9 Natural Remedies For Overactive Bladder, Causes, & Symptoms
A few natural ingredients can help you solve this "irritating" problem in no time!

Image: Shutterstock
An overactive bladder is a condition where one may experience an uncontrollable urge to pee frequently. It may also disrupt your daily activities. Natural remedies for overactive bladder greatly help. As per an estimate, 16.6% (33 million) of the US population is affected with an overactive bladder (1). Individuals may also feel that their bladder is controlling them. Keep reading to learn more about an overactive bladder and what treatment options you can opt for.

In This Article
What Is An Overactive Bladder?
Overactive bladder is a common condition that causes the affected individuals to develop a sudden urge to urinate. This urge is often difficult to control and may even result in the involuntary loss of urine. In such a situation, this condition may also be termed as urinary incontinence.
The sudden urge to urinate can occur at any time of the day. The frequency of the unpredictable urge to urinate can also have a negative effect on a person’s life.
An overactive bladder isn’t a disease in itself, but it represents a group of urinary symptoms. The common symptoms associated with this condition are discussed below.
Key Takeaways
- The symptoms of an overactive bladder include a sudden urge to urinate that may be difficult to control, urinary incontinence, frequent urination, and nocturia.
- While the specific cause of an overactive bladder is unknown, it is usually a result of the involuntary muscle contractions of the bladder.
- Pumpkin seed oil, vitamin D, Chinese herbal supplements, green tea, cranberry juice, and ginseng are some popular natural remedies for helping treat the symptoms of an overactive bladder.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Overactive Bladder?
The symptoms of an overactive bladder may include:
- A sudden urge to urinate that may be difficult to control
- Urinary incontinence – Involuntary loss of urine following a sudden urge to urinate.
- Frequent urination, usually 8 or more times in a day
- Nocturia – Awakening 2 or more times during the night to pee.
While the specific cause of an overactive bladder is unknown, it is usually a result of the involuntary muscle contractions of the bladder. What could probably be causing this condition? Let’s find out in the next section.
What Causes An Overactive Bladder?
Your kidneys produce urine, and the urine later drains into your bladder. As you urinate, the urine further passes through an opening at the bottom of your bladder and then flows out of your body through the urethra. In women, the urethra is located right above the vagina, whereas, in men, the urethra opens at the tip of the penis.
This entire process of urination is controlled by nerve signals. When your bladder is filled, your brain receives signals to trigger the urge to urinate. As you urinate, your brain again receives signals to relax the muscles of your pelvic floor as well as the urethra to help pass the urine. Simultaneously, your bladder tightens to push the urine out.
In the case of an overactive bladder, the contraction of the bladder occurs involuntarily, even when the volume of urine inside is relatively low. This action causes a sudden urge to pee.
While the exact cause of this occurrence is yet to be found, the following are some factors that could be contributing to the symptoms of an overactive bladder:
- Neurological disorders
- Certain medications like diuretics
- Diabetes
- Urinary tract infections
- Bladder abnormalities like tumors and/or bladder stones
- Medical conditions that may affect or obstruct bladder flow like enlarged prostate or constipation
- A history of surgery to treat incontinence
- Consuming caffeine or alcohol in excess
- A decline in cognitive function, mostly due to aging
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
 Quick Tip
Quick TipAn overactive bladder can take a toll on the affected individual’s life in more ways than you can imagine. There are several ways to maintain bladder control, including herbal remedies, pelvic floor exercises, dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, acupuncture, hypnotherapy, and other alternative treatments. Here are some wonderful home remedies that can help in managing the symptoms of an overactive bladder.
Home Remedies To Manage An Overactive Bladder
1. Pumpkin Seed Oil

You Will Need
Pumpkin seed oil supplement
What You Have To Do
Take pumpkin seed oil supplement daily. Talk to your doctor for the right dosage.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this once daily or as advised by your doctor.
Why This Works
Daily intake of pumpkin seed oil extracted from both Cucurbita pepo and Cucurbita maxima can help in reducing the symptoms of an overactive bladder (2).
A blogger shared her journey of overcoming an overactive bladder and discussed the remedies that helped her. She writes, “Pumpkin seeds are very effective in treating overactive bladder. Take a spoon every day, it has really helped me (i).” She also adds a word of caution: “I have experienced that too much smoking and alcohol drinking is making the problem worse, so try to quit if you can. Also too much caffeine is a negative thing as it functions as a diuretic.”
2. Chinese Herbs

You Will Need
Chinese herbal supplements like Gosha-jinki-gan (GJG) and Hachi-mi-jio-gan (HE)
What You Have To Do
Consume any of the above Chinese herbal supplements daily after consulting your doctor.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this once daily or as suggested by your physician.
Why This Works
Hachi-mi-jio-gan (HE) and Gosha-jinki-gan (GJG) are Chinese herbal supplements that are known to alleviate overactive bladder symptoms. They do so by inhibiting bladder sensation and contractions due to their relaxant effects (3).
3. Vitamin D

You Will Need
Vitamin D supplement
What You Have To Do
Consume vitamin D supplement daily after consulting with your doctor.
How Often You Should Do This
You can take this supplement daily.
Why This Works
Symptoms of overactive bladder and other pelvic floor disorders have been associated with vitamin D deficiency (4). Hence, restoring this deficiency may help in alleviating the condition.
4. Capsaicin

You Will Need
Capsaicin injections
What You Have To Do
Consult your doctor and talk about intravesical therapy using capsaicin. This procedure includes injecting liquid capsaicin directly into the bladder under medical supervision.
How Often You Should Do This
Do as directed by your doctor.
Why This Works
Intravesical instillation of capsaicin, which is the active component in hot peppers, can help reduce the symptoms of an overactive bladder by desensitizing the neurons that are responsible for overactivity of the bladder (5).
5. Green Tea

You Will Need
- 1 green tea bag
- 1 cup of hot water
What You Have To Do
- Steep the green tea bag in a cup of hot water for 5-10 minutes.
- Remove the used tea bag and enjoy your cup of green tea.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this two times daily.
Why This Works
Daily consumption of green tea is inversely associated with the symptoms of urinary continence (6). This could be due to the presence of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) in it (7).
Caution: Note that green tea may act as a diuretic (promotes urination). Generally, people with hyperactive bladders are advised against caffeine which includes coffee, tea, and green tea. Hence, the above remedy may not work for everyone.
6. Cranberry Juice

You Will Need
400 mL of unsweetened cranberry juice
What You Have To Do
Drink around 400 mL of cranberry juice.
How Often You Should Do This
You can drink this once daily.
Why This Works
One of the common causes of an overactive bladder is a urinary tract infection. Regular consumption of cranberry juice can help prevent such infections, thereby also preventing the symptoms associated with an overactive bladder (8).
7. Ginseng

You Will Need
- 1-2 teaspoons of dried ginseng
- 1 cup of hot water
What You Have To Do
- Add a teaspoon of ginseng tea to a cup of hot water.
- Steep for 5-10 minutes and strain.
- Allow the tea to cool a bit before drinking it.
How Often You Should Do This
You may drink this 1-2 times daily for best results.
Why This Works
An overactive bladder can turn complicated and lead to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BOH), which leads to the enlargement of the prostate gland. Regular consumption of ginseng tea has a therapeutic effect on the symptoms of BPH as it helps nerve growth factor activation (9).
8. Baking Soda

You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of baking soda
- 1 glass of water
What You Have To Do
1. Add a teaspoon of baking soda to a glass of water.
2. Mix well and drink the mixture.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this two times daily.
Why This Works
Drinking sodium bicarbonate solution leads to alkalinization of urine, thereby reducing lower urinary tract symptoms, including overactive bladder (10).
9. Chamomile Tea

You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of chamomile tea
- 1 cup of hot water
What You Have To Do
- Add a teaspoon of chamomile tea to a cup of hot water.
- Steep for 5-10 minutes and strain.
- Drink the warm tea.
How Often You Should Do This
You may drink this 1-2 times daily for best results.
Why This Works
The anti-inflammatory properties of chamomile, along with its sedative action, are great for alleviating the symptoms of an overactive bladder, especially if you experience them at night (11), (12).
You can also ask your healthcare provider about including magnesium-rich foods in your diet for managing the symptoms of an overactive bladder. A randomized, double-blind study of 40 women experiencing overactive bladder tested the effects of magnesium intake on easing the sense of urgency. The group of women who received magnesium hydroxide as treatment reported a subjective improvement of their urinary symptoms when compared to those who did not. There also was no report of any adverse effects to the treatment (13).
Thus, magnesium could be a good option for treating an overactive bladder. You could consume magnesium-rich foods like green leafy vegetables, unpolished grains, and nuts to reap the benefits (14).
Note: It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any natural remedy to avoid any potential interactions or adverse effects, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or using medication.
These remedies work best when used to assist ongoing medical intervention for an overactive bladder. The best medical treatments that are often suggested for severe cases of overactive bladder are as follows.
Medical Treatments
Treatments for an overactive bladder may include:
- Medications to relax the bladder, such as Tolterodine, Oxybutynin, and Trospium.
- Bladder injections like OnabotulinumtoxinA to help with incontinence.
- Nerve stimulation therapy.
- Surgery to increase the capacity of the bladder or to remove it altogether.
Your diet may also have a significant role to play in treating an overactive bladder and alleviating the symptoms.
What Foods Are Good For An Overactive Bladder?
Some foods may be beneficial in relieving the symptoms of an overactive bladder. They are (15):
- Vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, cheese, and egg yolks.
- Potassium-rich foods like bananas, oranges, cantaloupes, cucumbers, and apricots.
- Fiber-rich foods like lentils, beans, raspberries, and barley to prevent constipation that may further worsen your symptoms.
- Protein-rich foods like fish, chicken, and tofu.
You must also avoid the following trigger foods as they can aggravate your symptoms.
What Foods And Drinks To Avoid For An Overactive Bladder?
If you are dealing with an overactive bladder, avoid these foods (16):
- Carbonated beverages
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Chocolates
- Sports drinks like Gatorade
- Citrus fruits
- Spicy foods
- Artificial flavorings and preservatives
- Sugar
- Honey
- Raw onion
You may not have to eliminate all the above foods from your diet. Find out which of the above can be tolerated in small amounts by your body and make changes to your diet accordingly.
Listed below are some helpful tips to manage an overactive bladder and prevent recurrence of symptoms.
How To Manage An Overactive Bladder
- Do pelvic floor or Kegel exercises to strengthen your pelvic muscles.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Set a schedule for your toilet trips and follow it regularly.
- Train your bladder to hold in the urge to urinate every now and then. Gradually work your way to pee every 3-4 hours instead of every 20-30 minutes.
- Practice yoga.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipInfographic: Ingredients That May Treat An Overactive Bladder
The article above provides many simple and effective natural home remedies to help you say goodbye to the inconvenience of an overactive bladder. In the infographic below, we have highlighted the easy-to-implement remedies that can help you regain control and manage the symptoms of an overactive bladder comfortably at home. Check it out for more information.
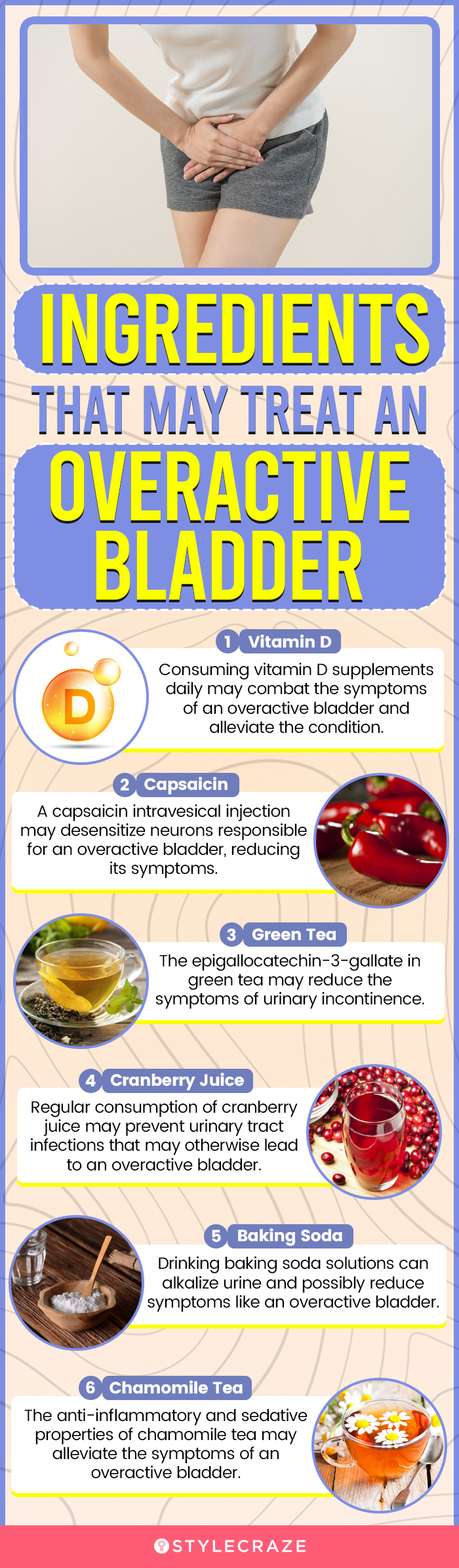
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
An overactive bladder is characterized by the need to urinate frequently. One may also find it difficult to control the urge to urinate. Urinary incontinence, frequent urination, and nocturia are the common symptoms of this condition. Diabetes, neurological disorders, medications like diuretics, urinary tract infections, and bladder abnormalities are the common causes of such bladder problems. However, there are some effective natural remedies for overactive bladder. Pumpkin seed oil, Chinese herbs, vitamin D, capsaicin, and green tea are popular remedies that may help improve the symptoms of an overactive bladder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best dietary changes for managing overactive bladder symptoms?
Reducing the consumption of caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and artificial sweeteners may help manage the symptoms of an overactive bladder, as they can irritate the bladder. Prioritize drinking enough water and eating foods high in fiber, potassium, and magnesium to support bladder health.
Is turmeric good for overactive bladder?
Yes, turmeric contains a compound known as curcumin, which may help improve the contractibility of the bladder and hence, help reduce the symptoms of an overactive bladder (17).
Does apple cider vinegar help with overactive bladder?
There is no evidence to suggest that apple cider vinegar may help with an overactive bladder.
Is ginger good for overactive bladder?
Ginger may help with the symptoms of an overactive bladder if the condition is caused by a urinary tract infection. That is because ginger is a great home remedy for UTI problems. The antibacterial properties of ginger fight the infection and relieve pain (18). However, ginger is also known to help relieve water retention in the body and may have gastrointestinal side effects if not used in moderation and with caution.
Is black sesame good for overactive bladder?
Black sesame is prized in Ayurvedic medicine for calming an overactive bladder.
Say goodbye to frequent urination with simple yet powerful home remedies. Check out this video to unlock the secrets to a more comfortable bladder control and be in charge of your daily routine.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How I overcame overactive bladderhttps://dalleeblog.wordpress.com/2016/11/23/how-i-overcame-overactive-bladder/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “The overactive bladder and quality of life.” International Journal of Fertility and Women’s Medicine, US National Library of Medicine.
- “Pumpkin Seed Oil Extracted From Cucurbita maxima Improves Urinary Disorder in Human Overactive Bladder” Journal Of Traditional And Complementary Medicine, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Use of Herbal Supplements for Overactive Bladder” Urology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Vitamin D Status – A Clinical Review with Implications for the Pelvic Floor” International Urogynecology Journal, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Intravesical neuromodulatory drugs: capsaicin and resiniferatoxin to treat the overactive bladder.” Journal of Endourology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “ Green tea drinking is inversely associated with urinary incontinence in middle-aged and older women.” Neurourology and Urodynamics, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Epigallocatechin-3-gallate alleviates bladder overactivity in a rat model with metabolic syndrome and ovarian hormone deficiency through mitochondria apoptosis pathways” Scientific Reports.
- “The role of cranberry juice in the treatment of urinary tract infections.” British Journal of Community Nursing, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Effects of Panax ginseng on the nerve growth factor expression in testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia” Saudi Journal Of Biological Sciences, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Effects of urine alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate orally on lower urinary tract symptoms in female patients: a pilot study.” International Urogynecology Journal, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Effects of an intervention with drinking chamomile tea on sleep quality and depression in sleep disturbed postnatal women: a randomized controlled trial.” Journal of Advanced Nursing, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Chamomile, an anti-inflammatory agent inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by blocking RelA/p65 activity” International Journal Of Molecular Medicine, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of magnesium hydroxide for treatment of sensory urgency and detrusor instability: preliminary results” British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Magnesium” Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride
- “Nutrient composition of the diet and the development of overactive bladder: a longitudinal study in women.” Neurourology and Urodynamics, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Evaluation and management of overactive bladder: strategies for optimizing care” Research And Reports In Urology, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Inhibitory Effect of Curcumin on the Contractility of Isolated Caprine Detrusor Muscle” Indian Journal Of Pharmaceutical Studies, US National Library Of Medicine.
- “The Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Selective Oral Microbes, Antioxidant Activity and Preliminary Phytochemical Screening of Zingiber officinale,” National Institutes Of Health
Read full bio of Dr. Zeel Gandhi
Read full bio of Shaheen Naser
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Payal Karnik
























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.