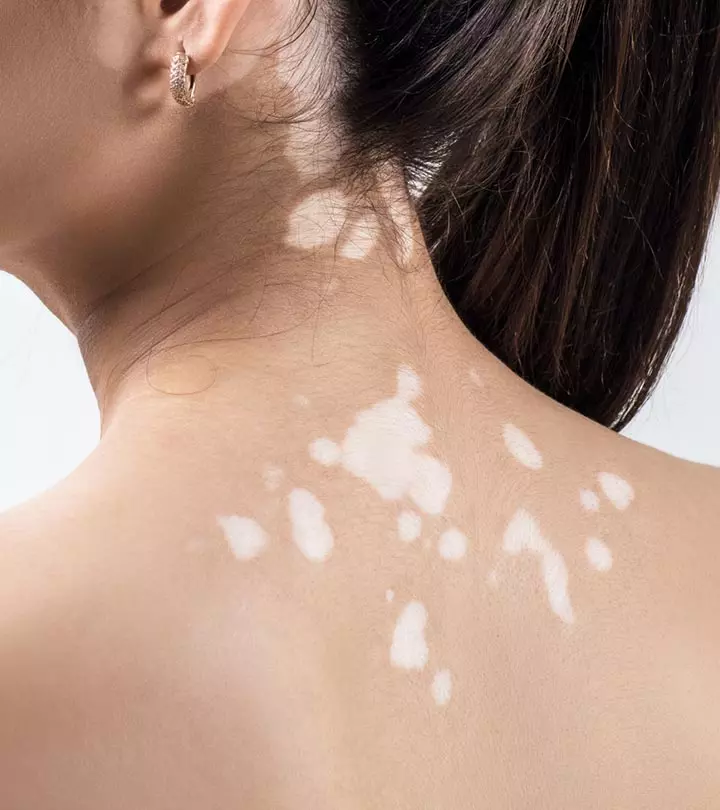
The primary symptom of melasma is the appearance of brown, gray, or discolored patches on your skin. These patches have a different color than your skin tone and usually develop on the following areas:
- Cheeks
- Upper lip
- Forehead
- Chin
- Nose
In some cases, people may also develop discolored patches on their neck, arms, and shoulders. Sometimes the patches can become inflamed and appear red.
Types Of Melasma
Based on the type of patches, amount of melanin, and color, melasma can be classified as any of the following three types:
1. Epidermal Melasma
Epidermal melasma is visible clearly under a wood lamp since the patches have well-defined borders and are in dark brown color. This type shows a good response to treatments.
2. Dermal Melasma
Dermal melasma consists of patches with irregular and poorly defined borders or discoloration. Usually, the patches have a light brown or blue-gray hue and show no noticeable difference under a wood lamp. This type is usually harder to treat.
3. Mixed Melasma
A mixed type of melasma is a combination of the other two types. It is seen more commonly and has a mix of dark brown, light brown, and blueish gray patches. This type of melasma could respond to treatment relatively slowly.
The exact causes of melasma could differ from person to person. In the following section, we have listed the major reasons.
Causes Of Melasma
Melasma on the face is largely attributed to sun damage or pregnancy. However, various other factors can cause brown patches on the face and body.
1. Genetic Predisposition
Some people are more likely to have melasma than others due to a genetic predisposition (2). This holds true for individuals with brown skin who live in the tropics and experience more sun exposure. About half of the people diagnosed with melasma reported a family history of the skin condition (3).
2. Pregnancy
Pregnancy melasma is very common in females. This could be attributed to hormonal changes. It is often called chloasma or the mask of pregnancy (4).
3. Hormonal Issues
Other hormonal issues or imbalances may also lead to melasma. Progesterone plays a primary role in the development of this skin condition (3). Birth control pills or hormone replacement medicines may increase the levels of progesterone in your body.
4. Certain Medications Or Scented Products
Consuming certain anti-seizure medications, oral contraceptives, certain steroids, photosensitizing drugs, and phototoxic drugs can also trigger melasma (3). Skincare products that irritate your skin may worsen the dark patches on the face.
5. Sun Exposure
Sun exposure can lead to melasma on the arms, neck, and face. The UV rays from the sun can stimulate melanocytes and also cause faded melasma to return (3). Even sunscreens can fail to block longer wavelengths of UV-A radiation that causes excessive production of melanin (3).
 Quick Tip
Quick TipWe now understand how melasma is diagnosed by medical professionals.
How Is Melasma Diagnosed?
Since melasma causes visible patches on the face and other parts of the body, it is fairly easy to diagnose. However, a dermatologist may carry out a few tests to rule out any other skin conditions and definitively determine the extent of pigmentation due to melasma.
A wood lamp is held over your patches to determine any other fungal or bacterial infection on the patches and to understand the extent of melasma. In some cases, a skin biopsy may also be carried out to differentiate melasma from other skin infections.
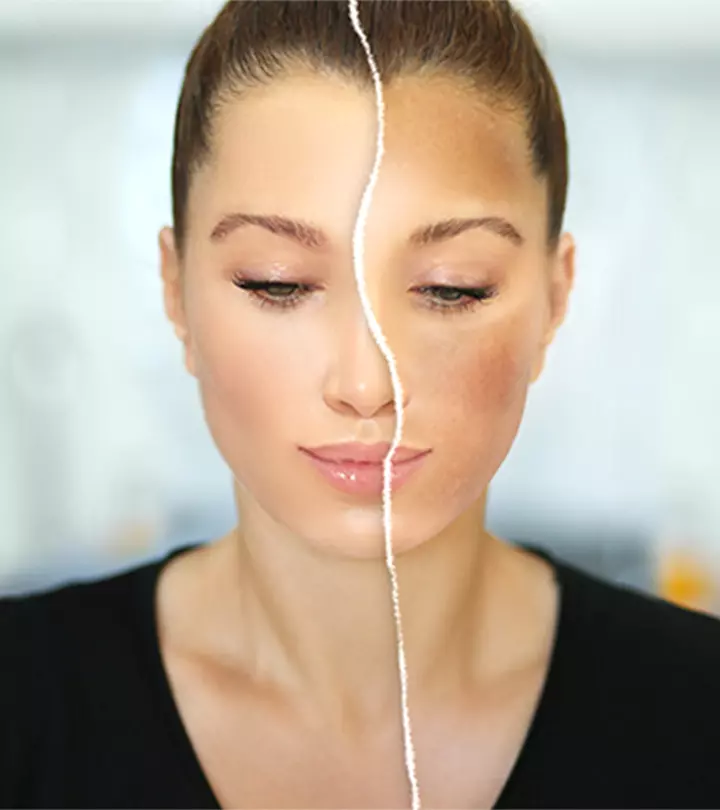
Melasma treatment involves the use of topical creams or oral pills that lighten the brown patches. Know more about these treatment options in the next section.
What Are The Best Treatment Options For Melasma?
Although there is no definitive cure, your doctor can prescribe you one of the many treatments used to combat melasma on your forehead, face, neck, and body.
Hydroquinone
Your dermatologist may prescribe a topical hydroquinone cream as the first line of treatment for melasma. This cream can lighten the brownish patches on your skin. It may be used in the form of a cream, gel, or lotion and is mostly safe for topical application (4).
Methimazole
For hydroquinone-resistant melasma, a treatment with methimazole is prescribed. It can be used as a topical anti-thyroid cream (5).
Hydroquinone, Tretinoin, And Fluocinolone Acetonide
A triple combination cream containing (hydroquinone 4%, tretinoin 0.05%, and fluocinolone acetonide 0.01%) is also used to treat melasma. The combination works to lighten the patches and get a more even skin tone (3).
Chemical Skin Peels
Skin peels using glycolic- or salicylic acid-based creams can help treat melasma to some extent. These peels will remove the top layer of the skin and reduce the dark hue of the patches (3).
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone, mometasone furoate, fluocinolone acetonide, and dexamethasone can help reduce pigmentation by decreasing the cell turnover, melanins synthesis, and the inflammation associated with melasma (4), (5). Your doctor may combine a mild topical corticosteroid with tretinoin to prevent the burning, itching, and irritation that might occur as a side effect of using medications or other topical treatments. Both medications are available in the form of gels, lotions, or creams. Consult your dermatologist to understand the benefits and risks of both treatments as well as which form is suitable for you before including them in your skincare routine.
Other Procedures
For more stubborn patches, other procedures like dermabrasion, microdermabrasion, and laser treatment could be suggested. These procedures have varied results for different people and must be performed only by a dermatologist (6). Advanced treatments by experienced dermatologists also give very good results such as ablative laser treatments or platelet rich plasma (vampire facelift).
Note that melasma is stubborn and requires proper care after treatment. The following natural methods could help reduce the risk of melasma.
How To Treat Melasma Naturally
Melasma treatments
are usually long and take time to completely heal your skin. While chloasma may disappear after a few months post-pregnancy, melasma caused due to other factors may need extended treatment.
Here are some natural remedies for melasma you can try today. However, these are not a replacement for medical treatments and must only be followed with normal dermatological treatments.
1. Use Natural Antioxidants
Vitamins C
and E are known to help in the treatment of chloasma (7).
You can either use a serum containing these vitamins or a homemade lemon juice, vitamin E (in a capsule form), and water mix to soothe the skin damage. The vitamin C in lemon juice can inhibit the tyrosinase enzyme and control melanin production (8).
2. Keep Your Skin Moisturized
Skin contains a natural fat barrier that protects it from the harsh sun. To keep the barrier healthy, you should moisturize your skin daily. Follow a regular cleansing and moisturizing routine to retain your skin’s natural moisture.
3. Utilize Alpha-Hydroxy Acids
Apply alpha-hydroxy acids such as lactic, malic, and glycolic acids to your skin. These acids can improve skin glow by reducing tyrosinase activity and may provide a natural relief from melasma (9).
Mix natural sources of alpha-hydroxy acids like milk, yogurt, cream, or Indian gooseberry with equal amounts of rosewater and lemon juice. Apply the mixture to your skin and rinse after 15 to 20 minutes.
Can Melasma Be Prevented?
Unfortunately, melasma cannot be prevented. Melasma due to genetics cannot be altered or changed. Chloasma cannot be prevented since pregnancy tends to create a natural influx of hormones.
Nevertheless, keeping your skin well protected will reduce your chances of developing melasma, more so if you have a family history of the disorder. As for chloasma, it may fade away on its own in a few months. Hence, it is not a very critical condition to worry about.
Here are certain ways to mitigate the effects of melasma on your face:
- A good diet rich in greens and micronutrients will improve your skin health and make it more resistant to sun damage.
- Consume a good amount of vitamin D to help fight sun damage.
- Use skin care products that do not irritate your skin.
- Use sunscreen daily. It is recommended to choose a cream with SPF between 30 to 50. Reapply it every 2 hours if you stay out in the sun for longer durations.
- Use makeup to cover dark spots or melasma. Choose a high coverage foundation or concealer to hide the melasma patches on your face and body.
- Commit to a skincare regimen to maintain an even skin tone. If you are not diligent in protecting your skin from the sun, the patches may return post-treatment.
Melasma is a pigmentation issue, and can irritate the affected individual and make them self-conscious. The good news is that you may lighten the patches with appropriate treatment and care. However, melasma usually takes a few months to clear out, so it is important to stick to the treatment plan and be patient with the outcomes.
Consult your healthcare practitioner about supportive services or therapists if you are self-conscious about your melasma. In addition, meeting other people who have the same illness or talking to someone about it can help you feel better. Melasma is very notorious to treat & outcomes may differ from person to person.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is aloe vera good for melasma?
Yes. A study conducted on pregnant women found that aloe vera gel extract helps reduce the severity of melasma (10). However, more studies are warranted to understand the benefit of aloe vera on melasma.
Is potato good for melasma?
Anecdotal evidence suggests that potatoes help improve melasma and also lighten dark spots. However, limited studies are available in this regard.
Watch this video to understand what melasma is, and explore some of the causes behind this common skin phenomenon. Also learn prevention tips and strategies for managing this condition with the help of this illustrative video.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- The history of melasma: Its roots and evolution,
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/der2.134 - Melasma: a clinical and epidemiological review,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4155956/ - Melasma,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459271/ - Medical therapies for melasma
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jocd.15242#:~:text=Corticosteroids%20such%20as%20hydrocortisone%2C%20dexamethasone,triple)%20combination%20therapy%20of%20melasma. - TOPICAL TREATMENT OF MELASMA
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2807702/ - MELASMA: WHO GETS AND CAUSES,
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/melasma-causes - Successful treatment of hydroquinone-resistant melasma using topical methimazole,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23384022/ - Effects of combination treatment with vitamins E and C on chloasma and pigmented contact dermatitis. A double blind controlled clinical trial,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7027767/ - Vitamin C Prevents Ultraviolet-induced Pigmentation in Healthy Volunteers: Bayesian Meta-analysis Results from 31 Randomized Controlled versus Vehicle Clinical Studies,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6415704/ - The inhibitory effect of glycolic acid and lactic acid on melanin synthesis in melanoma cells,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14756523/ - Clinical efficacy of liposome-encapsulated Aloe vera on melasma treatment during pregnancy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28139161/
Read full bio of Dr Ashok Gund
Read full bio of Annie Jangam
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Swathi E
























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.