Skin Lesions: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments
Days of struggling with this skin condition are over as you learn all about managing it.
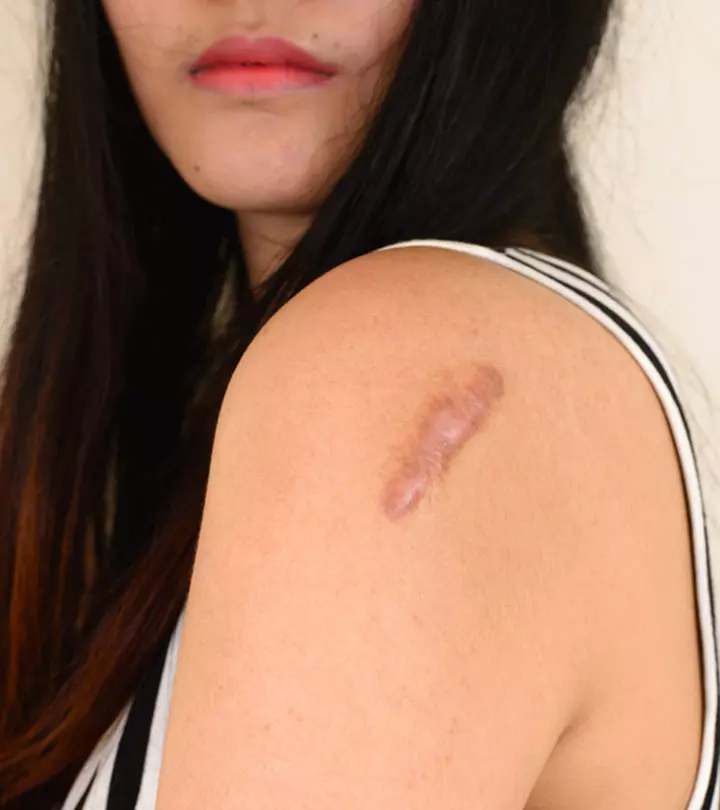
Image: Shutterstock
There is a good chance that, at some point, you might notice an abnormal growth or blemish on the skin that was not there before. Well, benign skin lesions are rather common. A variety of conditions can cause them. Most of these lesions do not pose any health issues. But the lesions that are accompanied by symptoms like bleeding, swelling, or pain may indicate an underlying condition and must be treated right away. Keep reading this article as it answers all the questions regarding skin lesions, their types, causes, symptoms, treatments, risk factors, and more. Scroll down!
In This Article
What Are Skin Lesions? Causes And Types Of Skin Lesions
A lesion is an abnormal growth compared to the surrounding skin (1). Lesions may look like bumps, lumps, or patches. A variety of factors can cause them. There are two types of skin lesions (2):
- Primary Skin Lesions: The abnormal skin growth that is present at birth or develops over time is called primary skin lesion. Moles and blisters are two examples of this type of lesion.
- Secondary Skin Lesions: These lesions form when a primary skin lesion has been aggravated or manipulated. Scars and crusts are two examples.
A variety of conditions can cause skin lesions. Here are some examples of potential causes and types:
A 44,689-person global cross-sectional study was conducted on participants from 27 different European nations. The findings revealed that 43.35% of the participants had at least one dermatological condition in the previous 12 months, and the most frequently reported conditions were atopic dermatitis or eczema (5.5%), acne (5.4%), and fungal skin infections (8.9%).
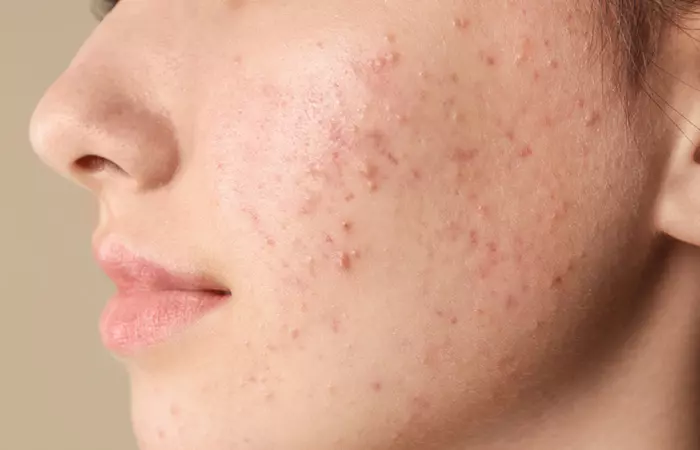
1. Acne
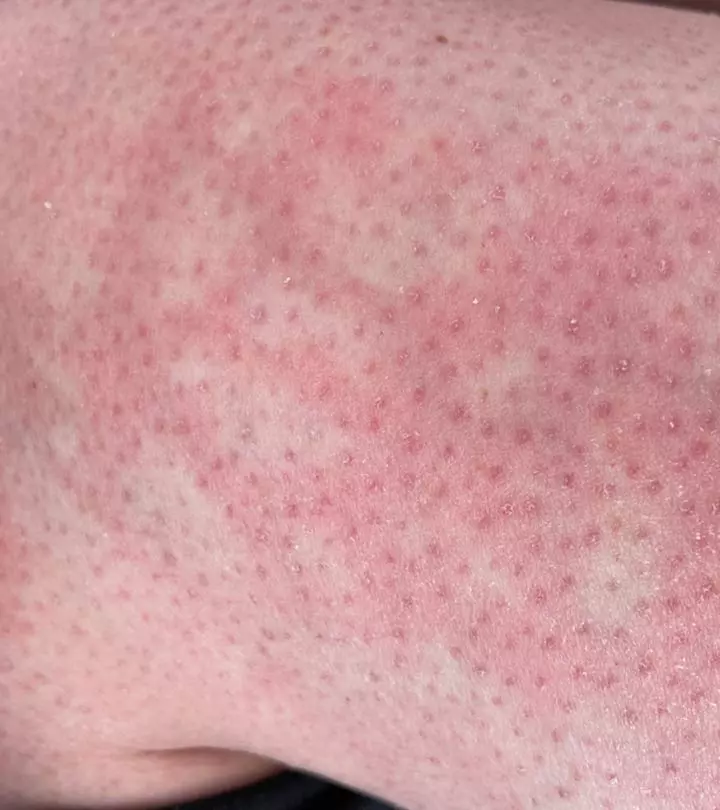
Acne develops when oil and dead skin cells block your pores (3). It results in red, white, or black bumps. Teenagers and young adults are prone to this condition. Hormones, family history, and certain medications may contribute to it. In addition, pricking acne, eating specific foods, stress, and environmental conditions can aggravate the condition (4). Treatments consist of medications and laser therapy.
 Quick Tip
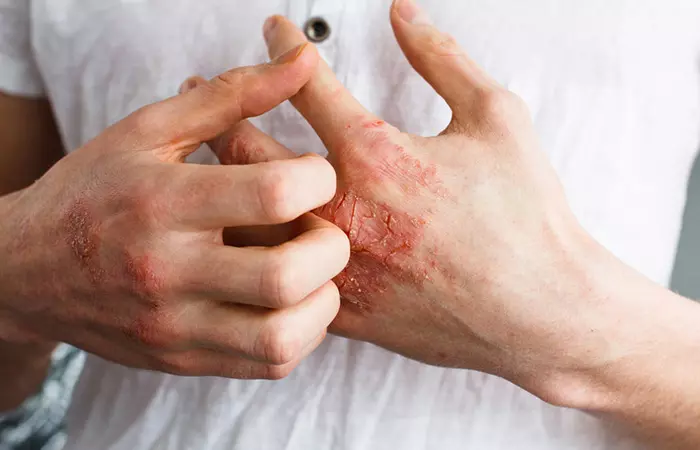
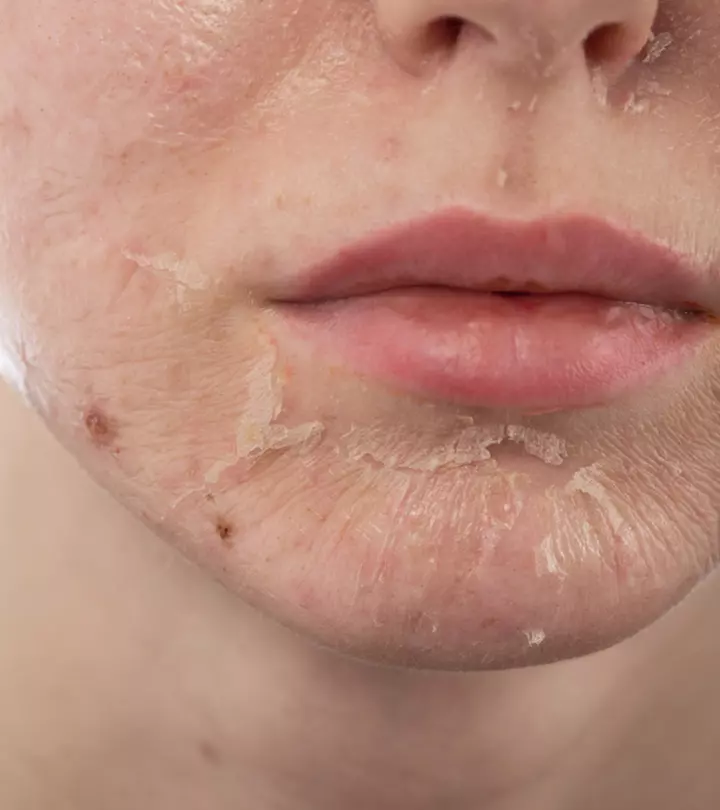
Quick Tip2. Eczema
Eczema is a skin condition that causes dry, scaly, or irritated skin. Hereditary and environmental factors may cause this chronic condition (5). Eczema can improve or deteriorate over time. Camille, a YouTuber, shares how she has been battling with eczema all her life. She says, “It used to burn like crazy during the nights I would never get any sleep and I just itched and itched to the point where I didn’t care if I tore all the skin off my body of my skin (i).” Treatment can help manage symptoms, but there is no cure. Consult a doctor if you are having discomfort and pain due to eczema.
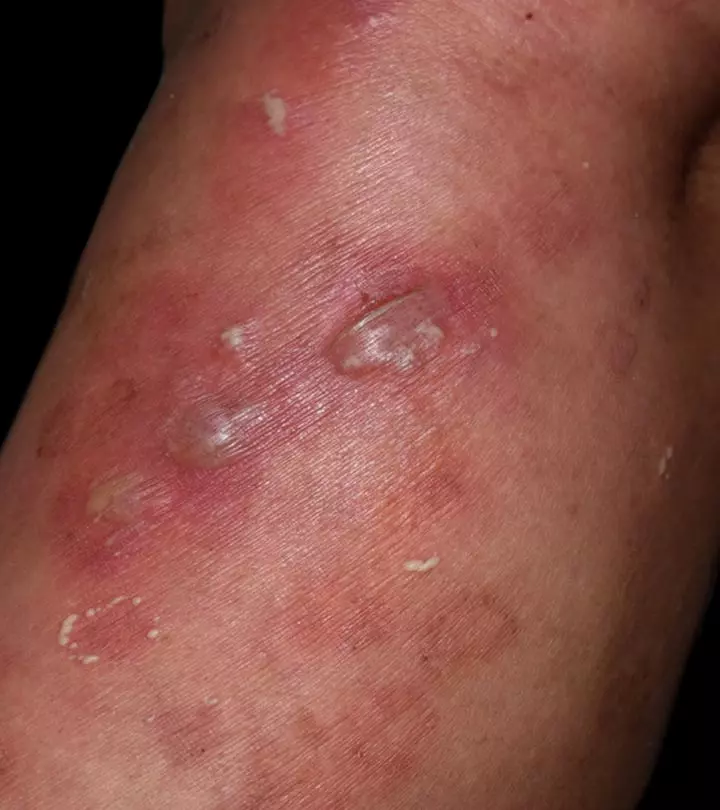
3. Blisters
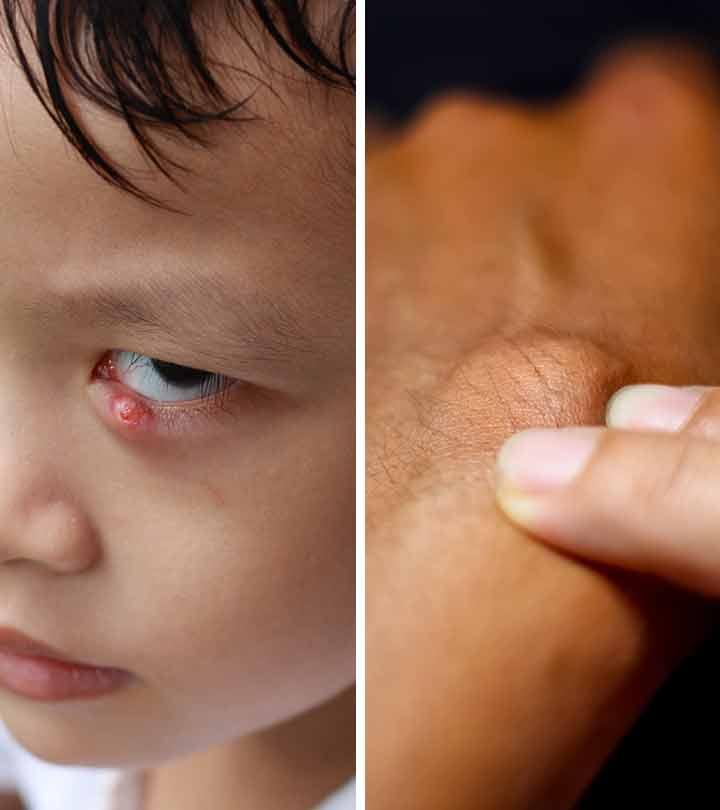
The tiny pockets of fluid that form when the upper layers of the skin are injured are called blisters. They can appear on hands and feet or anywhere on the body. They heal on their own in a few days (6). They don’t require medical attention unless they are severe, caused by burns, or have become infected.
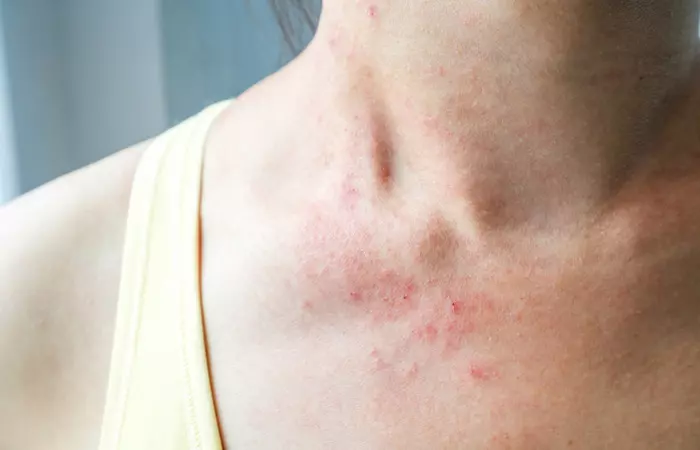
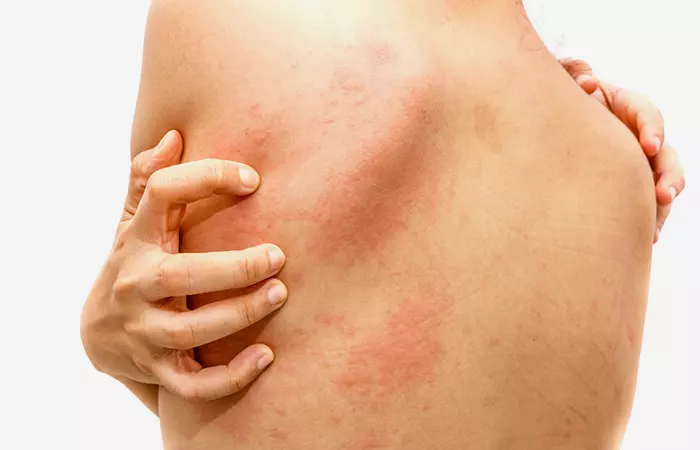
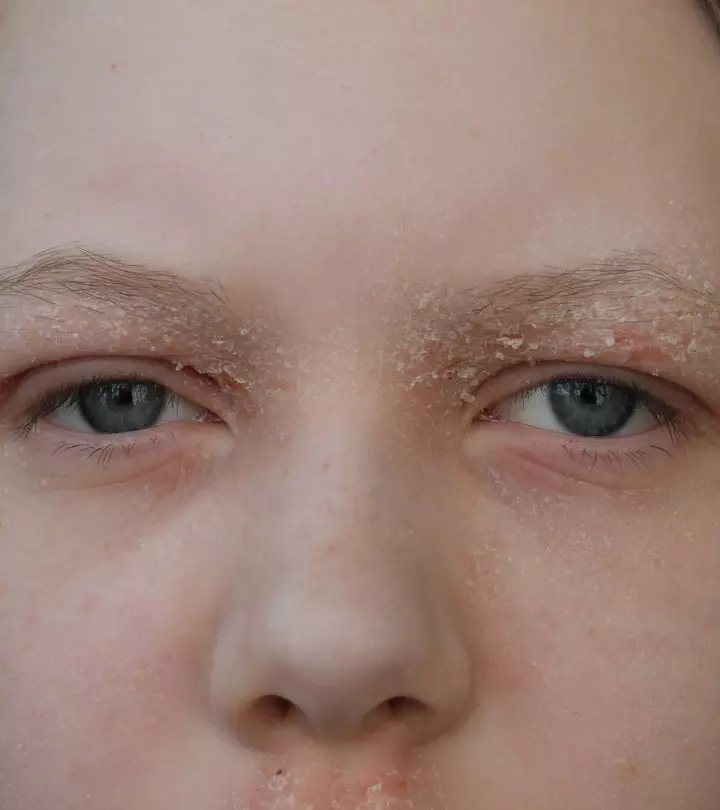
4. Rash
A rash is a group of small or large skin lesions that cover a region of the skin. It can occur for various reasons. Reaction to skin care products is the most common cause (7). The ingredients in these products can irritate the skin. Rashes are harmless and may go away on their own. Some may be persistent due to underlying causes or illnesses. If you experience any symptoms, consult a dermatologist.
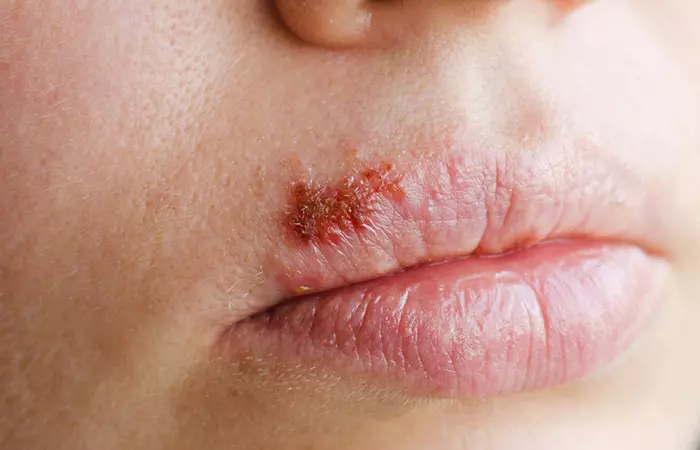
5. Cold Sores
Cold sores are fluid-filled blisters that appear on and around your lips (8). Exposure to the scorching sun, chilly wind, or cold can cause them. Other issues like a compromised immune system, fluctuating hormone levels, or stress can also lead to cold sores. These blisters are found in patches. A scab forms when the blisters split, which may last many days. Cold sores normally heal without leaving a scar in two to three weeks. If your symptoms are severe, consult a doctor right away.
6. Hives
Hives are reddish, itchy swellings that can appear anywhere on the body (9). It can be caused by an allergic reaction to food or materials. It can be treated with anti-allergic medications.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip7. Moles
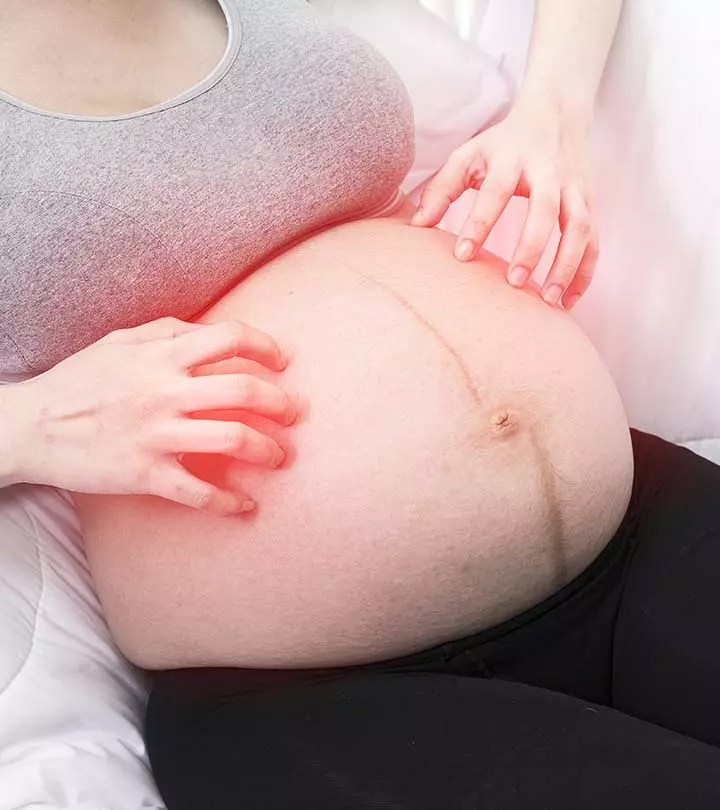
Moles form when skin cells grow in clusters instead of spreading evenly throughout the skin. These cells (melanocytesi Cells found in the bottom part of the epidermis of the skin, whose role is to produce melanin (a dark pigment occurring in the skin). ) produce the pigment that gives skin its natural color (10). Moles may turn dark due to sun exposure, during adolescence, and during pregnancy. If the color or appearance of a mole changes, you should see a dermatologist. If your moles bleed, ooze, seem scaly, or become irritating, you should get them checked.
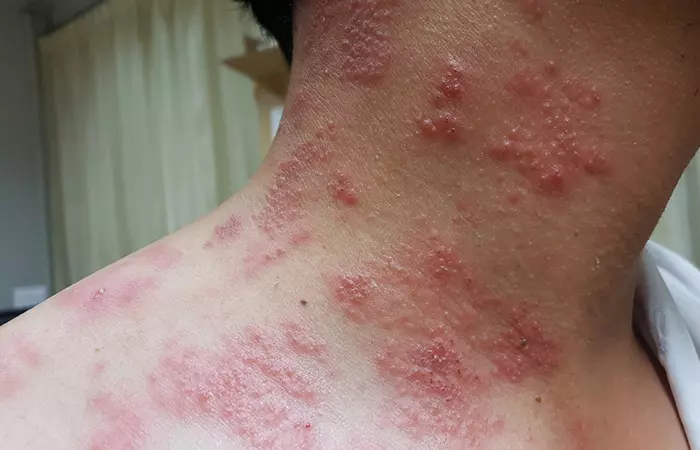
8. Shingles
Shingles cause rashes or blisters on the skin. It is caused by herpes zoster virus, which belongs in the same family of viruses that cause chicken pox (11). It looks like a ring of rashes or blisters in one area of the body and can be painful. Consult a doctor if you suspect a shingles infection. Antiviral drugs must be started to alleviate discomfort and shorten the length of your symptoms.
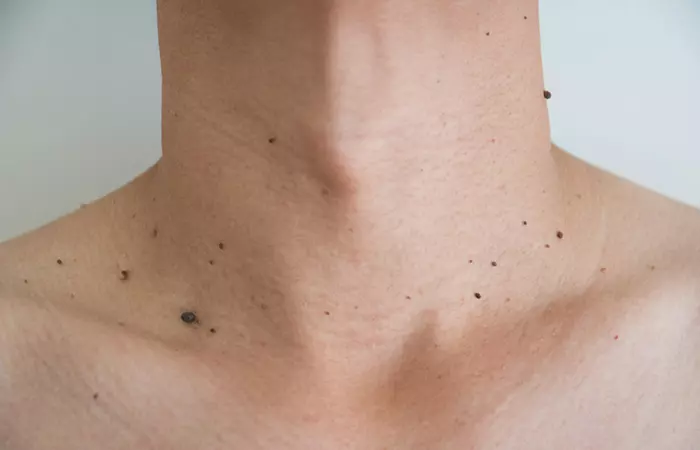
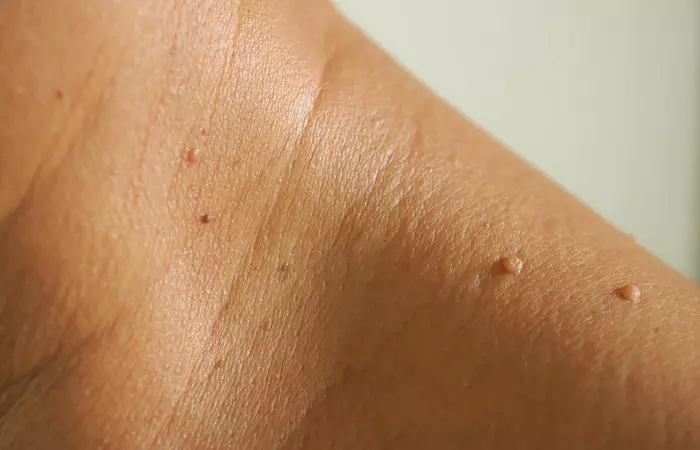
9. Skin Tags
A skin tag is a non-painful, benign growth of the skin (12). They grow for unknown reasons. They are common in locations where there is more friction of the skin. They are mostly found on the eyelids or other parts of the body with skin folds, like the neck, armpits, groin, and thighs.
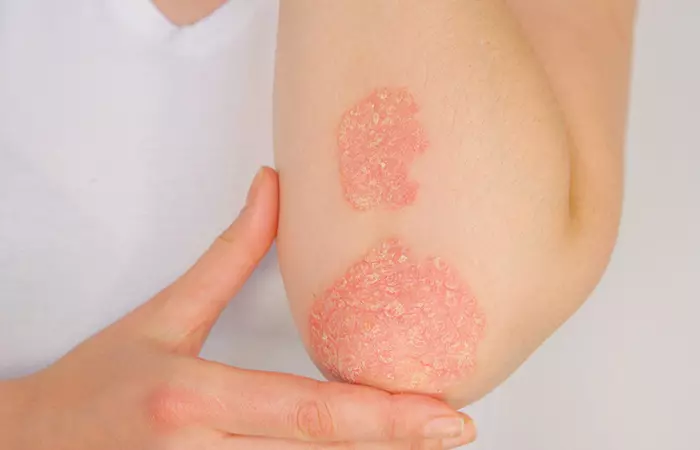
10. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin disorder that causes red, dry, crusty skin patches coated with silvery scales. These patches are mostly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back (13). The severity of psoriasis varies widely. It may be a little irritating for some, but it can severely impact the quality of life for others. A dermatologist can diagnose psoriasis and create a tailored treatment plan.
11. Epidermoid Cyst
An epidermoid cyst, also known as a sebaceous cyst, is a non-cancerous, closed sac or lump under the skin. It typically forms when skin cells and keratin, a protein found in hair and nails, get trapped beneath the skin’s surface. It is slow-growing and painless, with a firm, raised appearance. Epidermoid cysts are often found on the face, neck, chest, or back. While they are generally considered to be benign, new evidence indicates that they can develop malignancy (14). It can also rupture or become inflamed, which can lead to discomfort and potential scarring. Treatment options may include draining the cyst, excision, or corticosteroid injections, typically performed by a healthcare professional.
Now that you know the causes and types of skin lesions, let’s look at some of the most common symptoms of this condition.
Symptoms Of Skin Lesions
- Swelling
- Itchiness
- Redness
- Bleeding
- Sores containing discharge
- Pain
- Irritation
- Dryness
- Peeling
- Flaking
- Inflammation
- Infection
- Headache
- Sweating
- Fever
In the next section, we have answered how skin lesions are diagnosed. Keep reading.
How Are Skin Lesions Diagnosed?
The doctor may perform a physical examination to understand the condition. He may inquire about your symptoms, family history, and medical history.
Some skin lesions may necessitate additional tests to understand the cause. A biopsy may also be conducted if the diagnosis is still unclear.
Wondering how skin lesions can be treated? Keep reading to find out.
Treatments
The treatment for skin lesions depends on their type. Some lesions do not require treatment, while some may need special care.
1. Prescribed Medication
Topical medications like ointments and creams can reduce inflammation and calm the affected area. Itching, redness, and pain can be relieved with topical creams (15). If you have an infection, such as shingles, a doctor may prescribe oral medications.
2. Surgical Procedures
Surgery is an effective treatment option for several types of skin lesions. Some lesions can be removed permanently with surgery. The following surgical procedures may be used:
- Surgical removal of a lesion, usually a mole that has the potential to develop into a cancer like melanoma.
- Piercing and draining an infected lesion.
- Removal of damaged skin tissue through laser surgery. Doctors may recommend laser surgery to eliminate birthmarksi Common epidermal growths or lesions, also called vascular birthmarks or pigmented birthmarks, which appear at or soon after birth. .
- Cryotherapy, a treatment that uses liquid nitrogen to destroy the damaged skin tissue.
3. Self-Care At Home
There are a few types of lesions that do not require medical attention. You may try simple home treatments to gain relief from the symptoms.
You can use oatmeal to relieve irritation or swelling caused by certain skin lesions (16).
To prevent lesions from your skin rubbing against garments, apply absorbent powder.
Remember: While home remedies are becoming more popular, there is no evidence to support their effectiveness. It is best to follow a dermatologist’s advice.
Want to know when you should see an expert in dermatology? Keep reading to learn more.
When Should You See A Doctor?
If you observe any major symptoms, see a dermatologist right away. Here are a few instances:
- Any mole that is growing, bleeding, changing color, itching, or looking different.
- If your scalp develops a ringworm infectioni A ring-shaped rash caused by a fungus that results in discolored, scaly patches on the affected areas of the skin. .
- If eczema, dermatitis, or psoriasis persists despite the use of over-the-counter medications.
- You notice signs and symptoms of impetigo (a highly contagious skin infection).
Anyone can get skin lesions, but certain factors put some people at a higher risk. Read on to find out.
Who Are At Risk Of Skin Lesions?
- People with a family history of skin lesions.
- Skin that is exposed to the sun.
- People with a history of skin problems such as allergies, eczema, psoriasis, and so on.
- Old age.
- People with a lot of moles on their skin.
- People with a history of skin cancer.
Infographic: A Simple Guide To Skin Lesions
Skin lesions are abnormal growths or bumps that may develop at birth or due to changes in the skin. Understanding the different types and recognizing their symptoms can get you the right treatment on time. In the infographic below, we have compiled a simple guide to help you understand what they look like and their causes. Scroll down to know more!
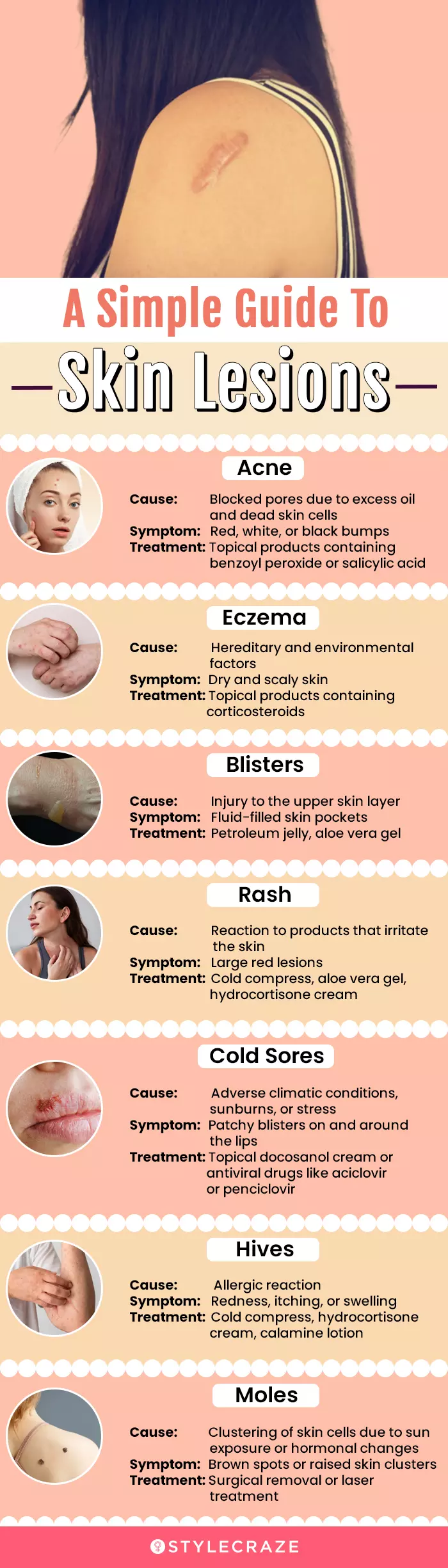
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
In A Nutshell
Skin lesions are a broad category of growths, bumps, and lumps on the skin surface. They can be moles, cysts, skin malignancies, etc. If you have any worries about a lesion, seek immediate medical attention. Early detection and treatment always lead to positive outcomes. You should also get any sudden changes in a lesion checked by a doctor.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do skin lesions indicate?
Skin lesions indicate skin damage or the presence of underlying medical conditions, allergies, infections, genetic issues, or diabetes.
What is a papule skin lesion?
A papule skin lesion is a solid skin lesion with a raised area and distinct borders. Warts are papule skin lesions.
What is a macule skin lesion?
It is a non-palpable and flat skin lesion. Freckles and flat moles are examples of macule skin lesions.
Key Takeaways
- Primary skin lesions are abnormal skin growths present at birth or develop over time.
- Eczema is a skin condition that causes dry, scaly, or irritated skin.
- Hereditary and environmental factors may cause eczema.
- Itching, redness, and pain caused by lesions can be relieved with topical ointments.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Expand your dermatological knowledge by watching this engaging lecture on primary and secondary skin lesions. Learn to differentiate between them and enhance your identification skills. Check it out now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My Eczema Story | Camille Knowleshttps://youtu.be/cA-H52Mc2pM?feature=shared
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Comparison and Analysis of Skin Lesion on Pretrained Architectures
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343125357_Comparison_and_Analysis_of_Skin_Lesion_on_Pretrained_Architectures - Skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK208/ - Acne: Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279211/ - Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173/ - Eczema
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538209/ - The Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune Blistering Skin Diseases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3123771/ - ASSESSMENT OF COSMETIC USE AND ITS SKIN REACTION AMONG POST GRADUATE STUDENTS IN UNIVERSITY OF GONDAR GONDAR NORTH EAST ETHIOPIA
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280565925_ASSESSMENT_OF_COSMETIC_USE_AND_ITS_SKIN_REACTION_AMONG_POST_GRADUATE_STUDENTS_IN_UNIVERSITY_OF_GONDAR_GONDAR_NORTH_EAST_ETHIOPIA - Cold sores: Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525782/ - Diagnosis and treatment of urticaria in primary care
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6526977/ - The Science Reality and Ethics of Treating Common Acquired Melanocytic Nevi (Moles) with Lasers
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3663172/ - Shingles: Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279624/ - Skin Tags
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547724/ - Psoriasis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/ - Epidermoid Cyst
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499974/ - Topical medications: a focus on antifungals and topical steroids
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12739320/ - Oatmeal in dermatology: a brief review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22421643/
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Swathi E