Tranexamic Acid For Skin: Benefits, Uses, And Side Effects
Once you try this ingredient on your skin, you will wonder why you didn't do it before.

Image: Shutterstock
The beauty and the cosmetic industry is buzzing with the latest ingredients and products. And tranexamic acid for skin is the latest addition in the skin care world and has gained much attention.
In the ever-growing trend of using acids in skin care and people’s need for bright, glowing skin, tranexamic acid for skin or TXA has emerged as the latest buzzword. While it is not new in the medical world, it is a relatively new ingredient in the skin care world. It is a popular ingredient in dermatology and cosmetic treatments as it may improve uneven skin tones, promote collagen production, and reduce the appearance of acne scars.
This article discusses the benefits of tranexamic acid in skin care, its side effects, and how to use it. Keep reading to know more.
 Know Your Ingredient: Tranexamic Acid
Know Your Ingredient: Tranexamic AcidWhat Is It?
A synthetic derivative of lysine, an amino acid with skin rejuvenating properties.
What Are Its Benefits?
It protects the skin against UV damage and helps treat skin issues, such as pigmentation, dullness, and dark spots.
Who Can Use It?
Anyone with skin disorders, such as melasma, rosacea, atopic dermatitis, and hyperpigmentation disorders.
How Often?
Orally, thrice a day for not more than five days. Topically, once or twice a day in a serum.
Caution
Perform a patch test on the skin before adding it to your skin care routine. Consult a dermatologist in case of a reaction.
In This Article
Tranexamic Acid For Skin: What Is It?
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic derivative of lysine (an amino acid). Topical tranexamic acid works by interrupting at least two pathways in the skin that, if left unchecked, can lead to skin pigmentation, including larger patches known as melasma (1).
Tranexamic acid is an effective remedy for treating pigmentation and dark spots and brightening your skin with great efficacy. It is primarily used for melasma (dark spots) treatment, including pregnancy melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (2).
Tranexamic acid skin whitening treatment also seems to work on the skin’s surface layers to make your skin less susceptible to UV light exposure.
It provides a powerful and specific anti-inflammatory action to the skin, thus inhibiting the melanocytesi Cells that are specialized in producing natural, protective skin-darkening pigment (melanin). ’ tyrosinase synthesis (3). Apart from this, it also blocks the transfer of pigment from melanocytesi Cells that are specialized in producing natural, protective skin-darkening pigment (melanin). to keratinocytesi A major and dominant cell type found in the outermost layer of the skin, which plays a vital role in skin's defense against infections. in the epidermis. All of this helps in reducing hyperpigmentation.
Tranexamic acid is considered safe to use on all skin types and colors. It also calms the skin and helps restore the skin barrier (4).
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?To understand the benefits of tranexamic acid for the skin, it is also important to know how it works, which is explained in the next section.
How Does Tranexamic Acid Work?

Traditionally, tranexamic acid has been used to treat various coagulation disorders. Still, recent studies have shown that this ingredient, when taken orally or applied on the skin, has visible benefits in treating melasma and other hyperpigmentation disorders such as post-inflammatory pigmentation (2).
Topical use of this ingredient is also suitable for anyone with skin disorders, such as rosaceai A common, chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes small, pus-filled red bumps or visible blood vessels on the face. and atopic dermatitisi A chronic allergic, inflammatory skin condition that causes itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. , where the skin is sensitive and products tolerated by the skin are restricted.
The action of tranexamic acid for skin care is linked to melanocytesi Cells that are specialized in producing natural, protective skin-darkening pigment (melanin). ’ activation to produce melanin, the cell responsible for producing the pigment. These cells are activated by the Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH), and TXA reduces various events that end in the MSH being produced. This means that fewer melanocytesi Cells that are specialized in producing natural, protective skin-darkening pigment (melanin). are activated and produce melanin (2).
Less melanin production means that fewer cells are darker, which means that the dark spots start to fade because fewer cells have been affected by the pigment. Further, tranexamic acid also reduces vascularization and is perfect for post-inflammatory pigmentation, as it reduces redness and capillary vessels (5).
Now that we know how tranexamic acid works let us explore its benefits for the skin.
Benefits Of Tranexamic Acid For Skin Care
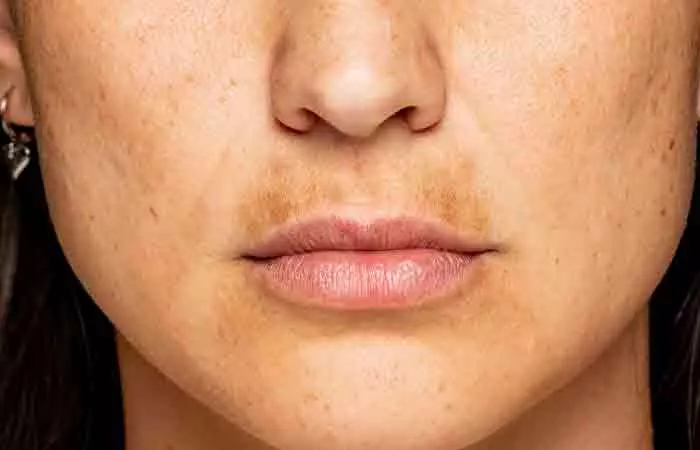
One of the key benefits of TXA is that it can be added to toners, serums, and moisturizers. Unlike other exfoliating hydroxy acids, tranexamic acid works specifically on pigmentation (6).
Among the other benefits of tranexamic acid include:
- The non-exfoliating nature of tranexamic acid serums and tranexamic acid lotions treats various skin issues such as dullness, discoloration, and pigmentation (7).
- It is an active ingredient for people looking to brighten their skin and even out their skin tone.
- Tranexamic acid helps you tackle melasma in several different ways (8).
- Tranexamic acid decreases inflammatory mediators that stimulate pigment production after constant UV exposure. Adding tranexamic acid products to your skin care routine helps in alleviating symptoms such as bumps and redness, which is likely due to its anti-inflammatory effect (8).
- TXA interferes with the interaction of the pigment-producing melanocyte cells and regular keratinocyte skin cells (3). Thus, it prevents hyperpigmentation.
- It decreases the number of MAST cells (also known as mastocyte or labrocyte), which release inflammatory mediators (9).
- Being structurally similar to tyrosine, it could also slow down the production of melanin (8).
- This powerful acid may help in wound healing (10).
In addition, anecdotal evidence suggests that this ingredient has anti-aging benefits and may protect your skin against sun damage by providing UV protection.
Amy, a registered nurse and YouTuber, shares her experience with maintaining skin results after an eight-week compound cream course for melasma. She cites topical tranexamic acid as a non-hydroquinone alternative, outlining its potential effectiveness. She says, “The one I’m currently using… is formulated with five percent tranexamic acid and additional ingredients of kojic acid, licorice root and niacinamide, all have properties to help reduce hyperpigmentation. It is fragrance free which helps to lower the risk of irritation, which is important when managing the last month. It has the consistency of a serum and that it’s not too liquidy which I find really nice (i).” She includes the acid in both her AM and PM routines and always follows up with a moisturizer.
Wondering if tranexamic acid is for everyone? Let us find out who can use it.
Who Should Use Tranexamic Acid?

Tranexamic acid is perfect for anyone looking to even out their skin tone or restore their natural glow.
Since it has various anti-inflammatory properties and an ability to minimize the transfer of pigmentation to the surface of the skin, tranexamic acid works very well to soothe skin that is quite prone to inflammation and pigmentation (8).
For instance, if you are someone dealing with acne or have blemish-prone skin that often leaves dark marks and scars on your skin, TXA can be a great option to help you both prevent and treat this kind of discoloration.
Let us now explore if it is ideal to use this ingredient during pregnancy. Continue reading.
Tranexamic Acid For Skin During Pregnancy
While tranexamic acid may be beneficial in treating pregnancy melasma, it is not usually recommended for use during the pregnancy period itself. This is because there is not enough scientific evidence to prove its safety for pregnant individuals and the health of the fetus.
Sometimes, pigmentation issues like melasma get resolved by themselves after pregnancy. However, if the issue is really distressing, you can consult your doctor who will then review your medication, assess your medical condition, and instruct you on the appropriate usage.
Adding to that, avoid harsh chemicals in general during pregnancy. Use sunscreens with an SPF of at least 30 or higher to keep your skin protected from hyperpigmentation and other skin issues.
Besides knowing who can use it, it is also essential to know how to use tranexamic acid for optimal benefits. Find out more in the next section.
How To Use Tranexamic Acid For Skin Care

To maximize the benefits of TXA for your skin, it is best to combine it with other skin care ingredients as this acid is quite gentle on its own. For instance, you can combine it with retinol or a chemical peel to treat melasma. Similarly, combining TXA with vitamin C or kojic acid helps maximize its skin-brightening power,, thus ensuring that you get the most out of the ingredient (6), (8).
There are multiple ways to take tranexamic acid, such as orally as a tablet, having it injected on the lower layer of the skin, or applying it topically as a lotion, moisturizer, cream, or serum. However, as with many other active ingredients, tranexamic acid is best used as leave-on formulations, such as tranexamic acid serums, tranexamic acid lotions, tranexamic acid creams, and moisturizers.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipHere is how you can use it topically in your skin care routine:
- Begin by using tranexamic acid once a day initially.
- Once you develop enough tolerance for it, move to two times a day morning and evening.
- To make sure it penetrates deep into your skin, use it after a vitamin C serum and before SPF in the morning, and after retinol in the evening.
- Tranexamic acid works quite well with the usual super-actives such as niacinamide, vitamin C, and exfoliating acids such as glycolic acid and salicylic acid.
Another point to keep in mind is always wearing sunscreen in the daytime since tranexamic acid is used specially to target hyperpigmentation. Constant exposure to harmful UVA and UVB rays can make all kinds of hyperpigmentation even worse, so there is no point in using a product that treats it without also preventing it from worsening further (8).
Have questions regarding the frequency of tranexamic acid use for the best skin care routine? You can find out more in the next section.
How Often Can You Use Tranexamic Acid For Skin Care?
If applied in a specific and controlled quantity as a topical serum or lotion, TXA is safe to use daily.
As an ingredient, tranexamic acid can be used both at night and in the daytime. However, sometimes it is specifically formulated in a format or with other ingredients that are better for use in the evening.
It is, therefore, recommended to check the directions on the product you purchase as it will mention if you cannot use it in the daytime or at any specific time.
If you use tranexamic acid in the form of a serum, apply this skin-lightening topical treatment after cleansing and toning but before moisturizing the skin. Use toners or serums with pH-dependent ingredients such as AHA, vitamin C, or BHA. Ideally, you should use those first and then apply the serum or lotion with tranexamic acid (11).
To use tranexamic acid for optimal skin care, it is also important to know the side effects of using it. You can learn more about it below.
What Are The Side Effects Of Tranexamic Acid?

While tranexamic acid in topical skin care products is generally safe to use and well-tolerated by all skin types, it is best to conduct a patch test before using it, especially if you are prone to reactions to new products.
It is also recommended to consult with a qualified dermatologist before incorporating TXA as an ingredient into your skin care routine. This is mainly because using too many new skin care products at once can do more harm than good and overwhelm your skin, thus causing several issues such as redness, itching, or flakiness.
It is also important to wear sunscreen with a good SPF and generally avoid the sun if that is the main cause of your pigmentation.
In extreme cases, the adverse effects of tranexamic acid on the skin include (8):
- Numbness or itching of the face, fingers, or toes
- Abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, and vomiting
- Facial hypertrichosisi A rare disorder that causes abnormal or excessive hair growth all over the body within a short period.
- Headache and transient amnesia
- Tremors
- Increased hair shedding
- Lip or periorbital swelling
- Palpitationsi A feeling that the heart is missing heartbeats and pounding due to stress, variation in breathing, and alcohol consumption.
Tranexamic acid is a derivative of lysine which is used to treat a variety of skincare issues. The benefits of using tranexamic for your skin include the treatment of pigmentation marks (melasma), reducing inflammation, and lightening the skin. Some of the best ways to use tranexamic acid are to combine with a chemical peel, vitamin C, or retinol to brighten and hydrate the skin. Read the instructions on the package before usage as excess tranexamic acid can lead to redness, itching, dizziness, tremors, or swelling.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is tranexamic acid better than hydroquinone?
Both tranexamic acid and hydroquinone for skin are comparably effective at treating melasma. However, tranexamic acid may lead to a reduction in dark spots over a larger area (12).
Is tranexamic acid better than vitamin C?
Both vitamin C and tranexamic acids are safe and effective on melasma and have similar effects. However, microneedling treatment with tranexamic acid may cause slightly more improvement than microneedling treatment with vitamin C (13).
Which is better azelaic acid or tranexamic acid?
Tranexamic may be better suited for sensitive skin than azelaic acid as it does not cause exfoliation. In addition, a study found combination therapy with oral and topical tranexamic acid to be more effective than combination therapy with oral tranexamic acid and topical azelaic acid (14).
Key Takeaways
- Tranexamic acid is a popular skin care ingredient that works well on pigmentation, dark spots, and dull skin.
- It is also known for its soothing and restorative properties and can be used on any skin type.
- It blocks melanin from reaching your skin cells, thereby even toning your skin and imparting a healthy glow.
- You can take it orally in tablet form or apply it topically with lotions, sunscreens, or toners.
Learn how tranexamic acid can help improve your skin’s appearance. Check out this video to know about its benefits and see if it is right for you.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Topical Tranexamic Acid For Treating Melasmahttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5HfQpVEvyEU
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Evaluation of oral tranexamic acid in the treatment of melasma,
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jocd.12830 - Tranexamic Acid for Melasma: Evaluating the Various Formulations,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6715124/#!po=2.94118 - Tranexamic Acid Diminishes Laser-Induced Melanogenesis,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4466276/#:~:text=Effects%20of%20tranexamic%20acid%20on,3) - Tranexamic acid in the treatment of melasma: A comprehensive review of clinical studies,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28133910/ - A prospective randomized controlled study of oral tranexamic acid for preventing postinflammatory hyperpigmentation after Q-switched ruby laser,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21457392/ - Effect of a Tranexamic Acid, Kojic Acid, and Niacinamide Containing Serum on Facial Dyschromia: A Clinical Evaluation,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31141852/ - Tranexamic acid: An emerging depigmenting agent ,
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311777944_Tranexamic_acid_An_emerging_depigmenting_agent - Topical tranexamic acid as a promising treatment for melasma ,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4235096/ - Effect of tranexamic acid on melasma: A clinical trial with histological evaluation ,
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221827731_Effect_of_tranexamic_acid_on_melasma_A_clinical_trial_with_histological_evaluation - The effect of antifibrinolytic agents on wound healing
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3139802/ - Topical 5% Tranexamic Acid as a Treatment for Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation Due to Acne Vulgaris,
https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03361345%20 - Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid 5% cream vs hydroquinone 4% cream in treating melasma: A split-face comparative clinical, histopathological, and antera 3D camera study
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/dth.14240 - A Split Face Comparative Study of Safety and Efficacy of Microneedling with Tranexamic Acid versus Microneedling with Vitamin C in the Treatment of Melasma
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32055507/ - Combination of Oral Tranexamic Acid with Topical 3% Tranexamic Acid versus Oral Tranexamic Acid with Topical 20% Azelaic Acid in the Treatment of Melasma
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31133144/
Read full bio of Dr. Rinky Kapoor
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty
























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.