Nodular Acne: Causes, Treatment Options, & Home Remedies
All about one of the most stubborn and painful forms of acne, including how to get rid of it.

Image: ShutterStock
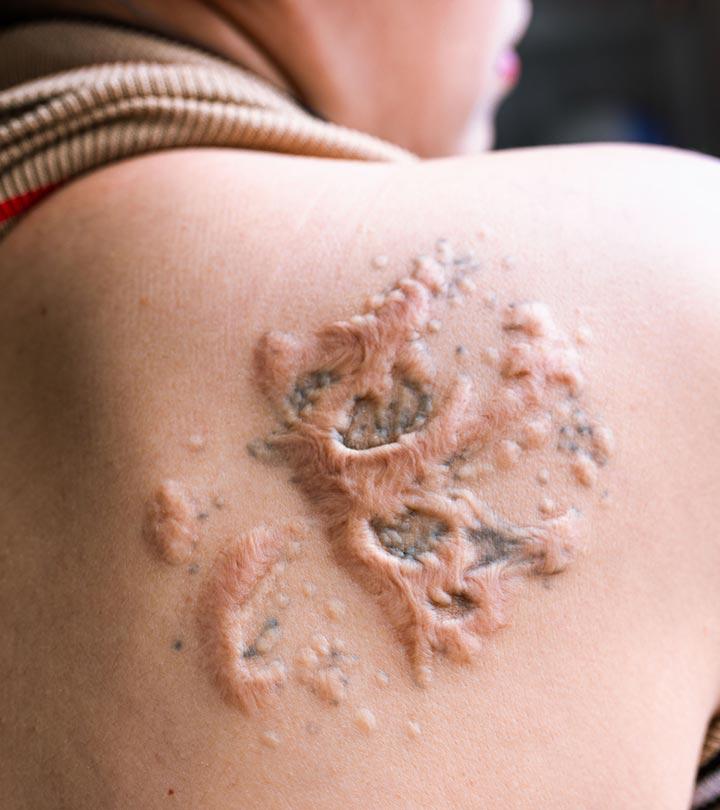
Nodular acne is a serious form of acne vulgaris and can become chronic. Unlike other forms of acne, the lesions are painful and affect the deeper skin layers. Therefore, nodular acne requires aggressive acne treatment and (1). It can be persistent and take months to heal. However, this skin condition has a chance of recurrence, and that is why you must have patience and stick to the treatment. This article delves deep into the causes of nodular acne and details the remedies, prevention, and risk factors related to this condition. Keep reading.
In This Article
What Is Nodular Acne And What Are The Causes?
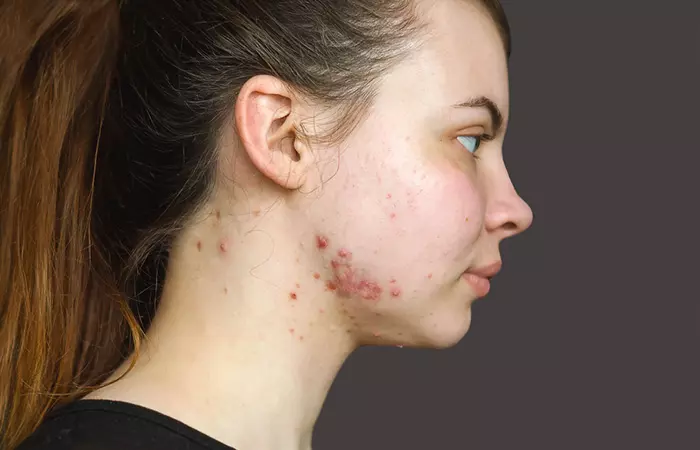
Nodular acne or nodulocystic acne looks like red bumps deep below the skin layers. Initially, it appears like raised, skin-colored bumps. However, infection and inflammation may make the bumps red and painful/tender.
Nodular acne is a severe form of acne and needs aggressive treatment. Oral and topical acne medications may not help in such cases. If you have nodular acne, consult a dermatologist immediately, who might recommend the below options.
- Genetic Factors: Clinical studies have found that acne runs in families (3).
- Hormonal Factors: Androgenic hormone stimulation in women can lead to excessive sebum production, along with P. acnes colonization, which can cause acne. Factors like menstruation, pregnancy, and thyroid issues may also cause hormonal imbalance, triggering acne (4).
- Stress: If you have acne-prone skin, emotional stress can increase the severity of the condition (5).
- Smoking: The chemicals in tobacco can contribute to acne prevalence and increase its severity (6).
- Other Factors: Using medications like corticosteroidsi A group of fast-acting drugs (steroids) that help suppress immune reactions and reduce inflammation. , oral contraceptives, bromides, lithium, iodides, and chemicals like dioxine can cause acne. Endocrine disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome and Cushing’s syndromei A condition in which excessive use of steroid drugs can lead to a rounded face, stretch marks on the skin, or high blood pressure. may also induce acne.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Nodular acne is often confused with cystic acne, which also forms deep within the skin layers. However, both are different.
How Is It Different From Cystic Acne?
| Difference Between Nodular And Cystic Acne | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nodular Acne | Cystic Acne | |
| Develops deep within the skin layers. | Develops underneath the skin layers. | |
| Appear like large skin-colored or red bumps. | Appear like raised bumps, similar to boils. | |
| Firm to touch and feels like a hard knot under the skin. | Pus-filled and are softer to touch. | |
| Does not have an opening and cannot be popped. | May burst open, spilling the pus. | |
| OTC treatment may not be enough. It needs oral prescription drugs. | OTC treatments may help reduce the size to some extent. | |
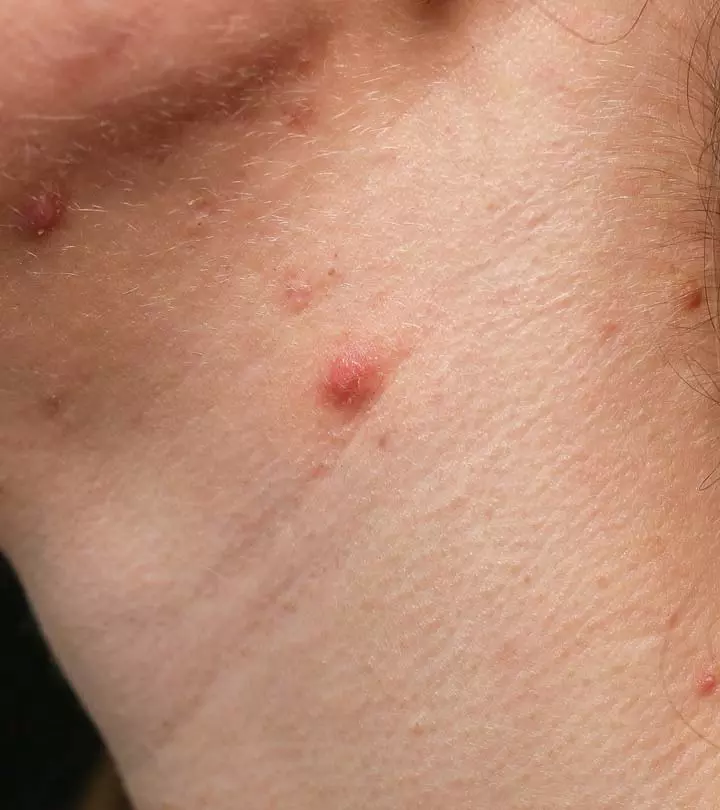
Unlike other acne, nodular acne may last for several weeks or months. It takes longer to heal and may cause scarring
Does Nodular Acne Cause Scarring?
Yes, nodular acne can cause scarring under two conditions:
- If left untreated
- If you try to squeeze or pick it, causing further injury
Without appropriate management and care, this inflammation can turn into dark spots and blemishes that may not fade away easily. Therefore, it is important to get immediate treatment and never, ever try to squeeze or drain it.
Symptoms Of Nodular Acne
- It appears mainly on the face, chest, and back.
- It looks like hard lesions and raised bumps and feels like knots under the skin.
- The raised bump may appear red or have the same color as your skin.
- It is painful to touch.
- The blemishes in nodular acne can be around half an inch in diameter.
- It may last from weeks to months.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Nodular acne is a severe form of acne and needs aggressive treatment. Oral and topical medications may not help in such cases. If you have nodular acne, consult a dermatologist immediately, who might recommend the below options.
Treatment Options For Nodular Acne
1. Oral Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin is a type of retinoid (vitamin A) and is the only medication with long-term benefits to reduce the severity of the condition. The recommended starting dose of isotretinoin is 0.5 mg/kg/day, which may gradually be increased, depending on many factors, including the dermatologist’s assessment, tolerability, and rate of improvement. Using isotretinoin may cause minor side effects like dryness, soreness of the skin, eyes, oral and nasal mucosa, pain, muscle aches, and impairment of night vision. However, these symptoms go away after treatment withdrawal or reducing the dosage (2), (7).
Dermatologists prescribe the medicine, depending on the severity of the condition. It is not safe for pregnant women, and you should avoid it if you are planning to conceive.
2. Combination Therapy
This is beneficial for those who cannot take isotretinoin. Combination therapy of oral doxycycline (200 mg) and topical adapalene (0.1%), and benzoyl peroxide (2.5%) gel can also reduce the severity of nodules, papules, and pustules and total lesions in 20 weeks (8).
While this treatment may not give the same results as oral isotretinoin, it can show similar benefits in reducing inflammation.
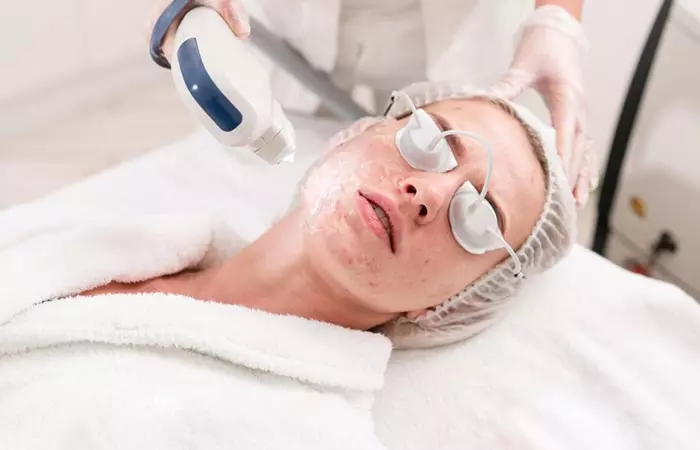
3. Laser Treatment
Using 585-nm pulse dye laser, 1320-nm Nd: YAG laser, and 1450-nm diode laser has shown clinical improvement in severe acne and scarring. They may lead to a long-term reduction in inflammatory acne and reduce acne scars (9).
4. Other Treatment Options
Depending on the severity of your condition, the doctor may also prescribe antibiotics, oral contraceptive pills (only in case of hormonal issues), and topical treatments like prescription-strength retinoids and salicylic acid.
Adding to these options, antibiotics could be another treatment option for nodular acne. Learn more about them in the next section.
Antibiotics For Nodular Acne
- Clindamycin
A 1% concentration clindamycin product is presently the preferred antibiotic medication for various types of acne vulgaris, including nodules (10). It is available in solution, gel, lotion, and pledget form. - Macrolide Antibiotic
Macrolides are a class of antibiotics that have antibacterial and immunomodulatory properties. Erythromycin is the most commonly prescribed macrolide for inflammatory acne and other bacterial infections (11). - Tetracycline
Tetracycline accounts for 75% of oral antibiotics prescribed for dermatological concerns, including moderate to severe acne (12). Doxycycline and minocycline are the commonly prescribed tetracyclines.
Do note that antibiotics are generally not considered long-term solutions due to the possibility of antibiotic resistance. Hence, they are only prescribed for a limited duration.
Besides adequate medication, taking care of your skin is equally important to prevent the discomfort caused by nodular acne. Although home remedies do not work on nodular acne, they can help minimize the discomfort. However, do a patch test before trying any of them, and if you experience any discomfort or irritation, discontinue using it.
Taking care of your skin is equally important to prevent the discomfort caused by nodular acne. Although home remedies do not work on nodular acne, they can help minimize the discomfort. However, do a patch test before trying any of them, and if you experience any discomfort or irritation, discontinue using it.
Home Remedies To Soothe Nodular Acne
1. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is said to maintain the skin pH and keep it comfortable. You can use diluted ACV spray to soothe the acne lesions.
Directions:
- Dilute equal parts of apple cider vinegar and distilled water.
- Pour the mixture in a spray bottle and spritz it on the affected area.
- Wash it off after half an hour.
2. Tea Tree Oil
Topical 5% tea tree oil may be effective in treating mild to moderate acne (13).
Directions
- Mix 2-3 drops of tea tree oil with a tablespoon of avocado oil.
- Apply the mixture to the affected area.
- Wash it off after 10-15 minutes.
Also, follow a good skin care regimen. Use prescribed cleansers and skin care products to care for your skin and soothe the inflammation.
Nodular Acne Prevention Tips
- Wash your skin with a mild cleanser and lukewarm water twice a day.
- After exercising, wash your skin to get rid of excess oil or dirt buildup that may clog your pores and worsen your condition.
- Avoid touching your face frequently to prevent transferring dirt and bacteria from your fingers to your facial skin.
- Avoid using makeup products on your skin. If you can’t do without makeup, use non-comedogenic products and remove them with a makeup remover as soon as possible.
- Use a lightweight, good-quality moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated.
- Do not skip sunscreen ever. Reapply every 4-6 hours. Make sure it has at least SPF 30 to protect your skin from sun damage.
- Avoid using physical scrubs. You can talk to your doctor and use products with low concentrations of AHAi A group of plant-or animal-derived natural acids used in skin care products to eliminate dead skin cells. and BHA for exfoliation.
- Avoid squeezing and scratching the nodules. This may cause blemishes and scarring.
- Follow a proper sleep schedule. The quantity and quality of sleep matter for healthy glowing skin.
- Keep up with your mental health. Avoid stress and practice meditation to fight anxiety and depression. Talk to a therapist if required.
Most importantly, avoid using any product or ingredient on your skin without consulting your doctor. Experimenting with random DIYs that claim to clear nodular acne and using multiple products and skin hacks can worsen your condition.
Infographic: Treatments And Home Remedies For Nodular Acne
Nodular acne not only affects your skin but also your day-to-day life. It is only natural for you to seek treatments and alternative measures to help manage the condition. The infographic below lists some of the best treatments and home remedies that you can try. Check it out!
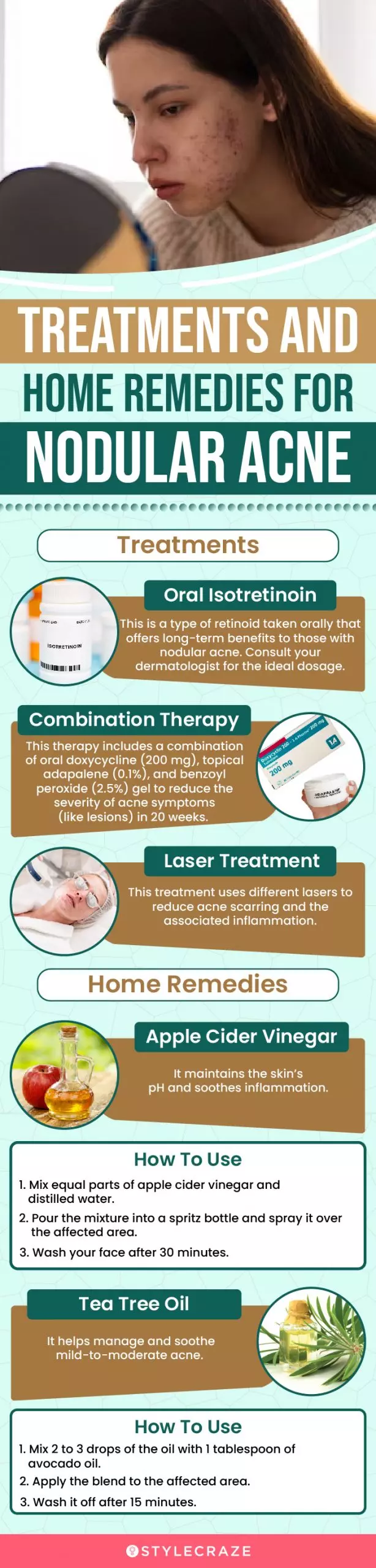
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Nodular acne looks like raised, painful, red bumps on your skin caused by factors such as genetics, hormonal imbalance, or stress. If not treated properly, they leave scars that may take months to heal. To make sure this does not happen, consult your doctor. They may prescribe oral isotretinoin or combination therapy depending on the cause and severity of the condition. You can also resort to natural remedies such as apple cider vinegar or tea tree oil to reduce the appearance of acne. Remember to conduct a patch test before using these ingredients.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does ice help nodular acne?
Yes, a cold compress may help reduce the pain and inflammation associated with nodular acne.
What foods cause nodular acne?
No particular foods cause nodular acne. However, refined sugars and grains, dairy products, whey protein, and processed and greasy foods may trigger or worsen symptoms of acne.
Does retinol help nodular acne?
Yes, retinol may help treat nodular acne. However, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist before using over-the-counter drugs for treating nodular acne as it is a severe form of acne.
Will zinc help nodular acne?
Dietary or oral zinc supplementation may help treat nodular acne. However, avoid taking zinc supplements without consulting a dermatologist as zinc can be toxic in the wrong doses.
Key Takeaways
- Nodular acne is a severe form of acne that affects the deeper skin layers.
- Genetic and hormonal factors, stress, and smoking are some of the causes of nodular acne.
- Nodular acne can cause scarring if left untreated.
- Oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, apple cider vinegar, and tea tree oil are some effective treatments for nodular acne.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Get a better insight into what cystic acnes are. Watch this video to learn what treatment you should opt for from a certified dermatologist.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Therapeutic Considerations for Severe Nodular Acne
https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165/11532280-000000000-00000 - Acne: more than skin deep
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2585707/ - The influence of genetics and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of acne: a twin study of acne in women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12485434/ - Adult female acne: a guide to clinical practice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6360964/ - The response of skin disease to stress: changes in the severity of acne vulgaris as affected by examination stress
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12873885/ - Epidemiology of acne in the general population: the risk of smoking
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11453915/ - Isotretinoin for acne vulgaris–10 years later: a safe and successful treatment
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8286227/ - A treatment for severe nodular acne: a randomized investigator-blinded, controlled, noninferiority trial comparing fixed-dose adapalene/benzoyl peroxide plus doxycycline vs. oral isotretinoin
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24934963/ - Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2884837/ - A review of diagnosis and treatment of acne in adult female patients
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986265/ - Topical antibiotics for acne
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6491308/ - Antibiotic Resistance Risk with Oral Tetracycline Treatment of Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9405006/ - The efficacy of 5% topical tea tree oil gel in mild to moderate acne vulgaris: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17314442/
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Shiboli Chakraborti