Neosporin For Acne: How Effective Is It?
To use or not to use? Learn how this medicated powder may help solve acne issues.

Image: ShutterStock
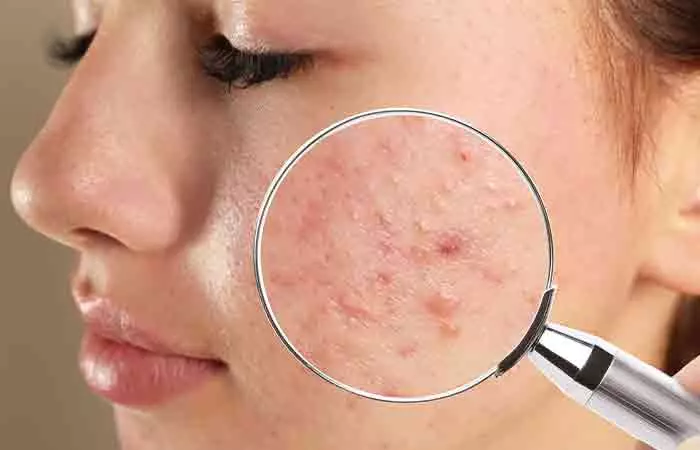
Acne can be painful, annoying, and affect your emotional well-being. Some of the home remedies available to treat acne can be useful, while some can worsen the condition. Using Neosporin for acne is one of the proven methods to subside the condition.
Around 9.4% of the world population is affected by acne at some time or the other, and globally, it is considered the eighth-most prevalent disease (1).
So, how does Neosporin help treat acne? Is it worth the hype? How it benefits your skin? This article will help you find answers to all your queries. Keep reading to know the science behind the effects of Neosporin on your skin.
In This Article
What Is Neosporin?
Neosporin is an ointment typically used for treating skin injuries or bacterial eye infections.
It is a combination of three antibiotics that keeps the wounds from getting infected. It is also known as a triple antibiotic ointment (or TAO).
The three antibiotics in Neosporin are as follows (2):
- Neomycin
Neomycin is an antibiotic that can fight gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli as well (3).
- PolymyxinB
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that can fight gram-negative bacterial infections. It can break down the cell membrane of the bacteria and kill them (4).
- Bacitracin
Bacitracin is an antibiotic that can work on gram-positive bacteria by breaking down their cell walls and interfering with their synthesis.
It stops bacterial proliferation (5).
Since Neosporin is a combination of these three antibiotics, it can fight both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Neosporin also contains cocoa butter, petroleum jelly, olive oil, and cottonseed oil (2).
While the ingredients in Neosporin sound promising, you should also understand the reason behind acne breakouts. Read on to learn more about the causes of acne.
What Causes Acne?
Acne occurs when the sebaceous glands become overly sensitive to normal hormone levels, only to be worsened by bacteria and inflammation. The development of acne usually occurs because of (6):
- Excess oil production in the skin pores
- Buildup of dead skin cells in the skin pores
- Growth of bacteria in the skin pores
Other factors that may increase the risk of or aggravate acne include (7):
- Certain medications
- Sun exposure
- Tight clothing
- Oil-based cosmetics
- Hormonal imbalances like polycystic ovarian syndrome
- Genetic factors
- Mechanical skin trauma
- Psychological stress
- Insulin resistance
- Unhealthy diet
Understanding the causes of acne is very important to determine its treatment. Now, let us find out how effective neosporin is in treating acne.
Neosporin For Acne Is It Effective?

Neosporin is not very effective for acne. In fact, anecdotal evidence suggests it may also cause adverse effects in some. It could be rather surprising that a medication designed to kill bacteria may not help treat a condition caused by bacteria.
However, it is important to note that while Neosporin may kill a wide range of bacteria, it does not work against others. A strain of bacteria called Propionibacterium acnes is responsible for acne in the vast majority of cases (8). While Neosporin works against Escherichia coli, and Neisseria species of bacteria, it may not be effective against P.acnes (3), (5).
Ellie, a blogger, shared that she had used Neosporin to treat acne scabs and it worked. She writes, “Truth is, I simply used Neosporin.” She also added that patience is key, stating, “I know you want it to go away overnight, but the truth is, that it simply won’t go that fast. Give it time, accept it. It’s okay (i).”
While acne may also be caused by other minor strains of bacteria that Neosporin can work against, the chances are thin. Hence, we recommend against using Neosporin for treating your acne. Consulting your doctor to understand the specific bacteria that has caused your condition is ideal.
Also, note that using Neosporin for treating the most common forms of acne can cause adverse effects. We have covered the same in the next section.
Side Effects Of Using Neosporin For Acne
- Increases The Antibiotic Resistance In Bacteria
Using the wrong medication for too long can cause the bacteria to build resistance against the antibiotics
(9). The medication then would stop working even against those strains of bacteria it was previously effective against.
Even if it has no impact on your acne, excessive use of Neosporin where it is not needed can decrease its chances of being effective when you apply it to another wound or an injury.
- May Damage Your Skin

Prolonged use of Neosporin for acne can have an adverse impact on your skin. Antibiotics, such as those present in Neosporin, alter the skin microbiome (10). They damage the upper layer of the skin and may leave it susceptible to acne and other infections.
Another component of Neosporin, called Neomycin, may cause allergic contact dermatitis (11).
- May Aggravate Your Acne

Neosporin contains comedogenic components (that can clog your pores). Clogged pores also may cause acne and trigger folliculitis (12), (13).
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Do these side effects mean you should never use Neosporin for treating acne? Not really. Certain situations warrant the use of Neosporin for acne treatment.
When To Use Neosporin For Acne?
Using Neosporin could be ideal only when your acne gets infected. It could be an excellent ointment for treating infected acne (14). The petroleum jelly in Neosporin is an emollient and may moisturize the skin surrounding the acne. However, information in this regard is limited. Consult your doctor for more information.
When To See A Doctor?

If your acne is getting too severe or painful, or the treatments are not delivering the right results, you must visit a dermatologist. You should also see a doctor if your acne appeared after taking any specific medication.
Visiting a doctor on time can arm you with the right information that can help resolve your issue faster.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipNeosporin is a combination of three antibiotics that help treat skin injuries and eye infections. Though many use Neosporin for acne management, it is not very effective. It may kill a wide range of bacteria, but it does not fight against acne-causing bacteria. Therefore, it is not recommended to use Neosporin for your acne issues. Moreover, it may cause serious side effects, including damaging your skin and aggravating your acne. You may use Neosporin to soothe the skin infection, but it is always best to consult your doctor before applying it. Also, in addition to using Neosporin, it’s important to follow a proper skincare routine and adopt healthy habits like eating a balanced diet and staying hydrated.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Neosporin help pimple scabs?
Neosporin may help accelerate the healing process when applied to pimple scabs.
Can you put Neosporin on a blind pimple?
Yes, you can. While it may not fight the bacteria causing the acne, Neosporin can reduce the inflammation around the blind pimple.
Is Neosporin good for scars?
Neosporin may speed up the wound healing process when applied to scabs. Thus, it might help reduce scarring. However, it cannot fade existing scars.
Does Neosporin help skin infections?
It depends on the bacteria causing the infection. Neosporin may be able to treat issues caused by some gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria like Escherichia coli and Neisseria.
Should I keep applying Neosporin?
Use Neosporin as instructed by the product label or as recommended by a dermatologist.
Does Neosporin help dry skin on the face?
There is a lack of evidence suggesting that Neosporin may benefit those with dry skin. Individuals with dry skin should opt for creams specifically formulated for that skin type.
Key Takeaways
- Neosporin is a topical ointment made of three antibiotics used to treat skin injuries and bacterial eye infections.
- Neosporin is not intended to treat acne and may even worsen it.
- Consult a dermatologist to discover the cause of your acne and the right treatment for it.
Illustration: Neosporin For Acne: How Effective Is It?

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Curious if Neosporin can zap away acne overnight? Tune in to this video to uncover the truth behind using Neosporin for acne and find out if it’s really a game-changer or just a myth.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How to heal ACNE SCABShttps://freshlysensual.wordpress.com/2013/05/27/how-to-heal-acne-scabs/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- A global perspective on the epidemiology of acne
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271021719_A_global_perspective_on_the_epidemiology_of_acne#:~:text=Acne%20is%20estimated%20to%20affect,severe%20forms%20of%20the%20disease. - NEOSPORIN ORIGINAL- bacitracin zinc, neomycin sulfate, and polymyxin b sulfate ointment Johnson & Johnson Consumer Inc
https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=b6697cce-f370-4f7b-8390-9223a811a005&type=display - Chapter 20 Anaerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8438/ - Polymyxin B Identified as an Inhibitor of Alternative NADH Dehydrogenase and Malate: Quinone Oxidoreductase from the Gram-positive Bacterium Mycobacterium smegmatis
https://academic.oup.com/jb/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/jb/mvp096 - Bacitracin Topical
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536993/ - What Is Acne
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/acne - Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173/ - PROPIONIBACTERIUM ACNES AND CHRONIC DISEASES
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83685/ - Systematic review of antibiotic resistance in acne: an increasing topical and oral threat
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26852728/ - Topical Antimicrobial Treatments Can Elicit Shifts to Resident Skin Bacterial Communities and Reduce Colonization by Staphylococcus aureus Competitors
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/aac.00774-17 - Topical antibiotics in dermatology: An update
http://www.gulfdermajournal.net/pdf/2010-04/1.pdf - Acne
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1271924/#:~:text=The%20cause%20of%20acne%20is,canals%20and%20large%20sebaceous%20glands. - Moisturizers: The Slippery Road
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4885180/ - Topical Treatment of Various Skin Infections with an Antibiotic Polymyxin B-Bacitracin-Neomycin Ointment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1824665/?page=1
Read full bio of Dr. John Paul Tutela
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty






















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.