PCOS Hair Loss: Causes, Signs, Treatment, Remedies, And More
Understand all about managing the hair loss associated with this hormonal disorder.
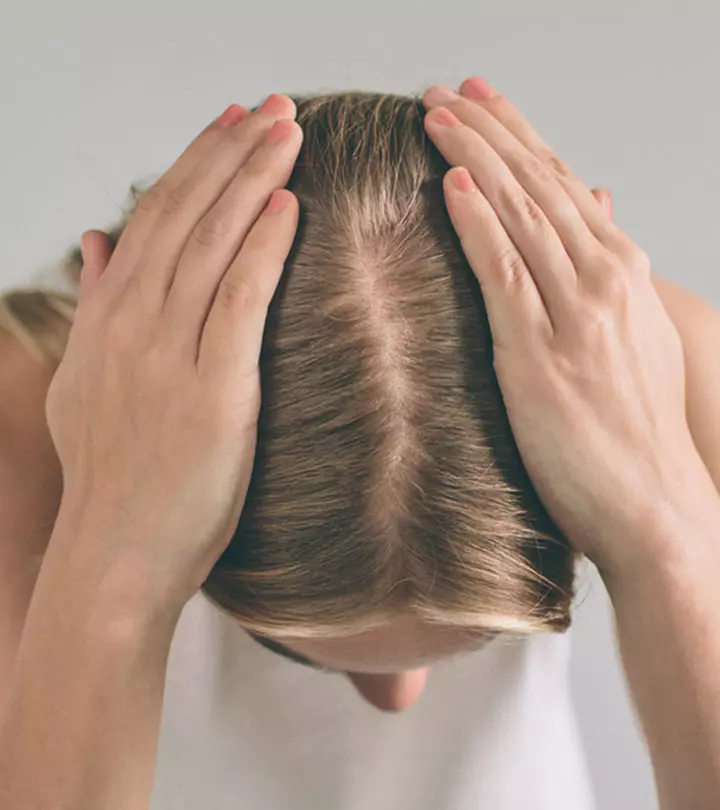

Image: Shutterstock
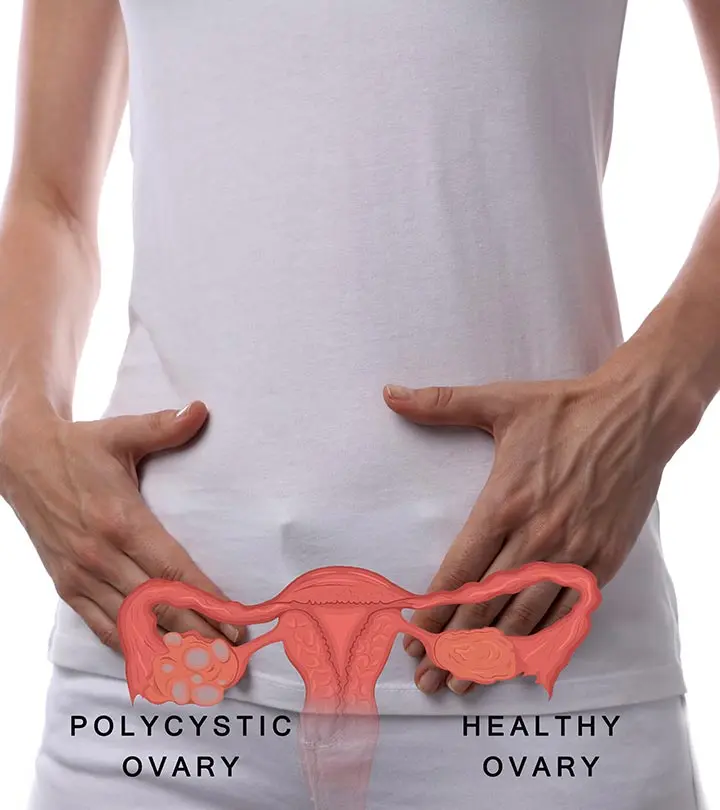
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common reproductive and hormonal disorder that affects 6-10% of the female population (1). It may cause irregular periods, weight gain, mood swings, and infertility. However, the relationship between PCOS and hair loss is quite interesting. While this disorder can cause hair loss and thinning on the front and in the center of your scalp, it can also induce hair growth on your face and the rest of your body (hirsutism). Fortunately, you can manage PCOS hair loss with the right treatment. Learn all about PCOS hair loss, its causes, symptoms, and how to treat it with medications and home remedies in this article. Keep reading!
In This Article
Why Does PCOS Cause Hair Loss?
PCOS is a reproductive disorder (also impacts metabolic processes) that causes enlarged ovaries with small cysts. The female body produces androgens or male hormones like testosterone that trigger puberty, hair growth, and other metabolic functions.
PCOS triggers excess androgen and dihydrotestosteronei An endogenous male sex hormone that stimulates the development of male sex characteristics. (DHT) production in women that regulates the hair growth cycle and blocks the hair follicles, leading to shorter, thinner hair and eventually, hair loss (1).
PCOS may trigger female pattern hair loss, and you will experience excess hair growth, and hair loss in different body parts.
Caiti, a blogger, shares the effect symptoms of PCOS hair loss have on her: “I lose hair ALL the time. I know it’s normal to lose some, but you wouldn’t believe how much I lose. The hairdresser told me I was balding, and I cried. I knew she was right, but it’s hard to hear (i)!”
Here is how you can differentiate PCOS hair loss from other types of hair loss.
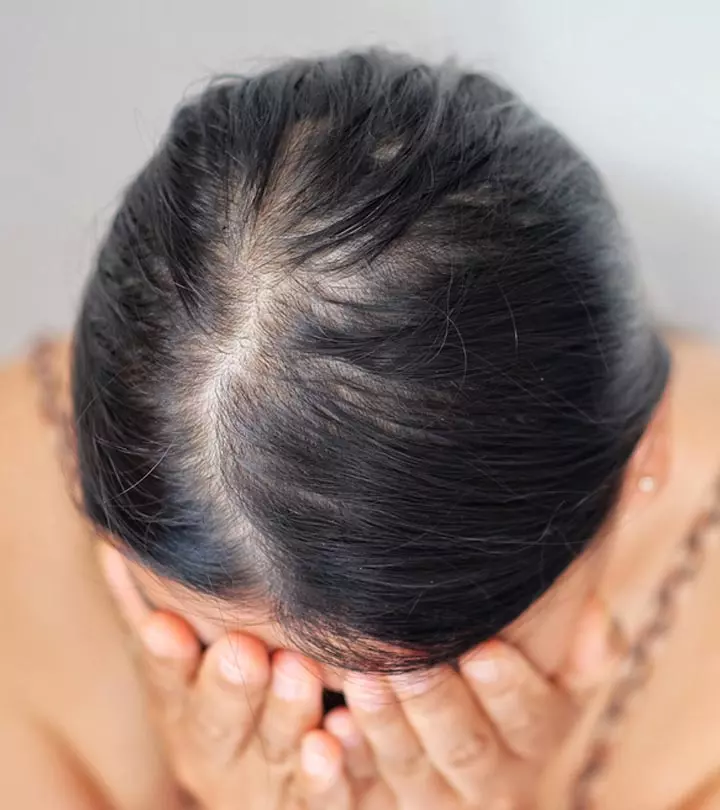
PCOS hair loss starts with hair thinning, especially at the frontal and the vertex (middle) region of the scalp. This is also known as androgenetic alopecia or female pattern hair loss, commonly associated with PCOS (2). However, PCOS hair loss does not involve any scarring, which means the hair follicles may still be active.
An early diagnosis is crucial for treating PCOS hair loss. If left untreated, PCOS may cause permanent hair loss and baldness. Here are the treatment options you should consider.
PCOS Hair Loss Treatment
1. Suppress The Male Hormone Production
To suppress excess androgen production, the doctor may suggest:
- Oral Contraceptive Pills: These pills contain estrogen that can lower the androgen levels (3). They can be used simultaneously with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors for treating hair loss.
- Antiandrogens: Research found that a daily dose of 250 mg of flutamide can reduce hair loss and improve female pattern baldness or alopecia (4).
2. Block Excess Male Hormones
This can be done by using antiandrogens like:
- Spironolactone (Aldactone): It blocks DHT and prevents hair loss. Spironolactone is popularly prescribed for treating hair loss in androgen excess cases (2).
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This FDA-approved drug promotes hair growth. A 2% minoxidil solution can increase hair count and weight (2), (5), (6). It may take a few months to show results (2). However, it may also cause side effects like allergic reactions or contact dermatitisi A skin condition where the skin develops rashes and irritation after coming in contact with an irritant or allergen. . Hence, consult a doctor before using minoxidil.
- Finasteride (Propecia) And Dutasteride (Avodart): There is limited evidence regarding the efficacy of using finasteride for hair loss caused due to hair loss. However, both finasteride and dutasteride are approved by the FDA for treating male pattern hair loss. Finasteride is shown to stabilize alopecia in women with hyperandrogenismi The effect of excessive male sex hormones, such as androsterone, androstenedione, and testosterone in women. (7). However, pregnant women should avoid it as it may cause genetic abnormalities in the fetus (8).
- Diane-35: This drug contains cyproterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol. It is shown to reduce hair loss and hair thinning within 6-9 months (9).
3. Cosmetic Procedures
The doctor may also suggest procedures like hair transplant and laser phototherapyi A non-invasive treatment that uses light energy to improve cell growth and regenerate hair follicles. , and microneedling with PRP (dermarollingi A minimally invasive treatment where a device is used to stimulate hair follicles by creating micro tears to increase hair growth. ) for covering bald spots. A study on male patients showed that laser phototherapy could stimulate hair growth (10). Hence, it may also work for female pattern hair loss.
4. Take Biotin Supplements
Biotin supplements are a popular method for treating hair and nail-related issues. While there is limited evidence to support the efficacy of biotin in reducing hair loss, a few case studies have suggested that it might be helpful to some extent. Hair loss is one of the symptoms of biotin deficiency and a study found that taking biotin supplements may help promote hair growth in those with low serum biotin levels. The same study also found that biotin supplements didn’t reduce hair loss in people with optimal serum biotin levels (11). You may take biotin only if you have a biotin deficiency. However, consult a doctor before taking the supplements to avoid any adverse effects.
Other than medical treatment options, you may also try home remedies to manage hair loss.
Home Remedies For PCOS Hair Loss
1. Fenugreek Seeds
As per anecdotal evidence, fenugreek seeds may help improve hair health and minimize hair fall.
You Will Need
- Fenugreek seeds
- A glass of warm water
- Honey (optional)
Process
Soak the fenugreek seeds in a glass of warm water overnight. You may add honey to this water and drink it early in the morning on an empty stomach.
2. Aloe Vera
Anecdotal evidence suggests that drinking a glass of aloe vera juice early in the morning on an empty stomach can regulate hormonal imbalances and may help reduce hair loss.
You will need
- Aloe vera juice
- 1 glass of warm water
- Honey (optional)
Process
Mix aloe vera juice in water. You can add honey (if required) and consume it every day early in the morning.
3. Cinnamon
Including cinnamon in your diet may help regulate hormone levels and minimize hair loss. However, there is no scientific evidence to prove these effects.
You will need
- A teaspoon of cinnamon powder
- 1 glass of hot water
- Honey (optional)
- ½ teaspoon lemon juice (optional)
Process
Mix cinnamon powder, honey, and lemon in a glass of warm water and drink on an empty stomach for best results.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Following a healthy, nutrient-rich diet is crucial for managing PCOS symptoms, including hair loss. Here is what you can eat to prevent PCOS hair loss.
What To Eat and Avoid To Prevent PCOS Hair Loss?
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Consume vitamin and antioxidant-rich foods, such as whole grains, eggs, healthy fats from nuts and avocado, spinach, citrus fruits, and carrots. A well-balanced diet provides the essential nutrients to your body to stay healthy and prevent hair loss. Consult a doctor to check if you need nutritional supplementation
- Protein-Rich Foods: Include sufficient proteins in your diet. Insufficient nutrients and protein levels in the body are linked to hair loss (12). Consume lean protein like fish, chicken, and lentils.
- Consume Zinc-Rich Foods: Research found that zinc supplementation in patients with PCOS could decrease hair loss (13). Consume foods, such as oysters, chickpeas, yogurt, beans, nuts, and whole grains (14). You may also consult the doctor and take zinc supplements.
- Eat Foods Rich In Iron: Include white beans, nuts, lentils, spinach, kidney beans, and peas in your diet (15). This is because iron deficiency may cause hair loss (12).
- Take Multivitamins: You may take multivitamin supplements to combat the lack of vitamins and minerals in your body. Consult a doctor for the proper dosage.
- Avoid eating processed foods, such as refined flour (like white bread, pizza dough, regular pasta, white rice), sugar, fried, and fast foods. These inflammatory foods can exacerbate metabolic conditions, such as insulin resistance, common in PCOS (16).
If you are wondering if hair loss from PCOS can be reversed, here is the answer.
Is PCOS Hair Loss Reversible?
Yes, it is reversible if the hair follicles are still active. There are medical treatments available to prevent hair loss and stimulate hair growth from the active hair follicles.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipInfographic: Top 7 Ways To Treat PCOS Hair Loss
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. One of the most distressing symptoms that they experience is hair loss. But don’t worry. The good news is there are various home remedies and medical treatments that can help treat PCOS hair loss. Check out this infographic to know more!

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
If you have PCOS hair loss, your hair starts thinning on the front and center of your scalp. Scalp hair loss is one of the common symptoms of PCOS, and it can get very annoying and stressful. Most people tend to become self-conscious about how they look. However, you can reverse and manage this condition. The right treatment and timely diagnosis can prevent thinning hair and promote hair regrowth. There are several medical treatments, cosmetic procedures, and home remedies to treat PCOS hair loss. Consult a doctor if the condition persists.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Metformin help with PCOS hair loss?
Yes, research suggests that Metformin can help reduce hair fall in people who take it as a treatment for PCOS (17).
Can PCOS cause B12 deficiency?
Studies suggest that people with PCOS and low insulin resistance tend to have low concentrations of serum vitamin B12 when compared to those without insulin resistance (18).
Can people with PCOS drink milk?
While low-fat milk and dairy products could have a positive effect on PCOS, people with acne-prone skin or lactose intolerance are advised to avoid them.
Is oily hair a sign of PCOS?
Yes, the hormonal imbalance may lead to excess sebum production resulting in greasy hair, oily skin, and acne.
How long does it take for metformin to work on PCOS?
It may take about 6 months to see results in menstrual regularity and lower BMI when people with PCOS are treated with Metformin (19).
Key Takeaways
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder causing excess production of male hormones in females.
- It is characterized by alopecia, which may lead to permanent baldness.
- It can be managed with biotin or zinc supplements, cosmetic procedures, and home remedies.
- Eating a well-balanced diet is crucial to managing PCOS hair fall.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: current status and future perspective
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4341818/ - Female Pattern Hair Loss
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3968982/ - Hair Loss in Women
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26807794_Hair_loss_in_women - Treatment of hyperandrogenic alopecia in women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12524069/ - Androgenetic alopecia in the female. Treatment with 2% topical minoxidil solution
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8129407/ - A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 5% and 2% topical minoxidil solutions in the treatment of female pattern hair loss
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15034503/ - Hair loss in women with hyperandrogenism: four cases responding to finasteride
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12399766/ - Androgenetic Alopecia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430924/ - [Assessment of efficacy of Diane-35 in androgenetic feminine alopecia]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12923971/ - HairMax LaserComb laser phototherapy device in the treatment of male androgenetic alopecia: A randomized, double-blind, sham device-controlled, multicentre trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19366270/ - Evaluation of serum level of biotin and effect of biotin replacement therapy in patients with telegon effluvium
https://bjas.journals.ekb.eg/article_189588_bb48cf1f99678c618b84566c772b3ba4.pdf - Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315033/ - Effects of Zinc Supplementation on Endocrine Outcomes in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26315303/ - Zinc
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/ - Iron
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-Consumer/ - Inflammation in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Underpinning of insulin resistance and ovarian dysfunction
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3309040/ - Comparison clinical and metabolic effects of metformin and pioglitazone in polycystic ovary syndrome
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27867884/ - Obesity and insulin resistance associated with lower plasma vitamin B12 in PCOS
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20021721/#:~:text=Insulin%20resistance%2C%20obesity%2C%20and%20elevated,12 - Metformin effects on clinical features, endocrine and metabolic profiles, and insulin sensitivity in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 6-month trial, followed by open, long-term clinical evaluation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10634377/
Read full bio of Dr. Shruti Chavan
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Swathi E