Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Benefits, Foods, And Dietary Tips
Harness the power of healthy eating to fight the inflammation in your body.
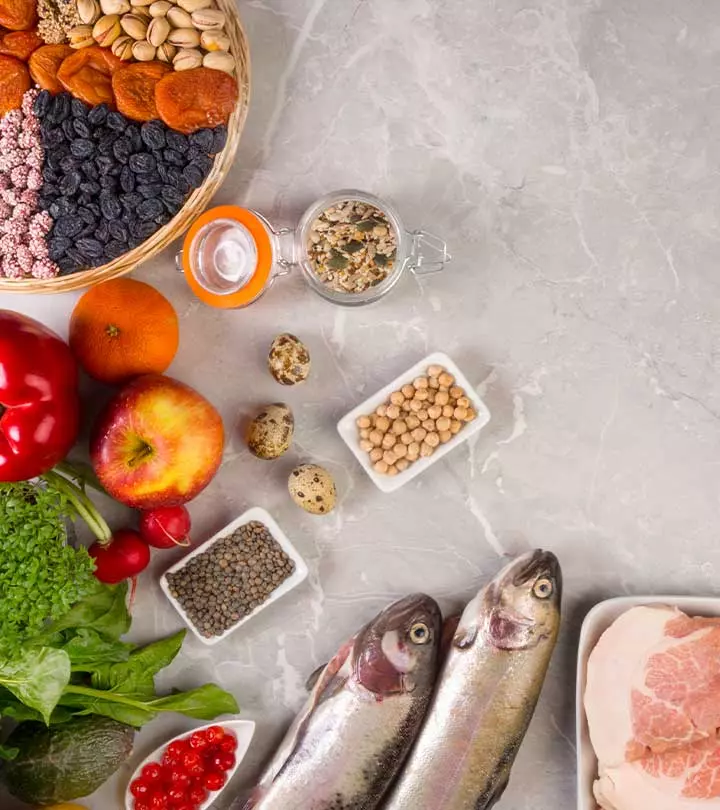

Image: Shutterstock
In this modern world where chronic illnesses are becoming more prevalent, the importance of planning our diet to safeguard our health has come to the forefront. One dietary strategy that has garnered significant attention is the Anti-Inflammatory Diet. It’s not just another trendy diet but a scientifically supported eating plan crafted to not only satisfy your taste buds but also protect against inflammation, a major culprit in many health problems. This comprehensive and well-researched diet offers a promising approach to enhance your overall well-being. Know more about this diet, its types and benefits, a sample diet plan, and the possible risks associated with it from the article below. Scroll down to know more!
 At A Glance: Anti-Inflammatory Diet
At A Glance: Anti-Inflammatory Diet- Principle: Emphasizes whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats and minimizes processed foods to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Purpose: To combat inflammation and improve overall health.
- Who It Is For: Those looking to manage inflammation-related conditions and promote well-being.
- Duration: Long-term
- Who Should Avoid: People with kidney problems and nutritional deficiencies or pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- Cons: Limited food variety, risk of nutrient deficiencies, and difficulty in long-term adherence.
In This Article
What Is An Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
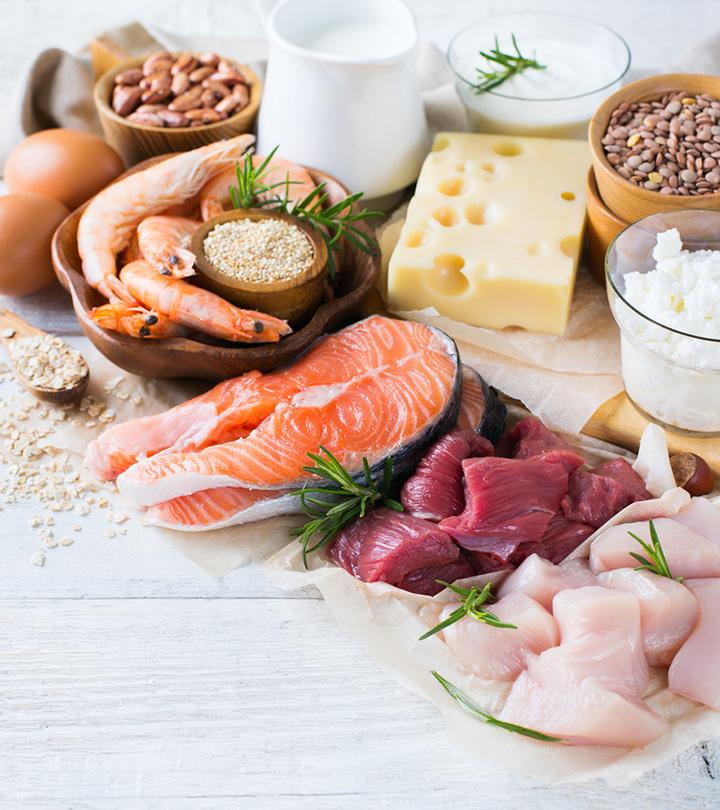
An anti-inflammatory diet is a wise choice for managing chronic body inflammation. It encourages the consumption of wholesome foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (such as fish and chicken), and healthy fats (like olive oil and nuts). Conversely, it steers clear of inflammatory culprits like processed foods, sugary snacks, and trans fats. Boosting its effectiveness and flavor profile are anti-inflammatory herbs and spices like turmeric. This diet is crafted to reduce the risk of inflammation-related diseases like heart problems and autoimmune disorders, all the while promoting your overall health.
Although the principle of limiting inflammation aggravating foods remains the same, there are many types of anti-inflammatory diets that you can pick from. Check them out in the section below.
Types Of Anti-Inflammatory Diet
1. Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet draws its inspiration from the countries in the Mediterranean Sea. It places a strong focus on incorporating fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, such as fish and poultry, and healthy fats, like olive oil and nuts, into daily meals. This eating plan restricts the consumption of red meat and processed foods, opting instead for rich natural seasonings like herbs and spices. This dietary approach may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases and inflammation and improve your body health (1).This makes it adaptable to a wide range of dietary preferences and health goals.
2. Paleo Diet
The Paleo Diet majorly focuses on whole, unadulterated foods. It celebrates the likes of lean meats, sea food, fruits and vegetables, nuts, and seeds. In its resolute exclusion of grains, dairy, and processed food, the Paleo Diet endeavors to mitigate inflammation, fostering an environment conducive to aiding your overall well-being (2).
3. Ketogenic Diet
Focusing on a path of high fat and meager carbohydrates, the Ketogenic Diet pushes the body into a state of ketosis. In this diet, fats are more emphasized, followed by the inclusion of moderate protein food sources. This dietary approach helps protect against inflammation and promotes your health (3). A few elements of the keto diet may have anti-inflammatory properties, even if it isn’t specifically designed to serve the purpose of reducing inflammation. If you want to follow this diet to reduce inflammation, consult a registered dietitian or a doctor for a customized plan that suits your health needs.
4. Vegan Diet
The Vegan Diet focuses on plant-based nourishment and includes a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains that are loaded with nutrients. This diet helps subdue inflammation and endorses optimal health by steering clear of saturated fats and drawing many health benefits from plant-derived antioxidants (4).
5. Autoimmune Protocol (AIP)
The AIP Diet is a special elimination plan for those dealing with autoimmune issues. It goes beyond the regular Paleo diet by excluding more possible triggers like processed foods, alcohol, additives, refined sugars, coffee, tea, and oils. This diet also helps calm the immune system and reduce inflammation (5).
Along with reducing inflammation, these diets and the foods included in them can also offer an array of health benefits. Check them out in the next section.
Benefits Of Anti-Inflammatory Foods
1. Helps Maintain A Stable Glycemic Response
Regular consumption of anti-inflammatory food has been linked to a decreased risk of various diseases by combating inflammation. It helps maintain a stable glycemic responsei XThe change in blood sugar levels after consuming carbohydrates. because of the food included, like whole grains and a few vegetables that are low in their glycemic index (6).
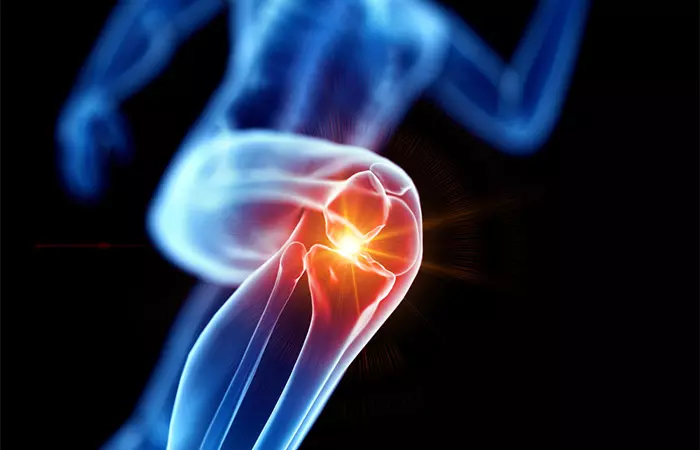
2. May Improve Joint Health
Conditions like arthritis may often cause pain, swelling, and limited mobility, significantly impacting one’s quality of life. Anti-inflammatory food may help manage these symptoms, reducing pain and improving mobility. They can be a valuable component in combating inflammation (7).
3. May Reduce The Risk Of Cancer
A diet that is packed with highly anti-inflammatory food may significantly reduce the risk of cancer. It can be attributed to the food included in these diets. Certain foods like vegetables, legumes, fruits, nuts, seeds, cereals, and olive oil may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer (8).
4. May Support Cognitive Function
Consuming anti-inflammatory food, particularly nuts, may help combat inflammation and support cognitive functioning (9). However, more research is warranted in this regard.
5. May Promote Skin Health
Acne is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition (10). Including anti-inflammatory foods like fresh vegetables, and fruits, grains and healthy fats may help you manage acne, prevent breakouts, and help promote skin health.
6. May Promote Gut Health
The anti-inflammatory diet is a potent promoter of gut health. By emphasizing high-fiber foods like fruits and vegetables, it nurtures a diverse gut microbiome, supporting digestive well-being (11). Furthermore, the antioxidant-rich foods in this diet enhance gut microbiota and prevent inflammation (12).
Key components in this diet, like ginger and turmeric, offer direct anti-inflammatory effects that may benefit individuals with gastrointestinal issues (13). In addition, the anti-inflammatory diet also includes foods like walnuts and fatty fish that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, known to reduce gut inflammation and contribute to a healthier gut environment (14).
7. Helps Reduce Oxidative Stress
The anti-inflammatory diet plays a pivotal role in reducing oxidative stress within the body. It counteracts the harmful effects of free radicals by focusing on antioxidant-rich foods like berries (15). Incorporating foods such as ginger, that possess potent anti-inflammatory properties, inhibits oxidative damage to cells (16). Also, this diet discourages the consumption of pro-inflammatory foods, like processed sugars and trans fats, that are known to increase oxidative stress.
Although an anti-inflammatory diet offers an array of benefits, there is also a popular opinion that it aids weight loss. Although there is no direct evidence for this, a few contributing factors are listed below.
Can An Anti-Inflammatory Diet Lead To Weight Loss?
- Good Foods: This diet encourages healthy eating with fruits, veggies, lean proteins, and good fats. These ingredients may aid weight loss as they are low in calories. These nutrient-rich foods also keep your energy levels high so you can exercise, burn calories, and stay in shape.
- No Junk Food: This diet avoids junk food like chips, soda, and unhealthy fats. Cutting these out can prevent weight gain and the lethargy that comes from eating processed and oily food.
- Balanced Meals: The diet promotes balanced meals with a mix of carbs, proteins, and fats. Balanced meals can keep you full and less likely to overeat.
- Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: Some of the food in this diet, like fish and nuts, have nutrients that make your body work better. This might help you control your weight.
- Healthy Digestion: Eating foods with fiber, like fruits and veggies, helps your stomach work well. A happy tummy can help with weight control.
- Less Sugar: By avoiding sugary stuff, this diet can help keep your blood sugar stable. That can stop energy crashes that lead to weight gain.
There are a wide variety of foods that can help you get all the benefits offered by an anti-inflammatory diet, including weight loss. Know what these foods are from the section below.
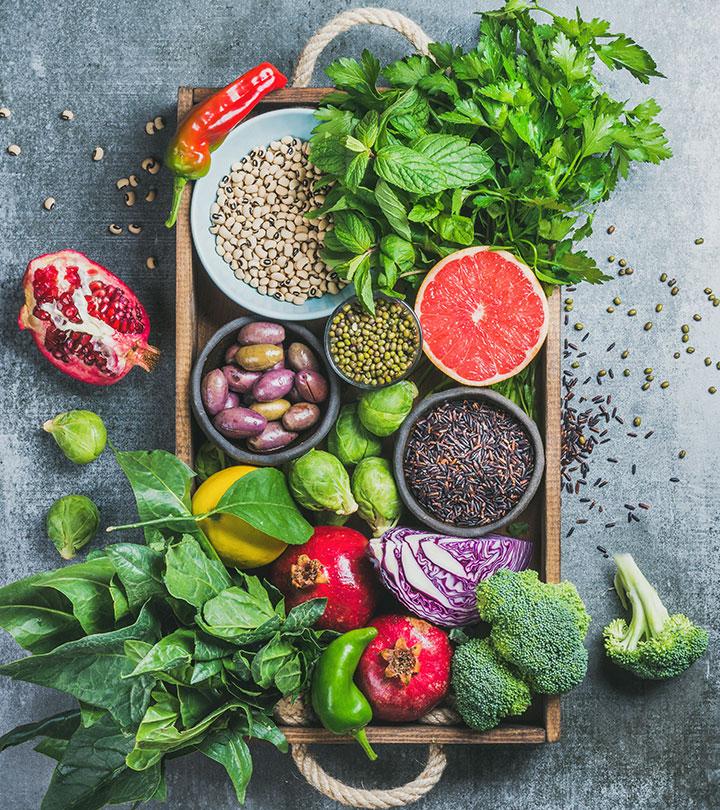
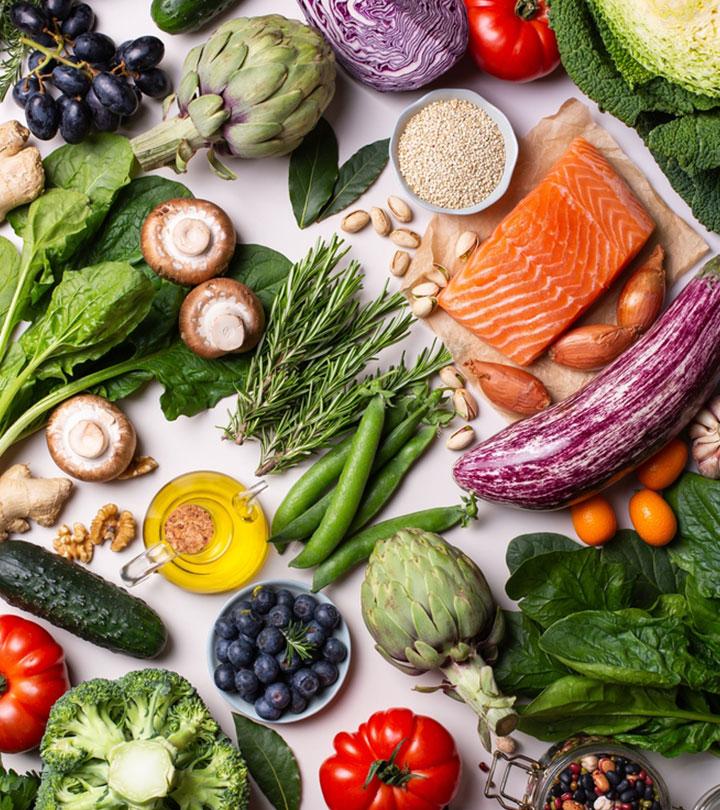
Foods To Eat On Anti-Inflammatory Diet
| Fruits | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Berries | 1/2 to 1 cup |
| Cherries | 1/2 to 1 cup |
| Oranges | 1 to 2 medium-sized ones |
| Apples | 1 to 2 medium-sized ones |
| Pineapples | 1 cup, diced |
| Papaya | 1 cup, diced |
| Vegetables | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Leafy greens (e.g., spinach, kale) | 1 to 2 cups, raw or cooked |
| Broccoli | 1 cup, chopped |
| Sweet potato | 1 medium-sized one |
| Tomato | 1 medium-sized one |
| Bell peppers | 1/2 to 1 cup, sliced |
| Carrots | 1 medium-sized one |
| Beetroot | 1/2 to 1 cup, sliced |
| Fatty Fish | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Salmon | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Mackerel | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Sardines | 3 to 4 |
| Trout | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Herring | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Anchovies | 3 to 4 |
| Healthy Fats | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Olive oil | 1 to 2 tablespoons |
| Avocado | 1/4 to 1/2 of an avocado |
| Coconut oil | Use sparingly in cooking |
| Whole Grains | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Brown rice | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Quinoa | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Whole wheat | 1 slice of bread |
| Oats | 1/2 cup, dry |
| Barley | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Bulgur | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Legumes | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Beans (e.g., black beans, kidney beans) | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Lentils | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Chickpeas | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Peas | 1/2 cup, cooked |
| Herbs And Spices | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Turmeric | 1/2 to 1 teaspoon |
| Ginger | 1/2 to 1 teaspoon |
| Garlic | 1 to 2 cloves |
| Cinnamon | 1/2 to 1 teaspoon |
| Basil | Use as a seasoning |
| Rosemary | Use as a seasoning |
| Oregano | Use as a seasoning |
| Beverages | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Green Tea | 2 to 3 cups |
| Herbal teas (chamomile, ginger) | 2 to 3 cups |
| Probiotic Foods | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Plain, Unsweetened Yogurt | 1 serving (check the label for serving size) |
| Kefir | 1 serving (check the label for serving size) |
| Sauerkraut | 1/2 cup |
| Kimchi | 1/2 cup |
| Miso | 1 serving (check the label for serving size) |
| Tempeh | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Lean Proteins | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Skinless poultry | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Tofu | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Tempeh | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Edamame | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Turkey | 3 to 4 ounces |
| Lean cuts of beef | 3 to 4 ounces (in moderation) |
| Nuts And Seeds | Per Day Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Almonds | 1 ounce |
| Walnuts | 1 ounce |
| Flaxseeds | 2 tablespoons |
| Chia seeds | 2 tablespoons |
| Hemp seeds | 2 tablespoons |
| Pumpkin seeds | 1 ounce |
You can improve your health by adding these foods to your daily meal plans. Plan a balanced meal by adding a bit of every food category. And stay consistent!
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Although the list may seem like it includes almost everything, you need to avoid a few foods when you are on an anti-inflammatory diet. Know what these are from the section below.
Foods To Avoid on Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Processed Foods:
- Sugary snacks (e.g., candy, pastries)
- Sugary drinks (e.g., soda, energy drinks)
- Fast food (e.g., burgers, fries)
- Processed meats (e.g., hot dogs, sausages)
- Packaged snacks (e.g., chips, crackers)
Trans Fats and Saturated Fats:
- Margarine and other trans fat-containing products
- Deep-fried foods (e.g., fried chicken, french fries)
- Fatty cuts of red meat (e.g., beef, pork)
- Full-fat dairy products (e.g., whole milk, cheese)
- Butter and lard
Refined Grains:
- White bread
- White rice
- Sugary cereals
- Most baked goods (e.g., cakes, cookies)
Excessive Added Sugars:
- High-sugar breakfast cereals
- Sugary desserts (e.g., ice cream, pastries)
- Sweetened beverages (e.g., fruit juices, sports drinks)
Processed and Red Meat:
- Bacon
- Sausages
- Processed deli meats (e.g., salami, bologna)
- Beef and pork with high fat content
Excessive Salt:
- Highly salted snacks (e.g., potato chips)
- Canned soups and processed foods with added salt
- Excessively salty condiments (e.g., soy sauce)
Food Additives:
- Artificial sweeteners (e.g., aspartame)
- Artificial coloring and flavoring
Although there are many foods excluded from the anti-inflammatory diet, by planning your meal correctly, you can create a healthy meal plan. Scroll down below for a handy sample meal plan to get an idea of how to plan your diet every week.
Sample 7-Day Anti-Inflammatory Diet Meal Plan
Note: The meals added below do not contain serving sizes. Please check the Foods To Eat section for them or consult a nutritionist or dietician for a personalized serving size.
| Day 1 |
|---|
| Breakfast | Berry and Almond Butter Smoothie: (Blend mixed berries, banana, almond butter, chia seeds, almond milk, turmeric, and honey (optional) until it’s a creamy smoothie.) |
| Lunch | Spinach and Chickpea Salad: (Toss together spinach, chickpeas, cucumber, cherry tomatoes, red bell pepper, olive oil, balsamic vinegar, oregano, and black pepper for a fresh salad.) |
| Snack | Greek Yogurt Parfait: (Layer Greek yogurt, kiwi, strawberries, and chopped nuts in a glass or bowl, then drizzle with honey if you like.) |
| Dinner | Grilled Chicken with Quinoa and Roasted Vegetables: (Grill chicken seasoned with lemon juice, olive oil, garlic, and dill. Serve it with quinoa and roasted veggies.) |
| Day 2 |
|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with Fresh Berries and Walnuts: (Cook rolled oats with water or almond milk, then add fresh berries, walnuts, and honey if desired.) |
| Lunch | Lentil and Vegetable Soup with a Side Salad: (Simmer lentil and vegetable soup and enjoy it with a side salad.) |
| Snack | Sliced Apple with Almond Butter: (Simply spread almond butter on apple slices. |
| Dinner | Baked Salmon with Steamed Broccoli and Brown Rice: (Bake salmon with lemon, olive oil, garlic, and dill, then serve it with steamed broccoli and brown rice.) |
| Day 3 |
|---|
| Breakfast | Greek Yogurt with Honey and Mixed Nuts: (Top Greek yogurt with honey and a handful of mixed nuts.) |
| Lunch | Quinoa and Black Bean Salad with Avocado Dressing: (Combine cooked quinoa, black beans, veggies, and creamy avocado dressing.) |
| Snack | Carrot and Celery Sticks with Hummus: (Dip carrot and celery sticks in hummus.) |
| Dinner | Grilled Shrimp with Garlic Quinoa and Roasted Asparagus: (Grill shrimp, prepare garlic-infused quinoa, and roast asparagus for a delightful meal.) |
| Day 4 |
|---|
| Breakfast | Chia Seed Pudding with Fresh Mango: (Make a chia seed pudding by mixing chia seeds with almond milk, then top it with fresh mango.) |
| Lunch | Turkey and Spinach Wrap with a Side of Sliced Cucumber: (Create a wrap with turkey and spinach, and serve it with sliced cucumber.) |
| Snack | Mixed Berries: (Enjoy a bowl of mixed berries like blueberries, raspberries, blackberries.) |
| Dinner | Baked Cod with Quinoa Pilaf and Steamed Green Beans: (Bake cod, prepare quinoa pilaf, and steam green beans for a wholesome dinner.) |
| Day 5 |
|---|
| Breakfast | Scrambled Eggs with Spinach and Tomatoes: Scramble eggs with spinach and tomatoes for a hearty breakfast. |
| Lunch | Chickpea and Vegetable Stir-Fry: (Whip up a quick chickpea and veggie stir-fry with your favorite sauce.) |
| Snack | Cottage Cheese with Pineapple Chunks: (Have a bowl of cottage cheese with pineapple chunks.) |
| Dinner | Grilled Tofu with Brown Rice and Stir-Fried Broccoli: (Grill tofu, cook brown rice, and stir-fry broccoli for a tasty dinner.) |
| Day 6 |
|---|
| Breakfast | Whole-Grain Toast with Avocado Slices and Poached Eggs: (Top whole-grain toast with avocado slices and poached eggs.) |
| Lunch | Spinach and Quinoa Stuffed Bell Peppers: (Make stuffed bell peppers with spinach and quinoa, then bake them to perfection.) |
| Snack | Almonds and Dried Cranberries: (Enjoy a handful of almonds and dried cranberries.) |
| Dinner | Roasted Chicken with Sweet Potato Mash and Steamed Asparagus: (Roast chicken, mash sweet potatoes, and steam asparagus for a comforting meal.) |
| Day 7 |
|---|
| Breakfast | Blueberry and Spinach Smoothie Bowl with Chia Seeds: (Blend blueberries, spinach, and chia seeds, and top with your favorite toppings.) |
| Lunch | Lentil and Kale Salad with Lemon-Tahini Dressing: (Mix lentils and kale with a zesty lemon-tahini dressing.) |
| Snack | Sliced Bell Peppers with Guacamole: (Dip sliced bell peppers in guacamole.) |
| Dinner | Baked Turmeric-Lemon Tilapia with Quinoa and Grilled Zucchini: (Bake tilapia with turmeric and lemon, and serve with quinoa and grilled zucchini.) |
In addition to this meal plan, there are a few specific foods you may need to include if you want to target certain conditions like IBS, Arthritis, Gastritisi XInflammation of the stomach lining caused by certain health conditions or medicines, excess alcohol, or smoking. , or if you want to follow a gluten-free anti-inflammatory diet. Check them out.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods For IBS
Soluble Fiber-Rich Foods:
These foods contain fiber that may effectively help manage IBS (17).
- Oats
- Apples
- Citrus fruits
- Carrots
- Psyllium husk
Ginger:
Ginger has proven to be effective in the management of IBS (18).
- Fresh ginger
- Ginger tea
- Ginger powder
Low-FODMAP Foods:
These are foods low in fermentable carbohydrates and have been proven effective in the management of IBS (19).
- Rice
- Chicken
- Strawberries
- Lactose-free dairy products
Probiotic-Rich Foods or Supplements:
Probiotics are proven effective in the management of IBS (20).
Yogurt with live cultures
Fermented foods (kimchi and sauerkraut)
Probiotic supplements
Anti-Inflammatory Foods For Arthritis
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish is rich in omega-3 fatty acids that may decrease interleukinsi XThe immune system-signaling proteins involved in inflammation. IL-1 and IL-6, inhibiting inflammation (21).
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Trout
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumini XAn active compound found in turmeric that has anti-inflammatory properties. . It is a natural anti-inflammatory compound (22).
Oil
Extra virgin olive oil is rich in antioxidants and also helps combat inflammation (23).
Anti-Inflammatory Foods For Gastritis
Whole Grains
Whole grains like bland oats and rice (avoid highly seasoned or spicy varieties) are gentle on the stomach and can help soothe irritation (24) (25).
Tea
Green tea is rich in antioxidants and is proven effective for combating inflammation (26).
Ginger
Ginger has been proven effective in combating gastritis (27).
- Ginger tea
- Ginger powder
- Ginger supplements
Gluten-Free Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Fruits And Vegetables
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, Swiss chard)
- Apples
- Broccoli
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
Fatty Fish
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Trout
Nuts And Seeds
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
Legumes
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Black beans
- Peas
Lean Proteins
- Chicken
- Turkey
- Tofu
- Lean cuts of beef or pork
Healthy Fats
- Avocado
- Olive oil
- Coconut oil
Herbs And Spices
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Cinnamon
- Garlic
Gluten-Free Whole Grains
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Millet
- Buckwheat
Dairy Alternatives
- Almond milk
- Coconut yogurt
- Cashew cheese
Anti-Inflammatory Teas
- Green tea
- Chamomile tea
- Turmeric tea (made from fresh turmeric)
Many aspects of these diet plans are often confused with autoimmune diets. Although both anti-inflammatory and autoimmune diets prioritize nutrient rich and healthy foods, they also differ in a few aspects. Check out how they compare and contrast from the section below.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet Vs. Autoimmune Diet
| Aspect | Anti-Inflammatory Diet | Autoimmune Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Main Objective | Reduces general inflammation in the body | Manages symptoms and flare-ups |
| Targeted Conditions | General health and inflammation-related conditions | Autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus) |
| Focus Foods | Whole, nutrient-dense foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, nuts, and seeds | Foods that specifically support autoimmune disease management, often emphasizing an elimination approach |
| Commonly Eliminated Foods | Highly processed foods, sugary snacks, trans fats, saturated fats, refined grains, and excessive added sugars | Potential trigger foods specific to the individual’s autoimmune condition that may include gluten, dairy, nightshades (tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants), or certain grains |
| Dairy Consumption | May include moderate dairy consumption, particularly low-fat or dairy alternatives | Often excludes dairy due to its potential to exacerbate autoimmune symptoms |
| Gluten Consumption | May include moderate gluten consumption. | Often excludes gluten ingredients due to its potential to exacerbate autoimmune symptoms |
| Medical Supervision | Generally suitable for most individuals without medical supervision | Requires guidance from healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians or physicians, due to individualized restrictions and sensitivities |
Every diet offers an array of health benefits. Some may be long term, while others are for a shorter time period. However, like any other diet, the anti-inflammatory diet also comes with its own set of disadvantages. Check them out in the section below.
Disadvantages Of The Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Lack Of Variety: Anti-inflammatory diets often limit the types of food you can eat. This means you might end up eating the same things over and over again, which can get boring.
- Expensive Groceries: Buying the special foods recommended for this diet can be costly and may strain your budget.
- Social Challenges: When you follow an anti-inflammatory diet, it can be tricky to go out with friends or attend social events. You might feel left out when others are enjoying foods you can’t have.
- Missing Nutrients: This diet may cause you to miss out on important nutrients. For example, if you cut out dairy, you might not get enough calcium, essential for strong bones.
However, to combat a few of these drawbacks, you may follow a few tips listed in detail in the next section
Anti-Inflammatory Diet Tips
- Stay Hydrated
Remember to drink enough water throughout the day. Water helps your body function properly and keeps inflammation in check.
- Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to when you feel hungry or full. Overeating can cause inflammation, so avoid it. Eat slowly, properly chewing your food. It is recommended to chew a morsel of food 20 times before you swallow it. You can also follow the Japanese principle of eating until you are 80% full. Drink a glass of water before and after your meal.
- Watch Your Portions
While the anti-inflammatory diet is favored for its lack of restriction and portion control, you should be mindful of how much food you put on your plate. Eating the right amount can help prevent inflammation caused by excessive calories.
- Cut Down on Sugary Drinks
Avoid consuming sugary drinks like soda and fruit juices. Too much sugar can lead to inflammation, so it’s a good idea to limit these.
- Cook Fresh at Home
When you can, cook your meals using fresh ingredients at home. This way, you have more control over what you eat, and it’s often healthier. Instead of deep frying or grilling your food, opt for healthier options like smoking or steaming.
- Avoid Processed Foods
Try to eat less processed and fast foods. These often have unhealthy fats, lots of salt, and additives that can make inflammation worse. Choosing natural, unprocessed foods is a better choice.
By following these tips and by incorporating a wide variety of fruits and vegetables, inflammation can be effectively managed. But you need not compromise on your taste. The section below lists a few yummy recipes you can try if you are on an anti-inflammatory diet.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet Recipes
1. Breakfast: Turmeric Oatmeal
Ingredients
- 1 cup rolled oats
- 2 cups water or almond milk
- 1 teaspoon ground turmeric
- 1/2 teaspoon ground cinnamon
- 1/4 teaspoon ground ginger
- 1 tablespoon honey or maple syrup (optional)
- Chopped nuts and fresh berries for topping
How To Prepare
- In a saucepan, bring the water or almond milk to a boil.
- Stir in the rolled oats, turmeric, cinnamon, and ginger.
- Reduce the heat to low and simmer for about 5 minutes or until the oats are creamy and cooked.
- Sweeten with honey or maple syrup, if desired.
- Serve in bowls, topped with chopped nuts and fresh berries.
2. Lunch: Quinoa And Chickpea Salad
Ingredients
- 1 cup cooked quinoa
- 1 can (15 oz) chickpeas, drained and rinsed
- 1 cup cherry tomatoes, halved
- 1 cucumber, diced
- 1/4 cup red onion, finely chopped
- 1/4 cup fresh parsley, chopped
- Juice of 1 lemon
- 2 tablespoons extra-virgin olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Combine the cooked quinoa, chickpeas, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, red onion, and fresh parsley in a large bowl.
- Whisk together lemon juice, olive oil, salt, and pepper in another bowl.
- Pour the dressing over the salad and toss to combine.
- Chill in the fridge for about 30 minutes before serving.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?3. Snack: Almond Butter And Banana Rice Cakes
Ingredients
- 2 rice cakes (choose whole-grain or brown rice)
- 2 tablespoons almond butter
- 1 ripe banana, thinly sliced
- 1 teaspoon honey (optional)
- A sprinkle of cinnamon
How To Prepare
- Spread the almond butter evenly on each rice cake.
- Top with banana slices.
- Drizzle honey on top, if desired, and sprinkle a pinch of cinnamon on top.
4. Dinner: Baked Salmon With Roasted Veggies
Ingredients
- 4 salmon filets
- 2 cups broccoli florets
- 2 cups cauliflower florets
- 1 red bell pepper, sliced
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 teaspoon dried rosemary
- 1 teaspoon dried thyme
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Lemon wedges for serving
How To Prepare
- Preheat the oven to 400°F (200°C).
- Combine broccoli, cauliflower, red bell pepper, olive oil, garlic, rosemary, thyme, salt, and pepper in a large bowl. Toss to coat the vegetables evenly.
- Place the salmon filets on a baking sheet lined with parchment paper.
- Arrange the seasoned vegetables around the salmon on the baking sheet.
- Bake in the preheated oven for about 15-20 minutes or until the salmon is cooked through and the vegetables are tender.
- Serve with lemon wedges for added flavor.
Infographic: Top Benefits Of The Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet is a tailored dietary approach that carefully incorporates food to effectively combat inflammation. Along with managing inflammation, this diet also offers an array of health benefits. Check out the infographic below to know what they are.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Inflammation is a major cause of many health conditions. To tackle this, one needs a tailored dietary approach including foods that effectively combat inflammation. The anti- inflammatory diet is one such diet that offers many additional benefits like weight loss, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and promoting skin health along with combating inflammation. It includes a wide range of food varieties and there are also a few foods one can choose to target and manage specific conditions like IBS or gastritis. However, like any other diet, it also comes with a set of its own drawbacks. Hence, consult a healthcare professional if you want to start this diet to minimize any unwanted side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a vegetarian diet reduce inflammation?
Yes, a well-balanced vegetarian diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and plant-based proteins can help reduce inflammation.
Is coffee acceptable on an anti-inflammatory diet?
In moderation, coffee can be part of an anti-inflammatory diet, but excessive consumption may have mixed effects.
Are eggs inflammatory?
Eggs are generally considered non-inflammatory (28). These can be part of an anti-inflammatory diet when prepared healthily.
What are some examples of cheap foods that fight inflammation?
Budget-friendly anti-inflammatory foods include oats, beans, lentils, frozen fruits and vegetables, and affordable spices like turmeric and ginger.
Which diseases can an anti-inflammatory diet help fight?
An anti-inflammatory diet may help in managing conditions like arthritis, heart disease, diabetes, and some digestive disorders by reducing inflammation in the body.
Key Takeaways
- An anti-inflammatory diet promotes whole foods and avoids processed ones to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Different types of anti-inflammatory diets cater to various dietary preferences and health goals.
- Anti-inflammatory foods offer benefits like stable blood sugar, joint health, reduced cancer risk, and potential cognitive support.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Although there are many foods claimed to effectively combat inflammation, there are a few ingredients that really work well. Check out the video below to know what foods the experts suggest.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Mediterranean Diet as a Tool to Combat Inflammation and Chronic Diseases. An Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7400632/# - Paleolithic and Mediterranean Diet Pattern Scores Are Inversely Associated with Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Balance in Adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4877627/#: - Ketogenic diet ameliorates inflammation by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome in osteoarthritis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9116003/ - Associations of a vegan diet with inflammatory biomarkers
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7005174/# - Efficacy of the Autoimmune Protocol Diet for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/mid/NIHMS889275/# - Anti-Inflammatory Diet in Clinical Practice: A Review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28350517/ - Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Diets on Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8706441/ - The inflammatory potential of diet in determining cancer risk; A prospective investigation of two dietary pattern scores
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6461253/ - Nut consumption for vascular health and cognitive function
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24866624/ - Dermatology: how to manage acne vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8510514/# - Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6682904/ - Diet-Derived Antioxidants and Their Role in Inflammation Obesity and Gut Microbiota Modulation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8146040/ - Turmeric the Golden Spice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92752/ - Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29215589/ - Free radicals antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249911/# - Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ginger in Health and Physical Activity: Review of Current Evidence
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3665023/ - The Effect of Fiber Supplementation on Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
https://journals.lww.com/ajg/abstract/2014/09000/the_effect_of_fiber_supplementation_on_irritable.12.aspx - Is ginger effective for the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome? A double blind randomized controlled pilot trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3958926/# - Low-FODMAP Diet for Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3966170/ - Effectiveness of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome: Updated systematic review with meta-analysis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25780308/ - Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Benefits and Endpoints in Sport
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6357022/# - Turmeric and Its Major Compound Curcumin on Health: Bioactive Effects and Safety Profiles for Food Pharmaceutical Biotechnological and Medicinal Applications
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7522354/# - Molecular mechanisms of inflammation. Anti-inflammatory benefits of virgin olive oil and the phenolic compound oleocanthal
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21443487/ - Oat porridge consumption alleviates markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in hypercholesterolemic adults
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31192555/# - Rice Protein Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect in Growing and Adult Rats via Suppressing NF-κB Pathway
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6941109/# - Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effects of green tea and black tea: A comparative in vitro study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3401676/ - A review of the gastroprotective effects of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23612703/ - Bioactive Egg Components and Inflammation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4586567/#