5 Impressive Health Benefits Of Soy Milk & Associated Risks
Get ready to swirl some truth into your smoothie. Dive into the real story behind soy milk!
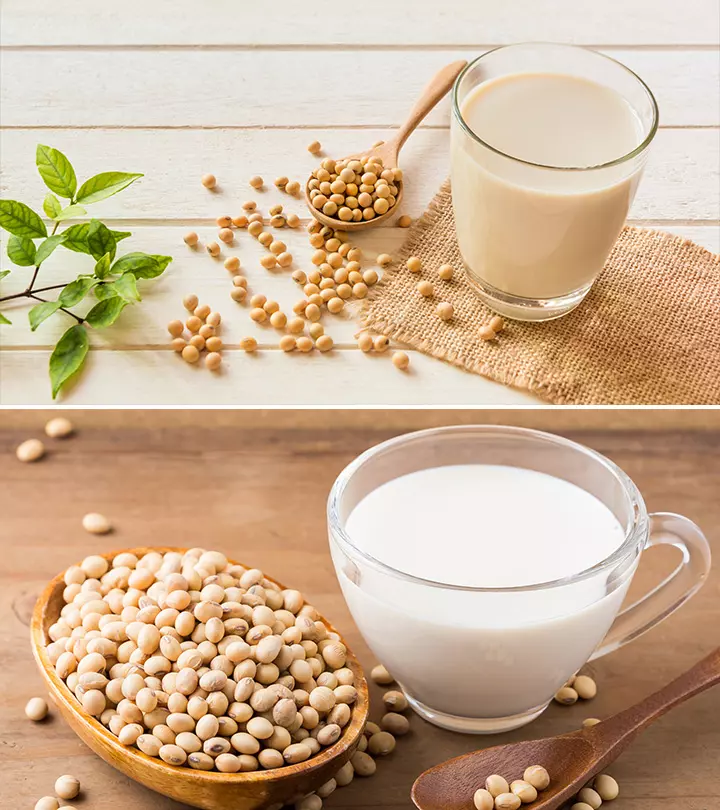

Image: Shutterstock
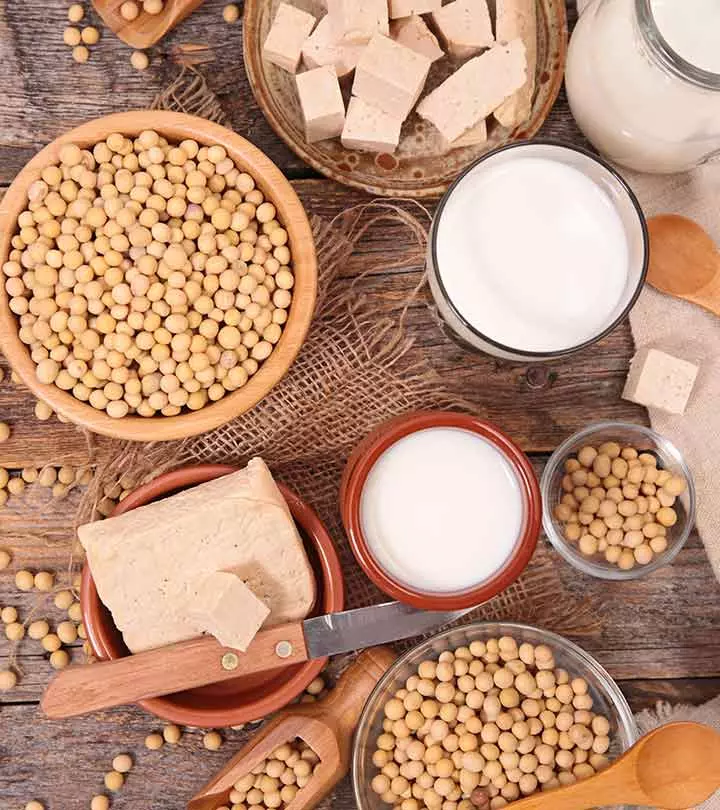
Soy milk is made from soybeans and is an excellent plant-based milk alternative for lactose intolerant individuals. Soy milk benefits include reducing cancer risk, improving heart health, preventing osteoporosis, and reducing menopause symptoms. There are many health benefits associated with this low-fat dairy milk substitute, attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The product is also rich in nutrition and contains no cholesterol. This article examines soy milk’s nutritional benefits, possible side effects, and health benefits. Check it out.
In This Article
What Is Soy Milk?
Soy milk is made from soybeans or full-fat soy flour and has a nutty flavor with a creamy texture. It is widely used as a dairy milk substitute by vegans. It is an intermediate product in tofu production with longer shelf life than dairy products. This drink can replace regular milk for making several dishes.
 Trivia
TriviaWhat is the nutrient breakdown of soy milk? Scroll down to know in detail.
Soy Milk Nutrition Facts
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, one cup (243 g) of unsweetened soy milk contains (1):
- Energy: 80.2 kcal
- Protein: 7 g
- Fat: 4.01 g
- Carbohydrate: 4.01 g
- Fiber: 0.972 g
- Sugars: 0.996 g
- Calcium: 299 mg
- Iron: 1.07 mg
- Magnesium: 38.9 mg
- Potassium: 299 mg
- Sodium: 85 mg
- Zinc: 0.608 mg
- Riboflavin: 0.51 mg
Folate: 24.3 µg
This wide range of vitamins and minerals in soy milk can do a world of good for you. Here are the health benefits of consuming soy milk.
Soy Milk Benefits
1. May Reduce Cancer Risk
From studies, a high intake of soy protein in childhood and/or adolescence significantly reduced the risk of breast cancer (2). Its consumption is safe for women, and the presence of isoflavones does not show its effect on breast cancer (3). A study by the University of Melbourne, Parkville, found that administration of soy/soy isoflavones may reduce prostate cancer risk (4). The presence of genistein, a phenolic compound in a soy-rich diet, acts as a chemotherapeutic agent that can offer protection against several cancers (5).
Also, soy products are rich in bioactive compounds such as phytoestrogens (6). These compounds can be used as chemo-preventive agents in the prevention and management of prostate cancer (7). Another study by the University of Tromso, Norway, found that men who consumed high soy milk may have a lower risk of prostate cancer (8).
2. May Prevent Osteoporosis
Approximately 10 million adults older than 50 years are estimated to have osteoporosis, and another 34 million adults are at risk of the same (9). A review published in the Journal of Medicinal Food suggests that soy isoflavones may enhance bone formation and decrease bone resorption (10). In addition, the phytoestrogens in soy may improve the absorption of calcium by your body to prevent the loss of bone mass (2). A study suggests that regular consumption of soy foods is useful for bone health and osteoporosis prevention (11). In another study conducted by Loma Linda University, Los Angles, women consuming soy milk once a day were found to have a 56% lower risk of osteoporosis (12).
As per a study, osteoporosis affects over 200 million people, with higher incidence in individuals aged 80 and above, especially among females. In the developed world, 2% to 8% of males and 9% to 38% of females experience osteoporosis. Globally, about 9 million fractures occur annually due to it. Among those over 50, 1 in 3 females and 1 in 5 males experience an osteoporotic fracture.
3. May Improve Heart Health
Studies suggest that intake of soy protein with isoflavones for six months reduced the heart disease risk (13). They can reduce the LDL cholesterol levels in serum and improve HDL cholesterol (14). However, more studies are warranted to understand this benefit of soy milk in humans.
4. May Decrease Symptoms Of Menopause
The sudden reduction in the estrogen levels in the menopause stage creates havoc in the health conditions of postmenopausal women. The phytoestrogens in soy products can provide relief from menopausal symptoms (15). From one study, isoflavone supplements were found to alleviate menopausal hot flashes symptoms (16). Also, soy milk intake for three months can enhance antioxidant levels and help reduce menopausal symptoms in postmenopausal women (17).
5. May Promote Weight Loss
Soy milk may help reduce waist circumference. A review published in the International Journal of Preventive Medicine found that the plant-based drink plays a key role in reducing waist circumference among obese and overweight individuals (18). Its calcium content may also have weight-loss benefits. A study conducted by Northern Illinois University, USA, found that taking 720 ml of soy milk daily may optimize the weight-loss effects of calcium (19). The extra dose of fiber in soy milk may also make you feel fuller for a long time.
Tofu (curdle soy milk) possesses antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties that may help treat liver damage in rats (20). However, more studies are needed to prove this claim.
These are the health benefits of soy milk. But, which type of soy milk is healthy and suitable for your diet plan? Scroll down to know this answer.
Which Soy Milk Is Healthy?
The rich nutritional profile of soy milk has several benefits. However, if you are currently working on a weight-loss diet plan, then you should select one of these soy milk types — unsweetened soy milk or soy milk that is fortified with vitamin D and calcium minerals.
Do soy milk and cow milk have the same nutritional profile and benefits? Here is the difference.
Soy Milk Vs. Cow Milk
Soy milk has lesser saturated fat than cow milk. It has an equal amount of protein in each serving and could be a good alternative for people with cow milk allergies. While both milk variants contain many vitamins and minerals, cow milk is richer in calcium.
One cup of cow milk gives you 150 calories, while a cup of soy milk has only 80 calories. But soy milk is low in leucine, an amino acid that helps build muscle and prevents muscle breakdown. Soy milk also contains lesser phosphorus, riboflavin, vitamin A, and zinc than cow milk.
Jonathan Adrian, a doctor and blogger, shared his experience about studying the benefits of soy milk consumption in his blog. He wrote, “I’ve noticed that I retain my weight a little better these days (cow’s milk and my body mass do not go hand-in-hand), and I’ve been feeling just a tad bit more responsible for the meals I’m consuming (i).”
How do you add soy milk to your diet to reap its benefits? Check the following section.
How To Add Soy Milk To Your Diet?
You can find soy milk easily in food or grocery stores. You can also prepare soy milk at your home with ease.
How To Prepare Soy Milk?
What You Need:
- Soybeans – 10 ounces
- Water – 12 cups
- Salt or sugar – 1 pinch
Process
- Soak 10 ounces of soybeans in water overnight.
- Then boil these beans in 12 cups of water for 10 minutes.
- Blend the water and soybeans until smooth, then simmer for another 40 minutes.
- If you like, you can add a pinch of salt or sugar to taste.
- When you finish simmering the soybeans, strain the mixture through a cheesecloth to remove solids.
- You can store the soy milk for up to a week.
Here Are Some Simple Ways To Include Soy Milk In Your Diet:
- Add it to a smoothie or curry.
- Use it in baked goods.
- Have it with cereal.
- Use it in your coffee or chai.
This is how you can easily prepare soy milk at your home and add it to your diet. But how much soy milk is safe to drink?
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?How Much Soy Milk Is Safe To Drink?
Daily intake of one to two servings of whole soy foods, including soy milk, is considered safe (21). Also, the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) notes that many studies show up to three servings per day in the long term also considered safe.
Intake of soy milk is safe. But are there any side effects associated with it? Find out the answer in the next section.
Soy Milk Side Effects
Soy milk is considered safe for most people. But some people have soy allergies. They are very common in children. Research suggests that soy is one of the top nine food allergies (22). It may cause stomach pain, redness, or hives. Consult your doctor if you experience these symptoms after consuming soy products.
Women with a history of hormone-sensitive cancers — breast cancer or ovarian cancer — should avoid taking soy milk. The isoflavone content in soy milk can mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. Also, people with thyroid problems should consume soy milk in moderation to avoid its adverse effects (23). However, limited studies are available on the side effects of soy milk.
But there is nothing to worry. Here are some alternatives for soy milk.
Soy Milk Alternatives
There are several options for soy milk substitutes, like:
- Oat milk
- Almond milk
- Hemp milk
- Oat milk
- Pea milk
- Rice milk
- Cashew milk
Among these, the most popularly used alternative is probably almond milk. Let us understand how it is different from soy milk in the next section.
Soy Milk Vs. Almond Milk
When weighing soy milk against almond milk, their nutritional profiles and tastes set them apart.
Soy milk boasts a higher protein content, making it a closer match to dairy milk, suitable for those seeking a protein-rich alternative. It also contains essential nutrients like calcium and isoflavones, known for potential health benefits (1).
Almond milk, on the other hand, is lower in calories and naturally free of saturated fats, making it a favorable choice for those watching their calorie intake. However, it tends to be lower in protein unless fortified (25).
Almond milk offers a nuttier flavor profile, while soy milk has a more neutral taste akin to traditional dairy milk.
Soy milk is a plant-based regular milk replacement with a rich nutritional profile. This low-fat milk exhibits several antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that help treat ailments. There are numerous benefits of soy milk. Drinking soy milk may offer protection against several cancers, prevent osteoporosis, improve heart health, decreases the symptoms of menopause, and promote weight loss. However, it may cause side effects in some people. It may cause allergies, stomach pain, redness, and hives. If you experience any side effects after consuming soy milk, stop drinking it and consult your doctor immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does soy milk improve skin?
Yes. Soy milk helps improve skin condition via enhanced levels of isoflavone absorption in the body (26).
Does soy milk make you sleepy?
Soy milk is rich in isoflavones, and those who consumed it have reported better sleep duration and higher sleep quality (27).
Key Takeaways
- Made from soybeans or full-fat soy flour, soy milk has a creamy texture, and a nutty flavor.
- Unsweetened soy milk or soy milk fortified with vitamin D, calcium, and minerals is good for weight loss.
- Oat milk, almond milk, hemp milk, pea milk, rice milk, and cashew milk are some soy milk alternatives.
Unveil the amazing health benefits of soy milk and what it can do for you. Watch this video to get a detailed overview of this vegan dairy alternative and its nutritional profile to help you make a healthy choice.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
(i) Should I Switch to Soy Milk?https://jonathanoei.medium.com/should-i-switch-to-soy-milk-4d3240f31993
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- SILK Unsweetened soymilk
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175223/nutrients - Soy and Health Update: Evaluation of the Clinical and Epidemiologic Literature
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5188409/ - Impact of Soy Foods on the Development of Breast Cancer and the Prognosis of Breast Cancer Patients
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27161216/ - Soy and soy isoflavones in prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24053483/ - Genistein and Cancer: Current Status Challenges and Future Directions
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4496735/ - Soy Soy Foods and Their Role in Vegetarian Diets
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5793271/ - Phytoestrogens and prostate cancer
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12643473/ - Does high soy milk intake reduce prostate cancer incidence? The Adventist Health Study (United States)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10189040/ - Soy Isoflavones and Osteoporotic Bone Loss: A Review with an Emphasis on Modulation of Bone Remodeling
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4717511/ - Soy Isoflavones and Osteoporotic Bone Loss: A Review with an Emphasis on Modulation of Bone Remodeling
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4717511/ - Soy foods: are they useful for optimal bone health?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3383497/ - Soy milk and dairy consumption is independently associated with ultrasound attenuation of the heel bone among postmenopausal women: the Adventist Health Study-2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22074801/ - Soy isoflavones improve cardiovascular disease risk markers in women during the early menopause
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29739677/ - Soya products and serum lipids: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26268987/ - A Meta-Analysis of 46 Studies Identified by the FDA Demonstrates that Soy Protein Decreases Circulating LDL and Total Cholesterol Concentrations in Adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6543199/ - Efficacy of phytoestrogens for menopausal symptoms: a meta-analysis and systematic review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4389700/ - Soy foods isoflavones and the health of postmenopausal women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24898224/ - The Effect of Soymilk on Alkaline Phosphatase Total Antioxidant Levels and Vasomotor Symptoms in Menopause Women
https://ijbms.mums.ac.ir/article_5290.html - Effect of Soymilk Consumption on Waist Circumference and Cardiovascular Risks among Overweight and Obese Female Adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3506092/ - Preliminary study: soy milk as effective as skim milk in promoting weight loss
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17904943/ - Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Properties of Tofu (Curdle Soymilk) against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Damage in Rats
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/btri/2013/230142/ - Soy: Intake Does Not Increase Risk for Breast Cancer Survivors
https://www.aicr.org/cancer-prevention/food-facts/soy/ - Common Allergens
https://www.foodallergy.org/living-food-allergies/food-allergy-essentials/common-allergens - Inactivation of thyroid peroxidase by soy isoflavones in vitro and in vivo
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12270219/ - Almond milk, unsweetened, plain, refrigerated
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/2257045/nutrients - Effects of fermented soymilk with Lactobacillus casei Shirota on skin condition and the gut microbiota: A randomised clinical pilot trial
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321981645_Effects_of_fermented_soymilk_with_Lactobacillus_casei_Shirota_on_skin_condition_and_the_gut_microbiota_A_randomised_clinical_pilot_trial - Relationship between daily isoflavone intake and sleep in Japanese adults: a cross-sectional study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4696198/
Read full bio of Dr Archana Batra
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli