Acne Papules: Your Guide To Causes, Treatments, And Prevention
If you are wondering how to manage them, these remedies could be what you are looking for.
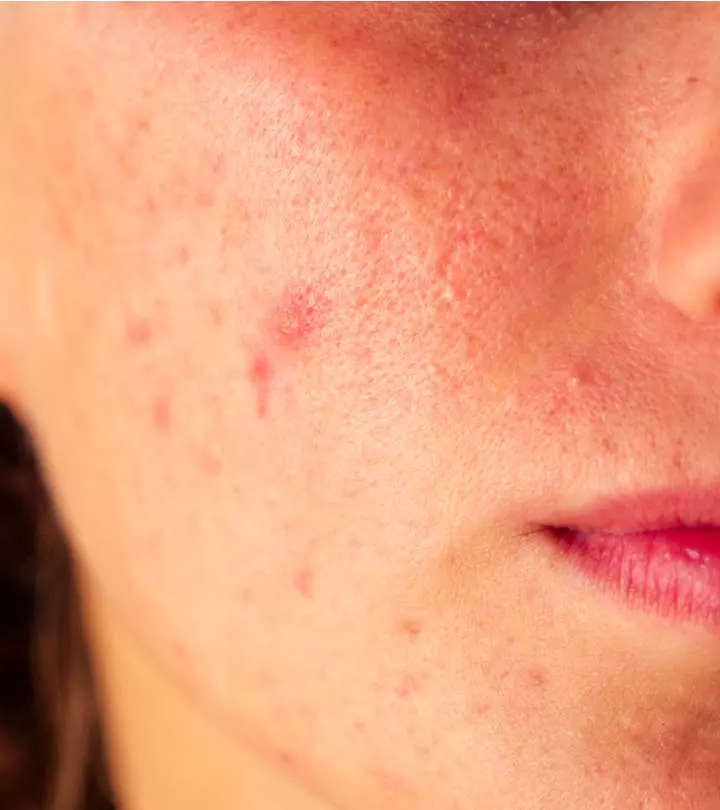
Image: Shutterstock
Acne is one of the most common skin disorders that affect individuals of all ethnicities and genders. This skin problem can progress to acne papules if left untreated. Acne papules can be unpleasant due to their appearance. In addition, they can be triggered by various factors, making them tough to manage. This article will go over all you need to know about acne papules, what causes them, how to get rid of them, and when to see a dermatologist. Keep reading to know more!

In This Article
What Are Acne Papules?
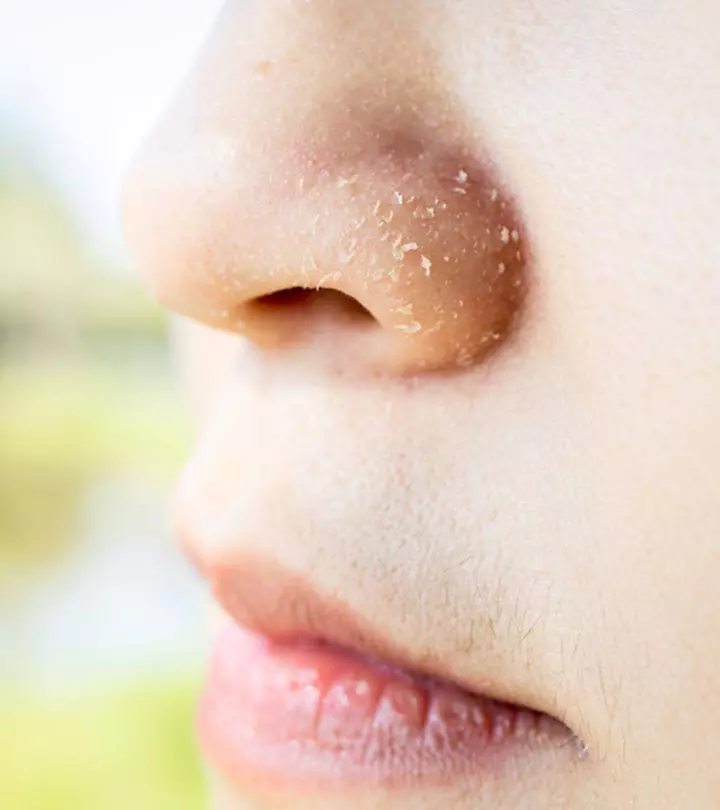
Acne papules are small, red, bumpy blemishes that appear on the skin’s surface. Such papules caused by acne typically measure between 5 mm and 1 cm. While they are not a major cause of concern, their high visibility can be damaging to an individual’s self-confidence. Furthermore, affect the skin’s appearance and texture permanently or semi-permanently.
According to the American Association of Dermatology, acne affects around 50 million Americans each year. It is estimated that 85% of people aged 12 to 24 experience minor acne and 15% of adult women experience acne.
It is worth mentioning here that acne papules and pustules are not the same, and we will be elaborating on their differences in a later section. On that note, let us take a look at how to recognize papules caused by acne.
Key Takeaways
- Acne papules are small, red lesions that measure less than one centimeter. They are commonly found on the face but can also occur in other body parts.
- Excess sebum, natural oils, and dead skin cells clog pores and follicles leads to this condition, allowing acne-causing bacteria to thrive and causing skin inflammation.
- Products containing salicylic acid, glycolic acid, benzoyl peroxide, and retinoids are usually prescribed for acne papules.
How To Recognize Acne Papules
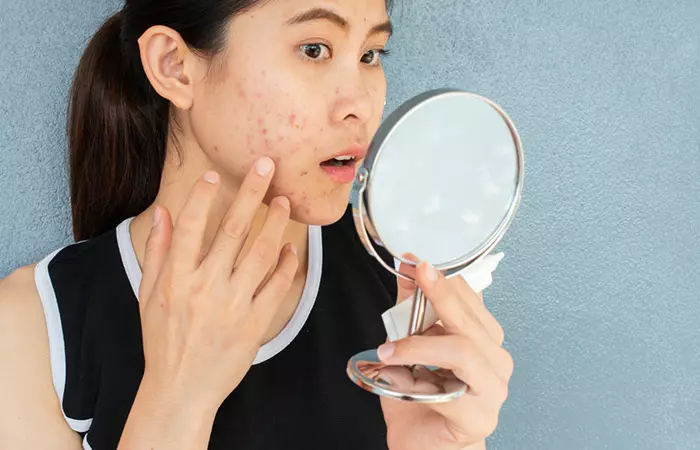

To effectively recognize them, we must understand what papules look like. Acne papules are small, red lesions that are less than 1 cm in size, i.e., approximately the width of a fingernail. Unlike hard pimples, these are tender to the touch and less painful.
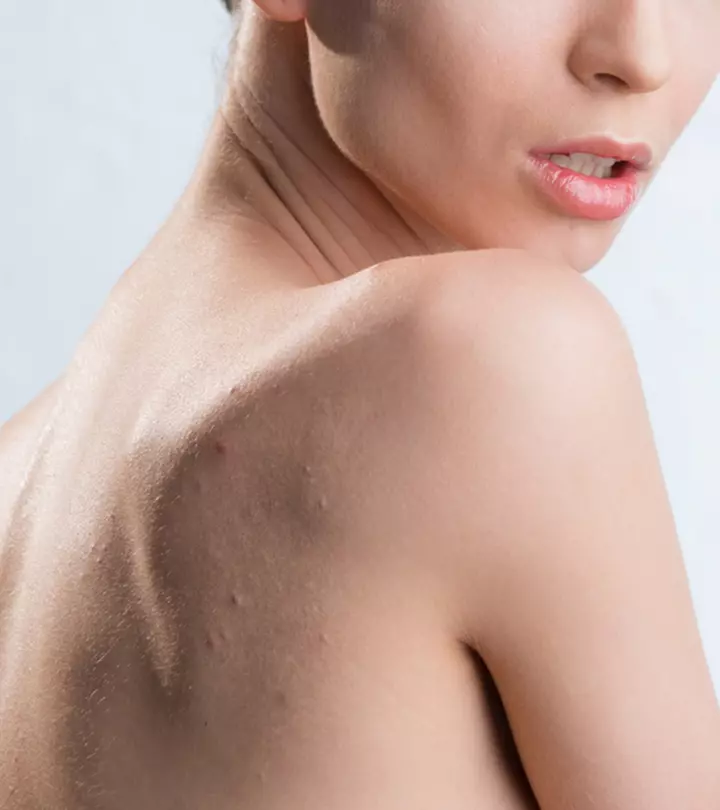
Acne papules are usually found on the face, especially on the forehead, the chin, and the cheeks. Occasionally, these papules may occur on the back, chest, upper arms, and shoulders.
You may normally find these acne papules on your face, especially on the chin and cheeks, and upper back. On rare occasions, you may discover them on your chest, neck, and shoulders.
Typically, these papules are accompanied by redness around the eruptions, bumpy skin texture, a flat top, and itching.
 Trivia
TriviaMany people get confused between acne papules, nodules, pustules, and macules. Let us take a look at the differences between them below.
Differences Between Acne Papules And Acne Nodules
While papules represent a minor to a mild form of acne, nodules indicate severe acne. As a result, nodules are larger, more swollen, and extremely painful. In addition, acne nodules are generally more angry-looking. They form deeper inside the skin and are more prone to scarring. So, consult a dermatologist to get your nodules treated.
Differences Between Acne Papules And Pustules
Acne pustules contain pus. As a result, they may look like papules but have a white, yellow, or red-brown spot in the center of the bump. Apart from this visual pustule vs. papule difference, it is also worth noting that papules can develop into pustules. This transformation occurs when the immune cells present in the papules die while fighting the bacterial infection, causing pus formation.
Differences Between Acne Papules And Macules
While papules are red, small, and bumpy lesions commonly formed on the skin, macules are flat, discolored spots that appear after an acne lesion has healed. These spots result from inflammation and damage to the skin’s deeper layers. Macules may appear red (erythematous macules) or dark (pigmented macules) Red macules usually appear on the spot of a freshly healed acne. On the other hand, dark and pigmented macules are caused by old acne and are common in people with a dark skin tone.
Macules are not considered active acne but are often a cosmetic concern. They usually fade over time. Distinguishing between papules and macules is important for understanding the progression of acne and selecting appropriate treatments.
Wondering what causes acne papules to form? Find out in the next section.
What Are The Causes Of Acne Papules?
Like every other skin lesion caused by acne, papules start developing when dead skin cells, natural oils, or sebum clog the pores or hair follicles
. This sealing of pores causes the formation of micro comedones. Microcomedones are tiny, raised pimples present beneath the skin’s surface. These microcomedones offer a fertile ground for acne-causing bacteria that feed on excess oil and dead skin. As the bacteria begin to reproduce, they trigger inflammation of the skin surrounding the clogged pores. This inflammation causes the red bumps we know as acne papules.
The common culprits of acne papules causes could be:
1. Hormones
Male sex hormones or androgens
stimulate the production of sebum. At the same time, they also play a role in regulating the body’s immune response to the inflammation caused by acne. Hence, the secretion of androgens serves as a prelude for acne papules.
2. Stress
Stress is one of the leading causes of acne. In fact, a study discovered that stress levels are directly linked to the severity of acne breakouts. It is speculated that the hormones released in response to stress (corticotropin-releasing hormone) trigger the secretion of sebum which, in turn, causes acne and acne papules.
3. Diet
While scientists continue to debate the role of diet in acne breakouts, it is still speculated that there may be a correlation between acne and dietary preferences. For instance, people have noticed that a high-sugar, high-fat diet causes them to experience acne eruptions. Clinical studies support this claim as they have discovered that food items like chocolate and dairy can worsen acne. A similar trend is seen in high glycemic diets, which reportedly aggravate acne, leading to the formation of acne papules and pustules.
4. Hygiene
While it is not supported by scientific research, it is a commonly held belief that poor hygiene can cause acne and aggravate it. This is based on the belief that poorly cared-for skin is more susceptible to clogging and bacterial infections. Not washing your face regularly or touching it too much may cause papules on the face. A study partially verifies this claim as it discovered that cleansing your skin at least twice a day reduces the number and severity of acne papules and lesions.
5. Genetics
If someone in your family has a history of acne, you might be more likely to get acne papules yourself. Studies show that people with first-degree relatives who have had acne can be up to three times more likely to develop it than those who don’t have a family history of acne.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipNow that you know what causes them, let’s talk about how to treat acne papules.
How To Get Rid Of Acne Papules

It is time to explore the possible management options of acne papules. If you are wondering how to get rid of papules, here are a few options that you can try out:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical creams and products specifically formulated for treating acne and reducing its appearance are commonly used.
While picking up any over-the-counter (OTC) treatment from your local pharmacy, look for products that contain ingredients such as salicylic acid (SA), glycolic acid, or benzoyl peroxide. These ingredients are said to be effective in sloughing off dead skin and removing excess sebum from the skin’s surface. As a result, they not only clear the existing acne papules but also prevent their reoccurrence in the future. Studies have shown that salicylic acid, glycolic acid, and benzoyl peroxide are effective mild acne papule treatments.
For the management of inflammatory papules, your dermatologist may prescribe retinoids or retinoid-like drugs that contain adapalene, tretinoin, or tazarotene. These topical applications address the primary cause of acne formation – like clogged pores – while also reducing inflammation. Your dermatologist may complement this papular acne treatment with a prescription of antibiotics to kill the acne-causing bacteria.
However, bear in mind that while topical treatments can be one f the most effective ways to treat acne papules, they cause some amount of skin dryness and mild irritation. The trick is to hydrate your skin with a water-based moisturizer.
2. Oral Medication
Oral medication is another option to treat papules caused by acne. Your dermatologist may prescribe antibiotics that can reduce swelling and redness. Their efficacy increases when used in combination with topical creams.
Apart from antibiotics, women can opt for oral contraceptives or hormone pills to regulate acne. Certain birth control pills, for instance, have been proven to reduce breakouts. These birth control pills trigger a hormone balancing effect that can mitigate acne formation and intensity. Similarly, your dermatologist may also prescribe androgen receptor blockers (anti-androgen pills) to regulate the levels of male sex hormones or block their effects on your oil glands.
The graph below shows the market value of acne medication in the US. According to market research firm NextMSC, the acne treatment market was valued at 10 billion US dollars in 2025 and is expected to rise to more than 14 billion US dollars by 2030.

Acne Medication Market Size Worldwide 2025 And 2030
Source: Statista3. Skin Care Products
Following a strict skin care routine can help you mitigate acne and acne papules. Maintain a reliable skin care routine that involves cleansing and moisturizing your skin, followed by sunscreen.
It would be best to pick skincare products that contain salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or benzoyl peroxide as they are proven to treat acne papules. Further, these products must be formulated specifically for acne-prone skin. Additionally, your dermatologist may advice monthly chemical peel treatments as they are said to be highly effective in unclogging pores and reducing acne papules.
4. Natural Remedies

Here are a few remedies that are traditionally and culturally thought to help reduce the appearance of acne and acne papules:
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Apply a solution of one part water and one part apple cider vinegar onto the skin’s surface. It is believed that the organic acids present in it can kill the acne-causing bacteria and reduce acne. However, there is not enough scientific evidence to prove the same.
Parita, a blogger, shared her experience of using apple cider vinegar for 3.5 weeks to combat acne in her blog. She said, “It didn’t necessarily get worse, but my face was definitely not clearing up either. And with that, I gave up on ACV once and for all (i).”
- Lemon Juice: Gently press a wedge of lemon against your acne papules to get rid of them. The citric acid will kill the acne-causing bacteria. However, there is not enough scientific evidence to prove the same.
- Green Tea: Apply a used green tea bag on your acne papule. Many skin care enthusiasts believe that green tea can fight off acne-causing bacteria. It has also been scientifically proven to reduce inflammation (redness and swelling), which is usually associated with acne papules.
- Honey: Dab some honey directly on your acne pimples. The antibacterial effect of honey may ward off the bacteria that is causing your acne.
- Ice: Wrap a few ice cubes in a clean cloth and press the pack against your acne papules. Hold it for a few seconds, then release it. This method can soothe the inflammation and itchiness that worsen papule formation.
Learn how to prevent acne papules before they form in the next section. Keep reading!
Tips For Preventing Acne Papule Formation

Dr. Laura Geige, a qualified cosmetic dermatologist, says, “While preventing acne papules entirely may not always be feasible, adopting a consistent skincare routine, avoiding harsh products, managing stress, and seeking professional guidance can help minimize their occurrence and reduce the risk of scarring.”
Listed below are a few things that you can do to prevent acne papules from forming in the first place:
- Wash your face with a mild cleanser and lukewarm water at least twice a day.
- Use skin care products that suit your skin type and incorporate them into your daily skin care regimen.
- Hydrate your skin with water-based (for dry skin) or gel-based (for oily skin) moisturizers.
- Follow a healthy diet and cut down on your sugar consumption.
- Take a shower after working out and after doing any intense activities.
- Use oil-free, non-comedogenic products.
- Avoiding picking at or popping your acne pimples.
- Apply sunscreen daily, especially when you are out in the sun for long.
- Drink a minimum of two liters of water daily.
- Do not self-medicate, and only use products and medications in their recommended doses.
- Practice meditation or self-care activities that help you de-stress.
Lastly, let’s talk about when your acne papules need medical intervention.
When Should You See A Doctor For Your Acne Papules?

For all it is worth, acne papules do not cause scarring. They also self-heal over time.
As such, they are not a major cause for alarm. However, you may consider seeing a dermatology expert for inflammatory papules that are oozing pus or forming cysts. Papules that are rapidly growing in number could also be concerning. You may also seek medical help if the acne papules are turning into pustules or nodules.
Infographic: Who Can Get Acne Papules
Acne papules are small, red bumps on your skin caused by excess oil, bacteria, and hormone changes. Though anyone can get them, they are most common in adolescents with a family history and who do not follow a proper skincare routine. In the following infographic, we further discuss who else can be at risk of developing acne papules. Take a look.
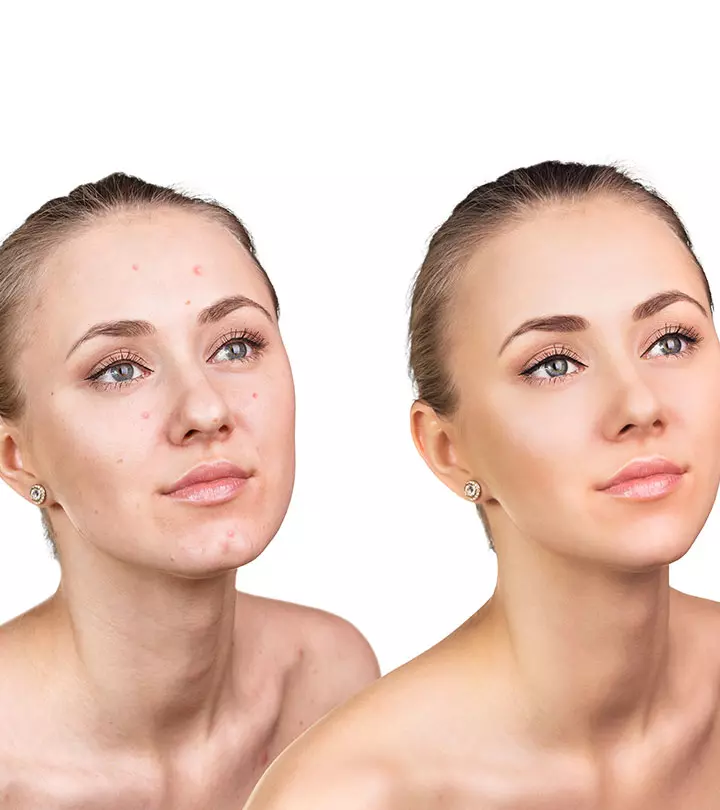
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxAcne papules are small, red skin lesions that are commonly found on the face, upper back, and shoulders. Factors such as hormonal changes, poor hygiene, and stress can clog your pores and lead to the development of acne papules. What differentiates papules from pustules and nodules is that the former is a milder form of acne. The good news is you can resort to topical creams and medications for the management of acne papules. If you are looking for natural remedies, you can use green tea or honey to reduce acne. Following simple tips such as a proper skincare routine and a balanced diet can prevent acne papules from developing in the first place.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I pop or squeeze acne papules?
Dr. Geige strongly advises against popping or squeezing acne papules. She says, “While it may be tempting to try to “clear out” the blemish, doing so can worsen inflammation, increase the risk of scarring, and introduce bacteria deeper into the skin, leading to further breakouts. Instead, focus on gentle cleansing, spot treatments, and seeking professional guidance for safe and effective acne management.”
Is a papule cancerous?
Papules are benign skin growths that do not pose any serious health risk.
How long does a papule last?
Papules may go away on their own. They may take a few weeks or months to fade away completely.
What’s the difference between a papule and a macule?
A papule is a red, small, and bumpy lesion generally on the skin while a macule is an unelevated discolored patch on the skin.
Some thing wrong with illustration image shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxDiscover more about what papules and pustules are in this informative video. Dive into the world of skincare as we unravel the best skincare regime to deal with these skin concerns.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
(i). My Experience with Apple Cider Vinegar
https://www.myinnershakti.com/2012/10/24/my-experience-with-apple-cider-vinegar/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Sex hormones and acne
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28274349/ - Study of psychological stress sebum production and acne vulgaris in adolescents
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17340019/ - Corticotropin-releasing hormone: An autocrine hormone that promotes lipogenesis in human sebocytes
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC124543/ - Double-blind Placebo-controlled Study Assessing the Effect of Chocolate Consumption in Subjects with a History of Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4025515/ - Dairy Intake and Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 78 529 Children Adolescents and Young Adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6115795/ - Significance of diet in treated and untreated acne vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4884775/ - A single-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial evaluating the effect of face washing on acne vulgaris
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17014635/ - Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173/ - Over-the-counter Acne Treatments
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3366450/ - The use of oral antibiotics in treating acne vulgaris: a new approach
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27306750 - Effect of birth control pills on acne in women
https://www.cochrane.org/CD004425/FERTILREG_effect-of-birth-control-pills-on-acne-in-women - Hormonal Treatment of Acne in Women
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2923944/ - Anti-inflammatory Action of Green Tea
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27634207/ - Honey: its medicinal property and antibacterial activity
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3609166/
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
- Laura Geige is a medical aesthetician with seven years of experience in laser aesthetics, injectables, neuromodulation, cosmetic dentistry, oral surgery, medical devices, skin conditions, and skin care. She is a clinical trainer for the Harley Academy and an expert advisor helping to formulate products for a beauty brand.
 Laura Geige is a medical aesthetician with seven years of experience in laser aesthetics, injectables, neuromodulation, cosmetic dentistry, oral surgery, medical devices, skin conditions, and skin care. She is a clinical trainer for the Harley Academy and an expert advisor helping to formulate products for a beauty brand.
Laura Geige is a medical aesthetician with seven years of experience in laser aesthetics, injectables, neuromodulation, cosmetic dentistry, oral surgery, medical devices, skin conditions, and skin care. She is a clinical trainer for the Harley Academy and an expert advisor helping to formulate products for a beauty brand.
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.