Vaginal Pimples: Expert Tips For Treatment And Prevention
Find out what causes pimples down there and how to get long-term relief.
Image: Shutterstock
Pimples on your back and shoulders are common, but have you ever experienced pimples in your vaginal area? Women experience breakouts “down there” due to tight yoga trousers and harsh waxes and other reasons. But, don’t worry – there are various vaginal pimple treatment options available now.

Pimples on the vagina are similar to facial breakouts and appear as little red bumps with a white pus-filled tip. They are usually painless and only cause minimal discomfort, but that does not mean you should avoid them. In many situations, bumps resembling pimples (medically referred to as folliculitis or boils) appear due to infections that, if left untreated, could spread to other areas.
Read on to find out more about the causes of vaginal pimples and how to treat and prevent them in the future.
In This Article
What Causes Pimples On Private Parts?
You should know what causes vaginal boils to treat the issue properly. Vaginal acne or boils form when sweat, dirt, and bacteria clog the genital pores and hair follicles, causing inflammation. These pimples may also be a result of hormonal changes.
These are some of the most common causes of pimples on the vaginal area:
1. Ingrown Pubic Hair
Waxing, plucking, or shaving pubic hair is the most common cause of ingrown vaginal hair. According to a recent study, around 32.7% of women who shave their pubic hair have the problem of ingrown vaginal hair at some point in life.
An ingrown pubic hair develops when the hair follicle curls downward, pressing the top of the hair to curve into the skin. This results in a skin reaction characterized by swelling, prickling pimples, and skin darkening. Apart from how you shave your hair, several genetic factors may make you more sensitive to developing ingrown pubic hair.
When an ingrown pubic hair grows, the first thing to do is to stop shaving. Usually, this will limit the inflammation within a few days. However, if the problem persists, you should visit a dermatologist. They may prescribe an oral antibiotic or topical lotion to relieve inflammation and prevent infection.
Medical intervention is necessary in this case. Laser hair reduction procedures work well and help resolve the issue. However, if left untreated, repeated ingrown hairs can become chronic and grow into an infection of the hair follicles called folliculitis.
2. Molluscum Contagiosum (MC)
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a viral infection that can cause small, elevated pimples to grow anywhere on the vagina.
There may be only one or a whole bunch of bumps. While these bumps are usually painless, they can become quite itchy, especially during the night. MC lumps are soft with a white, pink, or skin-colored spot in the center.
This infection spreads through sexual or non-sexual skin-to-skin contact and is a common problem in children, sexually active adults, and people with weak immune systems. Luckily, an MC infection usually goes away within 5-7 months, and there are numerous medications available to treat it.
Cryotherapy is one of the more efficient treatments for removing these bumps, depending on the skin type. Topical treatments include potassium hydroxide, and salicylic acid. Note that you should apply them as directed by a physician.
3. Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS)
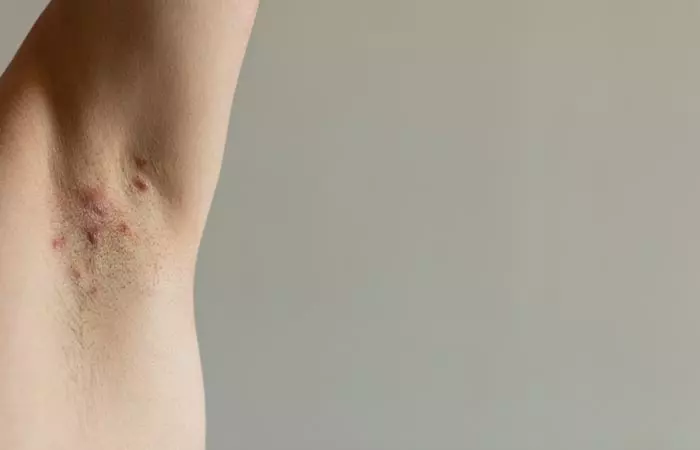
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a genetic skin condition that forms painful bumps under your epidermis in the hair bulbs near your sweat glands. This problem is usually known as acne inversa. These vaginal bumps can become infected. Openings form beneath your vaginal skin and swell with pus. Also, they can smell bad when they open and leave marks.
A study in PubMed Journal found the prevalence of hidradenitis suppurativa to be highest in African American populations (1.3%), lowest in Hispanics/Latinos (0.07%), and in the middle amongst Caucasian populations (0.75%). Also, the rate of prevalence in other ethnic groups (0.17%) was minor in comparison to African American and Caucasian populations.
If you are affected by HS, your doctor may prescribe a combination of oral and topical antibiotics, including clindamycin, a topical antibiotic. Apart from this, making some changes in your lifestyle and appropriate medication can give you some relief and reduce flare-ups.
 Trivia
Trivia4. Vulvar Vesicles
Cysts or vesicles are pocket-like structures filled with liquid that can develop almost anywhere on your body
. The majority of vulvar cysts are not a significant cause of worry, but they can sometimes be precancerous or cancerous. Hence, it is advisable to have them examined by a medical practitioner.
However, if you are not able to figure out the cause of the vaginal pimple, it is best to consult your doctor for a diagnosis. Keep reading to find out more.
Key Takeaways
- Women experience breakouts even at the vagina when they apply harsh waxes for hair removal or wear tight yoga pants. These pimples appear as red bumps with white pus-filled tips.
- While these are generally painless and cause a little discomfort, they may lead to infections if left untreated.
- Vaginal acne can be caused due to ingrown pubic hair, molluscum contagiosumi A fairly common skin infection caused by a virus that causes round, firm, painless bumps ranging in size from a pinhead to a pencil eraser. , hidradenitis suppurativa, and vulvar vesicles or cysts.
- While it is not safe to pop a vaginal pimple, there are other methods of treatment available such as maintaining good vaginal hygiene, using a cold or warm compress to relieve any discomfort, and topical medications you can apply to reduce and treat vaginal acne.
Diagnosis Of Vaginal Pimples
Your healthcare provider can diagnose vaginal pimples with a quick physical examination. If they suspect the issue is more than just a vaginal pimple, they will conduct a more detailed evaluation, which may include:
- Investigating any recent changes in your routine that could cause contact dermatitis.
- Discussing your hygiene practices.
- Asking about your sexual history and number of partners.
- Running tests to rule out sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
If these pimples take too long to heal, they may irritate your sensitive area and prompt you to pop them. But, is this really advisable? Read the next segment to find out.
Is It Safe To Pop A Vaginal Pimple?
No, it is best not to attempt to pop a vaginal pimple.
Popping vaginal acne can increase the chances of an infection in the genital area and create severe issues.
Also, vaginal pimples can sometimes turn into boils if they are filled with pus, thereby growing more prominent and painful. Hence, to avoid any infection in or near your genitals, you should never pop these boils and let them rupture themselves.
If you cannot resist popping these pimples or they take too long to heal, you should see a gynecologist. They can drain the boil in a manner that will prevent vaginal infection. Additionally, there are remedies and tips you can follow to learn how to prevent acne from forming on any body part, including the vagina.
There are safer ways than popping a pimple to eliminate vaginal acne. Explore some useful ways to treat the condition below.
How Are Vaginal Pimples Treated?
Pimples on the vagina usually go away on their own. However, if you think this problem is getting worse, it is advisable to see a doctor. Getting the proper medical attention can help you treat genital acne and other similar issues in and around your vagina.
Mentioned below are some common ways to treat vaginal pimples.
1. Identify What Causes Vaginal Pimples
To receive the correct medical treatment, you must keep a watch on any activities or products that may be causing your genital acne. Some factors that can affect the vaginal area include shaving, waxing, and hot tub usage.
Another lesser known cause of vaginal acne is a poor diet. Just like regular acne, the more fatty food you eat, the more breakouts you will have. For example, fungal acne caused by yeast infections may lead to vaginal pimples. This can be prevented by following a healthy diet.
You can also consider avoiding using any products in the vaginal area, including laundry soaps, for some time. Once the symptoms recede, gradually reintroduce these products one by one and record any unfavorable reactions.
2. Get Rid Of Irritants
Once you identify the cause of the vaginal irritation or infection, stop applying those products, wearing certain fabrics, or engaging in certain activities.
For instance, if shaving is the cause of your vaginal acne or inflammation, you can switch to other ways of removing your pubic hair or shaving in the same direction as your hair growth. Also, it is crucial to keep your bathtub clean and only use pools that are properly managed.
3. Maintain Good Vaginal Hygiene
The moisture and warmth in the genital area make it a perfect place for bacteria and other microorganisms to grow. Hence, to prevent and treat vaginal acne, it is important to wash your genitals every day with lukewarm water and mild soap.
Also, you should avoid using harsh cleansing products inside the vagina as these products can disturb the pH balance, which can cause an infection and pimples in the private area.
4. Warm Or Cold Compress

According to anecdotal evidence, a warm compress is beneficial for soothing inflamed ingrown pubic hair or cysts, whereas a cool compress works better for vaginal itching.
Even if your medical condition is infectious or you believe it might be, using a compress to alleviate discomfort is fine. However, in such cases, always exercise proper care and use a fresh towel every time, so you never get reinfected or spread the infection to other people.
5. Topical Medications
Topical medication is the most effective way to treat vaginal acne. These medications usually come in the form of lotions, gels, or antibiotics. There are medicated body washes made with benzoyl peroxide that may reduce these pimples. However, before using any topical medication, you must consult a medical practitioner who can prescribe the appropriate medication. There are also natural remedies like tea tree oil, witch hazel, and aloe vera that may help reduce the irritation caused by the pimples.
Zayleaaelyaz, a blogger, offers some advice on her blog based on her experience with pimple-like lumps in her vaginal area. She writes, “What I can advise you to do is to visit the doctor (either a general practitioner or a gynecologist) for advice because these lumps may mean different things for different people. For me, it could be an infection or a cyst but for you, it could be the same or something else that is more serious or perhaps not even serious at all (i).”
Sometimes, pimples in the genital area occur due to several other conditions. Let’s look at these in detail below.
Other Breakouts On And Around The Vagina
Many women mistake their vaginal bumps for pubic acne. However, they may indicate another serious underlying condition. Listed here are some other reasons why these bumps arise:
1. Bartholin’s Cyst
are noncancerous lumps that develop on either side of the labia. Around 2% of all women develop Bartholin’s cysts at least once in their lifetime, and they are most widespread among women in their mid-20s.
This type of bump develops when a Bartholin’s gland (responsible for sexual lubrication) gets obstructed. Since these bumps grow gradually and are usually painless, you may not recognize that you have a Bartholin’s cyst until years later.
Numerous medications are available for treating Bartholin’s cysts, depending on how much the bump has grown. While your doctor may prescribe antibiotics or topical creams for smaller growths, larger cysts may need surgical treatment to prevent the cyst from growing back.
2. Genital Warts
Genital warts are soft bumps that develop on the genital area. They can cause discomfort, pain, and itching. It is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by low-risk human papillomavirus (HPV). You may not begin to develop genital warts for various weeks or months post-infection. These warts resemble cauliflower and can be flesh-colored, dark purple, or light brown.
To diagnose this medical condition, your physician will ask questions about your sexual history and health. In addition to this, they will conduct a physical inspection of the areas where warts may be occurring.
Since genital warts can develop deep inside a woman’s vagina, your doctor might perform a pelvic examination. They may also use a mild acidic solution to make genital warts more noticeable.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?3. Genital Herpes
is another prevalent STI caused by HSV (Herpes simplex virus). After the primary infection, the virus slowly infects your body and can reactivate numerous times in a year.
Genital herpes can cause discomfort, itching, and pain in your vaginal area. Although you may experience no symptoms of genital herpes, you can spread this virus to other people.
If you are experiencing vaginal acne or a severe itch down there, it is best to get it diagnosed by a medical professional as the chances that you have contracted any sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are high. Your medical practitioner can diagnose you with herpes by checking the bumps. If required, the doctor can confirm their examination by a blood test. Antiviral drugs may help speed up the recovery time of genital herpes and reduce discomfort.
4. Vaginal Skin Tags
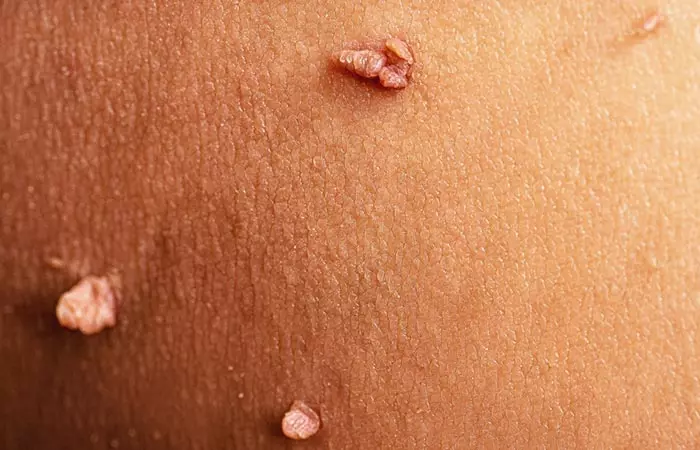
Vaginal skin tags are benign lumps of skin made of loose tissues of collagen. They can be pretty uncomfortable when they develop in and around the delicate vaginal area. Vaginal skin tags do not cause pain unless they are picked or infected.
Unlike genital warts, which look flat on the vaginal area, vaginal skin tags are attached to your skin by a small stalk. Also, skin tags never bleed unless you try to remove them from your skin. Sometimes these tags appear in clumps on your skin.
You might not initially notice vaginal tags as they are usually of the same color as the skin or slightly darker than your natural skin tone. These should always be carefully removed by a dermatologist.
5. Fordyce Spots
is an uncommon disease that causes chronic pain in the sweat glands in the vaginal area. During this infection, the apocrine glandsi Glands that release sweat in armpits, skin, and eyelids, and the ones found in breasts secrete fat droplets into breast milk. become swollen and infected with profoundly itchy bumps.
People with this condition usually develop numerous small skin-colored bumps on their labia, and itching them can cause infection in the hair follicles. Also, stress and laser hair removal can trigger or aggravate this problem in some people.
Once you identify the right cause of pimples on your private parts, you can take the necessary steps to prevent this problem from occurring in the future. Let’s look at a few tips to combat vaginal acne below.
Tips To Prevent Genital Acne
Listed below are some prevention tips against zitsi Often used as slang or a synonym for pimple and refers to a blackhead, whitehead, or a pustule on the skin. in the pubic area:
- Wear clean underwear made from breathable cotton fabric.
- Avoid clothes that are too tight or brush against your vaginal area.
- Always practice good genital hygiene, including a hot shower post-workout and changing out of sweaty clothes after working out.
- Change your tampon and sanitary pad often when you are menstruating.
- Trim your pubic hair rather than shaving it (if the bumps are caused by razor use).
- Avoid using scented products near the vaginal area.
Infographic: Acne Vs. Folliculitis
It is fairly common to confuse vaginal acne for folliculitis as the different forms of acne, especially pimples, look very similar to the bumps that appear when you have folliculitis. However, they are vastly different.
Check out the infographic to understand how they differ so that you can get the most appropriate treatment for what’s going on down there.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Vaginal pimples occur when sweat, bacteria, and dirt clog the genital pores. It can also be caused due to hormonal changes and infections and spread to other areas if left untreated. Vaginal pimples treatments include home remedies, warm or cold compresses, topical medications, and maintaining good vaginal hygiene.
If the vaginal pimple is causing pain and discomfort, it is best to consult your doctor. You may also follow the tips mentioned in the article to prevent pimples. Your doctor will help you identify the cause of vaginal pimples and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the possible side effects of different treatments for vaginal pimples?
Vaginal pimple treatments can cause side effects like dry and irritated skin, upset stomach, dizziness, sleepiness, difficulty peeing, blurred vision, and fatigue.
Is there any risk of scarring or other long-term effects from treating vaginal pimples?
Vaginal acne is characterized by sore bumps, usually filled with pus, that can leave scars.
What are some at-home remedies for treating vaginal pimples?
Home remedies commonly used for treating vaginal pimples include tea tree oil (diluted), neem-infused warm water compress, and turmeric paste. Although these ingredients are said to be effective due to their anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties, their use as a treatment for vaginal pimples is purely based on anecdotal evidence.
Can vaginal pimples go away on their own?
Yes, vaginal pimples often go away on their own, especially if they are caused by irritation or clogged pores. Keeping the area clean and avoiding tight clothing can help them heal faster. However, if they persist or become painful, it is best to consult a healthcare provider to rule out other conditions.
When should I see a doctor for vaginal pimples?
You should see a doctor if the vaginal pimples don’t go away after a few days and become painful, swollen, or filled with pus. Also, seek medical advice if you notice other symptoms like itching, burning, or unusual discharge, as these could indicate an infection or a more serious condition.
The appearance of itchy vaginal pimples can be due to various reasons. Watch the video below to learn what to look out for and how to treat them.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. PIMPLE-LIKE THING IN VAGINAhttps://zayleaaelyaz.wordpress.com/2014/05/04/pimple-like-thing-in-vagina/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Complications related to pubic hair removal
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4040320/ - Molluscum Contagiosum
https://www.cdc.gov/molluscum-contagiosum/about/index.html - Clinical Overview of Molluscum Contagiosum
https://www.cdc.gov/molluscum-contagiosum/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html - Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5402905/ - Overview of Extracellular Vesicles Their Origin Composition Purpose and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6678302/ - Bartholin Gland Cyst
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532271/ - About Genital HPV Infection
https://www.cdc.gov/sti/about/about-genital-hpv-infection.html - Genital Herpes – CDC Fact Sheet
https://www.cdc.gov/std/herpes/stdfact-herpes.htm - Giant skin tag on the labium majorum
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5419766/ - Clinicopathologic Manifestations of Patients with Fordyce\’s Spots
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3283840/ - Hidradenitis Suppurativa
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534867/
Read full bio of Dr. Sravya Tipirneni
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Swathi E



















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.