4 Side Effects Of Indian Gooseberry That Can Make You Think Twice About Consuming It
Amla is a superfood but beware of the surprising adverse effects before consuming it.

Image: iStock
The side effects of Indian gooseberry are worth considering before consuming it. Indian gooseberry (or amla) has been a staple in Ayurvedic medicine. Although it offers a variety of benefits, its excessive consumption can be harmful as well.
Further research is needed to confirm these side effects of amla. Nonetheless, you should understand the dangers of overeating gooseberries. This article examines the side effects of Indian gooseberry and its recommended dosage. Read on.
 Know The Flip Side: Amla
Know The Flip Side: AmlaShort-Term Effects
May cause acidity, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, stomach cramps, and heartburn.
Long-term Effects
May cause dry skin, dehydration, and weight loss.
Drug Interactions
May interact with diabetes, anticoagulant, and antiplatelet medications.
When To See A Doctor
If you experience excessive bleeding, especially post-surgery.
In This Article
What Are The Side Effects Of Indian Gooseberry?
The high vitamin C content in Indian gooseberry can cause problems if consumed in excess. The nutrient may cause acidity and other issues related to stomach acid. The fiber in the fruit may also cause constipation if you eat too many of them.
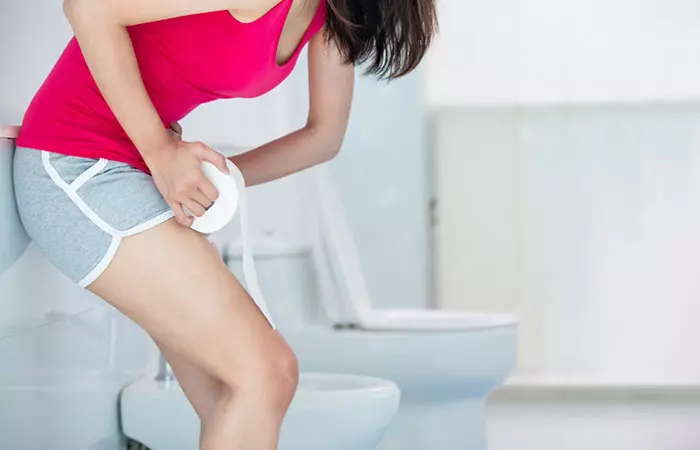
1. May Cause Acidity
Indian gooseberry is the second richest natural source of vitamin C. A single fruit contains over 600 to 700 mg of vitamin C (1).
Excess vitamin C intake can cause digestive distress. This may happen if you consume more than 2,000 mg of the nutrient at one go.
Some research suggests that excess intake of vitamin C may lead to acid reflux and other forms of gastrointestinal upset (2). These effects are more likely to occur in individuals with preexisting conditions.
Excess intake of vitamin C may also be accompanied by headache, dizziness, stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhea and nausea (3). However, findings are not conclusive and we need more research here.
If you experience symptoms of heartburn, there are certain home remedies to treat it. The simplest of those is using baking soda.
You can add a teaspoon of baking soda to a glass of water. Stir well and drink. Baking soda works as a natural antacid and relieves heartburn and other issues related to excess stomach acid (4).
 Trivia
Trivia Trivia
Trivia2. May Cause Constipation
Indian gooseberry is a rich source of fiber (1). While adequate fiber can treat constipation, some believe excess of it can lead to constipation. We need more evidence here, though.
Excess fiber can also have negative effects on colonic transit. It can get fermented rapidly in the colon, leading to a surge of microbial activity. This leads to abdominal cramps and bloating (5).
Consuming too many Indian gooseberries can bulk up and harden your stools.
Easing constipation is simple. All you need are a teaspoon of baking soda and a glass of warm water. Mix the soda in the water and drink the mixture. You will find relief in a short span of time.
If you are experiencing a more serious case of constipation, baking soda may not help. In such situations, please visit a doctor immediately to address the issue.
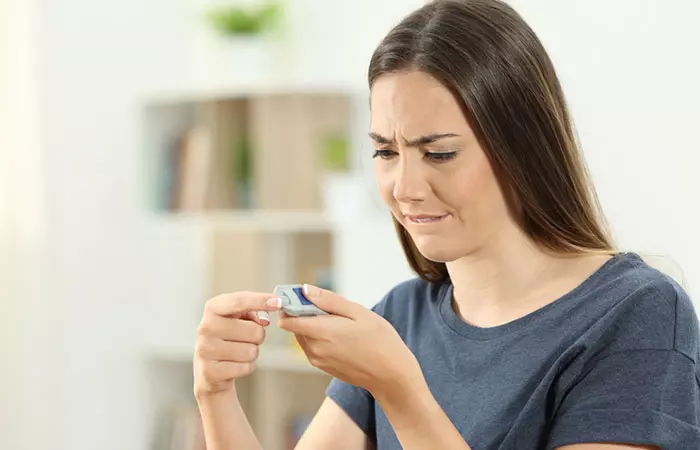
3. May Cause Complications In People With Diabetes
Amla is a popular treatment for diabetes. Extensive research has shown that the fruit exhibits anti-diabetic effects (6). The fruit also helps lower blood glucose levels (7).
These anti-diabetic benefits of amla may prove detrimental for a few individuals. Excessive or incorrect dosages of amla can cause blood sugar levels to fall too low. This can aggravate the situation if the individual is already on diabetes medications. Though it may not be possible to eat too many amlas (due to their sour taste), it is important to be careful.
There is no research that directly links diabetes complications to amla. But it is better you exercise caution and keep your doctor in the loop.
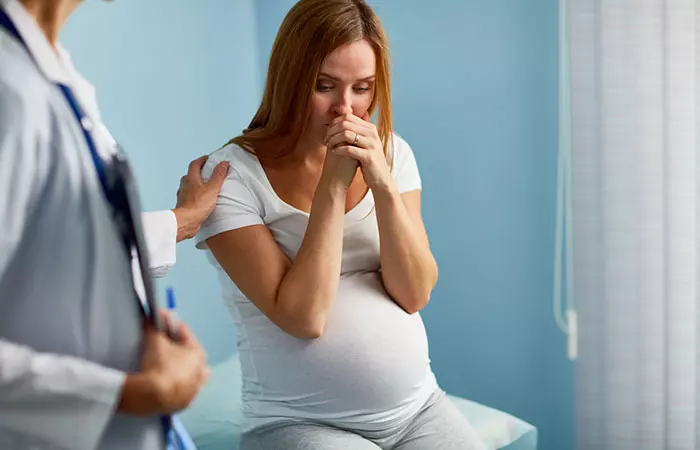
4. Might Cause Problems During Pregnancy
There is no documented evidence of Indian gooseberries causing trouble during pregnancy. But we suggest you check with your doctor before taking it.
While the Indian gooseberry is among the most nutritious foods, the only concern is the consequences of its excess intake. Hence, consume it in moderation.
How many of these gooseberries can you take in a day? Is there any specific dosage we can arrive at?
What About The Dosage?
One Indian gooseberry a day should be fine. This translates to 10 to 20 ml of the gooseberry juice or 4 grams of the powder.
Anything beyond this may cause side effects. If you have any specific medical condition, please consult your doctor on the dosage.
Infographic: 4 Side Effects Of Indian Gooseberry You Should Know
While Indian gooseberry is a great source of vitamin C, excess of it can cause issues. Its high acidic content may cause gastrointestinal issues as it interacts with stomach acids. There are other ways overconsumption of this fruit can harm your health. In the following infographic, we have listed the major side effects of Indian gooseberry to keep in mind. Take a look.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
The Indian gooseberry (amla) has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for its medicinal properties. It is replete with vital nutrients and has several benefits. However, excess consumption of Indian gooseberry may cause several side effects. Its high vitamin C composition may cause acidity and constipation and trigger complications in people with diabetes. It may cause allergic reactions and skin irritation in some people. In addition, it may cause problems during pregnancy too. Hence, an intake of one Indian gooseberry per day is recommended. Remember to consume it in moderation to avoid the above-mentioned side effects of amla juice or amla.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is amla a blood thinner?
Barbara Kovalenko, a nutritional consultant, says, “Amla contains high levels of vitamin C, which is known to have blood thinning properties.” However, more research is needed to determine the specific effects of amla on blood coagulation.
Does amla give you gas?
Kovalenko says, “Some people may experience digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, or loose stools when consuming amla, but it is not universally known to cause gas.”
Does amla increase BP?
Kovalenko says, “There is limited research on the effects of amla on blood pressure, and it is not definitively known to cause an increase in BP.”
Is amla good for heart blockage?
Kovalenko says, “In terms of heart health, amla has been used in traditional medicine to support heart health, but it is not a cure for heart blockages. More research is needed to determine its effects on heart health.”
Can amla cause hair loss?
No. On the contrary, amla has many nourishing benefits for hair and is also known to effectively boost hair health.
Does amla cause liver damage?
No. In fact, research shows amla is beneficial in promoting healthy liver functions (8).
When should we avoid amla?
Much anecdotal evidence suggests that amla is not recommended during and after surgery, as it might increase the risk of bleeding. Also, people with diabetes, gastrointestinal problems, and pregnant and breastfeeding mothers should avoid eating amla.
Does amla remove toxins from the body?
Yes. Much anecdotal evidence suggests that amla, which is high in fiber, can be quite effective at removing toxins from the body.
Is amla safe for kidneys?
The antioxidant activity of amla may be beneficial for the prevention of age-related renal or kidney disease (9).
Can Indian gooseberry cause allergic reactions?
Amla may cause allergic reactions in some people. Much anecdotal evidence suggests that amla may cause skin rashes, hives, nausea, vomiting, itching, dizziness, and swelling around the mouth.
Key Takeaways
- Overconsumption of vitamin C-rich Indian gooseberries may cause acidity.
- Excess or incorrect dosage of Indian gooseberries may cause very low blood pressure and blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
- Eating too many gooseberries may bulk up your stools and cause constipation.
- You can safely consume 1 whole fruit or 10 to 20 ml of Indian gooseberry daily.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Enhancing the functional properties and nutritional quality of ice cream with processed amla (Indian gooseberry), Journal of Food Science and Technology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4648887/ - Vitamin C in Health and Disease, The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15150630-vitamin-c-in-health-and-disease/ - Possible Adverse Health Effects of Vitamin C and Ascorbic Acid, Seminars in Oncology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6364356-possible-adverse-health-effects-of-vitamin-c-and-ascorbic-acid/ - Sodium Bicarbonate, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682001.html - Fiber and colorectal diseases: Separating fact from fiction, World Journal of Gastroenterology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4250613/ - Anti-diabetic Effects of the Indian Indigenous Fruit Emblica Officinalis Gaertn: Active Constituents and Modes of Action, Food & Function, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24577384-anti-diabetic-effects-of-the-indian-indigenous-fruit-emblica-officinalis-gaertn-active-constituents-and-modes-of-action/ - Effect of Amla Fruit (Emblica Officinalis Gaertn.) on Blood Glucose and Lipid Profile of Normal Subjects and Type 2 Diabetic Patients, International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21495900-effect-of-amla-fruit-emblica-officinalis-gaertn-on-blood-glucose-and-lipid-profile-of-normal-subjects-and-type-2-diabetic-patients/ - Hepatoprotective properties of the Indian gooseberry (Emblica officinalis Gaertn): a review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23978895/ - Clinical evaluation of Emblica Officinalis Gatertn (Amla) in healthy human subjects: Health benefits and safety results from a randomized, double-blind, crossover placebo-controlled study, Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6926135/
Read full bio of Madhu Sharma
- Barbara Kovalenko is a nutritional consultant with 4 years of experience in nutrition and mindful eating coaching. She earned her bachelor's degree in nutrition from Bogomolets National Medical University, Ukraine and master's degree from Boston University, USA.
 Barbara Kovalenko is a nutritional consultant with 4 years of experience in nutrition and mindful eating coaching. She earned her bachelor's degree in nutrition from Bogomolets National Medical University, Ukraine and master's degree from Boston University, USA.
Barbara Kovalenko is a nutritional consultant with 4 years of experience in nutrition and mindful eating coaching. She earned her bachelor's degree in nutrition from Bogomolets National Medical University, Ukraine and master's degree from Boston University, USA.
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti