6 Health Benefits Of Popcorn, Nutritional Facts, & Side Effects
You don't have to compromise on taste for health when it comes to this snack!

Image: Shutterstock
No “Netflix and chill” session is complete without a huge bowl of popcorn! Popcorn snacks are preferred over many low calorie snacks. As it is made with whole grain, it is believed to be loaded with important nutrients that offer a variety of health benefits. It is claimed to reduce the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension.
In this article, we will see what experts have to say about these purported benefits of popcorn, its side effects, and popcorn nutritional profile as well.
 Know Your Ingredient: Popcorn
Know Your Ingredient: PopcornWhat Is It?
A puffed up snack made when corn kernels are heated up.
What Are Its Benefits?
Boosts digestion, reduces constipation, aids weight management, may reduce the risk of heart diseases, reduces abdominal discomfort, and improves skin and gut health.
Who Can Use It?
It is a low-calorie snack, ideal for those looking to lose weight. It has a good fiber content for those with digestive issues.
How Often?
You can eat it daily but in moderation.
Caution
People allergic to corn should avoid it. Packaged popcorn contains sodium and fat that may affect those with high blood pressure, impact weight loss and digestive health, and cause other health issues.
What Is Popcorn?
Popcorn is made by heating corn kernels that contain starch. It is a very popular snack all over the world. Some strains of corn (Zea mays) are grown only for popping corn.
Eating popcorn can provide many health benefits due to its nutrient profile and low-calorie count. As one cup (8 g) of popcorn contains only 31 calories and a decent amount of fiber, it is the perfect snack for anyone trying to lose weight (1).
 Trivia
TriviaKnow what nutrients make popcorn so healthy in the next section.
In This Article
Popcorn – Nutritional Facts
100 g of popcorn contains the following nutrients (1):
Energy | 387 kcal |
Water | 3.32 g |
Protein | 12.9 g |
Fiber | 14.5 g |
Iron | 3.19 mg |
Magnesium | 144 mg |
Phosphorus | 358 mg |
Potassium | 329 mg |
Zinc | 3.08 mg |
Vitamin B6 | 0.157 mg |
Lipid | 4.54 g |
Popcorn healthy snacks are made of 100% natural whole grain, which makes it one of the best snack options. Scroll down to learn about all the health benefits offered by popcorn.
Health Benefits Of Popcorn
1. May Aid Weight Loss
Popcorn is a satiating food, i.e., it makes you feel full. It is 1.6 times more satiating than potato chips. Thus, it reduces the feeling of hunger and helps in managing body weight (2). A cup of air-popped popcorn also contains only 31 calories (1).
Popcorn can be seasoned with other healthy ingredients like spices and nuts to make it taste better and even healthier.
2. May Reduce The Risk Of Heart Disease
Cereals such as maize may help in reducing the risk factors of coronary heart diseases. It contains polyunsaturated oil, and fiber found in maize may also help reduce LDL cholesterol in your body (3).
Moreover, whole grain foods contain a low amount of saturated fats and bad cholesterol, which may help in reducing the risk of heart disease (3). However, moderation is key while eating popcorn.
3. May Reduce Constipation
Popcorn contains a good amount of fiber, which can improve your gut health. Dietary fiber intake can prevent and treat constipation in children and adults (4). However, research linking popcorn consumption with managing constipation is limited.
4. May Improve Digestive Health
According to a study conducted at the University of Miami, corn fiber improves laxation (loosening of the bowel). Adding corn fiber to your diet also reduces abdominal discomfort (5). These actions together may improve your digestive health when you eat popcorn in moderation.
Adults who consume healthy foods such as milk, whole grains, and popcorn had a 0.73 and 0.67 chance of being diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease, respectively, according to a survey of 33,672 people. Those who consumed cereals, fries, and other junk food had a 1.50 and 1.48 times greater chance of being diagnosed with IBD, respectively. As a result, eating whole-grain foods like popcorn can help reduce the risk of IBD.
5. May Promote Skin Health
Popcorn antioxidants are called polyphenols (2). Polyphenols are naturally occurring chemicals derived from plants, fruits, and vegetables. They fight oxidative stress to protect your skin from any damage (6).
 Fun Fact
Fun FactThe graph below shows the antioxidant content of raw and popped kernels of popcorn using two tests that measure the phenolic content present in popcorn. The study succeeded in proving that there is no reduction in the polyphenolic content when popcorn is exposed to heat, in this case, popped. It remains the same and can be considered a good source of polyphenolic antioxidants that can help protect your skin upon consumption.
6. May Help Boost Mood
Grains like corn contain tryptophan, a naturally occurring amino acid that may help increase the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with feelings of well-being and happiness. A study showed that a diet rich in tryptophan may influence brain serotonin levels (7). This indicates the potential for popcorn to have a positive impact on mood and cognition. However, more studies are required to prove these claims.
Also, remember that the relationship between diet and mood is complex and influenced by various factors, including genetics and individual differences. Still, incorporating tryptophan-rich foods like corn or popcorn into your diet may be a simple and natural way to potentially enhance your mood and overall mental health.
Antioxidants In Raw And Popped Popcorn
Source: Analysis of Popcorn - Zea Mays L. var. Everta- for Antioxidant Capacity and Total Phenolic ContentDietary polyphenols also prevent UV-induced skin photodamage and reduce the risk of skin cancer (8). However, more research is required to understand how popcorn can improve your skin.
Is popcorn healthy? The answer depends on how it’s prepared and consumed. While popcorn benefits are many, it’s also important to be aware of the disadvantages of eating popcorn. Popcorn itself is a nutritious food but you may add things to it that make it unhealthy. For example, adding loads of butter, salt, or oil to your popcorn increases the calorie and saturated fat content and negates some of its benefits.
Let us check out the potential downsides of excess popcorn consumption in the next section.
Side Effects Of Popcorn
1. May Aggravate Gastrointestinal Disorders
Popcorn kernels may cause large bowel obstruction by forming a phytobezoar. Gastric bezoars cause abdominal pain, acid reflux, and distention. In the small bowel, they can cause constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distension, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and weight loss (9).
2. Shortening Of Breath And Wheezing
Butter-flavored microwave popcorn contains diacetyl, which can cause a condition called popcorn lung (bronchiolitis obliterans). Shortness of breath and wheezing are symptoms of popcorn lung. Diacetyl is also dangerous when it is inhaled in large amounts (10). However, this is a very rare side effect of popcorn.
3. Allergic Reaction
People who are allergic to corn should avoid eating popcorn. Seek immediate medical help if you experience symptoms like swollen mouth or difficulty in breathing.
People with inflammatory bowel disease should also avoid popcorn as it may cause bowel irritation. However, not enough research exists in this regard.
Jenny Fox, a blogger, experiences an allergic reaction to popcorn if she has it after 8 p.m. Her body retains water from the salt which makes her puffy. On her blog, she writes, “But even the healthy way, I have my rules — no popcorn after 8 p.m. I know it sounds silly, but it never fails. Popcorn after 8:00 makes me puffy (i).”
Most of these side effects are rare and subside in a day or two with medical assistance.
One popular benefit associated with popcorn consumption is weight loss. Learn how popcorn helps with weight loss in the next section.
Can You Eat Popcorn For Weight Loss?
When paired with a balanced diet, popcorn can aid in weight loss. Air-popped popcorn (without any added flavors) is low in calories, fat, and sugar and high in fiber (1).
Popcorn also reduces hunger and helps in managing your body weight (2). You need to make sure that you do not add any fatty seasonings (like butter or oil) to it.
Popcorn is a better snack than potato chips and butter cookies. It is naturally fat-free and low in sugar, so you can savor it without any worry.
However, there is one thing that you need to keep in mind. If you are eating microwave popcorn or store-bought popcorn regularly, you may be taking in a lot of extra salt and calories, as well as potentially harmful artificial ingredients. Therefore, homemade popcorn made with olive oil or avocado oil can be a healthy addition to your diet.
 Fun Fact
Fun FactPopcorn is a whole grain, so it easily fits into many diets. But, can people with diabetes eat it? Keep scrolling to know more.
Is Popcorn Healthy For People With Diabetes?
Brenda Peralta, a registered dietician, says, “Popcorn is a good choice for those that have diabetes. Although it is a carb, it is a carb high in fiber. This means that it won’t spike your sugar levels as much. To have better control of your sugar levels, try adding healthy fat along with popcorn. For example, have some popcorn with almonds as a healthy snack.”
Infographic: How To Make Popcorn Easily At Home?
Popcorn is a popular snack around the world. It has a rich nutrient profile and low calorific values. Making perfect popcorn at home is easy. Click on the infographic below to learn how to do it with just a few ingredients. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team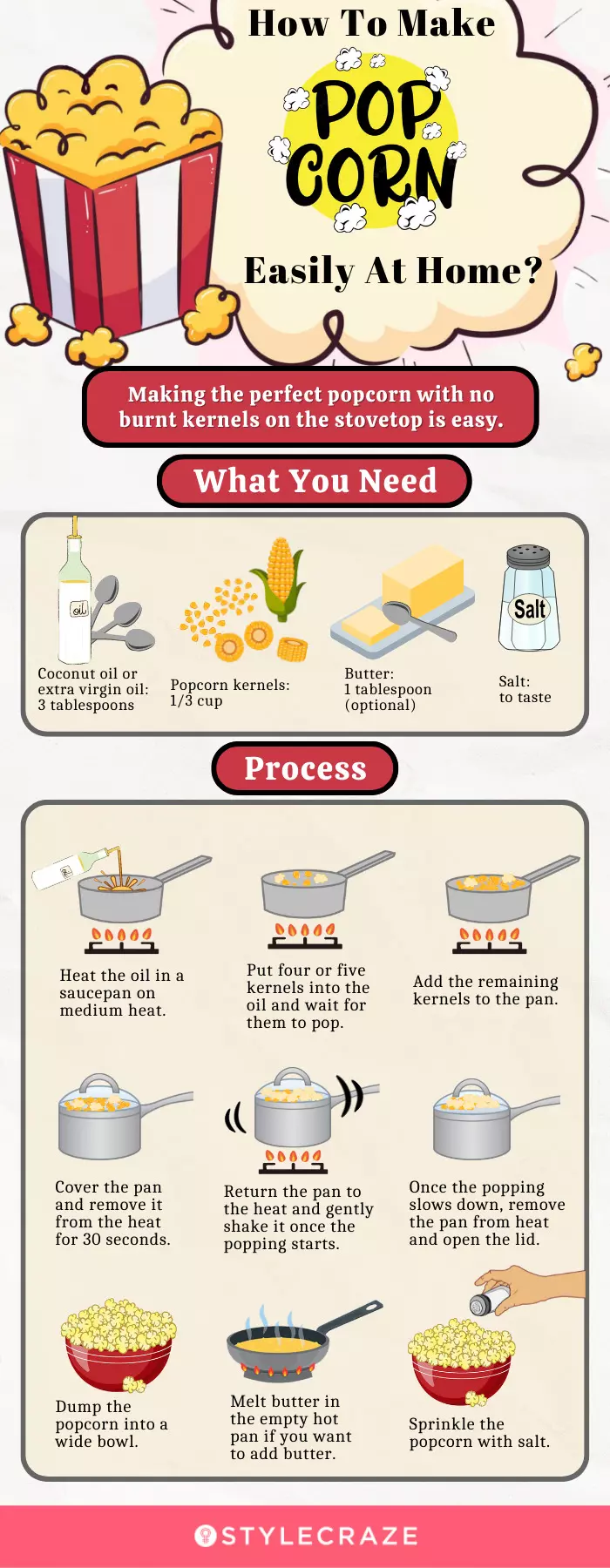
The health benefits of popcorn can be attributed to the whole grain and nutrients in it. Its low calorific value also adds to these benefits. Popcorn promotes satiety and aids in weight loss. In addition, the popcorn fiber reduces LDL cholesterol levels and minimizes the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Popcorn also reduces constipation and improves digestive health. The polyphenols and antioxidants in popcorn promote skin health. But, if consumed in excess, popcorn aggravates gastrointestinal disorders and may trigger allergic reactions in people with a corn allergy. However, having it in moderation along with a balanced healthy diet helps in reaping its benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it OK to eat popcorn every day?
As long as it is consumed in moderation, popcorn without artificial additives is safe to eat every day.
Is it safe to eat popcorn at night?
Yes. No scientific evidence suggests that a particular time to eat popcorn is better than another.
What is the healthiest popcorn to eat?
Air-popped, organic popcorn is considered the healthiest option to eat among all types of popcorn.
How much popcorn a day is healthy?
While the recommended daily intake of popcorn depends several factors like age, gender, weight, level of activity, and overall dietary needs, the intake of 25-30g of popcorn is considered healthy for daily consumption.
What is the best age to eat popcorn?
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that popcorn should not be given to children under the age of four (11).
Is popcorn gluten-free?
Yes. Popcorn is considered naturally gluten-free (12).
Is popcorn from India?
No, popcorn did not originate in India. It is believed to have come from Mexico.
Are there any precautions I should take when eating popcorn, such as avoiding unpopped kernels or seasoning with excess salt?
Yes, avoid eating popcorn with toppings and unpopped kernels, and also ensure you are consuming it in moderation.
Is it safe to eat flavored popcorn, such as caramel or cheddar popcorn?
Yes, eating these types of popcorn in moderation is essential to avoid side effects like gas or bloating.
What are the nutritional values of different types of popcorn, such as air-popped, microwave, or movie theater popcorn?
Air-popped, microwave, and movie theater popcorn contain 110, 122, and 169 calories respectively. Movie theater popcorn has higher carb and fat content than microwave and air popped popcorn while it has a lower protein content compared to the other two (1), (13), (14).
Key Takeaways
- Popcorn is a low-calorie snack with a decent amount of fiber.
- Air-popped and unsalted popcorn helps relieve constipation, reduces the risk of heart disease, aids weight loss, and promotes skin health.
- However, in some cases, popcorn may cause the formation of a gastric bezoar, shortness of breath, or an allergic reaction.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Popcorn is a healthy snack that can help you stay fit. Watch this video to learn about the important benefits of including this favorite movie snack in your diet.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. I’m puffy. The “popcorn hangover” and other morale saboteurs.https://thesveltegourmet.blogspot.com/2009/11/im-puffy-popcorn-hangover-and-other.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Snacks popcorn air-popped
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167959/nutrients - Analysis of Popcorn (Zea Mays L. var. Everta) for Antioxidant Capacity and Total Phenolic Content
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356482/#!po=66.3793 - Cereal grains and coronary heart disease
https://idp.nature.com/authorize?response_type=cookie&client_id=grover&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Farticles%2F1601283 - Effect of dietary fiber on constipation: A meta-analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544045/ - The Role of Fiber in the Treatment of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Children
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6267171/ - Dietary Polyphenols and Their Effects on Cell Biochemistry and Pathophysiology
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2012/583901/ - The relationship between whole-grain intake and measures of cognitive decline, mood, and anxiety—a systematic review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10334137/ - Polyphenols: Skin Photoprotection and Inhibition of Photocarcinogenesis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3288507/ - Colonic Phytobezoar Caused by Popcorn Kernels Resulting in a High-Grade Large Bowel Obstruction
https://clinmedjournals.org/articles/ijsrp/international-journal-of-surgery-research-and-practice-ijsrp-5-071.php?jid=ijsrp - Bronchiolitis obliterans and consumer exposure to butter-flavored microwave popcorn: a case series
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22550695/ - Prevention of choking among children
https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/125/3/601/72642/Prevention-of-Choking-Among-Children?autologincheck=redirected - Gluten-free cereals and pseudocereals as a potential source of exposure to toxic elements among polish resident
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9182656/ - Popcorn, microwave, low fat and sodium
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168139/nutrients - Popcorn, movie theater, unbuttered
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1101362/nutrients
Read full bio of Rowinda Dimech
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan






























