Thin Skin: 8 Effective Prevention Tips For Healthier Skin
More than just fragile: Building resilience and confidence with the best practical tips.
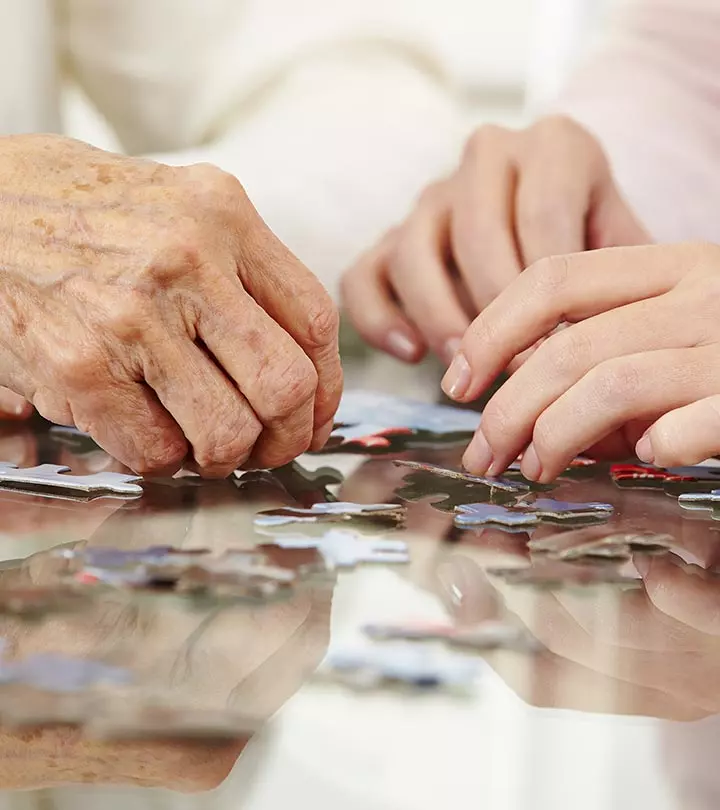

Image: Shutterstock
Your skin becomes thinner, sensitive, and wrinkled as you grow older. Other major causes of thin skin include excess UV exposure, certain medications, and unhealthy lifestyle habits. Unfortunately, there is no proven way to reverse the impact of thinning skin. However, you can follow some steps to prevent skin damage and improve the appearance of premature aging. This article will guide you through the causes and symptoms of thin skin and various ways to prevent it from exacerbating. Read on!

In This Article
What Is Thin Skin?
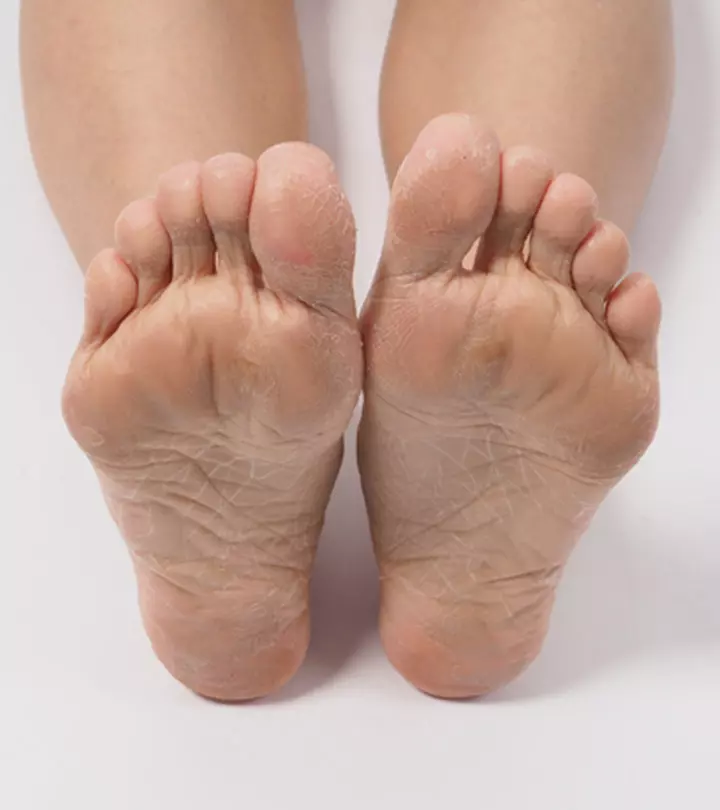
As we age, our skin tends to become thinner and may develop a tissue paper-like texture (also called crepey skin) (1). This is common in areas like the face, neck, and hands as the skin in these parts is thinner than the skin on other body parts (2).
The epidermis (outer layer) loses volume and its capacity to withstand mechanical forces as we age. The dermis (second layer) containing the fibroblasts (which produce collagen and elastin) also loses volume. The naturally occurring hyaluronic acid in the extracellular matrix (non-cellular part of the tissue) also diminishes with age. All these factors affect the integrity of the skin and its appearance, causing thin skin.
 Trivia
TriviaWhile this is a part of the aging process, multiple factors can accelerate the skin degradation process and cause premature aging and thin skin.
Key Takeaways
- UV exposure, medication, and steroids are some factors that can increase the risk of thin skin.
- To avoid skin thinning, apply sun protection cream daily, moisturize your skin regularly, and reduce the intake of alcohol.
- You can improve the appearance of thin skin with laser skin resurfacing treatment, microneedling, and dermal fillers. But consult a dermatologist before opting for any of these treatments.
Causes Of Thin Skin
The following factors increase the risk of thin skin:
- UV Exposure: UV rays can damage the skin cells and cause photodamage, including sagging, wrinkles, and pigmentation. Exposure to tanning beds can show a similar impact on the skin.
- Lifestyle Habits: Habits like smoking, drinking alcohol, and poor diet can affect overall health and contribute to skin thinning (2).
- Medication And Steroids: Excessive use of topical steroids may inhibit the fibroblasts, affecting collagen and elastin production and the natural hyaluronic acid synthesis in the body (3). This causes dryness, lack of moisture, and skin thinning. Medications like aspirin, blood thinners, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also contribute to thin and fragile skin.
- Other Factors: Other factors like allergic reactions, changes in climate, exposure to certain chemicals, and indoor heating may also contribute to skin thinning.
Look out for the below symptoms to check if your skin is thinning or not. Based on your symptoms, you may further consult a dermatologist for treatment.
Symptoms Of Thin Skin
The most common signs which indicate that your skin is thinning are:
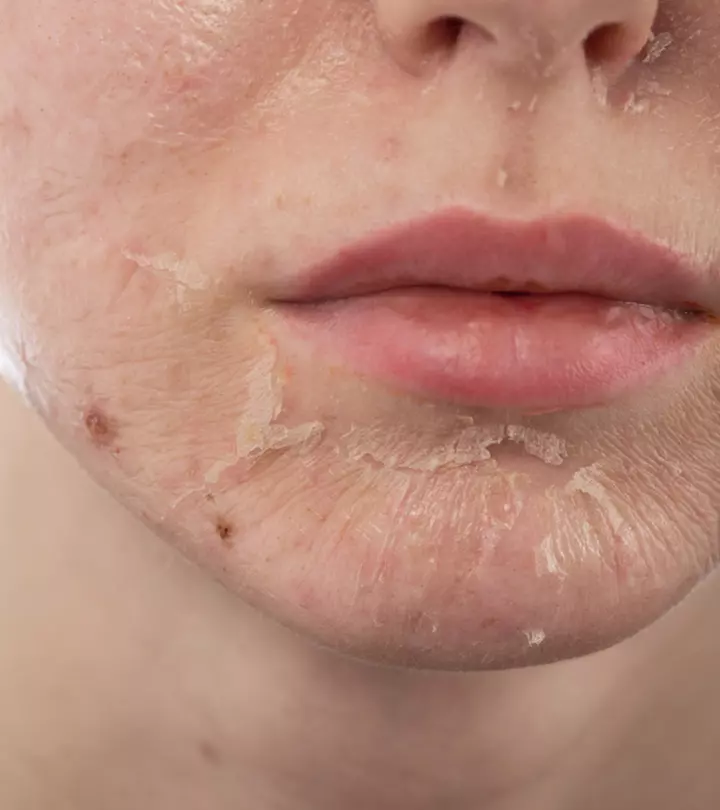
- Skin that appears thin, excessively dry, and transparent.
- Skin that looks dull, dehydrated, flaky and dry.
- The top layer of the skin (epidermis) appears thin.
- Skin that bruises easily after minor trauma.
Protecting the skin is crucial to prevent premature skin thinning. While you cannot reverse skin thinning and turn it thick, you can take steps to prevent further degradation and make it appear healthy. Let’s learn how.
Tips To Prevent Thin Skin And Further Damage
You can prevent premature thin skin by protecting it from external aggressors and damage. Here are a few tips:
- Wear a sun protection cream daily. Choose a product that offers an SPF rating of 30 and higher and provides broad-spectrum protection from UVA and UVB rays (look for PA++++ ratings). Cover and protect your skin, especially your face, hands, and neck.
- Moisturize your skin regularly to keep it hydrated and maintain the skin elasticity. Focus on your hands (back of the palms and fingers), neck and décolletage, and face (under-eye areas and around the mouth). Use ceramide-based products.
- Reduce your alcohol intake.
- Consume a healthy diet and drink enough fluids to stay hydrated and replenished from the inside. This will help the skin tissues and internal organs get enough nutrients.
- Check for nutritional deficiencies and consult a doctor for supplements.
- Avoid using skin products that are heavily perfumed.
- Use topical retinol to promote collagen and elastin production. This can prevent premature aging, wrinkles, and thin skin (4).
- Peptides, vitamin C serums, and resveratrol serums can also help in repair.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThere are several treatment options available for improving your skin health. If you are wondering whether they can thicken your thin and fragile skin, read the next section to find out.
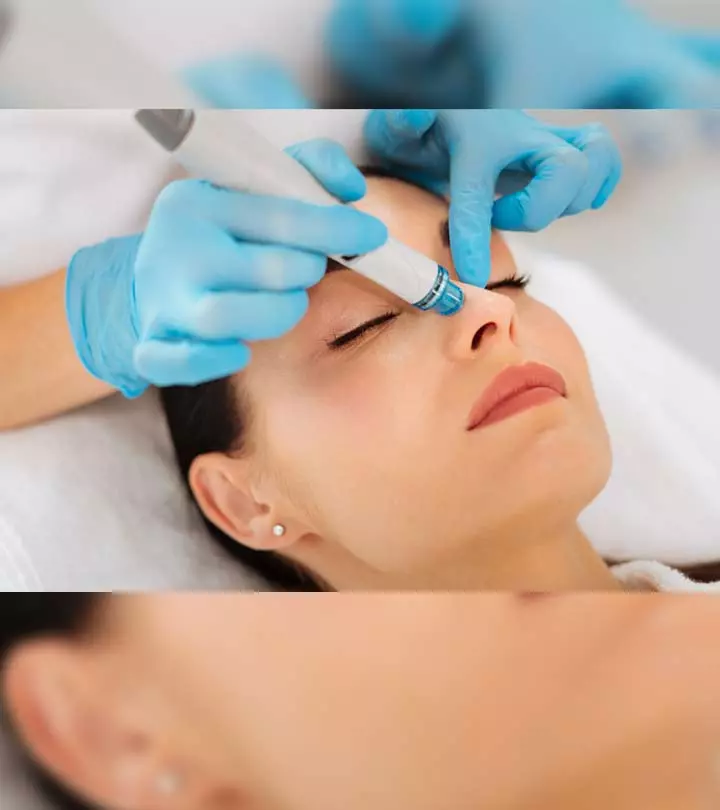
Can Thin Skin Be Thickened? Are There Any Treatment Options?
No. You cannot reverse thin and fragile skin. However, you can consult a dermatologist and go for treatments that may improve its appearance. Some treatment options include:
- Laser skin resurfacing treatment (to reduce visible signs of photodamage)
- Microneedling with radiofrequency (to rejuvenate the skin and boost collagen development)
- Dermal fillers (to give a plump and youthful appearance)
- Hyaluronic acid injectable skin boosters
There are other reasons why you should seek the help of a doctor on this matter.
When To See A Doctor
If home remedies and regular skin care are not improving your skin’s appearance, and if it is bothering you, consult a doctor for intensive treatments. Also, if the skin thinning is caused by medications or an underlying condition, consult a doctor. Treating the underlying condition and changing the medications might help.
Since there is no specific treatment for thin skin, it is better to find ways to prevent it by consulting a doctor well before you notice any serious damage.
Thinning skin is a natural part of the aging process. However, certain factors can accelerate the process and may cause premature skin thinning. The causes of thin skin may include UV exposure, side effects of medications, and an unhealthy lifestyle. If you think that your skin is thinning, it is best to consult a dermatologist. Also, take care of your skin and follow the tips discussed in the article. While you may not reverse the condition, you can improve the skin firmness and prevent further damage with proper measures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will thin skin grow back?
No, thin skin will not grow back thicker. Following simple tips like moisturizing daily and eating a healthy diet can make your skin more flexible and prevent it from breaking.
At what age does skin start to thin?
Your skin will start thinning and aging from 25 onwards.
If you think your skin is loosing its thickness, watch this video to uncover the signs and symptoms of thinning skin. Learn about the causes, preventive measures, and effective skincare routines to combat thinning skin,
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Chronic skin fragility of aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5788262/ - Characteristics of the aging skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3840548/ - Topical Steroid-Damaged Skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4171912/ - Topical retinol attenuates stress-induced ageing signs in human skin ex vivo, throughEGFR activation viaEGF, but notERK andAP-1 activation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29704879/
Read full bio of Dr. Saloni Vora-Gala
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Swathi E























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.