4 Benefits Of Retinaldehyde For Your Skin You Should Know
This powerful and skin-nourishing ingredient may be the answer to all your skin woes.

Image: ShutterStock
Vitamin A helps reduce wrinkles, prevent hyperpigmentation and premature aging, and improve skin tone (1). As a derivative of vitamin A, you can also use retinaldehyde for skin issues. It is one of the best solutions to minimize your skincare woes. Using it daily may help improve your skin health and improve aging signs like wrinkles and fine lines.
Due to its fewer side effects, retinaldehyde is considered a better alternative to retinol (another derivative of vitamin A) (2). This article discusses the benefits of retinaldehyde for the skin, how to use it, and the precautions to keep in mind. Read on.
 Know Your Ingredient: Retinaldehyde
Know Your Ingredient: RetinaldehydeWhat Is It?
A vitamin A derivative with anti-aging properties.
What Are Its Benefits?
Stimulates skin cell turnover, improves skin firmness and elasticity, and decreases the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and rough skin.
Who Can Use It?
People who want to reduce wrinkles, even their skin tone, and treat acne.
How Often?
Begin by using it two to three times a week. Once your skin becomes accustomed to it, you can even use it daily.
Caution
It may result in inflammation, scaly skin, dryness, and redness. Avoid using it with products containing vitamin C, BHAs, or AHAs, as this can make your skin more sensitive and irritated.
What Is Retinaldehyde?

Retinaldehyde is a stabilized form of vitamin A that converts to retinoic acid when applied topically. Retinoids like retinyl palmitate, retinol, and retinaldehyde convert to retinoic acid for the skin to make use of them. Their potency and efficacy depend on this conversion process. The retinoid gets weaker as the number of steps for its conversion increases. Retinaldehyde forms retinoic acid in just one conversion process and is more potent than other retinoids.
Retinaldehyde products may help treat acne. They may also reduce the signs of premature aging.
 Trivia
TriviaWe discuss the benefits retinaldehyde can have for the skin in the next section.
In This Article
What Are The Benefits Of Retinaldehyde For The Skin?

Among all the antioxidants for the skin, retinaldehyde is the one gentle enough for sensitive skin. It causes less irritation compared to its counterparts. It helps reduce wrinkles, lighten skin tone, rejuvenate skin, and treat acne. Retinaldehyde also speeds up skin cell turnover, reduces hyperpigmentation, and stimulates collagen production.
1. May Improve Skin Tone
The production of new skin cells to replace the existing ones (called skin cell turnover) slows down with age. Retinaldehyde (tretinoin) accelerates skin cell turnover and can make skin smooth and even-toned (3). A study shows that the use of cosmetic cream with retinaldehyde in it has improved the melanin index of the group (4).
2. May Improve Skin Texture And Hydration
Retinol, retinal and retinoic acid have the same biological features as vitamin A (3). Like retinoic acid, retinaldehyde is a retinoid that helps boost the production of epidermal proteins with less irritability. This may improve skin texture and hydration. A study shows that the ingredient is well tolerated and improves skin hydration and texture (4).
3. May Reduce Acne
To treat acne issues, usually one can do retinoid treatments that reduce sebum production and antibiotics that fight bacterial infections. Since retinaldehyde is a retinoid that has antibacterial properties, it may help reduce acne. A study shows that daily application of retinaldehyde has reduced the density of propionibacterium acnesi The bacteria that causes acne that is most common around the sebaceous glands (nose, chin, forehead, and back). (5).
Ashley Worsham, a blogger, shared her experience of using tretinoin for cystic acne in her blog. She said, “I woke up Sunday morning after applying it directly to my skin and all was well. I didn’t notice any irritation, just a little dryness, and I made sure to apply extra moisturizer and sunscreen while on a hike that day (i).”
4. May Reduce Aging And Photoaging Signs
Use of retinaldehyde increases epidermal thickness and cutaneous elasticity (6). This makes the skin thicker and more elastic, helping in reducing wrinkles and fine lines. Thus, it benefits the skin against aging signs. Studies also show it is an effective topical agent against
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?photoagingi Premature aging of the skin caused by prolonged exposure to sunlight, causing wrinkles, sun spots, and loose skin to appear. signs (7).
Retinaldehyde appears to be superior to other retinoids. But how do they compare?
Retinaldehyde Vs. Other Retinoids

Other retinoids include retinyl palmitate, retinol, retinoic acid, tazarotene, adapalene, and isotretinoin. However, retinoic acid is the purest form, and the other derivatives must get converted to it. Retinaldehyde has the most similar properties to retinoic acid and takes lesser time to convert and has a good tolerance profile (8). The metabolism of retinaldehyde to retinoic acid occurs only by keratinocytesi The cells found in the skin's outermost layer that form a protective layer to heal wounds and suppress inflammation. at an appropriate stage of differentiation. Hence, retinoic acid formed on the skin will be more controlled and shows no adverse effects (1).
People who used retinol and retinyl palmitate products may have had side effects like dry skin, sun sensitivity, flaky skin, peeling, etc. Retinaldehyde might help those with sensitive skin or those who have not seen good results after trying products containing other retinoids.
While retinaldehyde has fewer side effects compared to other retinoids, it is still important to know them. Keep reading.
Side effects Of Retinaldehyde

A common misconception is that retinaldehyde causes breakouts. But the chances are fewer as it helps unclog the pores. However, any other ingredient in a retinaldehyde product can cause breakouts. Retinaldehyde is less likely to have any other side effects. Use it with a moisturizer or minimize the quantity and frequency if you develop flaky skin or redness.
However, the safety of using topical retinoids during pregnancy is a controversial case as there have been cases of birth defects due to topical tretinoin use. Though it is not proved to be the reason for these defects, women are advised to not use topical retinoids, including retinaldehyde, during pregnancy (9).
 Quick Tip
Quick TipYou may now be willing to include retinaldehyde in your skincare regimen as it has fewer side effects. But how can you use it? Read to know more.
How To Use It?

It is important to observe your skin’s reaction after using a new product. Use retinaldehyde at the same frequency if you have already used other retinoid products. Otherwise, start using it twice a week. Apply it every night if the skin reacts positively. Minimize use a few times a week if the skin turns red or dry.
Apply only a pea-sized amount (0.25g) of the product for the whole face. Begin with a product whose retinaldehyde concentration is low. You may gradually use products of a higher retinaldehyde concentration if you do not experience any allergies.
The best products that contain retinaldehyde are face serums, anti-aging serums, eye creams, and face masks. A good retinaldehyde serum brightens the skin and maintains a moisture barrier. Retinaldehyde eye creams help reduce dark circles, fine lines around your eyes, and de-puff the face. Be consistent with your use. The best results may take more than six months.
Infographic: 4 Ways Retinaldehyde Is Great For Your Skin
Retinaldehyde, a derivative of vitamin A, is known for its anti-aging benefits. It is milder than retinol and more suitable for more sensitive skin types. It helps in treating issues like hyperpigmentation, uneven skin tone, and the premature appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Check out the infographic below to learn more about retinaldehyde’s benefits.
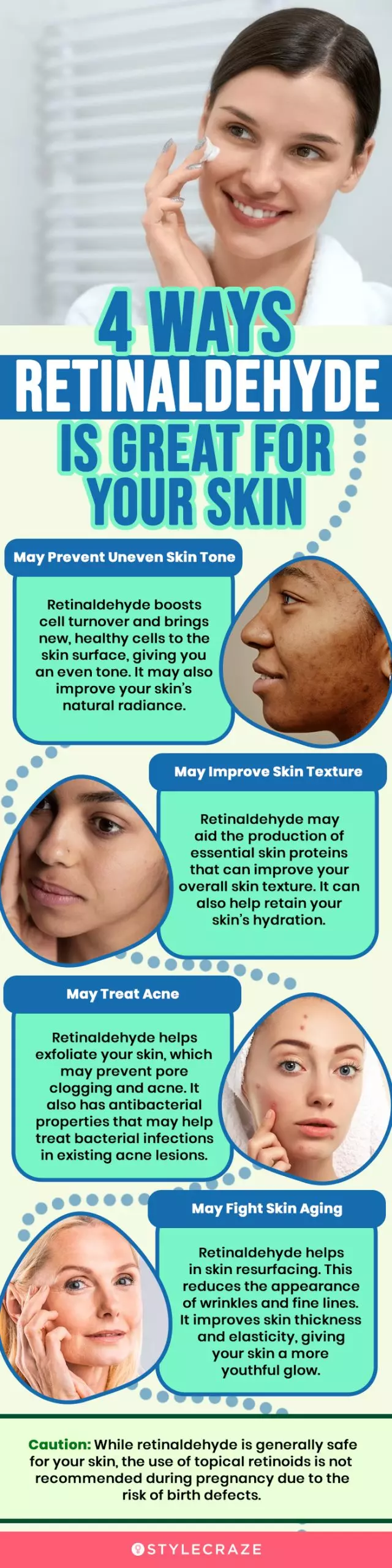
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Retinaldehyde, a derivative of vitamin A, has numerous skincare applications in dermatology. You can use retinaldehyde as a topical treatment for skin issues like wrinkles, uneven skin tone, blemishes, and hyperpigmentation. Due to its good tolerance profile and fewer side effects, it is considered one of the most effective vitamin A derivatives. It is more suitable for sensitive skin, and you can include it in your skin care regimen as serums, anti-aging serums, eye creams, and face masks. However, do a patch test before using retinaldehyde and consult a doctor if you experience any side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use niacinamide with retinaldehyde?
Yes, you can use niacinamide with retinaldehyde. You can either buy a serum or cosmetic cream with both ingredients or use separate products for each.
Can I use retinaldehyde with vitamin C?
No, you should not use retinaldehyde with vitamin C together as it can over-exfoliate your skin, resulting in increased skin sensitivity. If you wish to incorporate both ingredients into your beauty and skincare routine, ensure that you use one ingredient in the morning and the other at night.
What is the highest concentration of retinaldehyde?
The highest concentration of retinaldehyde available in the market is 2%. However, it is recommended to use a lower concentration. As per a study, both 0.1% and 0.05% of retinaldehyde can help treat photoaged skin, and 0.1% retinaldehyde has better results on melanin index (4).
Can retinaldehyde be used in combination with other skincare ingredients, such as vitamin C or AHAs/BHAs, and what are the potential benefits or drawbacks of doing so?
No, retinaldehyde cannot be used in combination with other skincare ingredients, such as vitamin C or AHAs/BHAs, as it can lead to dryness and irritation. Since all these ingredients are highly potent, it is best to use them by themselves. You can use vitamin C in the morning and alternate between retinaldehyde and AHAs/BHAs in your night skincare routine. You may also use skin-soothing skincare ingredients like hyaluronic acid and ceramides in combination with retinaldehyde. Always do a patch test and refer to a dermatologist before trying any skincare activities.
Key Takeaways
- Retinaldehyde is a stabilized derivative of vitamin A that quickly converts to retinoic acid when applied to the skin.
- Applying retinaldehyde may keep your skin hydrated, reduce acne, and improve the overall texture of your skin.
- However, pregnant women should avoid using topical retinaldehyde during pregnancy.
Are you confused about which retinoid to use? Learn about the different types and percentages of retinol, tretinoin, retinaldehyde, and tazarotene in this helpful video!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My Retin-A Journey: Part Ihttps://medium.com/@aaworsham/my-retin-a-journey-part-i-c6acf31e96b3
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2699641/ - Cosmeceuticals: the evidence behind the retinoids
https://academic.oup.com/asj/article/30/1/74/199813 - Retinoids: active molecules influencing skin structure formation in cosmetic and dermatological treatments
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6791161/ - Efficacy and safety of retinaldehyde 0.1% and 0.05% creams used to treat photoaged skin: A randomized double-blind controlled trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29663701/ - Antibacterial activity of retinaldehyde against Propionibacterium acnes
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10473957/ - Efficacy of topical 0.05% retinaldehyde in skin aging by ultrasound and rheological techniques
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10473959/ - Ultrasound imaging demonstration of the improvement of non-ablative laser remodeling by concomitant daily topical application of 0.05% retinaldehyde
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15370406/ - Tolerance profile of retinol retinaldehyde and retinoic acid under maximized and long-term clinical conditions
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10473963/ - Safety of skin care products during pregnancy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3114665/
Read full bio of Dr Ashok Gund
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty
























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.