Which Home Remedies For Pancreatitis Can Help Me Recover Quickly?
Get relief with some dietary changes, a healthy lifestyle, weight loss, and glutamine supplements.

Image: iStock
Sudden shooting pain across your upper abdomen maybe a worrying sign of pancreatitis. The organ resembling a leaf may not look like much but it does a brilliant task of keeping your digestive process going. If you have pancreatitis, it might mean that this organ is stressed out and needs a break. The home remedies for pancreatitis that you can read here along with a few diet tips, can be useful to restore it back to health as smoothly and safely as possible.
In This Article
What Is Pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. Located in the abdomen, the pancreas is an organ that is responsible for secreting digestive juices. In pancreatitis, not only the pancreas but even the surrounding blood vessels may get inflamed leading to possible bleeding and infection.
There are broadly two types of pancreatitis:
1. Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis begins suddenly and may last for a few days. It maybe life-threatening and needs to be treated right away. It most often presents as severe pain in the upper abdomen area that spreads towards the back. Other symptoms of acute pancreatitis include tenderness on the abdomen, fever, nausea, vomiting, and rapid pulse (1).
A study published in the National Library of Medicine found the prevalence of acute pancreatitis to be around 600 to 700 cases per 100,000 people in the United States with approximately 200,000 to 250,000 hospital discharges each year. Furthermore, the mortality rate from acute pancreatitis is estimated at 2%.
2. Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis on the other hand is a slowly progressing disease that may continue for years and occur intermittently.
Untreated chronic pancreatitis may result in serious health conditions like diabetes, pancreatic infection, respiratory problems, kidney failure, and may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Symptoms associated with this form of pancreatitis include unintended weight loss, upper abdominal pain that is worse after eating, and oily and smelly feces (2).
As you can see, the most common symptom of pancreatitis is abdominal pain. If you experience severe pain that does not subside or makes it difficult to sit still or be comfortable, contact your healthcare provider as early as possible.
Is there a way to know that you have pancreatitis before you visit your doctor? Let’s find out.
Key Takeaways
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas caused by excessive drinking of alcohol, gallstones, abdominal injury, and pancreatic cancer.
- Making dietary changes, losing weight, taking glutamine supplements may help alleviate symptoms of pancreatitis.
- Upper abdominal pain and tenderness are common symptoms of both acute and chronic pancreatitis.
How To Test For Pancreatitis At Home
You cannot self-diagnose pancreatitis at home as it requires multiple laboratory tests like a blood test, a CT scan, and sometimes, an ultrasound scan. Your doctor may also prescribe you a stool test to check for chronic pancreatitis.
The best way to be aware of whether your pancreas is inflamed is to touch your abdomen for tenderness on experiencing upper abdominal pain. The next step is to contact your doctor, as untreated pancreatitis can prove to be fatal.
Like similar symptoms, both acute and chronic pancreatitis have some common underlying causes. Let us take a closer look at them.
What Causes Pancreatitis?
There are many probable reasons why you may develop pancreatitis, including (3):
- Excessive drinking of alcohol
- Gallstones
- Certain medications
- Cystic fibrosisi A rare genetic disorder that causes sticky mucus to build up in organs, including the lungs, pancreas, and digestive tracts.
- Abdominal surgery
- High levels of triglyceridesi Naturally occurring fat that gives you energy and is stored in the blood, which the body uses in between meals. in the blood
- High levels of calcium in the blood
- Abdominal injury
- Pancreatic cancer
- Infections
- Genetic disorders of the pancreas
The most common reason behind acute pancreatitis is the formation of gallstones, whereas genetics and lifestyle factors play a more important role in the development of chronic pancreatitis. Some of these risk factors include (3):
- Heavy alcohol use
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Genetics
- Poor dietary choices like high sugar and fat consumption
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Acute pancreatitis generally requires hospitalization and depending on what has caused it, its treatment course is decided. Chronic pancreatitis, on the other hand, maybe managed at home if it is recurrent and not severe.
In either case, there are certain home remedies for pancreatitis that may support your recovery and alleviate some of its symptoms. Let us see what they involve.
Natural Remedies For Pancreatitis Relief
Pancreatitis treatment at home typically involves staying hydrated, avoiding fatty foods and alcohol, and fasting. In the case of mild pancreatitis, self-care measures can aid symptom management and support healing, but medical attention may still be necessary for more severe cases. It is always important to consult a doctor before trying any medical or natural remedies.
1. Make Dietary Changes

Medical professionals recommend that you avoid any food during an episode of pancreatic inflammation. This restriction may last from a few hours to a few days. You should stay hydrated with fluids during that time. In case you are required to go without food for a long period of time, you may have to be intravenously fed to get your supply of essential nutrients. When you are allowed to eat again, you should take several small meals throughout the day. Avoid food with high-fat content. In addition, incorporate plenty of fluids in your diet and limit your caffeine intake (5), (6).
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?2. Make Lifestyle Changes
Smoking, heavy drinking, and lack of an active lifestyle are closely linked to the development and worsening of pancreatitis (8). Completely stop consuming alcohol to lower the risk of triggering inflammation. Adopt a routine for exercise to help you manage your weight. Smoking cigarettes also puts you under oxidative stress and toxin load so quit it as early as possible (9), (10).
3. Lose Weight

Obesity has been linked to a higher risk of gallstones and pancreatitis. It also makes the severity of symptoms related to pancreatitis worse. Therefore, doctors routinely recommend those with pancreatitis to lose weight and manage it around a healthy BMI. Increased fat deposits in the abdominal area are linked to an increased risk of inflammation (11). To lose weight sustainably, you may need to:
- Control portion sizes
- Substitute simple and processed carbohydrates with complex carbohydrates and whole grains
- Limit added sugar and exclude sweetened carbonated drinks
- Limit fat intake
- Choose healthy snacks like nuts, fruits, and seeds
4. Take Glutamine Supplements
According to research, glutamine supplements may support treatment for pancreatitis by reducing the risk of associated complications and infections (12), (13). Glutamine is an amino acid that helps to break down food and gives a boost to the immune system. However, larger studies are warranted to establish the efficacy of glutamine supplementation for pancreatitis.
These home remedies for pancreatitis maybe supplemented with foods that can help with the condition. Let’s explore what makes up a pancreatitis diet.
Is There A Specific Diet For Pancreatitis?
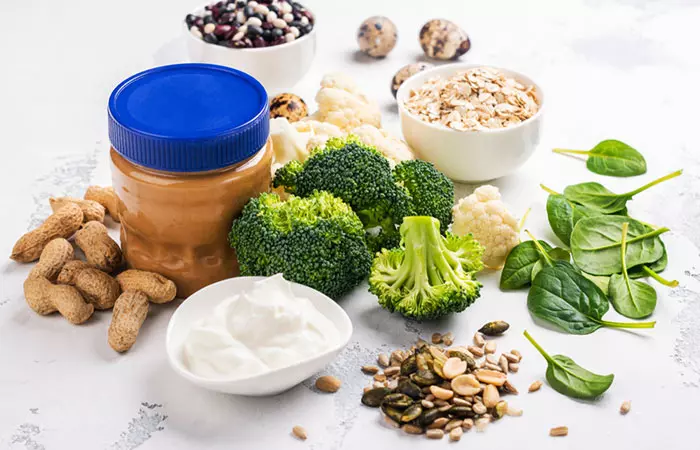

Your healthcare provider may work with you and design a specific diet based on the severity of your condition. As such, there is no one-size-fits-all diet specifically designed for pancreatitis. Having said that, there are definitely certain foods that can benefit you if you are recovering from an attack of acute pancreatitis or living with chronic pancreatitis. There are also a few foods that you are better off without. Some of them are listed below:
- Blueberries
Blueberries are packed with antioxidants which can help reduce the number of free radicals in your body and lower inflammation. Free radicals in the body can aggravate or play a part in the development of pancreatitis (14). Adding blueberries to your diet may help you improve your condition and prevent severe flare-ups (15), (16).
- Tofu
Tofu is a good alternative to meat for people with chronic pancreatitis. Red meat consumption is a risk factor for gallstones that can trigger an inflammation of the pancreas. The high-fat content in red meat may also exacerbate the condition (17). You can incorporate tofu-based meals in your diet to get your source of meaty, low-fat protein.
- Yogurt
Yogurt is a probiotic that can help you regulate the microbiomei The community or collection of all microorganisms that live on and inside the body, such as fungi and bacteria. in your gut and strengthen your immune system (18). A strong immune system can lower inflammation in and around your pancreas and also reduce the risk of infection, which is one of the most common causes of death associated with acute pancreatitis (19), (1).
- Reishi Mushrooms
Reishi mushrooms have been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It is densely packed with antioxidants and bioactive compounds. Additionally, it has antimicrobial, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties (20). There is some evidence to suggest that reishi mushrooms may protect pancreatic cells from damage when used in the diet for managing pancreatitis (21).
- Coconut Oil
Doctors often recommend a very low-fat diet for those with acute or chronic pancreatitis. Coconut oil, however, is one of the few cooking fats that maybe added to your diet. Coconut oil has a good balance of omega fatty acidsi Healthy fat mostly found in fish that reduce inflammation and the risk of heart diseases, and build brain cells. and contains medium-chain-triglycerides or MCTs which may help fight inflammation in the pancreas. Coconut oil may also help in better absorption of nutrients (22).
- Turmeric
Turmeric, with its active compound curcumin, is a potent anti-inflammatory agent and antioxidant that may have a protective effect on the pancreas. It may also help reduce inflammation in the body (23). You can add turmeric to your diet by adding it to low-fat milk, making turmeric pepper tea, or using it in stir-fries or in one-pot meals as a spice.
- Spinach
Leafy greens, especially spinach, are a great source of micronutrients (24). Pancreatitis may lead to poor absorption of nutrients. For instance, deficiency in vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and seleniumi An essential mineral that helps DNA synthesis and protects cells from oxidative damage and infections. have been linked with worsening conditions in pancreatitis (25), (26). Adding spinach to your diet is a good way of replenishing these nutrients.
A blogger spoke about the different foods that aggravated their pancreatitis in the blog. They said, “I was recently in NYC where I perhaps ate a little more all-natural sausage, steak, roast beef, chicken and yogurt. It’s not that I can’t have these foods. It is just that my pancreas doesn’t like it when I eat too much of them (i).”
The foods and natural ways to manage symptoms of pancreatitis should only be used in a supportive role as you go along with your prescribed treatment and work closely with your healthcare provider.
Severe cases of chronic pancreatitis may require medical treatment suggested by your doctor. Check them out in the next section.
Treatments For Chronic Pancreatitis
- Enzyme Supplements
Digestive enzyme supplements can assist in proper food digestion. A study found that pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) could be effective in reducing fecal fat excretion and symptoms like abdominal pain. Administering higher doses and specific formulations of enzymes seemed to work better (27). However, more research is needed to study their long-term impact.
- Endoscopic Or Surgical Interventions
Severe cases may require surgical procedures or endoscopic therapies to alleviate blockages, drain pseudocysts, or remove damaged tissue. A study comparing surgery and endoscopy found that surgery was more effective in controlling pain in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Further, it also showed potential benefits for preserving pancreatic function (28).
- Alternative Therapies
There are some alternative therapies that may help manage pancreatitis to some extent. Research suggests that acupuncture may be a beneficial addition to a pancreatitis treatment routine (29). Acupuncture may help your digestive system work better and improve overall recovery rates. Additionally, yoga may help improve physical and emotional well-being in people with chronic pancreatitis (30). Always consult a doctor before opting for these alternative treatments to avoid any complications and risks.
Many of the natural remedies available for managing pancreatitis are aimed at the prevention of further inflammatory attacks on the pancreas. Let’s take a look at some of them.
Prevention Tips
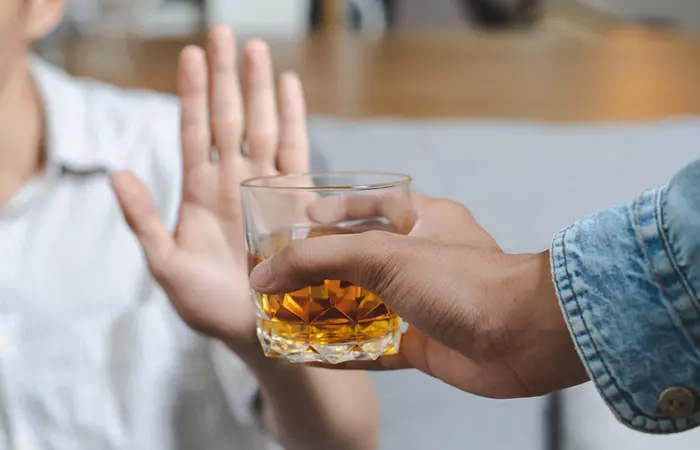

You may lower your risk of pancreatitis by taking a few steps for a healthy lifestyle, like:
- Stop drinking alcohol.
- Stop smoking.
- Lose weight.
- Avoid added sugar.
- Engage in physical activities like walking, swimming, cycling, or strength training for 30 minutes at least 3 days a week.
- Certain medications/supplements can also increase your risk, so discuss with your doctor all supplements you are on.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods.
In short, pancreatitis refers to the inflammation of the pancreas that maybe either acute or chronic. Acute pancreatitis may last up to a few days, after which you need to focus on recovery. Chronic pancreatitis can last over years and is characterized by recurrent inflammations. Management of this condition using home remedies for pancreatitis involves lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments. To prevent your risk of developing pancreatitis, it is essential to take care of oneself and quit smoking and drinking.
Infographic: Essential Foods For A Pancreatitis Diet
Pancreatitis is caused by the inflammation of the pancreas gland, which leads to severe pain. You should be mindful of your diet if you have this condition. There are certain essential foods that help in improving the health of your pancreas. Read through the following infographic to learn about them.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxFrequently Asked Questions
Is lemon water good for pancreatitis?
Lemon may have an antiinflammatory effect on the body, which can help with pancreatitis (31). However, research is limited in regard to the safety of lemon juice intake in different stages of pancreatitis and hence it should not be consumed without medical guidance.
Is ginger good for pancreatitis?
Ginger may have a protective effect against pancreatic cancer and reduce pancreatic damage (32). However, more research is warranted in this regard and ginger should not be consumed by individuals with pancreatitis without medical guidance.
Which tea is good for pancreas?
Green tea is rich in antioxidants and may help fight inflammation. However, it may also cause dehydration and lead to acute pancreatitis (33), (34). Therefore, individuals with pancreatic damage or pancreatitis are recommended to consult their healthcare provider before consuming green tea or any other tea.
What spices are good for pancreatitis?
Basil, mint, and tarragon are good spices for pancreatitis.
Is Honey OK for pancreatitis?
A little amount of honey is okay for pancreatitis, depending on the body’s ability to manage blood sugar levels.
Illustration: Home Remedies For Pancreatitis: How To Support Your Recovery At Home

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Following a healthy diet can help maintain a healthy pancreas. Check out this video to know more about what you need to eat to treat pancreatitis.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Living with pancreatitishttps://living-with-pancreatitis.blogspot.com/2011/09/pancreatic-diet-curry-rice.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Acute pancreatitis: current perspectives on diagnosis and management
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5849938/ - Chronic pancreatitis: review and update of etiology risk factors and management
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5958317/ - Symptoms & Causes of Pancreatitis
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes - Pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538337/ - Nutrition management in acute pancreatitis: Clinical practice consideration
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7211526/ - ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in acute and chronic pancreatitis
https://www.clinicalnutritionjournal.com/article/S0261-5614(20)30009-1/fulltext - Acute pancreatitis: a historical perspective
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19390402/ - Metabolic and lifestyle risk factors for acute pancreatitis in Chinese adults: A prospective cohort study of 0.5 million people
https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1002618 - Impact of Smoking on the Risk of Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0124075 - Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Pancreatitis: Effect of Antioxidant Therapy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4009983/ - Obesity and pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6640854/ - Glutamine supplementation in acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1424390313007606?via%3Dihub - The role of infection in acute pancreatitis
https://gut.bmj.com/content/45/2/311 - Role of oxygen free radicals in patients with acute pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4656475/ - Recent Research on the Health Benefits of Blueberries and Their Anthocyanins
https://academic.oup.com/advances/article/11/2/224/5536953 - Experimental and clinical evidence of antioxidant therapy in acute pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3482639/ - Dietary Factors Reduce Risk of Acute Pancreatitis in a Large Multiethnic Cohort
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5241169/ - Immunologic effects of yogurt
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/71/4/861/4729065 - Diet and Immune Function
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6723551/ - Antitumour Antimicrobial Antioxidant and Antiacetylcholinesterase Effect of Ganoderma Lucidum Terpenoids and Polysaccharides: A Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6017764/ - In vitro and in vivo protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on alloxan-induced pancreatic islets damage
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12941433/ - The Use of Medium-Chain Triglycerides in Gastrointestinal Disorders
https://med.virginia.edu/ginutrition/wp-content/uploads/sites/199/2014/06/Parrish-February-17.pdf - Effects of curcumin on oxidative stress inflammation and apoptosis in L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in mice
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844019358827 - Spinach raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168462/nutrients - Nutrition in chronic pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3831208/ - Chronic Pancreatitis and Nutrition Therapy
https://aspenjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ncp.10379 - Efficacy of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy in chronic pancreatitis: systematic review and meta-analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5530474/ - Endoscopic or surgical intervention for painful obstructive chronic pancreatitis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22258975/ - Acupuncture for acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31593017/ - Yoga: A tool for improving the quality of life in chronic pancreatitis
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4065893/ - Protective effect of citrus lemon on inflammation and adipokine levels in acrylamide-induced oxidative stress in rats
https://www.scielo.br/j/bjps/a/ZwxM39gGjtFB6CXhdZPQ77L/?lang=en - Anticancer Effect of Ginger Extract against Pancreatic Cancer Cells Mainly through Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Autotic Cell Death
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4427290/ - Epicatechin gallate and catechin gallate are superior to epigallocatechin gallate in growth suppression and anti-inflammatory activities in pancreatic tumor cells
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21241417/ - Can Green Tea Extract Become a Cause of Acute Pancreatitis?
https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-2009-1216532
Read full bio of Jennifer Roelands
Read full bio of Sanchari Bhattacharya
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Dipti Sharma


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.