Trichotillomania Hair Regrowth And Treatment
Counseling therapy may be your best to deal with this impulse control disorder.
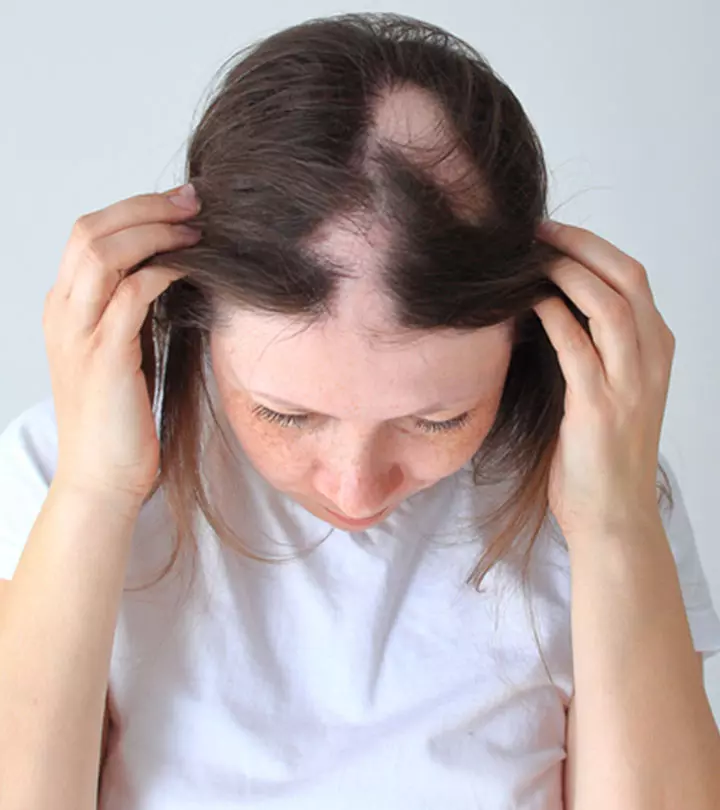

Image: Shutterstock
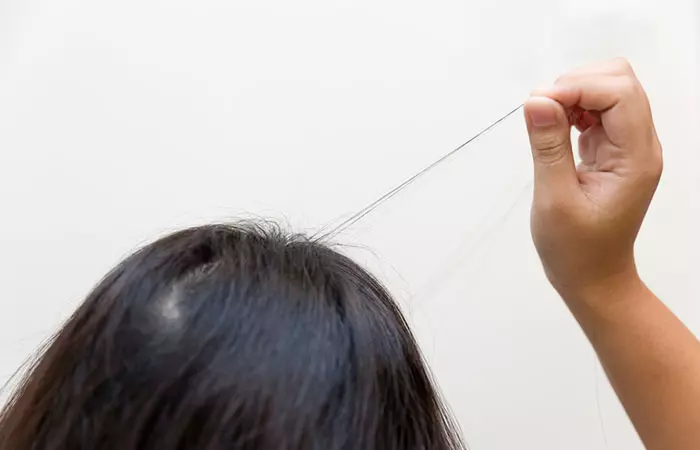
Some people struggle with the unusual urge to pull out their own hair. This is an impulse control disorder called trichotillomania, also known as the hair-pulling disorder. Here, we explain how to stimulate hair regrowth as you deal with trichotillomania.
Pulling out your hair can damage the scalp and hair shafts. Patients dealing with this disorder incur hair loss and hair regrowth issues. It affects their confidence and may even require counseling and therapy. But rest assured, as recovery from this disorder is possible in most cases. Keep reading to know what causes trichotillomania and how you can manage it effectively.
In This Article
What Is Trichotillomania?
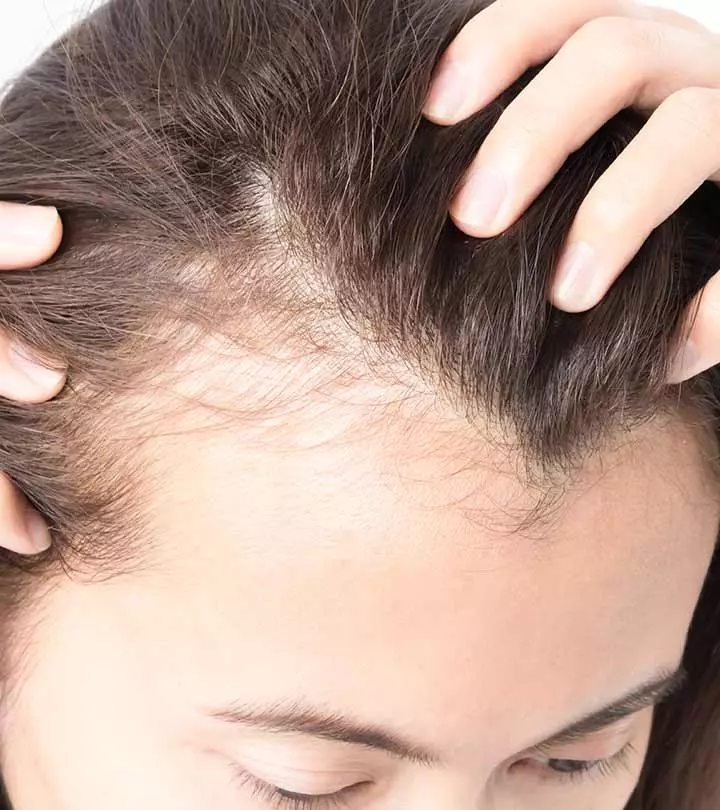
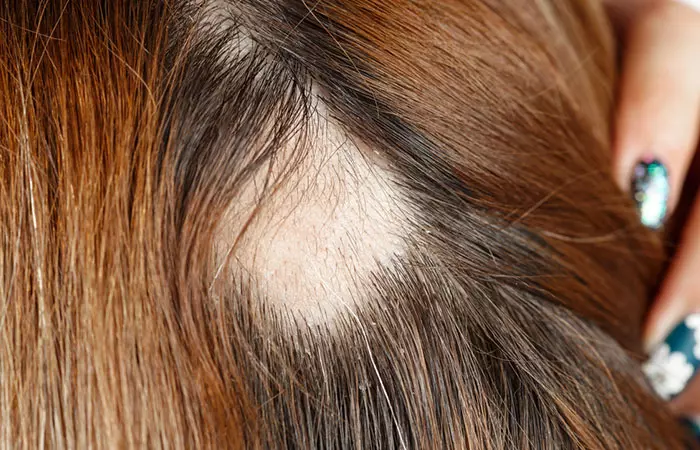
Trichotillomania is an impulse control disorder that leads to patients pulling out their hair (1). It may lie on the obsessive-compulsive spectrum, also encompassing obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), nail-biting, and skin picking (dermatillomania). People with this disorder have an intense urge to pull their hair out. They experience a sense of built-up tension that only pulling hair out can relieve. Over a period, trichotillomania damages the hair follicles.
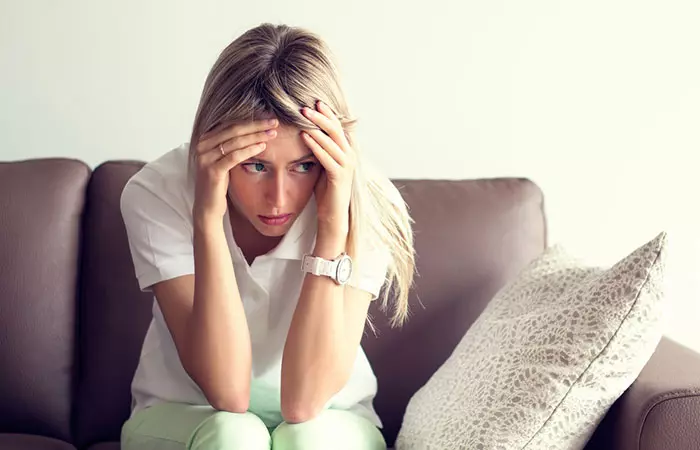
Patients develop bald patches, which often cause low self-esteem and a feeling of shame. Trichotillomania is also associated with depression and anxiety (2). Hair regrowth can elevate the self-esteem of such individuals and help them feel more confident.
What factors contribute to trichotillomania? Let us understand the same in the next section.
A survey of 10,169 adults in the US revealed that 1.7% had current trichotillomania, a condition characterized by hair pulling. While trichotillomania rates did not significantly differ between genders, the mean age of onset was 17.7 years, with a significant difference between males (19.0 years) and females (14.8 years). Those with trichotillomania reported high distress, and 79% had comorbid mental health conditions, including anxiety/depressive disorders, OCD, PTSD, and ADHD.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?What Factors Contribute To Trichotillomania?
A study conducted to understand the comorbidity of Trichotillomania found that 79% of the participating patients were suffering from one or more mental health disorders. The most common comorbidities were anxiety, depression, OCD, PTSD, and ADHD. The study with 10,169 people aged between 18-69 of the general US population validates that distress levels and other mental concerns could be defining factors for Trichotillomania.
Correlation Between Trichotillomania And Mental Distress
Source: Prevalence, gender correlates, and co-morbidity of trichotillomaniaWhile it is not clear as to what exactly causes trichotillomania, a lot of factors may contribute to its development. These include:
- Anxiety or trauma, shock, depression
- Childhood trauma or instance of conflict in the family, abuse, death, etc.
- Hormonal changes during the age of puberty
- Self-harm tendencies due to underlying distress
But how do you know for sure if a person has trichotillomania?
How To Diagnose Trichotillomania
Patients showing a few or all of these signs can be diagnosed with trichotillomania (3):
- Recurrent hair pulling that causes severe haphazard bald patches.
- Repeated attempts to stop hair pulling.
- Impacted social and occupational functioning due to hair pulling.
- Hair loss not attributed to any other medical or dermatological condition.
- Unexplained hair pulling that cannot be attributed to other mental disorders.
The onset of trichotillomania is usually seen in adolescents and young adults. As a lot of these patients often feel shame or embarrassment, they do not talk about the disorder. Trichotillomania in such patients can be diagnosed by keeping a few key symptoms in mind.
- Bald spots on the scalp.
- Broken hair of different lengths and uneven hair volume on the head.
- Uneven or scant eyelashes.
- Chewing of hair (in extreme cases).
- Unwillingness to socialize.
- Preference to stay indoors.
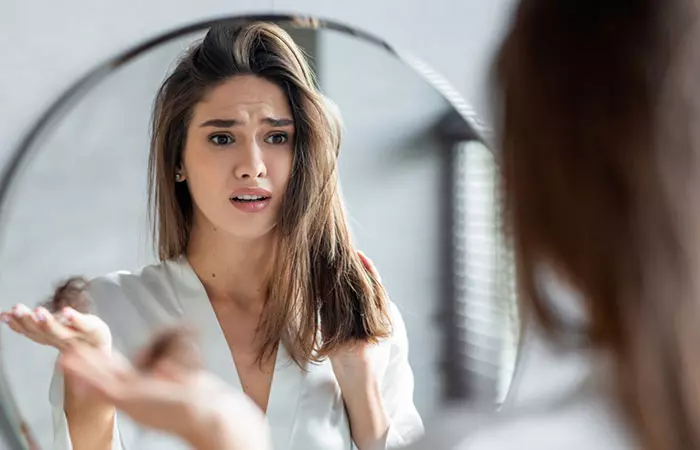
In this case, the differential diagnosis will include evaluation for alopecia, hypothyroidism, and iron deficiency. People with trichotillomania often hide bald spots and stay in denial about the underlying mental health issues that lead to hair pulling. There are many such complications associated with trichotillomania. We have covered a few below.
Complications Associated With Trichotillomania
- Delayed Diagnosis
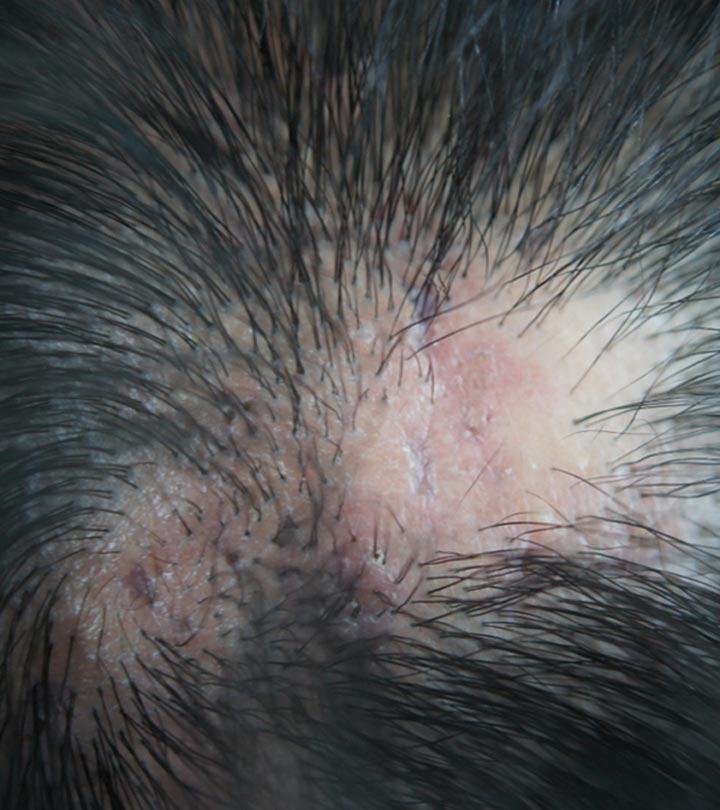
In a lot of cases, patients are often secretive about their habit of hair-pulling. They may also resort to lying due to shame. This can lead to misdiagnosis and wrong treatments being prescribed. The right treatment could get delayed and cause long-term skin and hair damage. Only a trained hair specialist can recognize trichotillomania associated with hair pulling with signs like stubby hair, and irregular and geometric bald spots.
- Emotional Distress
Hair loss associated with trichotillomania often results in more emotional distress, with people developing body issues and shame.
- Hair And Skin Damage
Pulling of hair can result in permanent skin damage over the years. It can also damage the hair follicles and impair the normal rate of hair growth, especially in cases where people pull out hair from private body parts.
- Poor Self-Esteem
Teenagers with trichotillomania can have a hard time developing stronger self-esteem and self-confidence. Even slight bald patches can hurt one’s self-confidence at that age. This may even affect their notion of self-worth.
- Social Dysfunctioning
People with trichotillomania often become too conscious about their appearance. A lot of them resort to wearing wigs, bandanas, or scarves. This affects their social and work life. Some people also suffer from intimacy issues due to the fear of their partners discovering their habits.
 Trivia
TriviaDoes The Pulled Out Hair Grow Back?
For most patients, recovering from the mental stress of trichotillomania can be much smoother if hair regrowth occurs and the bald patches subside. Patients must always visit a licensed practitioner who understands the condition better.
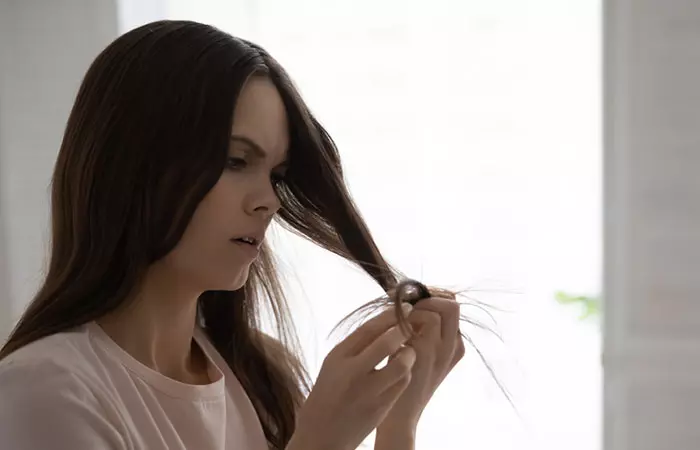
For the majority of people with trichotillomania, hair regrowth occurs naturally. It may take a little longer, but hair does grow back if the hair follicles are not completely damaged. However, those with broken hair shafts have a higher chance of permanent hair loss. The time taken for hair to grow back may also be higher than normal, especially if they have been pulling hair out for years. In some severe cases, the hair follicles may be too damaged to allow any regrowth.
There are several treatments available for trichotillomania. Here, we discuss some of them.
How Do You Treat Trichotillomania?
Trichotillomania is an impulse control disorder. Hence, those with the condition are often prescribed behavioral treatments.
- Habit Reversal Therapy (HRT)
Here, the undesirable habit is replaced with something that is not harmful – like journaling or keeping a squeeze ball and working on the triggers.
- Acceptance And Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Here, the patient is taught how to accept the urges and normally live with them without having to pull their hair out.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Here, patients learn to accept any form of distorted beliefs pertaining to compulsive hair pulling. This therapy may help reduce the frequency of hair pulling in patients.
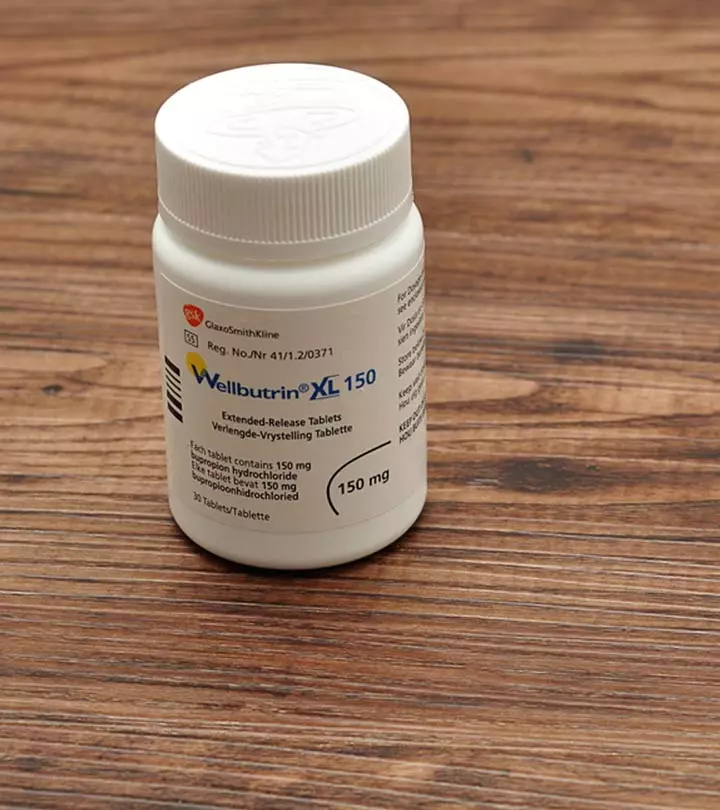
- Pharmacotherapy
A doctor may sometimes prescribe pharmacotherapyi A kind of therapy that involves the use of pharmaceutical drugs to treat diseases and disorders. – which includes a dose of 1200 mg of N-acetyl cysteine to be given twice a day (4). In a study, this treatment had shown remarkable results in 4 to 6 months (5). Doctors may also prescribe medications like serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRI), fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), fluvoxamine (Luvox), clomipramine (Anafranil), paroxetine (Paxil), valproate (Depakote), and lithium carbonate (Lithobid, Eskalith), depending on the case.
There are several other useful treatments that people with trichotillomania can follow. Check them out.
Other Treatments For Trichotillomania
The following treatments help improve the physical and mental well-being of patients.
- Seek help. Trichotillomania is triggered by underlying issues and trauma that can be treated only if you speak up and share. Don’t be afraid to accept that you have this condition. Seek help in time to prevent any permanent damage.
- Wear a wig or bandana, as hair pulling can be difficult under the headgear.
- Hair regrowth treatment can be a blessing. Various treatments for hair regrowth can help treat hair loss- and baldness-related stress in patients. Laser therapy also can help treat hair loss.
- One may also explore trichological therapyi A therapy that deals with and treats hair and scalp conditions like dandruff, hair loss, and split ends. that involves the stimulation of blood supply and vasodilationi A phenomenon where the blood vessels in your body widen to increase blood flow through the vessels, lowering your blood pressure. of the blood vessels at the base of the hair follicles.
- Trichotillomania is often associated with depression, abuse, trauma, or anxiety. Treating these underlying causes can also help – and one way to do that is by undergoing therapy for these mental health issues.
- Other simple methods include taking a relaxing bath, getting a shorter haircut, putting plaster or acrylic nails that make pulling hair impossible, and practicing deep breathing.
In addition, the intake of hair growth supplements, scalp massage, and hair transplantation may all be helpful in this condition. But can you prevent this condition? Are there any prevention tips? Let us find that out in the next section.
Tips To Prevent Trichotillomania
There is no definite method for preventing trichotillomania. However, addressing the root causes of negative emotions may be effective in preventing the recurrence of hair-pulling urges. Here are a few tips that may help prevent it:
- Understanding the triggers that urge you to pull hair can help you develop strategies to cope with them.
- Audrey Bradford, a YouTuber, recounted her experience of managing trichotillomania. She said “Keep busy. Don’t be alone for too long, because I definitely noticed it was a thing I did when I was alone (i).” She also suggested other tips such as stepping out in public or moving away from the space one is in if they have the real urge to pull their hair.
- Practice relaxation techniques, exercise, or hobbies to relieve anxiety, stress, and boredom.
- Keeping your hands busy with activities like squeezing a stress ball may reduce the impulse to pull hair.
- Keep objects like tweezers or mirrors, which can be used for hair-pulling, out of reach.
These are a few ways in which you can try to prevent this condition. However, it is necessary to seek medical support to manage and treat the issue.
Infographic: 5 Ways To Treat Trichotillomania And Regrow Your Hair
Trichotillomania can start early on in life and leave long-lasting adverse effects. The leading causes of this condition are trauma, distress, or poor habits. Ignoring the issue and delaying its treatment can negatively affect both the scalp and mental health in the long run. Therefore, if you have this problem, visit a trichologist and a therapist as soon as possible to find the root cause and avoid permanent hair follicle damage. Check out the infographic below to find the available treatment methods.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Trichotillomania, the hair-pulling disorder, can damage your scalp and hair follicles, leading to hair loss and bald patches. However, hair re-growth following trichotillomania occurs naturally in most people. But, it happens rather slowly. If the hair shafts are completely damaged following years of hair pulling, the chances of re-growth get slimmer. So, early diagnosis is essential. Besides behavioral treatments, your doctor may prescribe pharmacotherapy, which can show excellent results in 4-6 months. This disorder is mostly associated with depression, trauma, and anxiety. Focusing on treating these conditions may help reduce the urge to pull out your hair and aid in recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I shave my head if I have trichotillomania?
It depends entirely on you and your condition. However, shaving has been the solution for many individuals dealing with trichotillomania and the problems it causes. Moreover, some people experience pleasure and a sense of rediscovered freedom from the confines of this condition after shaving their head.
Can biotin help with trichotillomania?
Some people suggest using biotini A B-complex vitamin that helps the body produce energy and metabolize fats and proteins for healthy skin, hair, eyes, and liver. supplements to help with hair growth. However, there is no proof that it can help you deal with trichotillomania.
Does castor oil help with trichotillomania?
Castor oil naturally moisturizes and soothes itchy skin. Many people say that the compulsions they experience in trichotillomania are similar to itching. Therefore, it may be able to assist in reducing the symptoms of trichotillomania by getting rid of itchy skin.
What vitamins help trichotillomania?
According to a study, vitamin D intake not only decreases the urge to remove hair but also considerably enhances hair regeneration, which is sometimes not observed following treatment with antidepressants or other drugs alone. Additionally, vitamin D3 has been shown in studies to promote hair growth (6).
Key Takeaways
- Trichotillomania or the unusual impulsive urge to pull hair might lead to hair thinning, bald spots, and scalp damage.
- Hair regrowth options not only helps maintain your scalp health and hair volume but also helps regain your confidence.
- Addressing the root cause of anxiety and opting for hair regrowth therapy options can help get your hair back in its usual length, strength, and texture.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Do you suffer from trichotillomania? Hair tugging can be a nuisance. Learn how to deal with this difficult condition by using the ideas and tactics provided here. Watch this for more information.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How I stopped pulling my hair out || Trichotillomaniahttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7xnOAqHxHCs
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
Trichotillomania and Its Treatment: A Review and Recommendations
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3190970/
Trichotillomania and Its Clinical Relationship to Depression and Anxiety
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28429625/
Diagnosis Evaluation and Management of Trichotillomania
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4143797/
Trichotillomania
https://ajp.psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.15111432?cookieSet=1
N-Acetylcysteine in the Treatment of Trichotillomania: Remarkable Results in Two Patients
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jdv.13690
Trichotillomania associated with a 25-hydroxy vitamin D deficiency: A case report
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6956975/
#:~:text=In%20addition%20to%20reducing%20the,analogs%20to%20stimulate%20hair%20regrowth
Read full bio of Richard Spencer
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Medha Deb