13 Tips And Remedies To Prevent Acne And Pimples Naturally
Get spot-free and clear skin by incorporating some lifestyle and dietary changes.

Image: Shutterstock
Acne and pimples are not easy to deal with, and no one prefers to go through that ordeal. So, is not it better we prevent them? But how to prevent pimples and acne? Several factors cause them, and you need to follow a systematic skincare routine to prevent acne and pimples. Can home remedies prevent acne and pimples? Let us find out here. This article discusses the causes of pimples and acne and different remedies that help you prevent them. Keep reading to know more!

In This Article
Why Do We Get Pimples?
According to the dictionary, a pimple is an inflamed spot on your skin. A pimple is a type of acne that can occur at any age and at any time.
Before you try to treat it, you need to understand why you get pimples or acne. Mentioned below are the factors responsible for this condition:
- Clogged Pores: When the pores or sebaceous glandsi Minuscule glands in the skin that secrete sebum, a lubricant that forms a protective layer over the skin and hair. are blocked, they cannot release sebum (an oily substance that keeps your skin moisturized). A build-up of oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria in the area causes acne or a pimple.
- Genetics: If there is a history of acne in your family, it is likely that you will have it too. Your genes determine how sensitive your skin is to hormonal fluctuation, how quickly it sheds its cells, how much sebum it produces, and how it responds to inflammation. All these factors determine how readily you develop pimples.
- Hormones: Your estrogen and testosterone levels are directly related to pimples. That’s why you most often get pimples during puberty and pregnancy and when you are menstruating.
- Stress: Studies show that stress aggravates acne (1), (2). The sebaceous glands contain the receptors for stress hormones. When you are stressed, the hormones increase the sebum production in your skin and cause acne.
An international patient survey conducted on 6700 participants found that 51% of people with acne have extremely-high stress levels. Also, 54.6% of individuals with acne reported sleeplessness compared to those without acne. Therefore, stress is one of the main factors to cause acne.
- Depression: Depression is linked to acne and vice versa. Studies have found that acne is linked to an increased risk of depression (3), (4).
- Smoking: The relationship between smoking and acne is unclear. Clinical studies have found that smoking is an important contributory factor to the prevalence and severity of acne (5). Smoking often reduces oxygen flow to the skin cells, disrupts hormonal balance, and slows down the healing process.
- Alcohol Consumption: Although alcohol does not cause acne, it affects the levels of the hormones that regulate acne. A study found that alcohol could increase testosterone levels in women. It also shoots up estradiol (a form of estrogen) levels in women (6).
- Diet: Although the relationship between diet and acne is debatable, specific foods (such as processed and sugary foods) can make your condition worse. However, you can consider adding other food, such as seafood, veggies, and omega-3 fatty acids-rich ingredients, to your diet to improve overall skin health.
Acne can be inflammatory and non-inflammatory. Usually, non-inflammatory acne is mild and may go away with OTC medicines. Non-inflammatory acne can be deep and may take time to heal. Keep reading to learn more about different types of acne.
Key Takeaways
- Stress, genetics, and smoking are a few causes of pimples.
- Simple ingredients like honey and tea tree oil can help reduce inflammation and prevent acne.
- Hydrate your skin and avoid junk foods to keep your pimples in check.
- Your doctor may recommend laser treatment or salicylic acid to help treat your pimples.
Types Of Acne
The most common types of acne are (7):
- Whiteheads: These are closed comedones that occur when pores and follicles are blocked with oil and dead skin cells.
- Blackheads: These are open comedones and appear black as the dirt and sebum remain exposed and they oxidize.
- Papules: These are small, red, inflamed bumps without pus.
- Pustules: They are similar to papules and have a white or yellow center consisting of pus.
- Nodules: They are large, painful, and hard bumps that develop deep within the skin.
- Cysts: They are painful, pus-filled lumps under the skin, often causing scarring.
Whether hormonal issues or genetic factors triggered your pimples or acne, a dermatologisti A doctor with board certification who is qualified to identify and treat disorders of the skin, hair, and nails. can help diagnose and treat the root cause and you may also choose to get hormonal therapy. In case the pimples are caused by lifestyle issues or any other factors (other than genetics and hormonal conditions), what should be done? How to get clear skin with some lifestyle and skincare changes? Below are some ways to manage them that you can follow.
How To Prevent Pimples And Acne
1. Wash Your Face Properly

Gentle cleansing is the backbone of any skin care routine. Use a mild and non-comedogenici A skin care ingredient or cosmetic aimed at reducing acne and its related symptoms without blocking skin pores. cleanser to clean your face twice daily – once in the morning and once before going to bed. Cleanse your face if you sweat heavily. However, avoid excessive face washing as it may lead to redness or dryness. If your skin feels too oily, use blotting paper for oil control. Also, use warm water while washing to open up the pores.
2. Know Your Skin Type
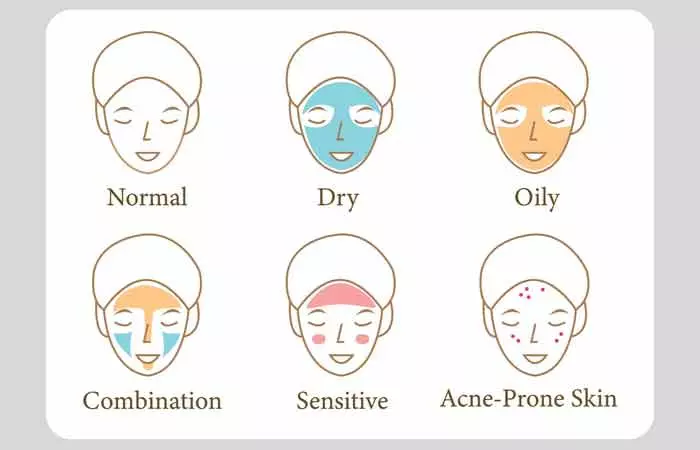
This is important as it will help you choose the right skincare products for your skin type. Products that are suitable for oily skin are not ideal for dry skin. Oily skin is the most prone to pimples because the sebaceous glands are overactive and produce a lot of sebum. Combination skin is also prone to pimples on the T-zonei The middle region of the face comprising the forehead, nose, and chin that is noted for being greasier than other areas of the face. . You should also regularly update your skincare routine. The skin changes due to stress, seasons, or hormonal shifts, making it crucial to switch your skincare routine regularly so that it suits the skin at every stage. Products that work well for you in summers may not be as effective in winters and vice versa.
3. Keep Your Skin Moisturized

Moisturizing your skin is essential for pimple prevention. However, avoid moisturizers that contain chemicals and synthetic fragrances. Always go for non-comedogenic moisturizers so that your skin does not feel dry after every wash. You can use face masks or serums to moisturize your skin and lock in hydration.
4. Use Acne Medication
There are over-the-counter medications available in drugstores that you can use to treat acne and pimples. Consult a dermatologist before taking any medicines. Also, make sure you follow the instructions properly.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip5. Drink Water (A Lot Of It!)

When your body is dehydrated, it signals your skin to produce more oil to keep it moisturized. This increases inflammation and worsens acne.
6. Use Makeup Wisely
You may be tempted to cover up your acne and scars with makeup. However, makeup can clog your pores further and aggravate your condition. When using makeup, choose non-comedogenic products and non-greasy formulas. Also, avoid heavy foundations and concealers.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip7. Avoid Touching The Pimple
Your fingers are home to germs and bacteria that might get transferred to your skin. Hence, do not squeeze, touch, or scratch the pimple. Avoiding touching the face prevents any skin irritation and aggravation of acne breakouts.
Ifeoma, a blogger, shared her history of acne and suggested to maintain proper hygiene and avoid touching one’s face. From her experience, she recommended to not try to pop the zit or acne. After getting impatient and popping a zit on her nose, she noted, “When I woke up the next day, it was bigger with another yellow head and even more painful. Now I have a semi-black spot at the tip of my nose (i).”
8. Keep Yourself Sun-Safe
Long-term sun exposure causes dehydration for your skin and makes it produce more oil, causing blocked pores and breakouts. Carry an umbrella and use sunscreen for sun protection when heading out.
9. Check Your Diet
What you eat reflects on your skin. Hence, be mindful of what you are putting on your plate. A review published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology suggests that certain foods can worsen acne. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as baked goodies, chips, soft drinks, and those made with white flour, can aggravate acne. Dairy products were found to trigger acne breakouts in some cases (8).
10. No Scrubbing
Avoid using face scrubs if you have acne. Avoid cleaning your face with cloth pads or washcloths. Scrubbing already irritated skin causes further inflammation and exacerbates pimples or acne breakouts.
11. Check Your Hair Care Products
Hair care products (shampoos, conditioners, and styling products) contain chemicals and oils that may clog the pores and cause acne and pimples near the hairline, forehead, and neck. This type of acne is often called Acne cosmetica. Use products that are non-comedogenic, oil-free, and non-acnegenic. Also, after using any hair product, wash the scalp well to clear any residue.
12. Reduce Stress
Stress can also cause pimples and acne. For stress management, try meditation, regular exercise, or any other activity that keeps you happy and relaxed.
13. Keep The Facial Accessories Clean
If you use makeup brushes, beauty blenders, facial cleaning brushes, make sure to keep them clean. Using unclean accessories that contain germs may cause pimples and acne. Hence, wash them thoroughly after every use. And always make sure to use clean towels and bedsheets, and maintain pillowcase hygiene.
Along with controlling your lifestyle habits, you also need to apply topical medications for acne. Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter treatments or prescription medications, ointments, and serums depending on the nature and severity of your condition. Let’s take a look at the potential treatments for pimples or acne.
Alternative Treatments To Stop Pimples And Acne
- Benzoyl Peroxide
Benzoyl peroxide is a very common ingredient in acne/pimple treatment creams (9). Usually, you will find creams containing 2.5%, 5%, or 10% benzoyl peroxide. Mild acne may require a low percentage of the ointment, while severe acne might need a higher percentage of benzoyl peroxide. Consult your doctor before making your purchase because the wrong percentage of the cream can make your skin dry and worsen your condition.
- Salicylic Acid
Compared to benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid is a safer treatment option for acne. It treats the condition without damaging your skin. It has keratolytic properties that dissolve the keratin and exfoliates the lesion (acne or a pimple), thus calming the inflammation (10).
- Sulfur
This antibacterial agent has been used for treating acne since the time of the ancient Egyptians. It dries or shrinks the pimple, thus reducing the inflammation. Sulfur doesn’t dehydrate your skin and is milder than benzoyl peroxide (11).
- Tretinoin
This is a type of trans-retinoic acid that is used for treating acne during its initial stages. It has comedolytic properties, which means it unclogs your pores, boosts the growth of new cells, and ensures smooth flow of sebum (12). Your doctor may recommend other topical retinoids depending on the severity of your acne condition.
- Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid has anti-inflammatory properties and is used for treating moderate acne. The effect of 20% azelaic acid was studied for acne treatment, and it was found that it was as effective as tretinoin cream in treating acne (13).
- Laser Treatment
is often used for treating moderate to severe acne and is considered a safe and effective method. This is a low or no-risk treatment option that uses light beams for clearing acne. However, it is not a stand-alone treatment. You have to use medicines along with the treatment procedure for complete clearance (14).
- Chemical Peeling
When done under the supervision of a professional, chemical peeling works like magic for skin brightening and treating acne and hyperpigmentation. It helps in reducing acne scars and other skin issues. The procedure may cause mild discomfort and irritation that can be managed easily (15).
- Microdermabrasion
This process involves gentle exfoliation of the affected area using handheld devices with diamond-studded tips for abrading the skin and vacuum suction for removing it. This topical peeling procedure is widely popular and is safe and effective for treating mild to severe acne (16).
How can you get rid of pimples fast? If you have mild pimples or acne, then try out some home remedies for treating it.
How To Prevent Pimples Using Home Remedies
| Ingredient | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Tea Tree Oil | It has antibacterial properties that help prevent acne and pimples. Click here to learn more. |
| Honey | It has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that help in reducing inflammation. Click here to learn more. |
| Aloe Vera | Apart from having antibacterial properties, it also helps in calming your skin. Click here to learn more. |
| Ice Cube | Rubbing an ice cube on the pimple reduces inflammation. For more details, click here. |
| Toothpaste | You can use toothepaste for treating acne and pimples. To learn how, click here. |
| Aspirin | Aspirin is not just used for relieving pain but also for managing acne. To learn how, click here. |
Infographic: Top 5 Tips To Keep Acne Breakouts At Bay
Acne can be frustrating. While there are numerous home remedies and treatments that can help you deal with it, a simple tip like keeping your facial accessories clean can work wonders, too. Check out the infographic below for more such easy tips to prevent acne.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Witch hazel, turmeric, garlic, cinnamon, and grapefruit seed extract are a few other natural remedies with anti-inflammatory properties that may reduce acne outbreaks. Identifying the factors that lead to acne formation and taking precautions beforehand is the best way to prevent acne and pimples. The lifestyle and skin care tips shared in the article can help you care for your skin properly and minimize the risk of breakouts. However, if your breakouts are due to underlying issues, it is best to consult a doctor, use prescribed medications, and follow their suggestions. You may not get rid of acne or pimples overnight. Have patience, allow your skin to heal, and stick to the treatment plan to see the results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What skincare routine is most ideal for acne-prone skin?
Opt for a gentle skin care routine if you have acne-prone skin. Use a cleanser, exfoliant, toner, and lightweight, oil-free moisturizer. Look for ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to target breakouts effectively. Avoid using heavy or oil-based products and opt for water-based ones instead.
At what age will I stop getting pimples?
Pimples should go away mostly once you are in your mid-20s, and the hormones in your body get balanced. However, if you have any hormonal issues, you may still continue to get pimples and acne.
How to stop pimples from growing?
Do not touch or poke the pimple. Visit a dermatologist and apply the prescribed medication to prevent further inflammation.
Does sleeping late cause acne?
If you don’t get enough restful sleep, your body may not feel refreshed, which could cause a cortisol spike and increase your chance of developing new pimples. However, more research is required to prove the same.
What are the seven types of acne?
Whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, nodules, cysts, and milia are some types of acne.
Illustration: Tips And Remedies To Prevent Acne And Pimples Naturally

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- The association between stress and acne among female medical students in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5722010/ - The Impact of Pyschological Stress on Acne., Acta Dermato- venereologica, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28871928/ - Comparison of Anxiety And Depression In Patients With Acne Vulgaris and Healthy Individuals, Indian Journal of Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3051295/ - Risk of depression among patients with acne in the U.K.: a population‐based cohort study, British Journal of Dermatology, ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322985966_Risk_of_depression_among_patients_with_acne_in_the_UK_A_population-based_cohort_study - Epidemiology of acne in the general population: the risk of smoking, The British Journal of Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11453915/ - Acute effect of alcohol on androgens in premenopausal women. Alcohol and Alcoholism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10684783/ - Acne Vulgaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173/ - Dairy Intake and Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 78,529 Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6115795/ - What is the Role of Benzoyl Peroxide Cleansers in Acne Management? The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3016935/ - Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads. Clinical Therapeutics, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1535287/ - An update on the management of acne vulgaris, Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3047935/ - Tretinoin: A Review of Its Anti-inflammatory Properties in the Treatment of Acne, The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3225141/ - Clinical studies of 20% azelaic acid cream in the treatment of acne vulgaris. Comparison with vehicle and topical tretinoin., Acta Dermato- venereologica, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2528257/ - Light-based therapies in acne treatment, Indian Dermatology Online Journal, Us National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4439741/ - Efficacy and safety of superficial chemical peeling in treatment of active acne vulgaris, Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5429107/ - The use of microdermabrasion for acne: a pilot study. Dermatologic Surgery, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11298700/
Read full bio of Cara Downey
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Krati Darak

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.