Top 11 Side Effects Of Drinking Beer
From impacting heart health to raising blood pressure, it can harm health in many ways.

Image: Shutterstock
Group of friends, clinking sounds of beer mugs, and lots of laughs. This is how many describe a perfect weekend. But is beer good for you? Are you aware of the side effects of drinking beer? Yes, and most of its side effects are associated with overconsumption of beer regularly.
Many recent studies have clearly stated that there are several health benefits associated with the limited consumption of beer. These benefits can be attributed to brewer’s yeast, a major component in beer. It is rich in nutrients and renders beer with certain healthy properties (1). But moderation is key. Too much of a good thing can be bad – and this definitely applies to beer. If you consume it without considering the limits (which are dependent on your age, medical history, and lifestyle), you may end up with many health issues, like liver damage and pancreatitis. Also, beer intake may not be safe for all. Read on to understand the negative effects associated with excess beer consumption. Making the right changes to your lifestyle today can have positive effects in the long run.
 Know The Flip Side: Beer
Know The Flip Side: BeerShort-Term Effects
It may lead to heartburn, intoxication, and a hangover.
Long-Term Effects
Can cause beer belly, increase blood pressure levels, worsen heart health, and lead to weight gain.
Drug Interactions
Can interact with sedatives and antibiotics.
When To See A Doctor
If you face sudden heartburn, get digestive issues, and have diabetes, you should visit a doctor.
In This Article
11 Side Effects Of Beer Consumption
Beer consumption in moderation can be good for health. However, when you drink in excess or gulp a glass too many in quick succession, it can also have a negative impact on health. Listed below are a few adverse effects of beer:
1. Interferes With The Blood Sugar Level
Beer drinking can actually interfere with your body’s blood sugar levels (2). The liver convertsglycogeni A stored form of glucose found in the liver and muscles that provides energy to cells and helps regulate blood sugar levels. stored in it into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream. Alcohol in beer actually interferes with this process. It can create hunger pangs and will leave you gorging on more food. This can pave the way to weight gain (3). This can be countered by taking a proper meal before gulping down beer.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip2. High In Calories
Commercial beer brands contain fewer amounts of nutrients, but come loaded with calories. This makes them less than ideal for people who are trying to lose excess weight. It makes your body burn fewer calories than it would do normally. The alcohol in beer is converted into acetate by the liver. The body then burns acetate for energy and the excess fat remains stored in parts like the hips and belly (3).
3. Works As Diuretic
When you want relief on a scorching day, a glass of chilled beer comes as a soothing relief. Natural Antidiuretic hormones aid the body to retain fluid and beer slow down the release of this hormone. As a result, you may feel an increased urge to urinate when you gulp down a few glasses of beer (4), (5). It can be especially harmful when you are into athletics. You lose fluid both through urine and sweat in such situations, which can lead to dehydration.
4. Gluten Insensitivity
A majority of beer variants found in the market contain malted barley. Barley contains gluten, a type of protein. Some people are found to be sensitive to gluten (6). If you are among them, opt for beers made with gluten-free compounds to avoid stomach discomfort.
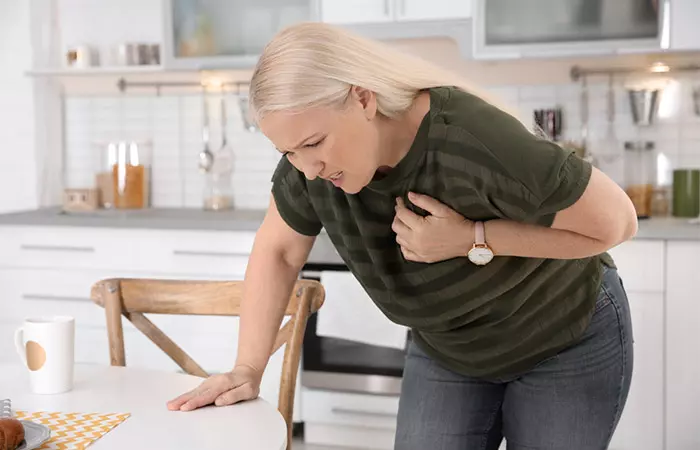
5. May Be Bad For Cardiovascular Health
Some studies have shown that drinking beer can actually be good for the heart, but that happens when you drink in limited amounts. At the time of drinking, alcohol in beer causes increased heart rate temporarily. However, in the long term, overconsumption of beer can result in an ongoing increase in heart rate. Besides, someone who has an existing cardiovascular ailment will not benefit from drinking beer at all. In fact, it will worsen their heart health (7), (8).
A study on the effects of beer consumption on heart health found that total cholesterol level was 65% (548) higher in beer drinkers compared to controls (532), regardless of whether they consumed alcohol-free beer.
6. Can Raise Blood Pressure Level
If you take several glasses of beer a day, it can lead to high blood pressure (9). So, stick to a mug or 2 of beer to keep your blood pressure levels under control.
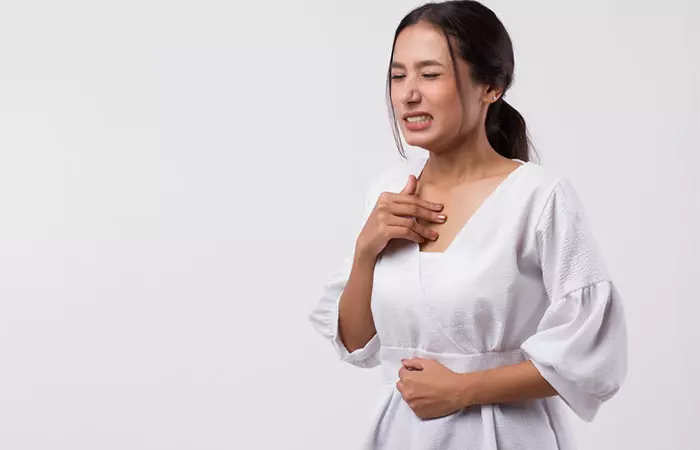
7. Can Lead To Heartburn
Beer contains some stimulants that work with gastric acid, which may lead to the onset of gastro-oesophageal refluxi A digestive disorder where the acidic contents of the stomach flow back into the food pipe and irritate the lining. and result in heartburn (10).
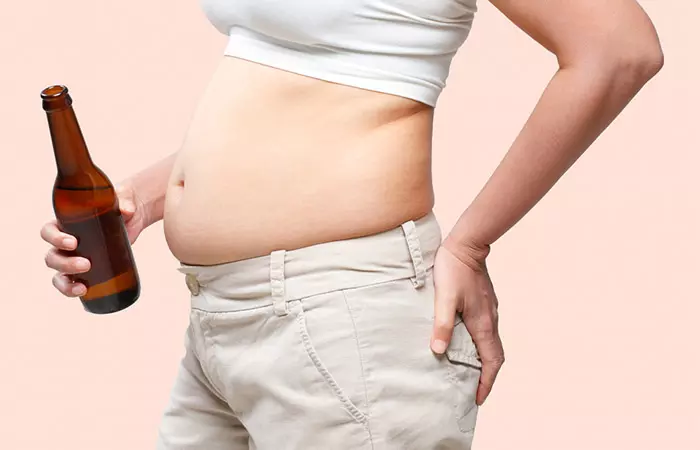
8. You May Develop Beer Belly
If you are proud of your slim waistline, it is time you quit drinking beer or at least bring down your consumption. Gulping down kegs of beer is only going to give you a beer belly—remember beer bellies are stubborn and really difficult to get rid of (3).
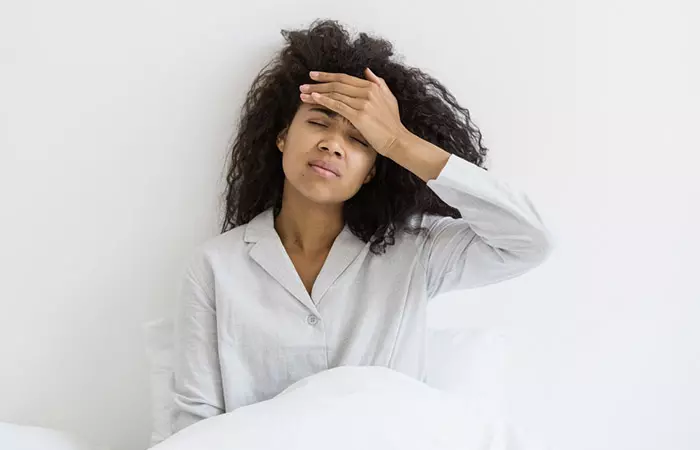
9. Leads To Intoxication And Hangover
Like all forms of alcohol, excess beer consumption does affect your nerves and motor skills. This results in reduced inhibitions, impaired judgement, and reduced coordination. This can lead to accidents. Lack of coordination of motor skills and nerves also causes slurred speech. You can also expect a bad hangover and memory loss after a night out binging on beer (11).
10. Interacts With Certain Medications
Sedatives and Erythromycin can interact with beer and can be bad for your health (12). Several antibiotics too interact with beer and can lead to side effects like headache and vomiting (13). The same holds good with a few pain medications.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip11. May Lead To Malnutrition
Excessive beer consumption may lead to malnutrition. Beer is high in empty calories and provides minimal nutritional value. Its excess consumption may displace essential nutrients from the diet, as heavy beer drinkers may prioritize alcohol over balanced meals.
Research also suggests that chronic alcohol use may interfere with the body’s ability to absorb and utilize essential vitamins and minerals, particularly those vital for overall health. These include glutamine, glucose, vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B9 (folate), C (ascorbic acid), zinc, selenium, and iron (14). This interference may result in malnutrition-related health issues such as anemia, weakness, and a weakened immune system.
A blogger experienced severe sinusitis headaches after consuming just one glass of beer or wine. She writes, “I should note what I drank and what symptoms I have afterwards. Alternatively, perhaps I’ll stick to hard cider; I’ve never noticed a problem when I am drinking that (i)”.
A mug or two of beer on a warm afternoon or at a friend’s birthday bash is certainly harmless. It is when drinking becomes an obsessive compulsion, that you stand the risk of being affected by the several effects of drinking beer daily. So, exercise in moderation and stay healthy! These were some of the major side effects of drinking beer.
Infographic: Unexpected Side Effects Of Drinking Beer
The intake of beer in moderation can be good for your health. However, excess consumption can lead to some adverse effects. While we have covered all the side effects of drinking too much beer in the article, you must be aware of a few serious effects of it. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Check the infographic below to learn about the unexpected side effects of drinking beer.
Beer is an alcoholic beverage that may have some health benefits. However, one also must note the side effects of drinking beer. Excess beer intake may lead to the development of alcoholism and interfere with blood sugar levels, work as a diuretic, cause cardiovascular disease, lead to heartburni A burning sensation in the throat or chest that often leaves a bitter taste in the mouth and may lead to inflammation of the food pipe. , increase blood pressure levels, and interact with certain medications. In addition, these adverse reactions may also depend on your lifestyle, medical history, and age. Hence, reduce its intake to avoid its side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many beers per day is healthy?
16 gms of alcohol or 1 beer per day for women and 28 gms or 1-2 drinks for men is considered a healthy amount.
Is beer better than whiskey?
Beer contains more antioxidants and less sugar compared to other alcoholic drinks like whiskey. Also, whiskey contains ethanol, which may cause serious health risks, including an increased risk of cancer.
Is beer good for the kidney?
Consuming alcohol in moderation (like a glass or two of beer) is fine for your body. But, overconsumption of beer may deteriorate kidney function and worsen existing kidney conditions.
Does beer increase cholesterol?
Beer contains carbohydrates and alcohol that can increase the triglyceride leveli The measure of triglycerides or fats in the blood, higher levels of which can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. in your body. Too many beers can increase this level, indirectly contributing to an increase in cholesterol levels.
Key Takeaways
- Beer consumption in excess may raise blood sugar levels and cause weight gain.
- Calories gained by drinking beer are stored as fat in the hips and belly, which may cause gain weight.
- Drinking excessive beer may negatively affect those with cardiovascular issues. and raise blood pressure levels.
- High consumption of beer may lead to heartburn, a beer belly, intoxication, and a hangover.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Drinking beer every day can have negative effects on your body like dehydration and nausea. Check out this video to know more about this popular alcohol.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i.Beer Allergieshttps://cdavies.wordpress.com/2007/03/27/beer-allergies/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Brewer’s Yeast Supplementation Enhances Immune Response of Aged Mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28502146/ - Effect of drinking bottled beer on plasma insulin and glucose responses in normal subjects
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7046102/ - Beer consumption and the ’beer belly’: scientific basis or common belief?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19550430/ - Health-Related Aspects of Beer: A Review
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232821963_Health-Related_Aspects_of_Beer_A_Review - Effects of a moderate intake of beer on markers of hydration after exercise in the heat: a crossover study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4459073/ - Beer and Celiac Disease
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123738912000560?via%3Dihub - Is Drinking Alcohol Really Linked to Cardiovascular Health? Evidence from the Kardiovize 2030 Project
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7551763/ - Benefits and Risks of Moderate Alcohol Consumption on Cardiovascular Disease: Current Findings and Controversies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7020057/ - Consumption of alcohol and blood pressure: Results of the ELSA-Brasil study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5757983/ - The Effect of Beer and Other Alcoholic Beverages on the Esophagus with Special Reference to Gastroesophageal Reflux
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123738912000572?via%3Dihub - Effects of Alcohol Hangover on Cognitive Performance: Findings from a Field/Internet Mixed Methodology Study
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331251567_Effects_of_Alcohol_Hangover_on_Cognitive_Performance_Findings_from_a_FieldInternet_Mixed_Methodology_Study - Fact versus Fiction: a Review of the Evidence behind Alcohol and Antibiotic Interactions
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7038249/ - RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION AMONG ROMANIAN UNIVERSITY STUDENTS- PRELIMINARY RESEARCH
https://journals.usamvcluj.ro/index.php/fst/article/view/12992 - The Influence of Alcohol Consumption on Intestinal Nutrient Absorption: A Comprehensive Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10096942/
Read full bio of Dr. Pallavi Srivastava
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan