Vitamin D For Acne: Benefits, How To Use, And Side Effects
Now know how this sunshine vitamin helps reduce acne flare-ups and pimples.

Image: Shutterstock
The benefits of using vitamin D for acne have been debated for a long time now. However, this micronutrient (that can best be obtained through sunlight) is commonly used in acne and skin care products. What does science say? If vitamin D reduces acne flare-ups, what are its best food sources? In this article, we will explain whether vitamin D helps treat acne, how to use it, and some natural ways to improve the levels of this ‘sunshine vitamin’. Keep reading.
 Trivia
TriviaIn This Article
Can A Lack Of Vitamin D Cause Pimples? – A Research-Backed Perspective
If you think vitamin D deficiency is not a global concern, think again. According to research, about 1 billion people worldwide have low vitamin D levels (1).
But, what is the link between vitamin D and acne? Can a vitamin D deficiency lead to acne breakouts? Here is what research tells us:
1. Vitamin D Regulates The Immune System

Vitamin D plays a key role in regulating the immune system. Further, its deficiency can lead to various skin diseases, such as psoriasisi A chronic skin condition characterized by itchy skin, rashes, and scaly patches, mostly on the knees, scalp, elbows, and trunk. . As per a study conducted in South Korea, vitamin D deficiency is more common in people who have acne than in people who don’t (2).
2. Vitamin D Deficiency And Nodulocystic Acne
Another study conducted in Turkey concluded that there is a connection between low vitamin D levels and nodulocystic acne (3). It found that the subjects with acne had relatively lower vitamin D levels than the control group.
3. Vitamin D Taken Orally Can Help With Acne
Yet another study conducted in Egypt found that people with acne are more prone to vitamin D deficiency compared to healthy people (4). Hence, administering vitamin D can play a beneficial role in acne management with no reported side effects.
Jesse, a make-up artist and a YouTube vlogger, has tried vitamin D for managing his acne and got positive results. He says ” When I made the decision to try vitamin D3, I didn’t really expect it to do anything. So, I was shocked when two weeks later my oil production had literally, virtually stopped and my acne had all but completely cleared up and has been clear for actually about the last two years (i).”
There is sufficient evidence to suggest that a lack of vitamin D can cause acne. In other words, using vitamin D appropriately and under expert guidance can keep acne breakouts at bay.
Moving on, let us look at the benefits of using vitamin D for acne.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin D’s anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory properties can help manage acne, rash, redness, and irritation.
- Consuming vitamin D-rich foods like egg yolks, cheese, mushrooms, and oily fish is one of the best ways to incorporate the nutrient into your lifestyle.
- Dietary supplements, adequate sun exposure, and topical application of vitamin D3 also may help prevent the deficiency.
Top 3 Benefits Of Using Vitamin D For Acne
1. Antimicrobial Properties

Research suggests that vitamin D is power-packed with antimicrobial properties (5). Vitamin D boosts the body’s innate immunity by modulating the production of antimicrobial peptides. This plays a powerful role in managing atopic dermatitis, psoriasisi A chronic skin condition characterized by itchy skin, rashes, and scaly patches, mostly on the knees, scalp, elbows, and trunk. , vitiligoi A chronic autoimmune condition that causes pale white patches on the skin due to lack of melanin. , acne, and rosaceai A chronic inflammatory condition that causes red and small pus-filled bumps on the skin, especially on the face. .
So if you have acne caused by bacteria, using vitamin D topically can help you manage acne and have a calming effect on your skin.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
A recent study also claims that vitamin D induces an anti-inflammatory effect on acne due to its immune-regulatory function
(6). So, taking an appropriate dose of vitamin D in the form of supplements can help tackle the inflammation issues that come along with acne, such as rash, redness, irritation, etc.
3. Antioxidant And Anti-Comedogenic Properties
Vitamin D has antioxidant and non-comedogenic properties (3). This means that it can scavenge the free radicals and unclog pores, which may help get rid of acne.
In the next section, let us look at how to use vitamin D for acne.
How To Use Vitamin D For Acne
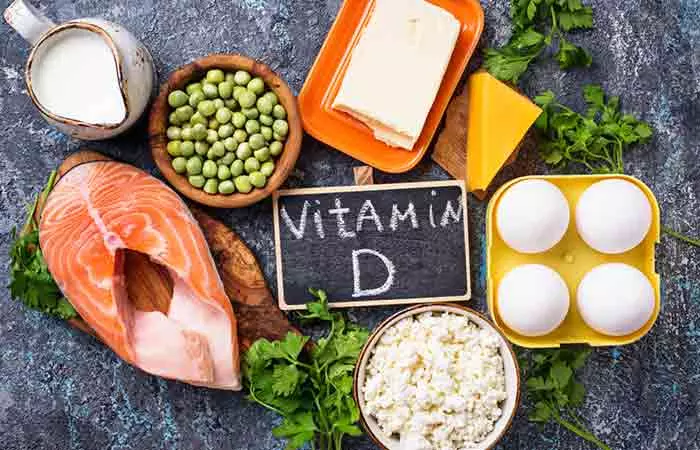

There are numerous ways to incorporate this vitamin into your daily living:
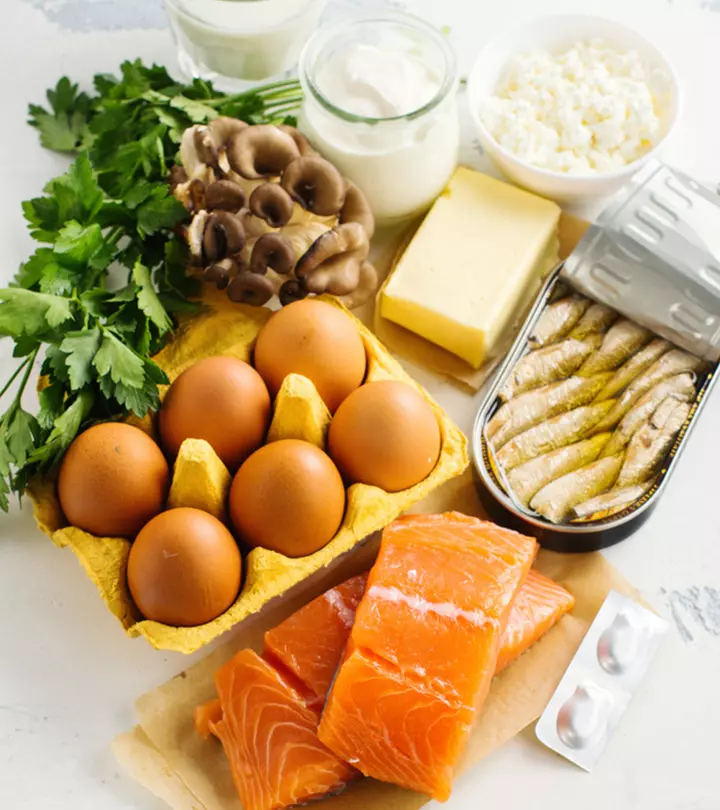
1. Consume Foods Rich In Vitamin D
A lot has been said about the potential link between diet and acne. Recent research suggests that high-glycemic load diets may exacerbate acne (7). So, keeping a food diary and noticing any patterns in your food intake and acne flare-ups can help you tackle acne.
That said, more research needs to be done to understand the categories of foods that cause acne and how they worsen the condition.
As a precautionary measure, you can consume the following vitamin D-rich foods (8):
- Oily fish like salmon, sardines, herring, and mackerel
- Red meat
- Liver
- Egg yolks
- Cheese
- Mushrooms
- Fortified foods, including fat spreads, milk, fruit juice, and breakfast cereals)
If you are thinking of consuming dairy products such as milk and cheese, exercise caution as they can make the acne symptoms worse (7).
2. Take Dietary Supplements
You can also take supplements to take care of the daily required dosage of vitamin D. As per the UK’s National Health Service, children from the age of 1 year and adults need 10 mcg of vitamin D a day (8). This includes pregnant and breastfeeding women and people at risk of vitamin D deficiency. Additionally, babies up to the age of 1 year need 8.5 to 10 mcg of vitamin D a day.
It is best to speak to your dermatologist, who can prescribe the right dosage and frequency based on the severity of your acne, your skin type, dietary and lifestyle choices, etc. Before recommending any vitamin D supplements, doctors typically suggest a blood test to check your current vitamin D levels. For most adults, the normal vitamin D level is 20 ng/mL or higher. Levels below this are considered low, while levels above 50 ng/mL may be too high (9).
Additionally, keep an eye out on the supplements you are taking, or else you might exceed the daily intake amount, leading to a vitamin D build-up in your system. Finally, remember to take vitamin D supplements along with your meal for the best results.
3. Apply Vitamin D3 Topically
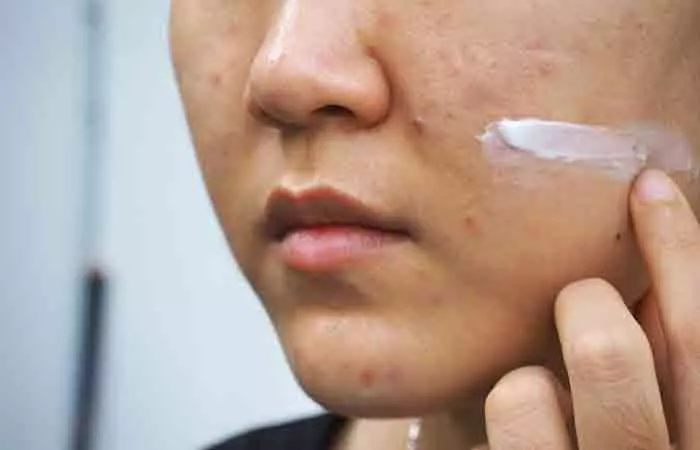
You can also apply vitamin D3 topically. Research suggests that topical application of vitamin D3 can safely help in treating a vitamin D deficiency (10).
4. Get Sun Exposure
Getting enough sunlight will not treat your acne, but it will raise your vitamin D levels. However, do not step out into the sun without wearing an SPF 30 (or higher) sunscreen. Otherwise, you run the risk of getting sunburn, premature signs of aging, and skin cancer.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipYou must also be careful not to take too much vitamin D. Scroll down to the next section to see the recommended daily vitamin D intake.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need Per Day?
As per studies, the standard recommendation for most individuals is 400-800 International Units (IU) per day. But, it may vary depending on factors like age, gender, sun exposure, and certain health problems (12). The table below gives a more precise insight into the recommended dosage.
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-12 months | 10 mcg (400 IU) | 10 mcg (400 IU) | ||
| 1–13 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | ||
| 14–18 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 19–50 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 51–70 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | ||
| >70 years | 20 mcg (800 IU) | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
Next, let us take a look at the side effects and risk factors to keep in mind when using vitamin D in any form.
Side Effects And Risks To Keep In Mind
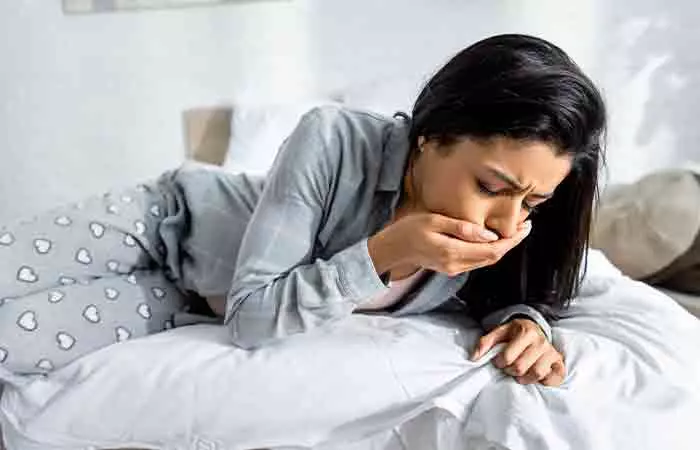

One of the most important things to remember when consuming vitamin D in any form is that exceeding the daily intake can have serious side effects. So if you are not pregnant or breastfeeding, the daily limit of vitamin D intake has been set to 100 mcg per day (12).
The typical side effects of vitamin D toxicity include (13):
- Confusion
- Apathy
- Recurrent vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Polyuria (urinating more than normal)
- Polydipsia (excessive thirst)
- Dehydration
- Hypercalcemia (above normal calcium level)
- Heart arrhythmiai A condition in which the heart beats irregularly because the electrical impulses that coordinate them do not work properly.
- Tissue calcification
- Kidney stones
- Organ damage
- Bone pain
- Weakness
Finally, remember that your vitamin D levels can also decrease if you are on corticosteroidi An anti-inflammatory medicine used to reduce swelling and suppress the immune system when it accidentally attacks its own tissues. medication.
Infographic: Tips To Stay Safe Under The Sun
Vitamin D is a power-packed nutrient that plays a vital role in major bodily functions. Its antimicrobial and antioxidant properties may help in reducing acne. Getting enough sunlight can raise your vitamin D levels. However, you must keep a few tips in mind when you go out in the sun.
Check out the infographic below to know more!
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Vitamin D plays an important part in maintaining the immune system. Therefore, vitamin D deficiency can cause several skin issues, especially acne. Vitamin D is a potent antioxidant and has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-comedogenic properties. It may help support skin health, strengthen bone health, maintain hormonal balance, and reduce sebum production in oily skin types. So, using vitamin D for acne and other conditions is one of the effective ways to manage them. Consuming vitamin D-rich foods, taking dietary supplements, or spending time under the morning sun may help solve the vitamin deficiency. However, you must be careful not to exceed the daily intake to avoid side effects. Consult a doctor before taking vitamin D supplements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can taking vitamin D cause acne?
No. In fact, a deficiency in vitamin D may cause acne, but more research needs to be done to conclusively prove this.
Can vitamin D cause skin problems?
Yes, a vitamin D deficiency can cause skin issues such as red, dry, and itchy skin. Daily intake of vitamin D under expert guidance can help you treat these kinds of skin problems.
Does vitamin D make your skin oily?
No, supplementation of vitamin D could suppress the production and secretion of sebum in patients with nodulocystic acne (3).
How long does it take for vitamin D to work on acne?
Generally, it can take up to 3 months for any acne treatment to show its results.
Learn how to reduce the appearance of acne using vitamin D. Check this video to discover simple steps to clear up your skin and get rid of acne for good.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. HOW TO CURE ACNE WITH VITAMIN D !!!!!https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=42hwmfD6yK4
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4018438/ - Comparison of Vitamin D Levels in Patients with and without Acne: A Case-Control Study Combined with a Randomized Controlled Trial
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306928886_Comparison_of_Vitamin_D_Levels_in_Patients_with_and_without_Acne_A_Case-Control_Study_Combined_with_a_Randomized_Controlled_Trial - Preliminary evidence for vitamin D deficiency in nodulocystic acne
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4580068/ - The impact of active vitamin D administration on the clinical outcomes of acne vulgaris
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31868550/ - Antimicrobial implications of vitamin D
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3256336/ - Vitamin D Levels in Patients with and without Acne and Its Relation to Acne Severity: A Case-Control Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7549021/ - Significance of diet in treated and untreated acne vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4884775/ - Vitamin D
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-d/ - Vitamin D fact sheet for consumers
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-Consumer/ - Topical Delivery of Vitamin D3: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3976443/ - UVR: sun, lamps, pigmentation and vitamin D
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27834434/ - Vitamin D
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/#h8 - Vitamin D Toxicity–A Clinical Perspective
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6158375/
Read full bio of Dr. Teo Wan Lin
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Swathi E


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.